Abstract
Vaccination is the most effective method of preventing infectious diseases. Since the eradication of small pox in 1976, many other potentially life compromising if not threatening diseases have been dealt with subsequently. This event was a major leap not only in the scientific world already burdened with many diseases but also in the mindset of the common man who became more receptive to novel treatment options. Among the many protozoan diseases, the leishmaniases have emerged as one of the largest parasite killers of the world, second only to malaria. There are three types of leishmaniasis namely cutaneous (CL), mucocutaneous (ML), and visceral (VL), caused by a group of more than 20 species of Leishmania parasites. Visceral leishmaniasis, also known as kala-azar is the most severe form and almost fatal if untreated. Since the first attempts at leishmanization, we have killed parasite vaccines, subunit protein, or DNA vaccines, and now we have live recombinant carrier vaccines and live attenuated parasite vaccines under various stages of development. Although some research has shown promising results, many more potential genes need to be evaluated as live attenuated vaccine candidates. This mini-review attempts to summarize the success and failures of genetically modified organisms used in vaccination against some of major parasitic diseases for their application in leishmaniasis.
Keywords: vaccines, immunology, Leishmania, genetically modified parasites, visceral leishmaniasis
Introduction
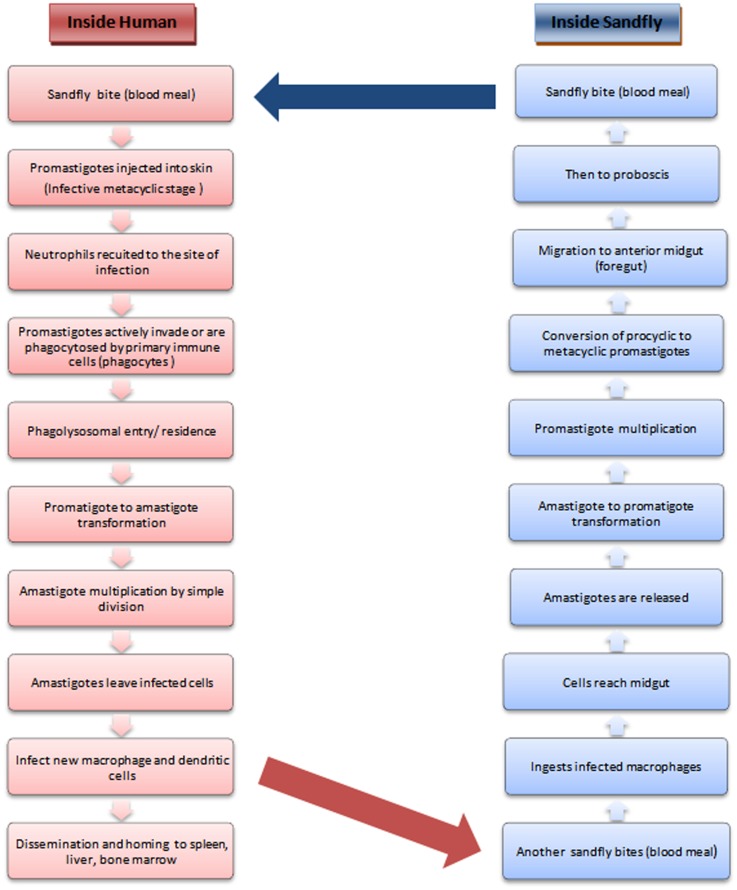
The leishmaniases comprise a group of largely neglected tropical diseases, transmitted during the blood meal of the phlebotomine sandfly (Figure 1). The disease outcome ranges from the mild cutaneous, more severe mucocutaneous to the almost fatal visceral leishmaniasis (followed by PKDL in a small proportion of VL patients) depending upon the transmitted species of Leishmania parasite. With more than 90% of the VL patients concentrated in south-east Asia and Africa, the statistics indicate that almost 200 million people are at risk worldwide, which is only a rough estimate, as a major population remains asymptomatic and hence unrecognized (1). VL ranks fourth in morbidity among all tropical diseases with an annual incidence of 2.5/1000 persons (2) and is second only to malaria in terms of mortality (3).
Figure 1.
Life cycle of Leishmania.
Despite abundant research in recent years, the available treatment options are far from satisfactory. The drugs are associated with toxicity, high cost, and/or resistance. In this context, multi-drug combinatorial therapies have shown some promise (4). Prevention by vaccination is favored by the fact that healing from leishmaniasis is almost always associated with lifelong resistance to infection. A desirable vaccine would provide long term immunity; elicit a T-cell immune response that would be a balance of Th1 mediated immune activation against the pathogen and Th2 mediated suppression to avoid excess tissue damage, produce a strong memory and effector response upon subsequent challenge, be persistent, and highly immunogenic (3). However, the vaccine should not elicit an auto-immune response and be safe even in immune-compromised SCID mice and HIV patients (5).
Based on the general nature of the formulation, there are three types of anti-leishmanial vaccines (6). The first generation of vaccines is comprised of live, virulent parasites injected at hidden body parts so as to avoid lesion visibility (leishmanization) or of inactivated parasites achieved by heat, radiation, antibiotics, chemical mutagenesis, and selection for temperature sensitivity or long passages in-culture (7). The second generation includes crude whole cell lysates, purified fractions, or subunit vaccines composed of single or multiple recombinant or native antigens. The only approved vaccine for human trial is Leish111f, a multivalent vaccine, composed of a thiol-specific antioxidant, Leishmania major stress inducible protein 1, and L. major elongation initiation factor (8). The third generation of vaccines consists largely of DNA in the form of mammalian expression plasmids or viral vectors encoding virulence factors (9). Unfortunately, the efficacy of available DNA and protein subunit vaccine candidates are limited (10). Recent concepts introduce the use of sandfly salivary antigens, T-cell epitope based peptides, antigen pulsed DC’s, and genetically modified live attenuated parasites (11). In contrast, vaccination using live attenuated parasites mimics natural infection and overcomes most of these limitations (12). Additionally, their persistence and display of parasites entire antigenic repertoire alleviates the need for an adjuvant. The recent success of live attenuated vaccination (LAV) in malaria, the clear genetic profile, and safety from reversion of complete knock-outs further encourages this endeavor.
Genetic Modification in Leishmania: Applications and Types
Due to advances in axenic parasite culture, transfection efficiency, availability of genetic manipulation vectors (for expression, recombination, or integration), and the plethora of sequence based information available (from databases, like GeneDB, LeishCyc, LeishBase, KEGG, TriTrypDB, and TDR Targets), the ease and scope of creating live attenuated parasites has increased tremendously (13). Such parasites can be used to elucidate novel drug targets as well as vaccine candidates based on whether the gene under study is essential for both the promastigote and amastigote stages of the parasite or, only the amastigote stage. In addition, genetically modified organisms can also be used in metabolic pathways studies, structure-function relationship investigates (14), screening of new drugs (15), host–parasite interaction, and post-infection analysis among others, to enhance our understanding of these lower eukaryotes. Considering the success of LAV strategies against many viral, bacterial, and protozoan diseases (although to different extents), these are now considered the gold standard for protection against intra-cellular pathogens (12).
Foreign or self genes can be introduced in either episomal or integrated form, for expression of particular proteins to study their effects on various aspects of the parasites life cycle. In the episomal form, the gene’s expression is under the control of the vector specific promoter, which can be inducible or not (for stage specific expression analysis). For integration, the genes are generally targeted downstream of the ribosomal RNA locus to study the effects of constitutive expression at all stages of the life cycle. In either case, the genes can be fused to fluorescent reporter genes for ease of monitoring their expression (15). In addition, there are methods to selectively knock-out particular regions of interest heterologously or homologously using gene specific targeting constructs (16–18). During deletion, the targeted region is replaced by an antibiotic selection marker. Its expression makes the modified cells resistant to that antibiotic, thereby facilitating selection. Multiple genes can be targeted simultaneously. This exchange is generally brought about by the double strand break repair model of homologous recombination (19) whose major role has been the maintenance of its multi-gene families, conferring a selective advantage to parasites stressed by antifolate drugs (by upregulation of resistance genes) (14, 16). Alternatively, the transcripts of the genes can also be simply knocked down by anti-sense RNA interference technique, thereby blocking translation. However, with a few exceptions most leishmanial species lack the RNAi machinery (20).
Success of Live Attenuated Vaccination in Other Diseases
Herein, we will discuss LAV strategies in various mosquito borne, viral, protozoal, and bacterial diseases. Malaria, which exerts significant mortality, morbidity, and economic burden, is spread by intra-cellular parasitic apicomplexans of the genus Plasmodium. Like Leishmania, Plasmodium has multiple hosts and forms and rapid amplification is key to its survival and spread. Their pathogenic liver and transmission stages have been the most often chosen targets for attenuation because compared to the blood stages, they are low in numbers and exhibit limited antigenic variation, making it less probable that a vaccine will fail against heterologous parasite strains. The search for a live attenuated malaria vaccine provided some invaluable insights that can be applied to leishmanial as well as other infectious diseases. The failure of the inactivated sporozoites, and success of γ-irradiated ones, demonstrated the requirement of live and host cell invasive parasites to confer protection (21–23). The ability of the UIS3−/− sporozoites to confer protection against sporozoite re-infection but not blood stage transfusion, demonstrates stage specific immunity, herein, liver stage. Hence, not all stages of a parasites cycle may be equally useful for LAV approaches (24). The deletion of liver stage specific fatty acid synthesis pathway genes, however, had no effect on replication and gametogenesis, indicating that only essential metabolic pathways should be targeted for attenuation. Furthermore, multiple deletions sometimes may be more effective, as combined p26/p52 knock-out provided better protection than either of the single knock-outs in both chimeric mouse harboring human hepatocytes as well as both low/high dose human trials (22, 25, 26). These mutants exhibited complete growth arrest during the liver stages. However, their pre-erythrocytic stages were unhampered, thereby not hindering the possibility of large-scale production. Similarly, for leishmania, an unaffected promastigote growth stage would be desirable for a strain to be used for vaccination.
Another virus that largely affects the cloven hoofed animals worldwide is the foot and mouth disease virus (FMDV). Control by limiting animal movements and herd destruction has been mostly practiced due to insufficient protection by the available inactivated vaccine against all three FMDV variants. Recently, however, a reverse genetics approach has yielded a novel vaccine candidate by substitutions in a few amino-acids showing remarkable protection. These mutants too had normal growth properties as desirable for large-scale vaccine production (27).
One of the most successful and oldest examples of live attenuated vaccines is the 17D strain of yellow fever virus. It has also served as a model for vaccination strategies against dengue, a viral disease caused by transmission of one of its four serotypes 1–4 by the Aedes mosquito. Sanofi Pasteur’s ChimeriVax Dengue tetravalent vaccine (CVD1–4) is the most advanced product so far and a chimera in the truest sense utilizing the licensed YFV 17D vaccine as backbone, each expressing the prM and E genes of one of the four DENV serotypes. An effective dengue vaccine should consist of a tetravalent formulation, with components representing each serotype (28). A “stem-loop” genomic region implicated in its pathogenicity has been deleted to create the rDEN(1,2,4)Δ30 strains that impart adequate protection. However, the rDEN3Δ30 was not protective, indicating differences among strains. Hence, a novel chimerization led to a creation of rDEN3/4Δ30(ME) – a recombinant virus backbone of serotype 4 with Δ30 deletion, containing the ME region of a naturally attenuated serotype 3 strain, having manifold lower replication and transmission. This is a perfect example of successful extrapolation from sabin polio virus whose second component was also a naturally attenuated polio strain (29).
The MMR vaccine against measles, mumps, and rubella given to expecting mothers is another successful example of a multivalent vaccine that reduces the number of doses and avoids unnecessary delays and problems of spacing live attenuated vaccines (30). With pandemic capacity (31), the influenza vaccine, has been a huge challenge with its constantly varying epitopes resulting in antigenically drifted strains (32). In such cases, focusing on the most constant regions is the best strategy. However, till a strain specific vaccine is available, reasonable protection can be offered by a recombinant adenoviral vector expressing antigens from H5, H7, and H9 avian influenza virus strains (33). The success of multivalent, dengue, influenza, and MMR vaccines offers the idea for such a vaccine against CL, ML, and VL too.
Among bacteria, Streptococcus suis, that causes swine flu is a global health hazard to the swine industry, associated with septic shock, pneumonia, meningitis, and arthritis. The current vaccine against it is a Sly gene deletion attenuated strain undergoing some refinement by association with other surface antigens and adjuvants (34). The Bacillus Calmette Guerin vaccine for tuberculosis is created by long in vitro passaging of the intra-cellular bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The gradual loss of the RD loci has been reported as the major cause for this attenuation. Hence, attempts at manually creating these deletions are on. Recombinant BCG vaccines co-expressing other antigens from pathogens are also in clinical trials (35, 36). For cholera too, many endogenously produced live attenuated vaccines (Peru15 and Bengal15) are available as a traveler’s vaccine in different countries (37–39).
Elucidation of Novel Vaccine Candidates and Drug Targets: Attempts Made in Leishmania
In contrast to leishmanial species causing CL, research on genetic modification in VL has been limited. However, recent years have seen a significant improvement in this scenario (Table 1). Though mostly focused at elucidating metabolic pathways, cellular processes, and host–parasite interactions; it has simultaneously led to the discovery of novel drug targets and vaccine candidates. The major pathways targeted were those that are unique to the parasite’s life cycle or metabolism, components sufficiently different from the homolog in hosts. Today, bio-informatic databases, proteomic screens (40), and reverse vaccinology, aid in the identification of novel vaccine candidates based on their expression stage, abundance, sub-cellular localization, sequence conservation in leishmanial species, non-homology to their human counterparts, trans-membrane helix predictions, and T-cell epitopic regions (12). Using the same genetically modified strain, research collaborations between labs working on different aspects of leishmaniasis can greatly speed up and enhance this search. Some of the most important pathways and their components, that have surfaced, are briefly discussed below.
Table 1.
Genetic deletions that led to the discovery of novel drug or vaccine candidates in VL causing organisms.
| Organism | Target gene | Animal model | Immune response | Persistence | Inference |
Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drug | LAV | ||||||
| L. mexicana | Arginase | NA | NA | NA | + | UC | (41–43) |
| L. major | |||||||
| L. donovani | Ornithine decarboxylase | BALB/c mice | Reduced virulence in vitro and in vivo | NA | + | + | (44–46) |
| L. donovani | Spermidine synthase | BALB/c mice | Decreased organ parasite burden | 4 weeks | + | UC | (47) |
| L. donovani | S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase | NA | NA | NA | + | UC | (48) |
| L. donovani | Trypanothione reductase | NA | Reduced virulence in vitro | NA | + | UC | (49–52) |
| L. donovani | Trypanothione synthetase | NA | NA | NA | + | UC | (42, 53) |
| L. donovani | Hypoxanthine–guanine phosphoribosyl transferase | NA | No effect on virulence in vitro and in vivo | NA | X | X | (54) |
| L. donovani | Adenine phosphoribosyl transferase | NA | No effect on virulence in vitro and in vivo | NA | X | X | (54, 55) |
| L. donovani | Xanthine phosphoribosyl transferase | NA | No effect on virulence in vitro and in vivo | NA | + | UC | (54, 56) |
| L. donovani | Inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase | BALB/c mice | No effect on virulence in vivo | NA | X | X | (57) |
| L. donovani | Adenine aminohydrolase | BALB/c mice | No significant effect on parasitemia in vitro or in organ parasite burden | NA | + | UC | (58) |
| L. donovani | Hypoxanthine–guanine phosphoribosyl transferase/xanthine phosphoribosyl transferase | NA | Highly reduced virulence in vitro | NA | – | + | (59) |
| L. donovani | Adenine aminohydrolase/hypoxanthine–guanine phosphoribosyl transferase/xanthine phosphoribosyl transferase | BALB/c mice | Avirulent in vitro and in vivo | 4 weeks | – | + | (58) |
| L. donovani | Adenylosuccinate synthetase | BALB/c mice | Reduced virulence in vitro but not in vivo | NA | X | X | (60) |
| L. donovani | Adenylosuccinate lyase | BALB/c mice | Reduced virulence in vitro and in vivo | NA | + | UC | (60) |
| L. donovani | Uridine monophosphate synthase | NA | NA | NA | + | UC | (61) |
| L. donovani | Uracil phosphoribosyl transferase | BALB/c mice | No effect on virulence in vitro or in vivo | NA | + | UC | (62, 63) |
| L. donovani | Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase | BALB/c mice | Reduced virulence in vitro and decreased parasite burden | NA | + | UC | (62) |
| L. donovani | Uracil phosphoribosyl transferase/carbamoyl phosphate synthetase | BALB/c mice | Reduced virulence in vivo | 4 weeks | – | + | (62) |
| L. donovani | Biopterin transporter 1 | BALB/c mice | Reduced virulence in vivo. Protective against challenge infection. Increased IFN-γ production upon splenocyte stimulation | 3 months | UC | + | (64) |
| L. donovani | Centrin | BALB/c mice, SCID mice, golden Syrian hamsters | Long term protection against challenge infection-early clearance. Protective Th1-type immune response. Increase of single and multiple cytokine (IFN-γ, IL-2, and TNFα) producing cells, IFN-γ/IL-10 ratio, IgG2a immunoglobulins and NO production. Reduced organ parasite burden. Cross-protective against L. braziliensis challenge | 10 weeks | UC | + | (65, 66) |
| L. donovani | P27, a cytochrome c oxidase component | BALB/c mice | Reduced virulence in vivo. NO generation, Ag-specific multifunctional CD4 and CD8 T-cells, enhanced secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines IFN-γ, TNF-α, IL-12, and anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-10, IL-4, and IL-13 | 20 weeks | UC | + | (67) |
| L. donovani | Ubiquitin fold modifier-1 | NA | Reduced virulence in human macrophages | NA | + | + | (68) |
| L. donovani | Golgi GDP mannose transporter | BALB/c mice | Reduced virulence in vitro and in vivo | Long term | + | + | (69) |
| L. donovani | Amastigote specific expression protein-2 | BALB/c mice | Decreased virulence in vitro and in vivo | NA | + | X | (70) |
| L. donovani | Cathepsin b cysteine protease | NA | Decreased virulence in U937 macrophage cells | NA | + | UC | (71) |
| L. donovani | Oligopeptidase b serine protease | BALB/c mice | Decreased virulence in the murine footpad infection model. Massive upregulation in gene-transcription | NA | + | UC | (72) |
| L. donovani | Subtilisin protease | BALB/c mice, golden Syrian hamsters | Reduced virulence in vivo | NA | + | UC | (73) |
| L. donovani | Myosin | NA | NA | NA | + | UC | (74) |
| L. donovani | 70 kDa subunit of outer dynein arm docking complex | NA | Increased virulence in vitro | NA | X | X | (75) |
| L. donovani | Actin | NA | Reduced survival in vitro mice peritoneal macrophage cells | NA | + | UC | (76) |
| L. donovani | ADP-ribosylation factor like protein-3A | NA | NA | NA | + | UC | (77) |
| L. infantum | Heat shock protein 70 type II | L. major model of infection in BALB/c mice, SCID mice, golden Syrian hamster | Increased NO production and protection by type 1 immune response in BALB/c mice | NA | UC | + | (78) |
| L. donovani | Small glutamine rich tetra trichopeptide | NA | NA | NA | + | UC | (79) |
| L. donovani | Casein kinase 1 isoform 4 | NA | Increased virulence in vitro mice peritoneal macrophage cells | NA | + | UC | (80) |
| L. donovani | Glyoxalase I | NA | NA | NA | + | UC | (81) |
| L. donovani | cyp5122A1, a cytochrome P450 | Golden Syrian hamsters | Decreased virulence in vitro and in vivo | NA | + | UC | (82) |
| Color codes | Role | Symbols/short forms | Interpretation | ||||
| Purple | Polyamine metabolism | NA | Not available | ||||
| Blue | Purine metabolism | + | Positive indication | ||||
| Gray | Pyrimidine metabolism | – | Not evaluated | ||||
| Green | Amastigote stage | UC | Uncertain | ||||
| Yellow | Protease | X | Negative indication | ||||
| Peach | Cytoskeletal involvement | ||||||
| Pink | Chaperones | ||||||
| White | Others | ||||||
Polyamine metabolism
Polyamines are essential for proliferative processes and trypanothione synthesis. Their biosynthesis involves arginase, ornithine decarboxylase, S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase, and spermidine synthase. In Leishmania, spermidine along with trypanothione reductase and trypanothione synthetase replace the antioxidant pathways of the host and are necessary for survival. Deletion of any of these enzymes implicates the essentiality of polyamine biosynthesis in both promastigotes and amastigotes, rendering them important drug targets.
Nucleotide metabolism
Purines and pyrimidines are indispensable to all life. However, Leishmania are purine auxotrophs. Surprisingly, deletion of any of the purine salvages enzymes, namely hypoxanthine–guanine phosphoribosyl transferase (Hgprt), adenine phosphoribosyl transferase (Aprt), and xanthine phosphoribosyl transferase (Xprt); guanylate nucleotide synthesis enzyme namely inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH) or; adenine aminohydrolase (Aah) does not prove their essentiality for either salvage, virulence, or viability. However, multiple knock-out strains such as Δhgprt/Δxprt and Δaah/Δhgprt/Δxprt are avirulent and hence potential vaccine candidates. However, the upregulation of Xprt in combined mutants implicate their therapeutic potential. Similarly, although both adenylosuccinate synthetase (Adss) and adenylosuucinate lyase (Asl) null mutants show diminished virulence, only the Δasl null mutants are profoundly incapacitated in their ability to infect mice and essential for purine salvage by both life cycle stages.
In contrast to purines, Leishmania are prototrophic for pyrimidines. Nevertheless, they also possess some salvage enzymes. Deletion of the uridine monophosphate synthase (Umps), a bifunctional enzyme for UMP biosynthesis established this enzyme as essential for pyrimidine biosynthesis. Additionally, although single deletions of either uracil phosphoribosyl transferase (Uprt) or carbamoyl phosphate synthetase (Cprt) did not affect parasite growth, their combined deletion mutants were completely attenuated exhibiting reduced survivability, hence potential live vaccine candidates.
Amastigote stage specific proteins
Amastigote stage specific genes are considered good targets for attenuation. Vaccination with null mutants of the biopterin transporter 1 (Bt1) gene, involved in biopterin transport; centrin (Cen), involved in the cell division cycle; p27, a cytochrome c oxidase complex component; Lpg-2 (Golgi GDP mannose transporter), involved in phosphoglycan synthesis, which is essential for host–parasite interactions or ubiquitin fold modifier-1 (Ufm-1) gene involved in fatty acid metabolism produced a strong protective immunity against challenge infection. Their reduced virulence and survivability confirms their vaccine candidature and demands further investigations. However, similar attempts with A2 (amastigote specific expression 2) genes failed due to their multiplicity and rapid compensation by amplification of the remaining genes.
Proteases
Proteases play key roles in the life cycle, host–parasite relationship and pathogenesis of parasitic diseases. The deletion of genes for cathepsin B cysteine protease, oligopeptidase B serine protease, or subtilisin protease resulted in avirulent strains causing proteome remodeling, upregulation of gene-transcription in macrophages, or reduced promastigote to amastigote differentiation in vitro, respectively. As in many other diseases, proteases form attractive drug targets.
Cytoskeletal elements
Some flagellar components were also found to play important roles in the parasites life cycle. The deletion of myosin XXI, that encodes a novel class of myosin; the 70 kDa subunit of the outer dynein arm docking complex; a novel actin related protein (ORF LmjF.13.0950) or the over-expression of ARL-3A (ADP-ribosylation factor like protein), a homolog of human ARL-3, all resulted in impairment of flagellar assembly, motility, and survival. They also affected intra-cellular trafficking, virulence in vitro and mitochondrial membrane potential to various extents. Hence, a novel group of putatively essential components that hold promise for further studies were identified.
In addition to these, components of some other pathways have also been manipulated to assess their functional role and dispensability. Heterozygous mutants of glyoxalase I (GLO I), involved in methylglyoxal metabolism and CYP5122A1, involved in xenobiotic metabolism and sterol biosynthesis, impaired growth, mitochondrial membrane potential, and normal metabolism. Altered drug susceptibility and virulence were also observed in the latter mutants. Moreover, attempts at homozygous deletions did not permit survival. In addition, knock-outs of some chaperone proteins like HSP70-II, HSP90, and co-chaperones like SGT (small glutamine rich tetra trichopeptide) also had deleterious effects. Also, trials of LiHSP70-II null mutants to provide protection against L. major infection model demonstrated both safety and protection. In another study, the over-expression of a kinase, CK1.4 (casein kinase 1 isoform 4), increased virulence and metacyclogenesis. As seen, majorly these studies implicate the therapeutic potential of the target genes. Simultaneous evaluation of their LAV potential would greatly fasten the search for an ideal leishmanial vaccine.
Challenges and Scope for the Future
Although a large proportion of currently licensed vaccines are based on inactivated or whole live attenuated organisms, the scope of LAV gets largely restricted due to safety issues. Foremost, is the risk of reversion to wild type or expression of compensatory genes. The Leishmania genome being highly plastic, this has a high probability. Additionally, critical consideration of the position of knock-outs, their effects on upstream and downstream genes, the restriction to manipulate only amastigote stage specific and single copy genes and availability of few selectable markers limits the potential targets and simultaneous multi-gene targeting, respectively (12). Furthermore, the retention of antibiotic resistance genes (20) and generation of cross resistance to anti-leishmanial drugs as in the case of neomycin to paromomycin is undesirable (83). Moreover, prior to human clinical trials, the cultivation of parasites in serum free media, their large-scale production, storage, validation of the best challenge methods-syringe or sandfly mediated, and many months of post challenge follow-up impose practical and as yet unresolved issues (84). In contrast, subunit and DNA vaccines are relatively safe and without these limitations. However, the low predictive power of available pre-clinical models to determine the human outcome of vaccination and the lack of knowledge of convincing markers to monitor their safety or efficacy remain common to all vaccination strategies (2).
The following road map may be considered a basic guideline while working with live attenuated vaccines. Preliminary phenotypic and genotypic screening of the parasites after each recombination event should be followed by vigorous in vitro studies on human cell lines. The parasites compartmentalization, proliferation, cellular responses, and activation markers should be closely monitored (85). After successful in vitro screening, the in vivo experiments in Golden Syrian hamsters and BALB/c mice models should be supported by those on chimeric humanized mice (25, 86). Continuous monitoring assays to test for reversion or attenuation retention by sensitive molecular biology techniques like PCR, microarrays should be done (87). Timely splenic biopsies for parasite load and multiparametric FACS analysis and ELISA for monitoring cytokine responses would help in elucidating the immune correlates of protection or disease development (6). Additionally, the comparison of these results among different groups, namely asymptomatic carriers, non-endemic healthy, endemic healthy, infected-cured, and infected individuals would greatly enhance our knowledge of disease pathogenesis. With the advent of modern imaging techniques, bioluminescent parasites can provide unsurpassable insight at each level of disease progression in real time (beginning from host cell–parasite interaction to dissemination and homing to various organs) also requiring lower number of animals to obtain statistically significant data (88). Lastly, human trials to provide proof of concept studies would strengthen our hypothesis derived from pre-clinical studies.
Parasite gene deletion mutants have helped in numerous pathway studies and elucidation of novel drug targets and vaccine candidates (Table 1). They also offer the possibility of co-administration with adjuvants or drugs to improve disease outcome. Moreover, vectored formulations in recombinant vaccinia (89), Lactobacillus (90), adenovirus, or Salmonella (91) carriers offer non-pathogenic and genetically modifiable alternatives for safe mucosal delivery, the major entry portal of pathogens. The concept of the flying vaccinator, genetically engineered blood-feeding insects to deliver vaccines to replace mosquito populations is a novel attempt tried in antimalarial programs and can be applied for sandfly eradication (92) too. Lastly, well-defined clinical trials with attenuated parasites will enhance the number of potential therapeutic targets, which are urgently needed to combat leishmaniasis.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, Government of India. We thank Md Asad and Anirban Bhattacharya for their help during preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1.Alvar J, Velez ID, Bern C, Herrero M, Desjeux P, Cano J, et al. Leishmaniasis worldwide and global estimates of its incidence. PLoS One (2012) 7:e35671. 10.1371/journal.pone.0035671 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Schroeder J, Aebischer T. Vaccines for leishmaniasis: from proteome to vaccine candidates. Hum Vaccin (2011) 7(Suppl):10–5 10.4161/hv.7.0.14556 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kaye PM, Aebischer T. Visceral leishmaniasis: immunology and prospects for a vaccine. Clin Microbiol Infect (2011) 17:1462–70 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2011.03610.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kumar N, Sinha PK, Pandey K, Verma N, Lal CS, Ranjan A, et al. A rare case of visceral leishmaniasis with multiple relapse and multi-drug unresponsive: successfully treated with combination therapy. Int J Clin Pharm (2011) 33:726–9 10.1007/s11096-011-9544-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Evans KJ, Kedzierski L. Development of vaccines against visceral leishmaniasis. J Trop Med (2012) 2012:892817. 10.1155/2012/892817 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Das A, Ali N. Vaccine development against Leishmania donovani. Front Immunol (2012) 3:99. 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00099 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Noazin S, Modabber F, Khamesipour A, Smith PG, Moulton LH, Nasseri K, et al. First generation leishmaniasis vaccines: a review of field efficacy trials. Vaccine (2008) 26:6759–67 10.1016/j.vaccine.2008.09.085 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Trigo J, Abbehusen M, Netto EM, Nakatani M, Pedral-Sampaio G, De Jesus RS, et al. Treatment of canine visceral leishmaniasis by the vaccine Leish-111f+MPL-SE. Vaccine (2010) 28:3333–40 10.1016/j.vaccine.2010.02.089 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Tabbara KS. Progress towards a Leishmania vaccine. Saudi Med J (2006) 27:942–50 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kedzierski L. Leishmaniasis. Hum Vaccin (2011) 7:1204–14 10.4161/hv.7.11.17752 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Okwor I, Uzonna J. Vaccines and vaccination strategies against human cutaneous leishmaniasis. Hum Vaccin (2009) 5:291–301 10.4161/hv.5.5.7607 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Silvestre R, Cordeiro-Da-Silva A, Ouaissi A. Live attenuated Leishmania vaccines: a potential strategic alternative. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) (2008) 56:123–6 10.1007/s00005-008-0010-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Timmers LF, Pauli I, Barcellos GB, Rocha KB, Caceres RA, De Azevedo WF, Jr, et al. Genomic databases and the search of protein targets for protozoan parasites. Curr Drug Targets (2009) 10:240–5 10.2174/138945009787581195 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Tobin JF, Wirth DF. A sequence insertion targeting vector for Leishmania enrietti. J Biol Chem (1992) 267:4752–8 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Singh N, Gupta R, Jaiswal AK, Sundar S, Dube A. Transgenic Leishmania donovani clinical isolates expressing green fluorescent protein constitutively for rapid and reliable ex vivo drug screening. J Antimicrob Chemother (2009) 64:370–4 10.1093/jac/dkp206 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Tobin JF, Laban A, Wirth DF. Homologous recombination in Leishmania enrietti. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (1991) 88:864–8 10.1073/pnas.88.3.864 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hwang HY, Gilberts T, Jardim A, Shih S, Ullman B. Creation of homozygous mutants of Leishmania donovani with single targeting constructs. J Biol Chem (1996) 271:30840–6 10.1074/jbc.271.48.30840 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Fulwiler AL, Soysa DR, Ullman B, Yates PA. A rapid, efficient and economical method for generating leishmanial gene targeting constructs. Mol Biochem Parasitol (2011) 175:209–12 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2010.10.008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Papadopoulou B, Dumas C. Parameters controlling the rate of gene targeting frequency in the protozoan parasite Leishmania. Nucleic Acids Res (1997) 25:4278–86 10.1093/nar/25.21.4278 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Roberts SC. The genetic toolbox for Leishmania parasites. Bioeng Bugs (2011) 2:320–6 10.4161/bbug.2.6.18205 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hoffman SL, Billingsley PF, James E, Richman A, Loyevsky M, Li T, et al. Development of a metabolically active, non-replicating sporozoite vaccine to prevent Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Hum Vaccin (2010) 6:97–106 10.4161/hv.6.1.10396 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Vaughan AM, Wang R, Kappe SH. Genetically engineered, attenuated whole-cell vaccine approaches for malaria. Hum Vaccin (2010) 6:107–13 10.4161/hv.6.1.9654 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Matuschewski K, Hafalla JC, Borrmann S, Friesen J. Arrested Plasmodium liver stages as experimental anti-malaria vaccines. Hum Vaccin (2011) 7(Suppl):16–21 10.4161/hv.7.0.14557 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Mueller AK, Labaied M, Kappe SH, Matuschewski K. Genetically modified Plasmodium parasites as a protective experimental malaria vaccine. Nature (2005) 433:164–7 10.1038/nature03188 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Vanbuskirk KM, O’neill MT, De La Vega P, Maier AG, Krzych U, Williams J, et al. Preerythrocytic, live-attenuated Plasmodium falciparum vaccine candidates by design. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (2009) 106:13004–9 10.1073/pnas.0906387106 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Spring M, Murphy J, Nielsen R, Dowler M, Bennett JW, Zarling S, et al. First-in-human evaluation of genetically attenuated Plasmodium falciparum sporozoites administered by bite of Anopheles mosquitoes to adult volunteers. Vaccine (2013) 31:4975–83 10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.08.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Li P, Bai X, Sun P, Li D, Lu Z, Cao Y, et al. Evaluation of a genetically modified foot-and-mouth disease virus vaccine candidate generated by reverse genetics. BMC Vet Res (2012) 8:57. 10.1186/1746-6148-8-57 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Wan SW, Lin CF, Wang S, Chen YH, Yeh TM, Liu HS, et al. Current progress in dengue vaccines. J Biomed Sci (2013) 20:37. 10.1186/1423-0127-20-37 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Blaney JE, Jr, Hanson CT, Firestone CY, Hanley KA, Murphy BR, Whitehead SS. Genetically modified, live attenuated dengue virus type 3 vaccine candidates. Am J Trop Med Hyg (2004) 71:811–21 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.White SJ, Boldt KL, Holditch SJ, Poland GA, Jacobson RM. Measles, mumps, and rubella. Clin Obstet Gynecol (2012) 55:550–9 10.1097/GRF.0b013e31824df256 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Lopez-Macias C. Virus-like particle (VLP)-based vaccines for pandemic influenza: performance of a VLP vaccine during the 2009 influenza pandemic. Hum Vaccin Immunother (2012) 8:411–4 10.4161/hv.18757 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Wikramaratna PS, Sandeman M, Recker M, Gupta S. The antigenic evolution of influenza: drift or thrift? Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci (2013) 368:20120200. 10.1098/rstb.2012.0200 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Vemula SV, Ahi YS, Swaim AM, Katz JM, Donis R, Sambhara S, et al. Broadly protective adenovirus-based multivalent vaccines against highly pathogenic avian influenza viruses for pandemic preparedness. PLoS One (2013) 8:e62496. 10.1371/journal.pone.0062496 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Du H, Huang W, Xie H, Ye C, Jing H, Ren Z, et al. The genetically modified suilysin, rSLY(P353L), provides a candidate vaccine that suppresses proinflammatory response and reduces fatality following infection with Streptococcus suis. Vaccine (2013) 31:4209–15 10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.07.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kaufmann SH, Gengenbacher M. Recombinant live vaccine candidates against tuberculosis. Curr Opin Biotechnol (2012) 23:900–7 10.1016/j.copbio.2012.03.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Romano M, Huygen K. An update on vaccines for tuberculosis – there is more to it than just waning of BCG efficacy with time. Expert Opin Biol Ther (2012) 12:1601–10 10.1517/14712598.2012.721768 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ryan ET, Calderwood SB, Qadri F. Live attenuated oral cholera vaccines. Expert Rev Vaccines (2006) 5:483–94 10.1586/14760584.5.4.483 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Chowdhury MI, Sheikh A, Qadri F. Development of Peru-15 (CholeraGarde), a live-attenuated oral cholera vaccine: 1991-2009. Expert Rev Vaccines (2009) 8:1643–52 10.1586/erv.09.137 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Shin S, Desai SN, Sah BK, Clemens JD. Oral vaccines against cholera. Clin Infect Dis (2011) 52:1343–9 10.1093/cid/cir141 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Paape D, Aebischer T. Contribution of proteomics of Leishmania spp. to the understanding of differentiation, drug resistance mechanisms, vaccine and drug development. J Proteomics (2011) 74:1614–24 10.1016/j.jprot.2011.05.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Roberts SC, Tancer MJ, Polinsky MR, Gibson KM, Heby O, Ullman B. Arginase plays a pivotal role in polyamine precursor metabolism in Leishmania. Characterization of gene deletion mutants. J Biol Chem (2004) 279:23668–78 10.1074/jbc.M402042200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Heby O, Persson L, Rentala M. Targeting the polyamine biosynthetic enzymes: a promising approach to therapy of African sleeping sickness, Chagas’ disease, and leishmaniasis. Amino Acids (2007) 33:359–66 10.1007/s00726-007-0537-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Reguera RM, Balana-Fouce R, Showalter M, Hickerson S, Beverley SM. Leishmania major lacking arginase (ARG) are auxotrophic for polyamines but retain infectivity to susceptible BALB/c mice. Mol Biochem Parasitol (2009) 165:48–56 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2009.01.001 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Jiang Y, Roberts SC, Jardim A, Carter NS, Shih S, Ariyanayagam M, et al. Ornithine decarboxylase gene deletion mutants of Leishmania donovani. J Biol Chem (1999) 274:3781–8 10.1074/jbc.274.6.3781 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Boitz JM, Yates PA, Kline C, Gaur U, Wilson ME, Ullman B, et al. Leishmania donovani ornithine decarboxylase is indispensable for parasite survival in the mammalian host. Infect Immun (2009) 77:756–63 10.1128/IAI.01236-08 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Roberts SC, Kline C, Liu W, Ullman B. Generating knock-in parasites: integration of an ornithine decarboxylase transgene into its chromosomal locus in Leishmania donovani. Exp Parasitol (2011) 128:166–9 10.1016/j.exppara.2011.02.020 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Gilroy C, Olenyik T, Roberts SC, Ullman B. Spermidine synthase is required for virulence of Leishmania donovani. Infect Immun (2011) 79:2764–9 10.1128/IAI.00073-11 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Roberts SC, Scott J, Gasteier JE, Jiang Y, Brooks B, Jardim A, et al. S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase from Leishmania donovani. Molecular, genetic, and biochemical characterization of null mutants and overproducers. J Biol Chem (2002) 277:5902–9 10.1074/jbc.M110118200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Kelly JM, Taylor MC, Smith K, Hunter KJ, Fairlamb AH. Phenotype of recombinant Leishmania donovani and Trypanosoma cruzi which over-express trypanothione reductase. Sensitivity towards agents that are thought to induce oxidative stress. Eur J Biochem (1993) 218:29–37 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18348.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Dumas C, Ouellette M, Tovar J, Cunningham ML, Fairlamb AH, Tamar S, et al. Disruption of the trypanothione reductase gene of Leishmania decreases its ability to survive oxidative stress in macrophages. EMBO J (1997) 16:2590–8 10.1093/emboj/16.10.2590 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Tovar J, Cunningham ML, Smith AC, Croft SL, Fairlamb AH. Down-regulation of Leishmania donovani trypanothione reductase by heterologous expression of a trans-dominant mutant homologue: effect on parasite intracellular survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (1998) 95:5311–6 10.1073/pnas.95.9.5311 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Tovar J, Wilkinson S, Mottram JC, Fairlamb AH. Evidence that trypanothione reductase is an essential enzyme in Leishmania by targeted replacement of the tryA gene locus. Mol Microbiol (1998) 29:653–60 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1998.00968.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Saudagar P, Dubey VK. Cloning, expression, characterization and inhibition studies on trypanothione synthetase, a drug target enzyme, from Leishmania donovani. Biol Chem (2011) 392:1113–22 10.1515/BC.2011.222 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Boitz JM, Ullman B. Leishmania donovani singly deficient in HGPRT, APRT or XPRT are viable in vitro and within mammalian macrophages. Mol Biochem Parasitol (2006) 148:24–30 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2006.02.015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Kaur K, Iovannisci DM, Ullman B. Adenine phosphoribosyltransferase-deficient Leishmania donovani. Adv Exp Med Biol (1986) 195(Pt B):553–7 10.1007/978-1-4684-1248-2_86 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Jardim A, Bergeson SE, Shih S, Carter N, Lucas RW, Merlin G, et al. Xanthine phosphoribosyltransferase from Leishmania donovani. Molecular cloning, biochemical characterization, and genetic analysis. J Biol Chem (1999) 274:34403–10 10.1074/jbc.274.48.34403 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Fulwiler AL, Boitz JM, Gilroy C, Yates PA, Jardim A, Ullman B. IMP dehydrogenase deficiency in Leishmania donovani causes a restrictive growth phenotype in promastigotes but is not essential for infection in mice. Mol Biochem Parasitol (2011) 180:123–6 10.1016/j.molbiopara.2011.08.006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Boitz JM, Strasser R, Hartman CU, Jardim A, Ullman B. Adenine aminohydrolase from Leishmania donovani: unique enzyme in parasite purine metabolism. J Biol Chem (2012) 287:7626–39 10.1074/jbc.M111.307884 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Boitz JM, Ullman B. A conditional mutant deficient in hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase and xanthine phosphoribosyltransferase validates the purine salvage pathway of Leishmania donovani. J Biol Chem (2006) 281:16084–9 10.1074/jbc.M600188200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Boitz JM, Strasser R, Yates PA, Jardim A, Ullman B. Adenylosuccinate synthetase and adenylosuccinate lyase deficiencies trigger growth and infectivity deficits in Leishmania donovani. J Biol Chem (2013) 288:8977–90 10.1074/jbc.M112.431486 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.French JB, Yates PA, Soysa DR, Boitz JM, Carter NS, Chang B, et al. The Leishmania donovani UMP synthase is essential for promastigote viability and has an unusual tetrameric structure that exhibits substrate-controlled oligomerization. J Biol Chem (2011) 286:20930–41 10.1074/jbc.M111.228213 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Wilson ZN, Gilroy CA, Boitz JM, Ullman B, Yates PA. Genetic dissection of pyrimidine biosynthesis and salvage in Leishmania donovani. J Biol Chem (2012) 287:12759–70 10.1074/jbc.M112.346502 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Soysa R, Wilson ZN, Elferich J, Forquer I, Shinde U, Riscoe MK, et al. Substrate inhibition of uracil phosphoribosyltransferase by uracil can account for the uracil growth sensitivity of Leishmania donovani pyrimidine auxotrophs. J Biol Chem (2013) 288:29954–64 10.1074/jbc.M113.478826 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Papadopoulou B, Roy G, Breton M, Kundig C, Dumas C, Fillion I, et al. Reduced infectivity of a Leishmania donovani biopterin transporter genetic mutant and its use as an attenuated strain for vaccination. Infect Immun (2002) 70:62–8 10.1128/IAI.70.1.62-68.2002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Selvapandiyan A, Dey R, Nylen S, Duncan R, Sacks D, Nakhasi HL. Intracellular replication-deficient Leishmania donovani induces long lasting protective immunity against visceral leishmaniasis. J Immunol (2009) 183:1813–20 10.4049/jimmunol.0900276 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Fiuza JA, Santiago Hda C, Selvapandiyan A, Gannavaram S, Ricci ND, Bueno LL, et al. Induction of immunogenicity by live attenuated Leishmania donovani centrin deleted parasites in dogs. Vaccine (2013) 31:1785–92 10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.01.048 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Dey R, Dagur PK, Selvapandiyan A, Mccoy JP, Salotra P, Duncan R, et al. Live attenuated Leishmania donovani p27 gene knockout parasites are nonpathogenic and elicit long-term protective immunity in BALB/c mice. J Immunol (2013) 190:2138–49 10.4049/jimmunol.1202801 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Gannavaram S, Connelly PS, Daniels MP, Duncan R, Salotra P, Nakhasi HL. Deletion of mitochondrial associated ubiquitin fold modifier protein Ufm1 in Leishmania donovani results in loss of beta-oxidation of fatty acids and blocks cell division in the amastigote stage. Mol Microbiol (2012) 86:187–98 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2012.08183.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Gaur U, Showalter M, Hickerson S, Dalvi R, Turco SJ, Wilson ME, et al. Leishmania donovani lacking the Golgi GDP-man transporter LPG2 exhibit attenuated virulence in mammalian hosts. Exp Parasitol (2009) 122:182–91 10.1016/j.exppara.2009.03.014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Zhang WW, Matlashewski G. Characterization of the A2-A2rel gene cluster in Leishmania donovani: involvement of A2 in visceralization during infection. Mol Microbiol (2001) 39:935–48 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2001.02286.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Mundodi V, Kucknoor AS, Gedamu L. Role of Leishmania (Leishmania) chagasi amastigote cysteine protease in intracellular parasite survival: studies by gene disruption and antisense mRNA inhibition. BMC Mol Biol (2005) 6:3. 10.1186/1471-2199-6-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Swenerton RK, Zhang S, Sajid M, Medzihradszky KF, Craik CS, Kelly BL, et al. The oligopeptidase B of Leishmania regulates parasite enolase and immune evasion. J Biol Chem (2011) 286:429–40 10.1074/jbc.M110.138313 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Swenerton RK, Knudsen GM, Sajid M, Kelly BL, Mckerrow JH. Leishmania subtilisin is a maturase for the trypanothione reductase system and contributes to disease pathology. J Biol Chem (2010) 285:31120–9 10.1074/jbc.M110.114462 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Katta SS, Tammana TV, Sahasrabuddhe AA, Bajpai VK, Gupta CM. Trafficking activity of myosin XXI is required in assembly of Leishmania flagellum. J Cell Sci (2010) 123(Pt 12):2035–44 10.1242/jcs.064725 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Harder S, Thiel M, Clos J, Bruchhaus I. Characterization of a subunit of the outer dynein arm docking complex necessary for correct flagellar assembly in Leishmania donovani. PLoS Negl Trop Dis (2010) 4:e586. 10.1371/journal.pntd.0000586 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Singh K, Veluru NK, Trivedi V, Gupta CM, Sahasrabuddhe AA. An actin-like protein is involved in regulation of mitochondrial and flagellar functions as well as in intramacrophage survival of Leishmania donovani. Mol Microbiol (2014) 91:562–78 10.1111/mmi.12477 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Cuvillier A, Redon F, Antoine JC, Chardin P, DeVos T, Merlin G. LdARL-3A, a Leishmania promastigote-specific ADP-ribosylation factor-like protein, is essential for flagellum integrity. J Cell Sci (2000) 113(Pt 11):2065–74 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Carrion J, Folgueira C, Soto M, Fresno M, Requena JM. Leishmania infantum HSP70-II null mutant as candidate vaccine against leishmaniasis: a preliminary evaluation. Parasit Vectors (2011) 4:150. 10.1186/1756-3305-4-150 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Ommen G, Chrobak M, Clos J. The co-chaperone SGT of Leishmania donovani is essential for the parasite’s viability. Cell Stress Chaperones (2010) 15:443–55 10.1007/s12192-009-0160-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Dan-Goor M, Nasereddin A, Jaber H, Jaffe CL. Identification of a secreted casein kinase 1 in Leishmania donovani: effect of protein over expression on parasite growth and virulence. PLoS One (2013) 8:e79287. 10.1371/journal.pone.0079287 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Chauhan SC, Madhubala R. Glyoxalase I gene deletion mutants of Leishmania donovani exhibit reduced methylglyoxal detoxification. PLoS One (2009) 4:e6805. 10.1371/journal.pone.0006805 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Verma S, Mehta A, Shaha C. CYP5122A1, a novel cytochrome P450 is essential for survival of Leishmania donovani. PLoS One (2011) 6:e25273. 10.1371/journal.pone.0025273 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Titus RG, Gueiros-Filho FJ, De Freitas LA, Beverley SM. Development of a safe live Leishmania vaccine line by gene replacement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A (1995) 92:10267–71 10.1073/pnas.92.22.10267 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Selvapandiyan A, Duncan R, Debrabant A, Lee N, Sreenivas G, Salotra P, et al. Genetically modified live attenuated parasites as vaccines for leishmaniasis. Indian J Med Res (2006) 123:455–66 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Guy B. The perfect mix: recent progress in adjuvant research. Nat Rev Microbiol (2007) 5:505–17 10.1038/nrmicro1681 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Gupta S. Visceral leishmaniasis: experimental models for drug discovery. Indian J Med Res (2011) 133:27–39 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Moreira N, Vitoriano-Souza J, Roatt BM, Vieira PM, Ker HG, De Oliveira Cardoso JM, et al. Parasite burden in hamsters infected with two different strains of Leishmania (Leishmania) infantum: “Leishman Donovan units” versus real-time PCR. PLoS One (2012) 7:e47907. 10.1371/journal.pone.0047907 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Beattie L, Evans KJ, Kaye PM, Smith DF. Transgenic Leishmania and the immune response to infection. Parasite Immunol (2008) 30:255–66 10.1111/j.1365-3024.2008.01020.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Verheust C, Goossens M, Pauwels K, Breyer D. Biosafety aspects of modified vaccinia virus Ankara (MVA)-based vectors used for gene therapy or vaccination. Vaccine (2012) 30:2623–32 10.1016/j.vaccine.2012.02.016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Leblanc JG, Aubry C, Cortes-Perez NG, De Moreno De Leblanc A, Vergnolle N, Langella P, et al. Mucosal targeting of therapeutic molecules using genetically modified lactic acid bacteria: an update. FEMS Microbiol Lett (2013) 344:1–9 10.1111/1574-6968.12159 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Chorobik P, Marcinkiewicz J. Therapeutic vaccines based on genetically modified Salmonella: a novel strategy in cancer immunotherapy. Pol Arch Med Wewn (2011) 121:461–6 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Yamamoto DS, Nagumo H, Yoshida S. Flying vaccinator; a transgenic mosquito delivers a Leishmania vaccine via blood feeding. Insect Mol Biol (2010) 19:391–8 10.1111/j.1365-2583.2010.01000.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]