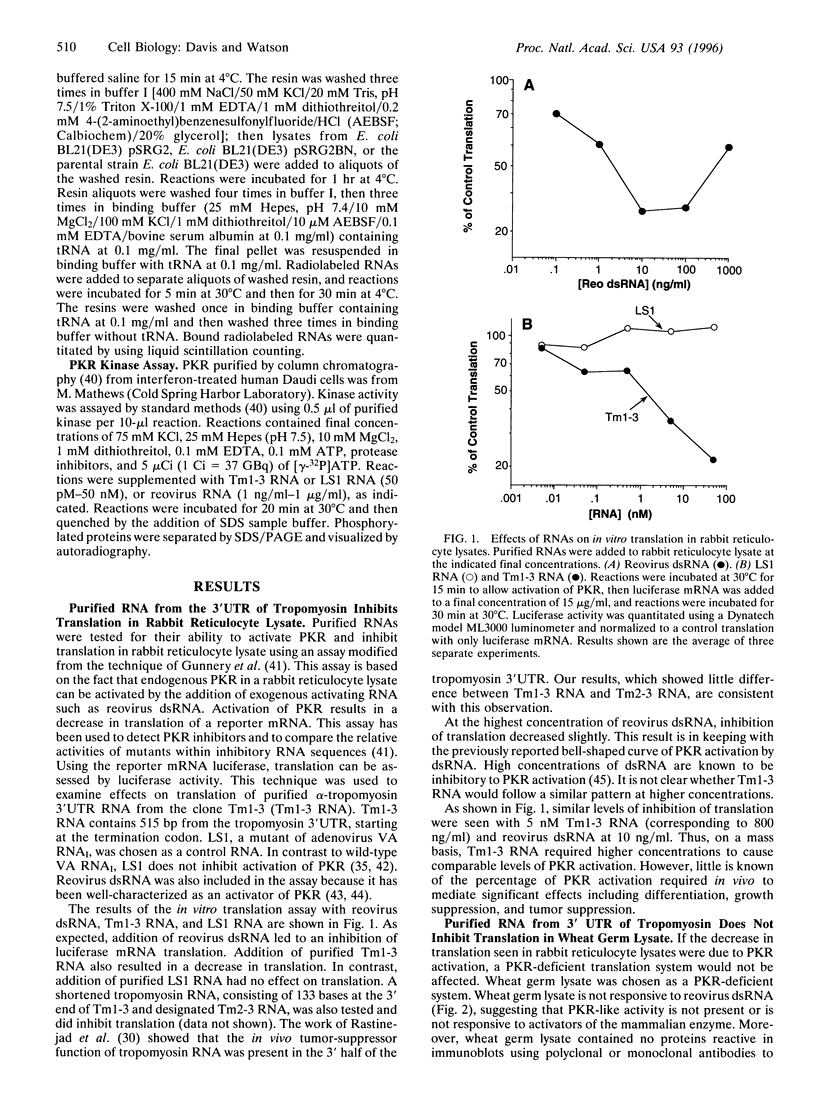
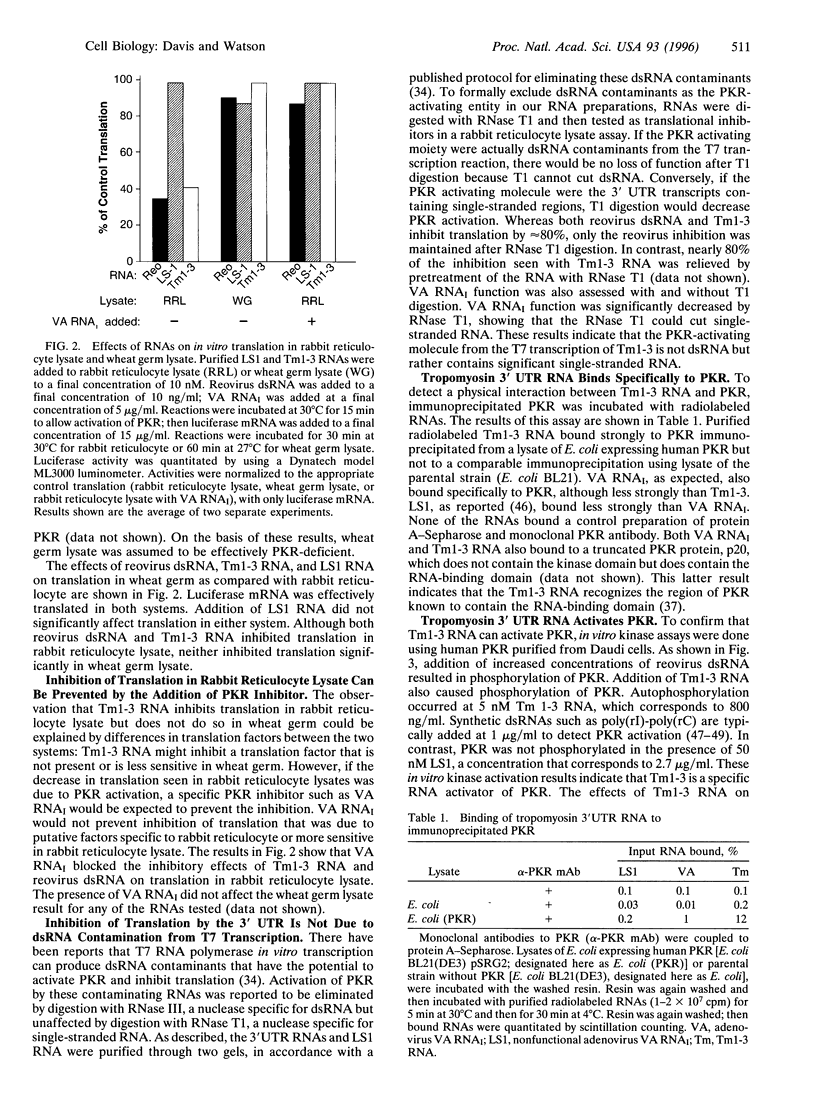
Abstract
The cellular kinase known as PKR (protein kinase RNA-activated) is induced by interferon and activated by RNA. PKR is known to have antiviral properties due to its role in translational control. Active PKR phosphorylates eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha and leads to inhibition of translation, including viral translation. PKR is also known to function as a tumor suppressor, presumably by limiting the rate of tumor-cell translation and growth. Recent research has shown that RNA from the 3' untranslated region (3'UTR) of human alpha-tropomyosin has tumor-suppressor properties in vivo [Rastinejad, F., Conboy, M. J., Rando, T. A. & Blau, H. M. (1993) Cell 75, 1107-1117]. Here we report that purified RNA from the 3'UTR of human alpha-tropomyosin can inhibit in vitro translation in a manner consistent with activation of PKR. Inhibition of translation by tropomyosin 3'UTR RNA was observed in a rabbit reticulocyte lysate system, which is known to contain endogenous PKR but was not seen in wheat germ lysate, which is not responsive to a known activator of PKR. A control RNA purified in the same manner as the 3'UTR RNA did not inhibit translation in either system. The inhibition of translation observed in reticulocyte lysates was prevented by the addition of adenovirus virus-associated RNA1 (VA RNAI), an inhibitor of PKR activation. Tropomyosin 3'UTR RNA was bound by immunoprecipitated PKR and activated the enzyme in an in vitro kinase assay. These data suggest that activation of PKR could be the mechanism by which tropomyosin 3'UTR RNA exerts its tumor-suppression activity in vivo.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beattie E., Tartaglia J., Paoletti E. Vaccinia virus-encoded eIF-2 alpha homolog abrogates the antiviral effect of interferon. Virology. 1991 Jul;183(1):419–422. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90158-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black T. L., Barber G. N., Katze M. G. Degradation of the interferon-induced 68,000-M(r) protein kinase by poliovirus requires RNA. J Virol. 1993 Feb;67(2):791–800. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.2.791-800.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black T. L., Safer B., Hovanessian A., Katze M. G. The cellular 68,000-Mr protein kinase is highly autophosphorylated and activated yet significantly degraded during poliovirus infection: implications for translational regulation. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2244–2251. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2244-2251.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boone R. F., Parr R. P., Moss B. Intermolecular duplexes formed from polyadenylylated vaccinia virus RNA. J Virol. 1979 Apr;30(1):365–374. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.1.365-374.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll K., Elroy-Stein O., Moss B., Jagus R. Recombinant vaccinia virus K3L gene product prevents activation of double-stranded RNA-dependent, initiation factor 2 alpha-specific protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 15;268(17):12837–12842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. W., Watson J. C., Jacobs B. L. The E3L gene of vaccinia virus encodes an inhibitor of the interferon-induced, double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):4825–4829. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.4825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong K. L., Feng L., Schappert K., Meurs E., Donahue T. F., Friesen J. D., Hovanessian A. G., Williams B. R. Human p68 kinase exhibits growth suppression in yeast and homology to the translational regulator GCN2. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1553–1562. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05200.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper H. L., Feuerstein N., Noda M., Bassin R. H. Suppression of tropomyosin synthesis, a common biochemical feature of oncogenesis by structurally diverse retroviral oncogenes. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):972–983. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. J., Sen G. C., Dubois M. F., Ratner L., Slattery E., Lengyel P. Interferon action: two distinct pathways for inhibition of protein synthesis by double-stranded RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5893–5897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galabru J., Hovanessian A. Autophosphorylation of the protein kinase dependent on double-stranded RNA. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15538–15544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghadge G. D., Swaminathan S., Katze M. G., Thimmapaya B. Binding of the adenovirus VAI RNA to the interferon-induced 68-kDa protein kinase correlates with function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7140–7144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunnery S., Green S. R., Mathews M. B. Tat-responsive region RNA of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 stimulates protein synthesis in vivo and in vitro: relationship between structure and function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11557–11561. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Hunt T., Jackson R. J., Robertson H. D. The characteristics of inhibition of protein synthesis by double-stranded ribonucleic acid in reticulocyte lysates. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 25;250(2):409–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imani F., Jacobs B. L. Inhibitory activity for the interferon-induced protein kinase is associated with the reovirus serotype 1 sigma 3 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7887–7891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Judware R., Petryshyn R. Mechanism of action of a cellular inhibitor of the dsRNA-dependent protein kinase from 3T3-F442A cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 25;267(30):21685–21690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katze M. G., DeCorato D., Safer B., Galabru J., Hovanessian A. G. Adenovirus VAI RNA complexes with the 68 000 Mr protein kinase to regulate its autophosphorylation and activity. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):689–697. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04809.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koromilas A. E., Roy S., Barber G. N., Katze M. G., Sonenberg N. Malignant transformation by a mutant of the IFN-inducible dsRNA-dependent protein kinase. Science. 1992 Sep 18;257(5077):1685–1689. doi: 10.1126/science.1382315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostura M., Mathews M. B. Purification and activation of the double-stranded RNA-dependent eIF-2 kinase DAI. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1576–1586. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langland J. O., Pettiford S., Jiang B., Jacobs B. L. Products of the porcine group C rotavirus NSP3 gene bind specifically to double-stranded RNA and inhibit activation of the interferon-induced protein kinase PKR. J Virol. 1994 Jun;68(6):3821–3829. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.6.3821-3829.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasky S. R., Jacobs B. L., Samuel C. E. Mechanism of interferon action. Characterization of sites of phosphorylation in the interferon-induced phosphoprotein P1 from mouse fibroblasts: evidence for two forms of P1. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):11087–11093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent A. G., Krust B., Galabru J., Svab J., Hovanessian A. G. Monoclonal antibodies to an interferon-induced Mr 68,000 protein and their use for the detection of double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4341–4345. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebleu B., Sen G. C., Shaila S., Cabrer B., Lengyel P. Interferon, double-stranded RNA, and protein phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3107–3111. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. G., Tomita J., Hovanessian A. G., Katze M. G. Characterization and regulation of the 58,000-dalton cellular inhibitor of the interferon-induced, dsRNA-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):14238–14243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. G., Tomita J., Hovanessian A. G., Katze M. G. Purification and partial characterization of a cellular inhibitor of the interferon-induced protein kinase of Mr 68,000 from influenza virus-infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6208–6212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lengyel P. Biochemistry of interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:251–282. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J., Petryshyn R. A. Activation of the double-stranded RNA-dependent eIF-2 alpha kinase by cellular RNA from 3T3-F442A cells. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Jan 1;195(1):41–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15673.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manche L., Green S. R., Schmedt C., Mathews M. B. Interactions between double-stranded RNA regulators and the protein kinase DAI. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;12(11):5238–5248. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.11.5238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maran A., Mathews M. B. Characterization of the double-stranded RNA implicated in the inhibition of protein synthesis in cells infected with a mutant adenovirus defective for VA RNA. Virology. 1988 May;164(1):106–113. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90625-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M. B., Shenk T. Adenovirus virus-associated RNA and translation control. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5657–5662. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5657-5662.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellits K. H., Kostura M., Mathews M. B. Interaction of adenovirus VA RNAl with the protein kinase DAI: nonequivalence of binding and function. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):843–852. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90194-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellits K. H., Pe'ery T., Mathews M. B. Role of the apical stem in maintaining the structure and function of adenovirus virus-associated RNA. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2369–2377. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2369-2377.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meurs E. F., Galabru J., Barber G. N., Katze M. G., Hovanessian A. G. Tumor suppressor function of the interferon-induced double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 1;90(1):232–236. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minks M. A., West D. K., Benvin S., Baglioni C. Structural requirements of double-stranded RNA for the activation of 2',5'-oligo(A) polymerase and protein kinase of interferon-treated HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10180–10183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minks M. A., West D. K., Benvin S., Greene J. J., Ts'o P. O., Baglioni C. Activation of 2',5'-oligo(A) polymerase and protein kinase of interferon-treated HeLa cells by 2'-O-methylated poly (inosinic acid) . poly(cytidylic acid), Correlations with interferon-inducing activity. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6403–6407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mordechai E., Kon N., Henderson E. E., Suhadolnik R. J. Activation of the interferon-inducible enzymes, 2',5'-oligoadenylate synthetase and PKR by human T-cell leukemia virus type I Rex-response element. Virology. 1995 Feb 1;206(2):913–922. doi: 10.1006/viro.1995.1014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen T. W., Maroney P. A., Baglioni C. Inhibition of protein synthesis in reovirus-infected HeLa cells with elevated levels of interferon-induced protein kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14593–14596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel R. C., Stanton P., Sen G. C. Role of the amino-terminal residues of the interferon-induced protein kinase in its activation by double-stranded RNA and heparin. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 15;269(28):18593–18598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad G. L., Fuldner R. A., Cooper H. L. Expression of transduced tropomyosin 1 cDNA suppresses neoplastic growth of cells transformed by the ras oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 1;90(15):7039–7043. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.7039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rastinejad F., Blau H. M. Genetic complementation reveals a novel regulatory role for 3' untranslated regions in growth and differentiation. Cell. 1993 Mar 26;72(6):903–917. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90579-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rastinejad F., Conboy M. J., Rando T. A., Blau H. M. Tumor suppression by RNA from the 3' untranslated region of alpha-tropomyosin. Cell. 1993 Dec 17;75(6):1107–1117. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90320-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. K., Hovanessian A., Brown R. E., Clemens M. J., Kerr I. M. Interferon-mediated protein kinase and low-molecular-weight inhibitor of protein synthesis. Nature. 1976 Dec 2;264(5585):477–480. doi: 10.1038/264477a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel C. E., Duncan R., Knutson G. S., Hershey J. W. Mechanism of interferon action. Increased phosphorylation of protein synthesis initiation factor eIF-2 alpha in interferon-treated, reovirus-infected mouse L929 fibroblasts in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13451–13457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp T. V., Xiao Q., Jeffrey I., Gewert D. R., Clemens M. J. Reversal of the double-stranded-RNA-induced inhibition of protein synthesis by a catalytically inactive mutant of the protein kinase PKR. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Jun 15;214(3):945–948. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17998.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J. C., Chang H. W., Jacobs B. L. Characterization of a vaccinia virus-encoded double-stranded RNA-binding protein that may be involved in inhibition of the double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase. Virology. 1991 Nov;185(1):206–216. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90768-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberstein A., Federman P., Shulman L., Revel M. Specific phosphorylation in vitro of a protein associated with ribosomes of interferon-treated mouse L cells. FEBS Lett. 1976 Sep 15;68(1):119–124. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80418-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberstein A., Kimchi A., Schmidt A., Revel M. Isolation of two interferon-induced translational inhibitors: a protein kinase and an oligo-isoadenylate synthetase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4734–4738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




