Abstract
Background
Theileria and Babesia protozoan parasites are transmitted mainly by tick vectors. These parasites cause heavy economic losses to the live-stock industry, as well as affecting the health of wild animals in parasite-endemic areas. Identification of infectious agents in wild animals is not only crucial for species preservation, but also provides valuable information on parasite epidemiology. Here, we conducted a molecular surveillance study in Northwestern China to assess the prevalence of blood pathogens in cervids.
Methods
PCR analysis and microscopic evaluation of blood smears to detect Theileria- and Babesia-related diseases in Cervidae were conducted, in which 22 blood samples from red deer (n = 22) in Qilian Mountain and 20 from sika deer (n = 20) in Long Mountain were collected and tested for the presence of Theileria and Babesia. The 18S rRNA gene was amplified, and selected polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-positive samples were sequenced for species identification.
Results
PCR revealed that 9.1% of the Qilian Mountain samples and 20% of the Long Mountain samples were positive for Theileria uilenbergi; 90.09% of the Qilian Mountain samples (n = 22) were positive for T. capreoli, but all of the Long Mountain samples (n = 20) were negative for T. capreoli; no other Theileria or Babesia species were found. PCR showed that T. uilenbergi and T. capreoli were present in red deer in Qilian Mountain, while only T. uilenbergi was found in sika Deer in Long Mountain. The 18S rRNA gene sequences were aligned against the corresponding GenBank sequences of known isolates of Theileria and Babesia and subjected to phylogenetic analysis. The phylogenetic tree showed that the newly isolated Theileria spp. could be classified as belonging to two clades: one group belonged to the same clade as T. uilenbergi, the other to a clade containing T. capreoli.
Conclusions
Our results provide important data to increase understanding of the epidemiology of Cervidae theileriosis, and will assist with the implementation of measures to control theileriosis transmission to Cervidae and small ruminants in central China.
Keywords: Theileria and Babesia, Molecular detection, Cervid, PCR, Northwestern China
Background
Theileria and Babesia, parasites that are mainly transmitted by tick vectors, cause heavy economic losses to live-stock and affect the health of wild animals where ever such parasites are endemic. Theileria and the closely related genus, Babesia, exhibit complex life cycles that involve mammalian intermediate hosts and hard ticks as the definite hosts [1]. Theileria is an obligatory intracellular parasite that infects leukocytes and erythrocytes in the intermediate host, unlike Babesia, which only infects erythrocytes. Among the Theileria and Babesia parasites that infect cervids, several Theileria spp. (e.g. T. cervi, T. capreoli, Theileria sp. OT3, Theileria sp. ZS OT4, and T. ovis), and Babesia spp. (e.g. B. bigemina, B. bovis, B. capreoli, B. divergens, and B. odocoilei) are described as being moderately pathogenic or benign. Theileria and Babesia are cosmopolitan parasites [2] that have been detected in wild ruminants in many countries including Japan [3-5], South Korea [6], Brazil [7,8], the United States [9-12], Italy [13], eastern Austria [14], northern and central Spain [15-17], and the United Kingdom [18]. In China, He et al. [19] first reported the existence of Theileria infection in sika deer in the Hubei province of central China.
Although there are no published epidemiological data on the Cervidae of northwestern China, no suspected cases of theileriosis in small ruminants have been observed here. In the current study, we performed an epidemiologic survey of Theileria and Babesia infections of Cervidae in northwestern China. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis and microscopic examination of blood smears were used for species identification and to elucidate the evolutionary relationships among the newly identified hemoparasite species based on the 18S rRNA gene sequences of known Theileria and Babesia species.
Methods
Sample collection
The two regions investigated in northwestern China are located at latitudes 34° 44′ to 73° 28′ north and longitudes 97° 20′ to 106° 35′ east. The study period was August 2013. Twenty-two blood samples (n = 22) were collected randomly from wild red deer in Qilian Mountain, and 20 blood samples (n = 20) were collected randomly from domesticated sika deer at a ranch in Long Mountain, northwestern China. Blood smears were prepared for both groups (Table 1). During the blood collection process, cases of suspected theileriosis and babesiosis were investigated. Theileriosis and/or babesiosis should be suspected in tick–infested animals with a fever, enlarged lymph nodes (only for theileriosis), anemia and jaundice, or hemoglobinuria (only for babesiosis).
Table 1.
Sequences of the oligonucleotide primers used in this study
| Pathogen | Target gene |
Oligonucleotide sequences (5′-3′) |
Final amplicon size (bp) | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Forward | Reverse | ||||
| Hemoparasite |
18S rRNA |
AACCTGGTTGATCCTGCCAGT |
GATCCTTCTGCAGGTTCACCTAC |
1750 |
Medlin et al., [20] |
|
Theileria spp. |
18S rRNA |
AGTTTCTGACCTATCAG |
TTGCCTTAAACTTCCTTG |
1098 |
Allosop et al., [21] |
|
T. annulata |
30 kDa |
GTAACCTTTAAAAACGT |
GTTACGAACATGGGTTT |
721 |
d’Oliveria et al., [22] |
|
T. sergenti |
MPSP |
CACGCTATGTTGTCCAAGAG |
TGTGAGACTCAATGCGCCTA |
875 |
Liu et al., [23] |
|
T. sinensis |
MPSP |
CACTGCTATGTTGTCCAAGAGATATT |
AATGCGCCTAAAGATAGTAGAAAAC |
887 |
Liu et al., [23] |
|
T. orientalis |
MPSP |
CTTTGCCTAGGATACTTCCT |
ACGGCAAGTGGTGAGAACT |
776 |
Ota et al., [24] |
|
T. cervi (Type F) |
18S rRNA |
TTCCCTTTGAGGGGT |
AAGCCTATTCCCGTACC |
654 |
Boes et al., [25] |
|
T. cervi (Type G) |
18S rRNA |
CTTCCCGTTATGGAGG |
CTTAACCTATTCCCGTGAG |
654 |
Boes et al., [25] |
|
T. luwenshuni |
18S rRNA |
GGTAGGGTATTGGCCTACTGA |
TCATCCGGATAATACAAGT |
340 |
Yin et al., [26] |
|
T. uilenbergi |
18S rRNA |
GGTAGGGTATTGGCCTACCGG |
ACACTCGGA AAATGCAAGCA |
340 |
Yin et al., [26] |
|
T. ovis |
18S rRNA |
TCGA-GACCTTCGGGT |
TCCGGACATTGTAAAACAAA |
520 |
Altay et al., [27] |
|
T. lestoquardi |
18S rRNA |
GTGCCGCAAGTGAGTCA |
GGACTGATGAGAAGACGATGAG |
785 |
Aktas et al., [28] |
|
T. capreoli |
18S rRNA |
gtcttgtaattggaatgatgg |
ccaaagactttgatttctctc |
580 |
Slemenda et al., [29] |
|
Babesia spp. |
18S rRNA |
TGTCTTGAATACTT(C/G)AGCATGGAA |
CGACTTCTCCTTTAAGTGATAAC |
950 |
Ramos et al., [10] |
|
B. odocoilei |
18S rRNA |
CACCGTATTTTGACTTTTTGTCGACTGTCGG |
CCCGTAACGGACGAACCTTCTCACGGG |
900 |
Ramos et al., [10] |
|
B. bovis |
18S rRNA |
CTGTCGTACCGTTGGTTGAC |
CGCACGGACGGAGACCGA |
541 |
Guido et al., [30] |
|
B. ovata |
AMA-1 |
GATACGAGGCTGTCGGTAGC |
AGTATAGGTGAGCATCAGTG |
504 |
Sivakumar et al., [31] |
|
B. bigemina |
18S rRNA |
TGGCGGCGTTTATTAGTTCG |
CCACGCTTGAAGCACAGGA |
1124 |
Guido et al., [30] |
|
B. ovis |
18S rRNA |
TGGGCAGGACCTTGGTTCTTCT |
CCGCGTAGCGCCGGCTAAATA |
549 |
Aktas et al., [32] |
| B. motasi | 18S rRNA | AAGAATTTCACCTCTGACAG | GCTTGCTTTTTGTTACTTTG | 179 | Shayan et al., [33] |
Microscopy of blood smears
Blood smears were air-dried, fixed in methanol, stained with a 10% solution of Giemsa in phosphate-buffered saline (pH 7.2), and then subjected to microscopic analysis and photography.
DNA extraction
Genomic DNA from 42 whole blood samples was extracted using a genomic DNA extraction kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The DNA yields were determined using a NanoDrop ND-2000 Spectrophotometer (Nanodrop Technologies, Wilmington, DE, USA).
Molecular detection of Theileria and Babesia using species-specific primers
PCR was used to detect and differentiate Theileria and Babesia using species-specific primers [10,20-32], the details of which are shown in Table 2. PCR reactions were performed in an automatic DNA thermocycler (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) and PCR products were separated by 1.5% agarose gel electrophoresis to assess the presence of specific bands indicative of Theileria spp. and Babesia spp.
Table 2.
Prevalence of Theileria and Babesia in red deer and sika deer in northwestern China, 2013
| Collection sites | Host |
Prevalence of
Theileria
spp. and
Babesia
spp. in blood samples |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ME * | T. capreoli | T. uilenbergi | Babesia spp. | ||
| Qilian Mountain |
Red deer |
72.7% (16/22) |
90.9% (20/22) |
9.1% (2/22) |
0% (0/22) |
| Long Mountain | Sika deer | 10% (2/20) | 0% (0/20) | 20% (4/20) | 0% (0/20) |
*ME, microscopic examination of blood smears.
PCR amplification of the 18S rRNA gene of Theileria
PCR was used to amplify protozoan 18S rRNA gene sequences with primers A/B as described by Medlin et al. [20]. The DNA fragments generated were ligated into pGEM T easy vectors (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) and transformed into competent JM109 cells (Takara Bio Inc., Shiga, Japan). The transformed bacteria were plated onto selective LB medium, and at least three positive clones identified by the 989/990 primers specific to Theileria spp. [21] were sequenced by the GenScript Corporation (Piscataway, NJ, USA). Representative sequences of the newly identified Theileria and Babesia 18S rRNA genes from this study were deposited in the GenBank database of the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/).
Sequence alignments and phylogenetic analysis
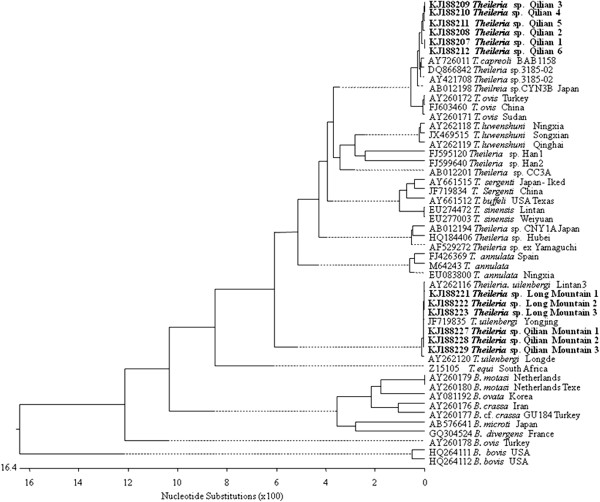
Compilation, editing, and assembly of the multiple sequences generated from each template were performed using the EditSeq and SeqMan algorithms of the Lasergene software package for Windows (DNASTAR, Madison, WI, USA). Sequence alignment and phylogenetic analysis performed by the MegAlign component of the Lasergene program ver. 4.01 (DNASTAR) were used to perform multiple sequence alignments with the ClustalW algorithm and phylogenetic analysis by the neighbor-joining method. A phylogenetic tree was constructed (Figure 1) based on the Theileria and Babesia 18S RNA gene sequences determined in the present study, other sequences from our laboratory, and those obtained from GenBank under the following accession numbers: KJ188207-KJ188232, AY726011, DQ866842, AY421708, AY661512, AY661515, EU274472, EU277003, AY260171, AY260172, FJ603460, EU083800, FJ426369, M64243, AY262116, AY262118, AY262119, JX469515, AY262120, JF719835, FJ595120, FJ599640, AB012201, AB012194, HQ188406, AF529272, Z15105, AY260176, AY260177, AY260178, AY260179, AY260180, AB576641, AB012198, GQ304524, AY260180, AY081192, HQ264111, and HQ264112. In the phylogenetic tree, the length of each branch pair represents the distance between sequence pairs, while the units on the horizontal axis indicate the number of substitution events (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
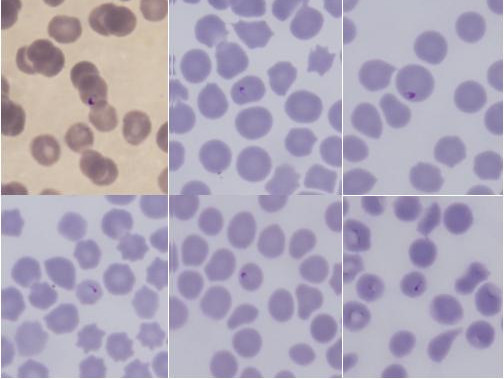
Piroplasms in blood smears from Cervidae.
Ethical approval and consent
This molecular approach was then employed to identify Theileria parasites of northwestern Chinese cervidae at Lanzhou Veterinary Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Science. Use of these clinical samples was approved by the National Review Board (China).
Results
Microscopic examination of thin blood smears
Piroplasm infections in the blood smears were observed microscopically in samples from Qilian Mountain (72.7%, 16/22) and Long Mountain (10%, 2/20); all infections exhibited low parasitemia levels (0.01–2.5%) (Table 2). The piroplasms were polymorphous, and most presented as rod-like, needle-like, pear-shaped, or spherical forms (Figure 1). Cases of theileriosis and babesiosis were not seen in the Qilian Mountain and Long Mountain regions of northwestern China.
PCR detection of Theileria and Babesia using species-specific primer sets
All 42 blood samples were negative for Babesia spp. using Babesia genus and Babesia species-specific primer sets; 24 of them (n = 42) were positive for Theileria spp. using Theileria genus and Theileria species-specific primer sets. PCR using twenty sets of primers revealed that only two Theileria species, T. capreoli and T. uilenbergi, were detectable in the blood samples. The PCR-positive rates for T. uilenbergi in the blood samples from red deer in Qilian Mountain and sika deer in Long Mountain were 9.1% (2/22), and 20% (4/20), respectively. While the PCR-positive rates for T. capreoli in blood samples from red deer in Qilian Mountain were 90.9% (20/22), T. capreoli was not detected in the blood samples from sika deer in Long Mountain (Table 2). These results confirm that all of the samples that were blood smear-positive were also PCR-positive for Theileria parasites. Of the 24 samples for which no piroplasms were observed by microscopy, we found that one was T. capreoli- and T. uilenbergi-positive, three were T. capreoli-positive, and two were T. uilenbergi-positive by PCR. Compared with microscopy of blood smears, the PCR method had higher sensitivity and was recommended to be utilized in the diagnosis of piroplasmosis.
18S rRNA amplification
The 18S rRNA gene sequences were determined for the Theileria spp. isolates from Qilian Mountain and Long Mountain. The length of the 18S rDNA gene was 1,751 bp (T. capreoli) and 1,745 bp (T. uilenbergi) using the A/B primers, which are specific for hemoparasites. The 18S rRNA gene sequences obtained from red deer and sika deer in northwestern China have been deposited in GenBank under the following accession numbers: KJ188207-KJ188220 for the T. capreoli isolates from Qilian Mountain red deer; KJ188227-KJ188232 for the T. uilenbergi isolates from Qilian Mountain red deer; and, KJ188221-KJ188226 for T. uilenbergi isolates from Long Mountain sika deer.
Sequence alignments and phylogenetic analysis
The Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (BLAST) at NCBI was used to analyze the sequences obtained in our study. The results showed that there were two Theileria sequences from Cervidae in Qilian Mountain; one shared 99–100% homology with Theileria sp. 385/02, T. capreoli isolate BAB1158, and Theileria sp. CNY3B, while another shared 100% homology with the following isolates: T. uilenbergi Longde, T. uilenbergi Yongjing, and T. uilenbergi Zhangchuan. However, only one species of Theileria was found in Long Mountain Cervidae, and its 18S rRNA gene sequence shared 100% homology with the T. uilenbergi Longde isolate, the T. uilenbergi Yongjing isolate, and the T. uilenbergi Zhangchuan isolate. Sequence alignments showed that the newly identified Theileria spp. sequences with accession numbers KJ188207-KJ188220 were highly homologous to each other with identity values of 100%, while the other set of newly identified Theileria sequences (KJ188221-KJ188232) also were highly homologous to each other with identity values of 100%. Consistent with the BLAST results, the phylogenetic tree constructed in this study showed that one newly sequenced Theileria isolate appeared in the same clade as T. capreoli, while another appeared in the same clade as T. uilenbergi (Figure 2); both of the new 18S rDNA gene sequences show obvious differences to those from Babesia (such as those from B. ovis, B. bovis, B. motasi, B. ovata, and B. divergens) or other Theileria sequences (such as those from T. ovis, T. luwenshunli, T. sinensis, T. buffei/T. sergenti, T. equi, and T. annulata).
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic tree of Theileria and Babesia spp. based on 18S rRNA gene sequences.
Discussion
To the best of our knowledge, this study is the first to report on cervine theileriosis in northwestern China. Molecular screening for Theileria and Babesia in red deer and sika deer in northwestern China showed that the most prevalent species of Theileria in the deer were T. capreoli and T. uilernbergi; however, no Babesia parasites were found. The prevalence of T. capreoli was very high in Qilian Mountain deer, unlike T. uilenbergi, the prevalence of which was relatively low in Qilian Mountain. In contrast, the prevalence of T. uilenbergi was relatively low in Long Mountain, and no T. capreoli infections were found at this location. In both of the areas investigated, no Babesia spp. (including B. odocoilei, B. bovis, B. ovata, B. bigemina, B. ovis, and B. motasi) or infections with other Theileria spp. (including T. cervi, T. luwenshuni, T. ovis, T. sergenti/T. buffeli/T. orientalis, T. annulata, and T. sinensis) were detected using genus- and species-specific primers. It has been speculated that in areas with high infection rates, there is an inverse relationship between age and resistance to infection, where fawns gradually acquire immunity without showing clinical symptoms, and immunity is maintained by repeated challenges with the parasites. Consequently, a persistent parasite reservoir is established in the wild ruminants [16]. However, in these hosts, stressors like high parasitemia, poor nutrition, high population density, harsh weather conditions, or handling (e.g. translocation) can lead to symptomatic piroplasmosis, a cause of severe disease and death [15].
The diagnosis of parasitic diseases and detection of parasite species is often difficult at the carrier stage and in animals with mixed infections. Nevertheless, molecular diagnostic methods can enable the direct, specific, and sensitive detection of parasite species [27,34]. PCR-based molecular techniques allow the detection and discrimination of these parasites at low parasitemias and in animals with mixed infections [33,34]. The PCR methods used in this survey can detect cervine Theileria and Babesia directly in the same samples based on the 18S rRNA gene sequence using Theileria and Babesia specific primer sets. In the present study, the prevalence of Theileria infections in red deer and silk deer, which were detected by PCR, was statistically higher than that observed via microscopic examination. These results were expected because carrier animals often have low parasitemias, which are difficult to detect microscopically.
The maximum parsimony tree of the 18S rRNA genes indicated that the cervid infections detected in this study could be divided into two groups within the Theileria species clade. Group 1 sequences fell within the low-pathogenicity clade containing T. capreoli BAB1158 (AY7266011: isolated from European roe deer in Spain), Theileria spp. 3185/02 (AY421708: isolated from red deer in Spain), and Theileria spp. 3185/02 (DQ866842: isolated from roe deer from the Basque Country of Spain), and were also present in roe deer and red deer from northern Spain [16], and in fallow deer from Italy [13], but absent from chamois. In contrast, group 2 Theileria spp. fell into the same clade as the high-pathogenicity T. uilenbergi Longde isolate (AY262120), as did the T. uilenbergi Lintan isolate (AY262116) and the T. uilenbergi Yongjing isolate (JF719835), which are all widely present in sheep and goats and transmitted by Haemaphysalis qinghaiensis and H. longicornis in northern and northwestern China; their sequences were almost identical to each other with high bootstrap values (Figure 1). Clustering of the 18S rRNA sequences into two groups indicates the heterogeneity of the 18S rRNA genes of cervine Theileria spp. in China. Therefore, the two Theileria spp. newly identified in Cervidae in northwestern China should be classified as T. capreoli and T. uilenbergi. The 18S rRNA gene sequence of T. capreoli was most closely related to Theileria CYN3B of Japan and T. ovis, which belong to an evolutionary distinct lineage of non-lymphoproliferative Theileria species. This species was clearly divergent from Babesia and a second lineage of lymphoproliferative Theileria species that included T. annulata and T. parva.
Ideally, tick transmission studies on ticks that are associated with infected herds should be conducted to identify the species involved in transmitting theileriosis to Cervidae. In this study, no ticks were collected from the deer or the surrounding environments of the two areas investigated because the sampling was carried out in August, a time of year when the ticks are inactive. Yin et al.[35] and Li et al.[36] identified H. qinghaiensis and H. longicornis as vectors for T. uilenbergi in China. H. qinghaiensis is a triphasic tick common in Northwestern China and H. longicornis is a ubiquitous triphasic tick found in most parts of China. Therefore, it can be speculated that H. qinghaiensis and H. longicornis may play an important role as natural vectors of T. uilenbergi in northwestern China. Galuppi et al. [13] detected T. capreoli DNA in Ixodes ricinus, but whether other vectors transmit T. capreoli remains unclear. At present, identification of the full range of tick species that can transmit T. capreoli to Cervidae awaits further investigation.
Conclusions
Our results provide important data that should increase understanding of the epidemiology of cervine theileriosis, and assist with the implementation of measures to control theileriosis transmission to Cervidae and small ruminants in northwestern China. Clarification of the role that Cervidae might have as reservoir hosts for maintaining T. capreoli and T. uilenbergi is critical to understanding whether Cervidae contribute to the spread of ruminant theileriosis in China.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
YL, ZC, ZL, and JL carried out the molecular genetic studies; JY, QL, YL; SC participated in the sequence alignment, GG and QR collected the samples; YL, JL and HY drafted the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Contributor Information
Youquan Li, Email: youquan-li@163.com.
Ze Chen, Email: chenze@caas.cn.
Zhijie Liu, Email: liuzhijie@caas.cn.
Junlong Liu, Email: liujunlong@caas.cn.
Jifei Yang, Email: yangjifei@caas.cn.
Qian Li, Email: liqian0225@126.com.
Yaqiong Li, Email: liyaqiong624@163.com.
Shuangqing Cen, Email: 358735218@qq.com.
Guiquan Guan, Email: guanguiquan@caas.cn.
Qiaoyun Ren, Email: renqiaoyun@caas.cn.
Jianxun Luo, Email: luojianxun@caas.cn.
Hong Yin, Email: yinhong@caas.cn.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from the NSFC China (Nos. 31272556, 31372432, 31101621), ASTIP, CAAS, Creative Research Groups of Gansu Province (1210RJIA006) and “948” (2010-S06), NBCIS (CARS-38), State Key Laboratory of Veterinary Etiological Biology Project. The research was also supported by CRP No. 16198/R0 IAEA, and PIROVAC (KBBE-3-245145) of the European Commission.
References
- Bishop R, Musoke A, Morzaria S, Gardner M, Nene V. Theileria: intracellular protozoan parasites of wild and domestic ruminants transmitted by ixodid ticks. Parasitol. 2004;129(Suppl):271–283. doi: 10.1017/s0031182003004748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chae JS, Allsopp BA, Waghela SD, Park JH, Kakuda T, Sugimoto C, Allsopp MT, Wagner GG, Holman PJ. A study of the systematics of Theileria spp. based upon small-subunit ribosomal RNA gene sequences. Parasitol Res. 1999;85:877–883. doi: 10.1007/s004360050651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inokuma H, Tsuji M, Kim S, Fujimoto T, Nagata M, Hosoi E, Arai S, Ishihara C, Okuda M. Phylogenetic analysis of Theileria sp. from sika deer, Cervus nippon, in Japan. Vet Parasitol. 2004;120:339–345. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2004.01.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inokuma H, Nagata M, Hosoi E, Itamoto K, Okuda M. Divergence of p33/34 gene of Theileria found in Cervus nippon in Japan. J Vet Med Sci. 2008;70(4):401–405. doi: 10.1292/jvms.70.401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikawa K, Aoki M, Ichikawa M, Itagaki T. Occurrence of two distinct Theileria lineages in sika deer (Cervus nippon) of Iwate Prefecture. Japan J Vet Med Sci. 2011;73(10):1371–1373. doi: 10.1292/jvms.11-0094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han JI, Jang HJ, Na KJ. Molecular detection of Theileria sp. in wild Chinese water deer (Hydropotes inermis argyropus) J Wildl Dis. 2009;45(4):1213–1216. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-45.4.1213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- da Silveira JA, Rabelo EM, Ribeiro MF. Detection of Theileria and Babesia in brown brocket deer (Mazama gouazoubira) and marsh deer (Blastocerus dichotomus) in the State of Minas Gerais, Brazil. Vet Parasitol. 2011;177(1–2):61–66. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2010.10.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silveira JA, Rabelo EM, Lacerda AC, Borges PA, Tomás WM, Pellegrin AO, Tomich RG, Ribeiro MF. Molecular detection and identification of hemoparasites in pampas deer (Ozotoceros bezoarticus Linnaeus, 1758) from the Pantanal Brazil. Ticks Tick Borne Dis. 2013;4(4):341–345. doi: 10.1016/j.ttbdis.2013.01.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kocan A, Kocan KM. Tick-transmitted protozoan diseases of wildlife in North America. Bull Soc Vector Ecol. 1991;16:94–108. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos CM, Cooper SM, Holman PJ. Molecular and serologic evidence for Babesia bovis-like parasites in white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) in South Texas. Vet Parasitol. 2010;172(3–4):214–220. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2010.05.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holman PJ, Carroll JE, Pugh R, Davis DS. Molecular detection of Babesia bovis and Babesia bigemina in white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) from Tom Green County in Central Texas. Vet Parasitol. 2011;177(3–4):298–304. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2010.11.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner BC, Holman P, Berent LM. Theileriosis in a reindeer (Rangifer tarandus tarandus) associated with a potentially novel Theileria sp. Vet Clin Pathol. 2012;41(4):497–501. doi: 10.1111/j.1939-165x.2012.00475.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galuppi R, Aureli S, Bonoli C, Caffara M, Tampieri MP. Detection and molecular characterization of Theileria sp. in fallow deer (Dama dama) and ticks from an Italian natural preserve. Res Vet Sci. 2011;91(1):110–115. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2010.07.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuehrer HP, Biro N, Harl J, Worliczek HL, Beiglböck C, Farkas R, Joachim A, Duscher GG. Molecular detection of Theileria sp. ZS TO4 in red deer (Cervus elaphus) and questing Haemaphysalis concinna ticks in Eastern Austria. Vet Parasitol. 2013;197(3–4):653–657. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2013.07.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höfle U, Vicente J, Nagore D, Hurtado A, Pena A, De La Fuente J, Gortazar C. The risks of translocating wildlife pathogenic infection with Theileria spp. and Elaeophora elaphi in an imported red deer. Vet Parasitol. 2004;126:387–395. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2004.07.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Sanmartin J, Aurtenetxe O, Barral M, Marco I, Lavin S, García-Pérez AL, Hurtado A. Molecular detection and characterization of piroplasms infecting cervids and chamois in Northern Spain. Parasitology. 2007;134:391–398. doi: 10.1017/S0031182006001569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Sanmartin J, Barandika JF, Juste RA, García-Pérez AL, Hurtado A. Distribution and molecular detection of Theileria and Babesia in questing ticks from Northern Spain. Med Vet Entomol. 2008;22:318–325. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2915.2008.00748.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langton C, Gray JS, Waters PF, Holman PJ. Naturally acquired babesiosis in a reindeer (Rangifer tarandus tarandus) herd in Great Britain. Parasitol Res. 2003;89:194–198. doi: 10.1007/s00436-002-0737-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He L, Khan MK, Zhang WJ, Zhang QL, Zhou YQ, Hu M, Zhao J. Detection and identification of Theileria infection in sika deer ( Cervus nippon ) in China. J Parasit. 2012;98(3):598–603. doi: 10.1645/JP-GE-2883.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medlin L, Elwood HJ, Stickel S, Sogin ML. The characterization of enzymatically amplified eukaryotic 16S-like rRNA-coding regions. Gene. 1988;71:491–499. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allsopp BA, Baylis HA, Allsopp MT, Cavalier-Smith T, Bishop RP, Carrington DM, Sohanpal B, Spooner P. Discrimination between six species of Theileria using oligonucleotide probes which detect small subunit ribosomal RNA sequences. Parasitology. 1993;107:157–165. doi: 10.1017/S0031182000067263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- d’Oliveira C, van der Weide M, Habela MA, Jacquiet P, Jongejan F. Detection of Theileria annulata in blood samples of carrier cattle by PCR. J Clin Microbiol. 1995;33(10):2665–2669. doi: 10.1128/jcm.33.10.2665-2669.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu A, Guan G, Liu Z, Liu J, Leblanc N, Li Y, Gao J, Ma M, Niu Q, Ren Q, Bai Q, Yin H, Luo J. Detecting and differentiating Theileria sergenti and Theileria sinensis in cattle and yaks by PCR based on major piroplasm surface protein (MPSP) Exp Parasitol. 2010;126(4):476–481. doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2010.05.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ota N, Mizuno D, Kuboki N, Igarashi I, Nakamura Y, Yamashina H, Hanzaike T, Fujii K, Onoe S, Hata H, Kondo S, Matsui S, Koga M, Matsumoto K, Inokuma H, Yokoyama N. Epidemiological survey of Theileria orientalis infection in grazing cattle in the eastern part of Hokkaido. Japan J Vet Med Sci. 2009;71(7):937–944. doi: 10.1292/jvms.71.937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boes KM, Goncarovs KO, Thompson CA, Halik LA, Santos AP, Guimaraes AM, Feutz MM, Holman PJ, Vemulapalli R, Messick JB. Identification of a Mycoplasma ovis-like organism in a herd of farmed white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus) in rural Indiana. Vet Clin Pathol. 2012;41:77–83. doi: 10.1111/j.1939-165X.2011.00376.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin H, Liu Z, Guan G, Liu A, Ma M, Ren Q, Luo J. Detection and differentiation of Theileria luwenshuni and T. uilenbergi infection in small ruminants by PCR. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2008;55(5–6):233–237. doi: 10.1111/j.1865-1682.2008.01031.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altay K, Dumanli N, Holman PJ, Aktas M. Detection of Theileria ovis infected sheep by nested PCR. Vet Parasitol. 2005;127:99–104. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2004.09.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aktas M, Altay K, Dumanli N. Survey of Theileria parasites of sheep in eastern Turkey using polymerase chain reaction. Small Ruminant Res. 2005;60:289–293. doi: 10.1016/j.smallrumres.2005.01.002. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Slemenda SB, Chauvin A, Camacho AT, Malandrin L, L'Hostis M, Herwaldt BL, Pieniazek NJ. Re-description and molecular taxonomy of Babesia capreoli Enigk and Friedhoff, 1962 and Theileria capreoli Rukhlyadev, 1939 - piroplasms of the European roe deer (Capreolus capreolus) 2005. Unpublished. [ http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/AY726008.1]
- Guido FCL, Angela PS, Liyod HL, Claudio RM. Assessment of primers designed from small ribosomal subunits RNA for specific discrimination between Babesia bigemina and Babesia bovis by PCR. Ciencia Animal Brasileria V. 2002;3(2):27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Sivakumar T, Tagawa M, Yoshinari T, Ybañez AP, Igarashi I, Ikehara Y, Hata H, Kondo S, Matsumoto K, Inokuma H, Yokoyama N. PCR detection of Babesia ovata from cattle reared in Japan and clinical significance of coinfection with Theileria orientalis. J Clin Microbiol. 2012;50(6):2111–2113. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00220-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aktas M, Altay K, Dumanlı N. Development of a polymerase chain reaction method for diagnosis of Babesia ovis infection in sheep and goats. Vet Parasitol. 2005;133:277–281. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2005.05.057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shayan P, Rahbari S. Simultaneous differentiation between Theileria spp. and Babesia spp. on stained blood smear using PCR. Parasitol Res. 2005;97(4):281–286. doi: 10.1007/s00436-005-1434-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wamwiri FN, Alam U, Thande PC, Aksoy E, Ngure RM, Aksoy S, Ouma JO, Murilla GA. Wolbachia, Sodalis and trypanosome co-infections in natural populations of Glossina austeni and Glossina pallidipes. Parasit Vectors. 2013;6(1):232. doi: 10.1186/1756-3305-6-232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin H, Guan GQ, Ma ML, Luo JX, Lu BY, Yuan GL, Bai Q, Lu CP, Yuan ZP, Preston P. Haemaphysalis qinghaiensis ticks transmit at least two different Theileria species: one is infective to yaks, one is infective to sheep. Vet Parasitol. 2002;107:29–35. doi: 10.1016/S0304-4017(02)00096-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y, Luo J, Guan G, Ma M, Liu A, Liu J, Ren Q, Niu Q, Lu B, Gao J, Liu Z, Dang Z, Tian Z, Zhang B, He Z, Bai Q, Yin H. Experimental transmission of Theileria uilenbergi infective for small ruminants by Haemaphysalis longicornis and Haemaphysalis qinghaiensis. Parasitol Res. 2009;104(5):1227–1231. doi: 10.1007/s00436-009-1347-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]