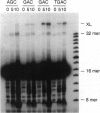
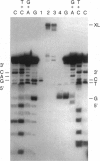
Abstract
Phosphoramide mustard-induced DNA interstrand cross-links were studied both in vitro and by computer simulation. The local determinants for the formation of phosphoramide mustard-induced DNA interstrand cross-links were defined by using different pairs of synthetic oligonucleotide duplexes, each of which contained a single potentially cross-linkable site. Phosphoramide mustard was found to cross-link dG to dG at a 5'-d(GAC)-3'. The structural basis for the formation of this 1,3 cross-link was studied by molecular dynamics and quantum chemistry. Molecular dynamics indicated that the geometrical proximity of the binding sites also favored a 1,3 dG-to-dG linkage over a 1,2 dG-to-dG linkage in a 5'-d(GCC)-3' sequence. While the enthalpies of 1,2 and 1,3 mustard cross-linked DNA were found to be very close, a 1,3 structure was more flexible and may therefore be in a considerably higher entropic state.
Full text
PDF

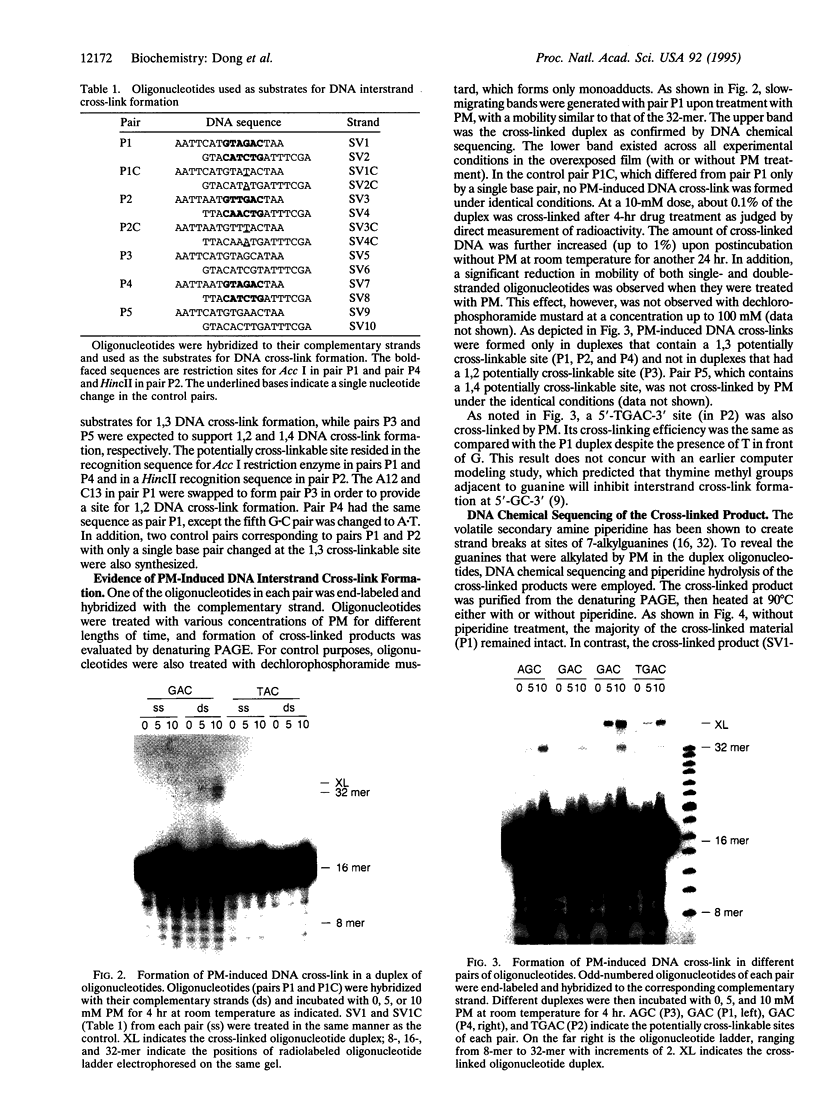

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brookes P., Lawley P. D. The reaction of mono- and di-functional alkylating agents with nucleic acids. Biochem J. 1961 Sep;80(3):496–503. doi: 10.1042/bj0800496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colvin M., Brundrett R. B., Kan M. N., Jardine I., Fenselau C. Alkylating properties of phosphoramide mustard. Cancer Res. 1976 Mar;36(3):1121–1126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colvin M., Hilton J. Pharmacology of cyclophosphamide and metabolites. Cancer Treat Rep. 1981;65 (Suppl 3):89–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritsch V., Ravishanker G., Beveridge D. L., Westhof E. Molecular dynamics simulations of poly(dA).poly(dT): comparisons between implicit and explicit solvent representations. Biopolymers. 1993 Oct;33(10):1537–1552. doi: 10.1002/bip.360331005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamcsik M. P., Ludeman S. M., Shulman-Roskes E. M., McLennan I. J., Colvin M. E., Colvin O. M. Protonation of phosphoramide mustard and other phosphoramides. J Med Chem. 1993 Nov 12;36(23):3636–3645. doi: 10.1021/jm00075a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausheer F. H., Singh U. C., Saxe J. D., Colvin O. M. Identification of local determinants of DNA interstrand crosslink formation by cyclophosphamide metabolites. Anticancer Drug Des. 1989 Dec;4(4):281–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemminki K., Ludlum D. B. Covalent modification of DNA by antineoplastic agents. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1984 Nov;73(5):1021–1028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohn K. W., Spears C. L., Doty P. Inter-strand crosslinking of DNA by nitrogen mustard. J Mol Biol. 1966 Aug;19(2):266–288. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAWLEY P. D., BROOKES P. FURTHER STUDIES ON THE ALKYLATION OF NUCLEIC ACIDS AND THEIR CONSTITUENT NUCLEOTIDES. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:127–138. doi: 10.1042/bj0890127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattes W. B., Hartley J. A., Kohn K. W. Mechanism of DNA strand breakage by piperidine at sites of N7-alkylguanines. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Oct 16;868(1):71–76. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(86)90088-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ojwang J. O., Grueneberg D. A., Loechler E. L. Synthesis of a duplex oligonucleotide containing a nitrogen mustard interstrand DNA-DNA cross-link. Cancer Res. 1989 Dec 1;49(23):6529–6537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remias M. G., Lee C. S., Haworth I. S. Molecular dynamics simulations of chlorambucil/DNA adducts. A structural basis for the 5'-GNC interstrand DNA crosslink formed by nitrogen mustards. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1995 Feb;12(4):911–936. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1995.10508784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rink S. M., Hopkins P. B. A mechlorethamine-induced DNA interstrand cross-link bends duplex DNA. Biochemistry. 1995 Jan 31;34(4):1439–1445. doi: 10.1021/bi00004a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh U. C., Weiner S. J., Kollman P. Molecular dynamics simulations of d(C-G-C-G-A) X d(T-C-G-C-G) with and without "hydrated" counterions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):755–759. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sladek N. E. Metabolism of oxazaphosphorines. Pharmacol Ther. 1988;37(3):301–355. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(88)90004-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streeper R. T., Cotter R. J., Colvin M. E., Hilton J., Colvin O. M. Molecular pharmacology of hepsulfam, NSC 3296801: identification of alkylated nucleosides, alkylation site, and site of DNA cross-linking. Cancer Res. 1995 Apr 1;55(7):1491–1498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]