Abstract
A protein analog of a purple copper center has been constructed from a recombinant blue copper protein (Pseudomonas aeruginosa azurin) by replacing the loop containing the three ligands to the blue copper center with the corresponding loop of the CuA center in cytochrome c oxidase (COX) from Paracoccus denitrificans. The electronic absorption in the UV and visible region (UV-vis) and electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectra of this analog are remarkably similar to those of the native CuA center in COX from Paracoccus denitrificans. The above spectra can be obtained upon addition of a mixture of Cu2+ and Cu+. Addition of Cu2+ only results in a UV-vis spectrum consisting of absorptions from both a purple copper center and a blue copper center. This spectrum can be converted to the spectrum of a pure purple copper by a prolonged incubation in the air, or by addition of excess ascorbate. The azurin mutant reported here is an example of an engineered purple copper center with the A480/A530 ratio greater than 1 and with no detectable hyperfines, similar to those of the CuA sites in COX of bovine heart and of Paracoccus denitrificans.
Full text
PDF
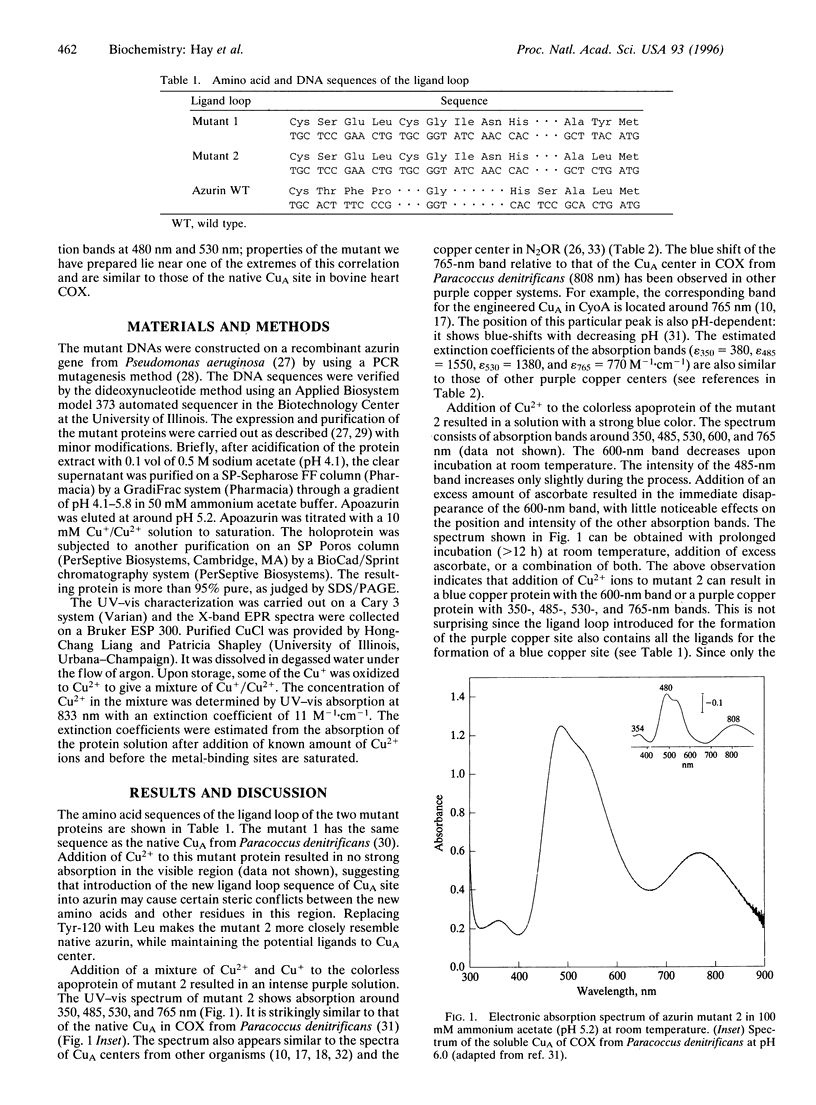
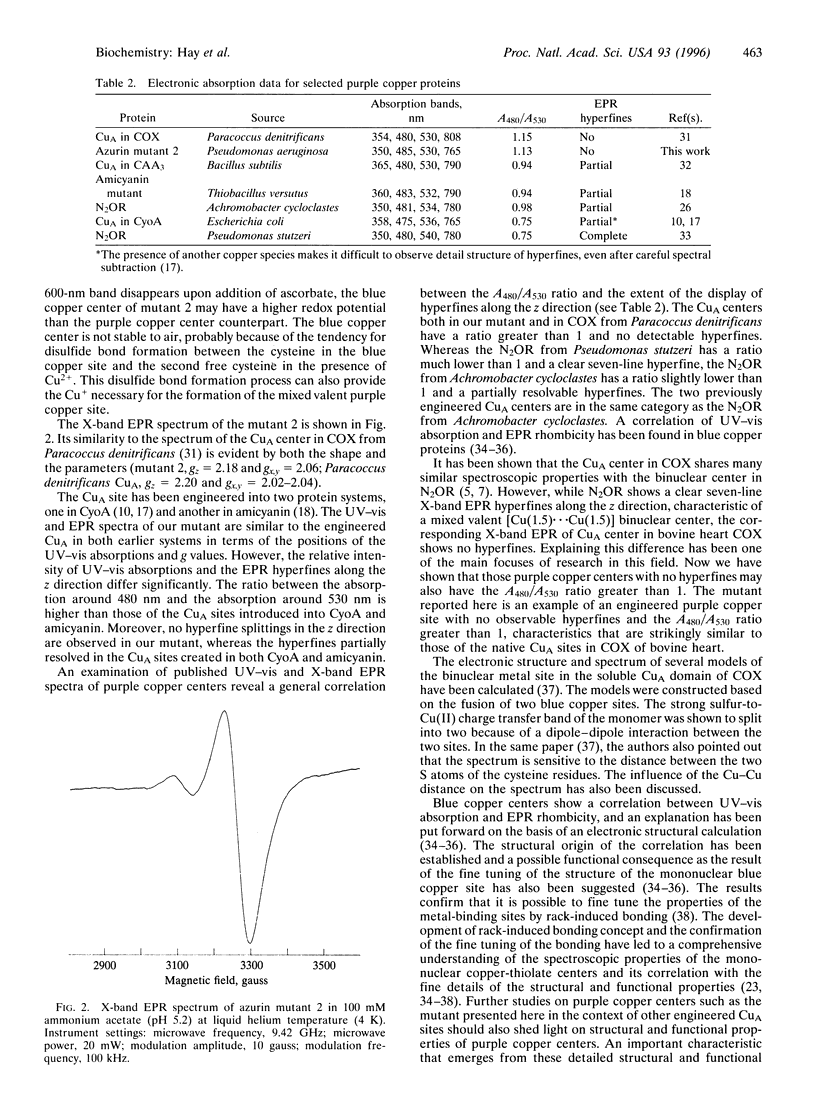

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adman E. T. Copper protein structures. Adv Protein Chem. 1991;42:145–197. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60536-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antholine W. E., Kastrau D. H., Steffens G. C., Buse G., Zumft W. G., Kroneck P. M. A comparative EPR investigation of the multicopper proteins nitrous-oxide reductase and cytochrome c oxidase. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Nov 1;209(3):875–881. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17360.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babcock G. T., Wikström M. Oxygen activation and the conservation of energy in cell respiration. Nature. 1992 Mar 26;356(6367):301–309. doi: 10.1038/356301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn N. J., Barr M. E., Woodruff W. H., van der Oost J., de Vries S. Metal-metal bonding in biology: EXAFS evidence for a 2.5 A copper-copper bond in the CuA center of cytochrome oxidase. Biochemistry. 1994 Aug 30;33(34):10401–10407. doi: 10.1021/bi00200a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canters G. W., Gilardi G. Engineering type 1 copper sites in proteins. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jun 28;325(1-2):39–48. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81410-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang T. K., Iverson S. A., Rodrigues C. G., Kiser C. N., Lew A. Y., Germanas J. P., Richards J. H. Gene synthesis, expression, and mutagenesis of the blue copper proteins azurin and plastocyanin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1325–1329. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennison C., Vijgenboom E., de Vries S., van der Oost J., Canters G. W. Introduction of a CuA site into the blue copper protein amicyanin from Thiobacillus versutus. FEBS Lett. 1995 May 22;365(1):92–94. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)00429-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fee J. A., Sanders D., Slutter C. E., Doan P. E., Aasa R., Karpefors M., Vänngård T. Multi-frequency EPR evidence for a binuclear CuA center in cytochrome c oxidase: studies with a 63Cu- and 65Cu-enriched, soluble domain of the cytochrome ba3 subunit II from Thermus thermophilus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995 Jul 6;212(1):77–83. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.1938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulse C. L., Averill B. A. Isolation of a high specific activity pink, monomeric nitrous oxide reductase from Achromobacter cycloclastes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jan 30;166(2):729–735. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90870-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwata S., Ostermeier C., Ludwig B., Michel H. Structure at 2.8 A resolution of cytochrome c oxidase from Paracoccus denitrificans. Nature. 1995 Aug 24;376(6542):660–669. doi: 10.1038/376660a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin K. D. Metalloenzymes, structural motifs, and inorganic models. Science. 1993 Aug 6;261(5122):701–708. doi: 10.1126/science.7688141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M., Lappalainen P., Talbo G., Haltia T., van der Oost J., Saraste M. Two cysteines, two histidines, and one methionine are ligands of a binuclear purple copper center. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 5;268(22):16781–16787. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langen R., Chang I. J., Germanas J. P., Richards J. H., Winkler J. R., Gray H. B. Electron tunneling in proteins: coupling through a beta strand. Science. 1995 Jun 23;268(5218):1733–1735. doi: 10.1126/science.7792598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lappalainen P., Aasa R., Malmström B. G., Saraste M. Soluble CuA-binding domain from the Paracoccus cytochrome c oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 15;268(35):26416–26421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson S., Källebring B., Wittung P., Malmström B. G. The CuA center of cytochrome-c oxidase: electronic structure and spectra of models compared to the properties of CuA domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Aug 1;92(16):7167–7171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.16.7167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li P. M., Morgan J. E., Nilsson T., Ma M., Chan S. I. Heat treatment of cytochrome c oxidase perturbs the CuA site and affects proton pumping behavior. Biochemistry. 1988 Sep 20;27(19):7538–7546. doi: 10.1021/bi00419a054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malmström B. G., Aasa R. The nature of the CuA center in cytochrome c oxidase. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jun 28;325(1-2):49–52. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81411-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malmström B. G. Rack-induced bonding in blue-copper proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Aug 1;223(3):711–718. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb19044.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raitio M., Jalli T., Saraste M. Isolation and analysis of the genes for cytochrome c oxidase in Paracoccus denitrificans. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2825–2833. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02579.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riester J., Zumft W. G., Kroneck P. M. Nitrous oxide reductase from Pseudomonas stutzeri. Redox properties and spectroscopic characterization of different forms of the multicopper enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jan 2;178(3):751–762. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14506.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffens G. J., Buse G. Studies on cytochrome c oxidase, IV[1--3]. Primary structure and function of subunit II. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1979 Apr;360(4):613–619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukihara T., Aoyama H., Yamashita E., Tomizaki T., Yamaguchi H., Shinzawa-Itoh K., Nakashima R., Yaono R., Yoshikawa S. Structures of metal sites of oxidized bovine heart cytochrome c oxidase at 2.8 A. Science. 1995 Aug 25;269(5227):1069–1074. doi: 10.1126/science.7652554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zumft W. G., Dreusch A., Löchelt S., Cuypers H., Friedrich B., Schneider B. Derived amino acid sequences of the nosZ gene (respiratory N2O reductase) from Alcaligenes eutrophus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Pseudomonas stutzeri reveal potential copper-binding residues. Implications for the CuA site of N2O reductase and cytochrome-c oxidase. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Aug 15;208(1):31–40. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17156.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Oost J., Lappalainen P., Musacchio A., Warne A., Lemieux L., Rumbley J., Gennis R. B., Aasa R., Pascher T., Malmström B. G. Restoration of a lost metal-binding site: construction of two different copper sites into a subunit of the E. coli cytochrome o quinol oxidase complex. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3209–3217. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05398.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Wachenfeldt C., de Vries S., van der Oost J. The CuAsite of the caa3-type oxidase of Bacillus subtilis is a mixed-valence binuclear copper centre. FEBS Lett. 1994 Feb 28;340(1-2):109–113. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80182-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



