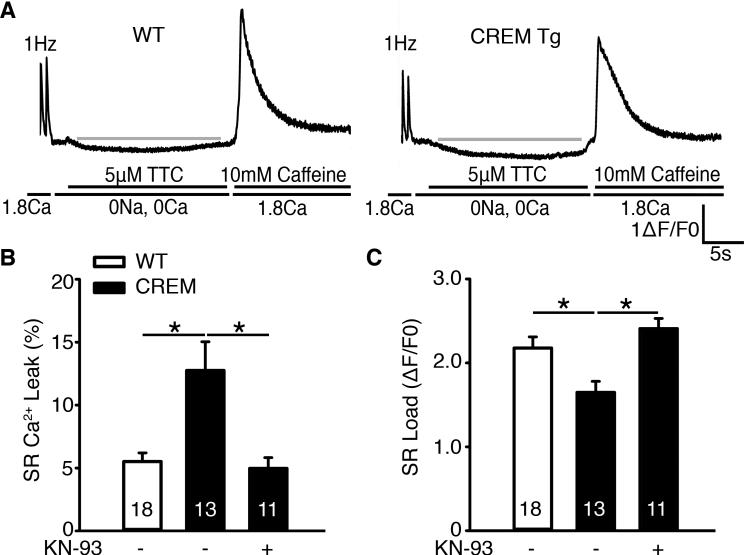
Figure 3.
Inhibition of CaMKII reduces SR Ca2+-leak in CREM-mice. (A) Representative [Ca2+]i tracings from atrial myocytes paced at 1 Hz followed by rapid switch to Tyrode solution containing 0 Na+, 0 Ca2+, and 5 μmol/L tetracaine (TTC) to block RyR2-mediated SR Ca2+-leak. 10 mM caffeine was added to measure SR Ca2+-content. At the age of 7 months, CREM-mice exhibited increased SR Ca2+-leak, measured as the curve below the red baseline. (B) Quantification of SR Ca2+-leak normalized to SR Ca2+-load revealed that increased leak in CREM-mice was normalized by CaMKII inhibition using KN-93. (C) Bar graph showing reduced SR Ca2+-load in CREM-mice, which was normalized using KN-93. Number in the bars indicated the number of cells studied from 3-4 animals. *P<0.05.