A nonapoptotic function of the Dcp-1 caspase regulates mitochondrial morphology and promotes autophagy in Drosophila by negatively regulating SesB and ATP levels.
Abstract
Increasing evidence reveals that a subset of proteins participates in both the autophagy and apoptosis pathways, and this intersection is important in normal physiological contexts and in pathological settings. In this paper, we show that the Drosophila effector caspase, Drosophila caspase 1 (Dcp-1), localizes within mitochondria and regulates mitochondrial morphology and autophagic flux. Loss of Dcp-1 led to mitochondrial elongation, increased levels of the mitochondrial adenine nucleotide translocase stress-sensitive B (SesB), increased adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and a reduction in autophagic flux. Moreover, we find that SesB suppresses autophagic flux during midoogenesis, identifying a novel negative regulator of autophagy. Reduced SesB activity or depletion of ATP by oligomycin A could rescue the autophagic defect in Dcp-1 loss-of-function flies, demonstrating that Dcp-1 promotes autophagy by negatively regulating SesB and ATP levels. Furthermore, we find that pro–Dcp-1 interacts with SesB in a nonproteolytic manner to regulate its stability. These data reveal a new mitochondrial-associated molecular link between nonapoptotic caspase function and autophagy regulation in vivo.
Introduction
Autophagy is a cellular self-digestion process in which long-lived proteins and organelles are engulfed in double-membrane vesicles called autophagosomes. After fusion with lysosomes to form autolysosomes, the cellular contents are degraded, and the resulting breakdown products, including constituents for ATP production and protein synthesis, are recycled back into the cell (Rabinowitz and White, 2010). Autophagic flux, which refers to the complete process of autophagy, occurs at basal levels and is also up-regulated in response to various cellular stresses, including nutrient deprivation (Filkins, 1970; Scott et al., 2004), chemotherapies (Bursch et al., 1996; Kanzawa et al., 2003; Høyer-Hansen and Jäättelä, 2008), and reactive oxygen species (Scherz-Shouval et al., 2007; Chen et al., 2009). As such, autophagy acts to remove toxic metabolites, harmful protein aggregates, and damaged organelles and provides a mechanism for energy production in instances of metabolic stress to promote cell survival. It is therefore not surprising that defects in autophagic flux have been implicated in several human diseases, including cancer (Kondo et al., 2005; Kimmelman, 2011) and neurodegeneration (Wong and Cuervo, 2010).
The relationship between apoptosis and autophagy is complex, as core machinery components and signaling molecules of the pathways are interconnected (Eisenberg-Lerner et al., 2009). However, the molecular mechanisms governing these interactions are largely unknown. Several studies have begun to examine the multifunctional signaling molecules that take part in each pathway. For example, antiapoptotic Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL bind Beclin1, a core autophagy component of the class III phosphoinositide 3-kinase complex, and inhibit autophagy (Pattingre et al., 2005; Maiuri et al., 2007). Furthermore, the core autophagy protein Atg12 enhances mitochondrial apoptosis by binding to and inactivating antiapoptotic family members, including Bcl-2 and Mcl-1 (Rubinstein et al., 2011). Several studies have also revealed that core autophagy proteins undergo proteolytic processing, and in some cases, the newly generated fragment gains a novel proapoptotic role (Yousefi et al., 2006; Cho et al., 2009; Wirawan et al., 2010; Zhu et al., 2010).
Studies using Drosophila melanogaster have also examined the complex relationship between autophagy and apoptosis. Overexpression of the autophagy gene Atg1 in the larval fat body, a nutrient storage organ analogous to the mammalian liver, induces apoptosis in a caspase-dependent manner (Scott et al., 2007). Degradation of larval tissues, including the salivary gland (Berry and Baehrecke, 2007) and the midgut (Denton et al., 2009), during development requires autophagy. Although these studies show that autophagy can lead to the induction of death as well as contribute to death-related processes, autophagy functions primarily as a cell survival mechanism in Drosophila in response to cellular stress. For example, JNK signaling in the intestinal epithelium and fat body stimulates autophagy gene transcription to promote cell survival during oxidative stress (Wu et al., 2009). Furthermore, autophagy is induced to high levels in the larval fat body (Scott et al., 2004) and the midgut (Wu et al., 2009) to remobilize nutrients and promote cell survival after starvation.
The Drosophila ovary is also sensitive to nutritional cues. The ovary is made up of 15–20 ovarioles, each containing a series of developing egg chambers that arise from the germarium and progress through 14 well-defined stages. Each egg chamber is made up of 15 germline nurse cells and one oocyte surrounded by a layer of somatically derived follicle cells. Cell death in midstage egg chambers occurs sporadically and in response to environmental cues, including nutrient deprivation (Drummond-Barbosa and Spradling, 2001). Midstage egg chambers undergoing cell death are characterized by nurse cell nuclei condensation and fragmentation, engulfment of the nurse cell cytoplasm by the surrounding follicle cells and follicle cell death (Giorgi and Deri, 1976). Autophagy has been observed in degenerating midstage egg chambers (Hou et al., 2008; Nezis et al., 2009), and we previously showed that both cell death and autophagy are dependent on the effector caspase Drosophila caspase-1 (Dcp-1; Song et al., 1997; Laundrie et al., 2003; Hou et al., 2008). However, whether autophagic flux occurs in response to starvation in nondegenerating and degenerating midstage egg chambers and the mechanism of Dcp-1–induced autophagy remain to be identified.
In this study, we demonstrate that autophagic flux occurs in healthy and degenerating midstage egg chambers in response to starvation in a Dcp-1–dependent manner. We find that Dcp-1 localizes to the mitochondria under nutrient-rich conditions in which it functions to regulate mitochondrial network morphology and ATP levels. The proform of Dcp-1 interacts with the adenine nucleotide translocase (ANT) stress-sensitive B (SesB), a mitochondrial protein that functions to regulate ATP levels, in a nonproteolytic manner. SesB mutant analysis reveals a new role for SesB as a negative regulator of autophagic flux in Drosophila midstage egg chambers. Depletion of ATP or SesB loss-of-function flies can rescue the autophagy defect in Dcp-1 loss-of-function flies, demonstrating that SesB acts downstream of Dcp-1 in the regulation of autophagy. These data uncover a novel mechanism of caspase-mediated regulation of autophagy in vivo.
Results
Starvation-induced autophagic flux occurs during Drosophila midoogenesis and is regulated by Dcp-1
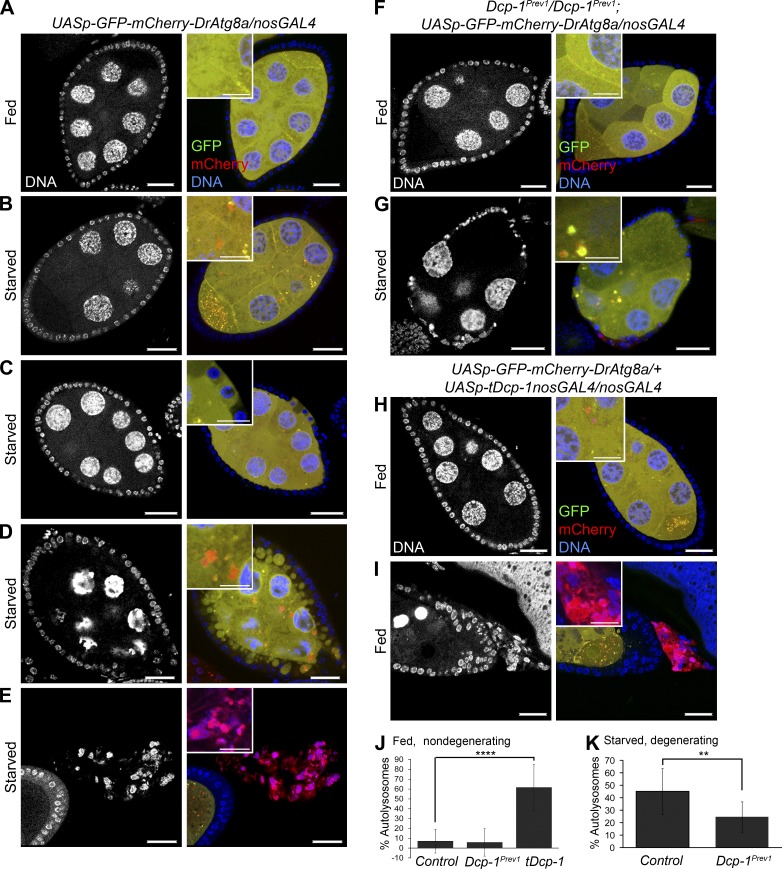
Using GFP-LC3 as a marker of autophagosomes, we previously showed that loss of Dcp-1 results in a reduction of starvation-induced autophagosome formation in vitro in Drosophila l(2)mbn cells and in vivo in degenerating midstage egg chambers (Hou et al., 2008). However, whether Dcp-1 affects autophagic flux, including the degradative completion of autophagy in the lysosome, remains to be identified. To test this, we first examined transgenic flies expressing a UASp-GFP-mCherry-DrAtg8a transgene specifically in the germline using the nosGAL4 driver. Under nonautophagy-inducing conditions, the dual-tagged Atg8a protein is diffuse throughout the cytoplasm and appears yellow (overlap of green and red). When autophagy is induced, Atg8a becomes lipidated and associates with the autophagosomal membrane where it fluoresces as yellow puncta. Once autophagosomes fuse with lysosomes, GFP fluorescence is quenched by acidic hydrolases, and the resulting autolysosome fluoresces red, signifying that autophagic flux has occurred (Nezis et al., 2010). Healthy egg chambers from flies conditioned on yeast paste (fed) showed diffuse yellow GFP-mCherry-DrAtg8a staining throughout the nurse cells (Fig. 1 A). After amino acid deprivation (starvation), we observed an increase in the percentage of autolysosomes (68 vs. 7% in fed conditions) in healthy nondegenerating midstage egg chambers (Fig. 1 B and Fig. S1 C), indicating that autophagic flux occurs in otherwise healthy egg chambers. In response to a cell death signal, nurse cell nuclei condense and fragment, follicle cells take up portions of the nurse cell cytoplasm, and this is followed by follicle cell death (Giorgi and Deri, 1976). In addition to the cell death phenotype, degenerating midstage egg chambers taking up nurse cell cytoplasm (Fig. 1 C) and those later in the degeneration process (Fig. 1 D) contained both autophagosomes and autolysosomes. In late degenerating midstage egg chambers, the GFP signal was lost, and the remaining follicle cells fluoresced red (Fig. 1 E), indicating that there may be a late stage acidification of the dying follicle cells. All together, these data show that autophagic flux occurs in the germline in response to starvation.
Figure 1.
Dcp-1 is necessary for autophagic flux during midoogenesis. GFP-mCherry-DrAtg8a was expressed in the germline using the nosGAL4 driver. Staining shows DNA, GFP, and mCherry. (A) UASp-GFP-mCherry-DrAtg8a/+;nosGAL4/+ flies conditioned on yeast paste had diffuse GFP-mCherry-DrAtg8a staining in midstage egg chambers. (B) Nondegenerating midstage egg chambers from starved flies contained autophagosomes (yellow) and autolysosomes (red). (C and D) Egg chambers early in the degeneration process showed follicle cells that take up portions of the nurse cell cytoplasm (C) followed by condensation and fragmentation of the nurse cell nuclei and further uptake of the nurse cell cytoplasm into follicle cells (D). (E) Late stage degenerating egg chambers lose all GFP staining and fluoresce red. (F) Fed Dcp-1Prev1/Dcp-1Prev1;UASp-GFP-mCherry-DrAtg8a/nosGAL4 flies showed diffuse GFP-mCherry-DrAtg8a staining in the germline. (G) Starved Dcp-1Prev1/Dcp-1Prev1;UASp-GFP-mCherry-DrAtg8a/nosGAL4 flies showed reduced autolysosomes in degenerating midstage egg chambers. (H and I) Fed flies overexpressing truncated Dcp-1 (tDcp-1) in the germline showed increased autophagosomes and autolysosomes in nondegenerating midstage egg chambers (H) and also contained degenerating midstage egg chambers that lose all GFP fluorescence and fluoresce red (I). Bars: (main images) 25 µm; (insets) 12.5 µm. Insets in A–I show diffuse cytoplasmic staining of Atg8a or autophagosomes and autolysosomes. (J and K) The percentages of autolysosomes (autolysosomes/total autophagic structures) were manually calculated in at least eight egg chambers for each genotype as indicated. Error bars represent the means ± SD. Statistical testing was performed using one-way ANOVA with a Dunnet post test (****, P < 0.0001) or a two-tailed Student’s t test (**, P < 0.005).
We next examined whether Dcp-1 regulates autophagic flux in the germline. Well-fed Dcp-1 loss-of-function flies (Dcp-1Prev1) expressing GFP-mCherry-DrAtg8a in the germline had diffuse yellow staining (Fig. 1, F and J). After starvation, degenerating midstage egg chambers from Dcp-1Prev1 flies, which are characterized by a premature loss of follicle cells and persisting nurse cell nuclei (Laundrie et al., 2003), contained a reduction in the percentage of autolysosomes compared with the control (Fig. 1, G [compare with D] and K). Nondegenerating midstage egg chambers from starved Dcp-1Prev1 flies also had reduced autophagic flux (Fig. S1), indicating that the reduction in autophagy in Dcp-1Prev1 flies is not simply caused by a lack of engulfment of dying nurse cells by follicle cells. To determine whether Dcp-1 is sufficient to induce autophagic flux, GFP-mCherry-Atg8a and an active form of Dcp-1 lacking its prodomain (tDcp-1) were expressed in the germline. We observed an increase in the percentage of autolysosomes in both nondegenerating (Fig. 1, H and J) and degenerating (Fig. 1 I) midstage egg chambers even in the absence of starvation.
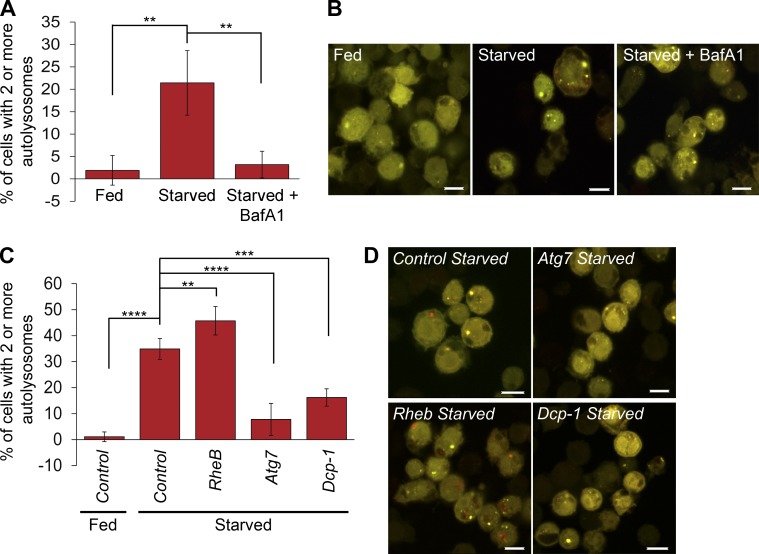
To confirm our in vivo findings, we examined the role of Dcp-1 in autophagic flux in vitro using a Drosophila S2 cell line stably expressing GFP-RFP-Atg8a. To validate the cell line, we first starved cells and observed a significant increase in autolysosomes that could be inhibited by addition of the late stage autophagy inhibitor Bafilomycin A1 (Fig. 2, A and B), as expected. Next, we used RNAi to knock down Rheb, a negative regulator of autophagy, or Atg7, a positive regulator of autophagy, and detected an increase and reduction in autolysosomes, respectively (Fig. 2, C and D). Dcp-1 RNAi resulted in a significant reduction in autolysosomes (Fig. 2, C and D), consistent with the Dcp-1Prev1 phenotype in midstage egg chambers, confirming a role for Dcp-1 as a positive regulator of autophagic flux.
Figure 2.
Dcp-1 regulates autophagic flux in vitro. (A) Drosophila S2 cells stably expressing GFP-RFP-Atg8a showed an increase in the percentage of cells containing two or more autolysosomes after starvation, which was blocked after Bafilomycin A1 (BafA1) treatment. At least 50 cells were manually quantitated in three independent experiments (n = 3). Statistical significance was determined using one-way ANOVA with a Dunnett post test (**, P < 0.01). (B) Representative images of S2-GFP-RFP-Atg8a cells after the indicated treatments. (C) S2-GFP-RFP-Atg8a cells were treated with dsRNAs and subjected to fed or starvation conditions as indicated. At least 50 cells were manually quantitated in three independent experiments (n = 3). Statistical significance was determined using one-way ANOVA with a Dunnett post test (**, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001). (D) Representative images of S2-GFP-RFP-Atg8a cells after the indicated RNAi treatments. Error bars represent the means ± SD. Bars, 10 µm.
We also investigated whether Dcp-1 regulates starvation-induced autophagy in the larval fat body using LysoTracker red (LTR), an acidotropic dye that labels both autolysosomes and lysosomes. After 1 h of starvation, fat bodies from larvae overexpressing Dcp-1 contained increased LTR and Atg8a puncta, whereas control larvae contained low LTR levels and diffuse Atg8a staining (Fig. S2, A and B). Fat bodies from 4-h-starved wild-type and Dcp-1Prev1 flies had high LTR and Atg8a puncta (Fig. S2, C and D), indicating that although Dcp-1 overexpression can enhance the autophagic response, Dcp-1 is not required for starvation-induced autophagy in the fat body.
Dcp-1 is required for the degradation of Ref(2)P after starvation
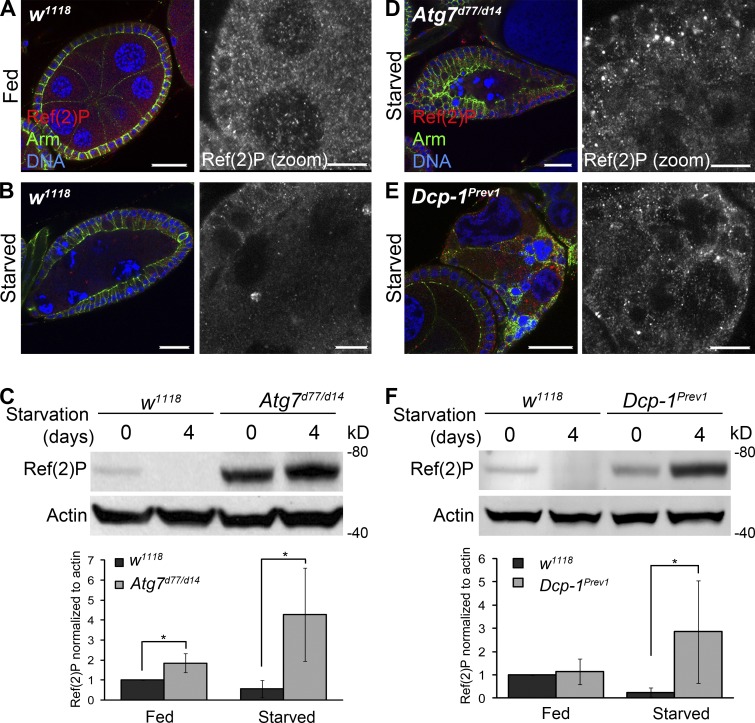
Ref(2)P, the Drosophila homologue of p62 (Nezis et al., 2008), is a substrate of autophagy and was shown to be a marker of autophagic activity (Nezis et al., 2010; Bartlett et al., 2011). Therefore, we used Ref(2)P analyses to confirm that Dcp-1 is a positive regulator of autophagic flux. Compared with fed wild-type flies (Fig. 3 A), nutrient-deprived flies had reduced Ref(2)P in follicle cells and nurse cells (Fig. 3 B), and Western blot analysis of wild-type ovaries revealed that the level of Ref(2)P was reduced after starvation (Fig. 3 C). Ovaries from fed or starved Atg7d77/d14 mutant flies showed an accumulation of Ref(2)P (Fig. 3, C and D). It was reported that starvation itself leads to transcriptional activation of Ref(2)P (Érdi et al., 2012), and this is likely why we see an even further increase in Ref(2)P levels after starvation in Atg7 flies. Compared with starved wild-type flies, degenerating midstage egg chambers from starved Dcp-1Prev1 flies contained increased levels of Ref(2)P (Fig. 3 E), and Western blot analysis of whole ovaries confirmed that Ref(2)P failed to be completely degraded after starvation (Fig. 3 F). The effect of Dcp-1 on Ref(2)P levels is modest compared with Atg7: we found that Ref(2)P accumulates only in degenerating midstage egg chambers of Dcp-1Prev1 flies after starvation. The variability in the levels of Ref(2)P, as shown in Fig. 3 F, is most likely caused by the extent of the persisting or “undead” egg chambers present in the samples. In contrast to Atg7 flies, Dcp-1 does not affect basal autophagy. Altogether, these data show that Dcp-1 is a positive regulator of starvation-induced autophagic flux during Drosophila midoogenesis.
Figure 3.
Ref(2)P analyses confirm that Dcp-1 is required for autophagic flux in ovaries. Staining shows DNA, Ref(2)P, and Armadillo. Zoomed insets show Ref(2)P staining. (A) Nondegenerating midstage egg chambers from fed w1118 flies showed Ref(2)P staining in follicle cells and nurse cells. (B) Starved w1118 flies contained degenerating midstage egg chambers with reduced Ref(2)P. (C) A representative Western blot of ovaries from w1118 and Atg7d77/d14 flies subjected to fed or starvation conditions for 4 d. Ref(2)P was detected by immunoblotting. Actin served as a loading control. Densitometry was performed to quantitate Ref(2)P protein levels relative to actin. Graph represents ± SD from five independent experiments (n = 5). Statistical significance was determined using a two-tailed Student’s t test. *, P = 0.004 for fed samples; *, P = 0.008 for starved samples. (D) Starved Atg7 flies showed an accumulation of Ref(2)P in the follicle cells and nurse cells of degenerating midstage egg chambers. (E) Starved Dcp-1Prev1 flies contained increased levels of Ref(2)P in degenerating midstage egg chambers. (F) A representative Western blot of ovaries from w1118 and Dcp-1Prev1 flies that were subjected to fed or starvation conditions for 4 d. Ref(2)P was detected by immunoblotting. Actin served as a loading control. Densitometry was performed to quantitate Ref(2)P protein levels relative to actin. Graph represents ± SD from five independent experiments (n = 5). Statistical significance was determined using a two-tailed Student’s t test. *, P = 0.03. Bars: (main images) 25 µm; (zoomed images) 10 µm.
Dcp-1 localizes to the mitochondria
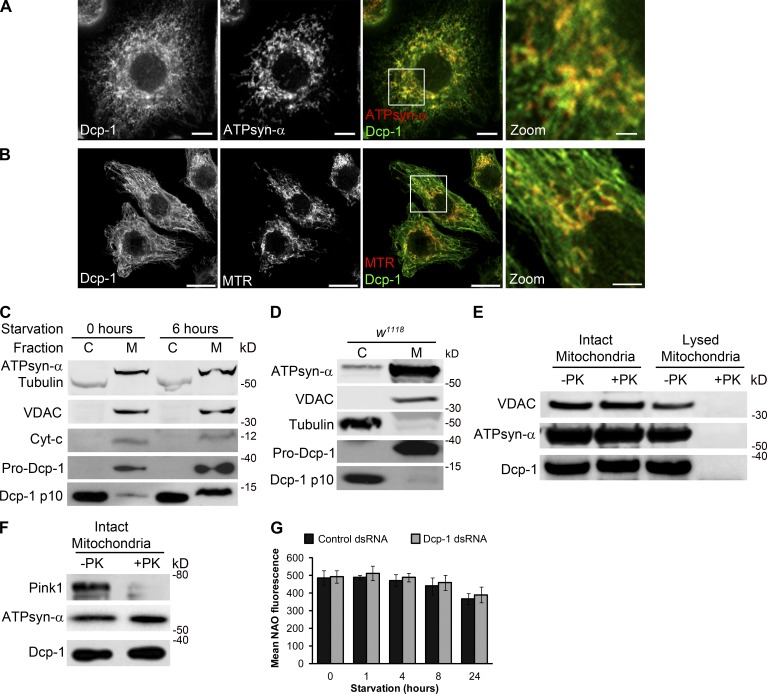
To elucidate the mechanism by which Dcp-1 mediates autophagic flux, we first determined the subcellular location of Dcp-1 in Drosophila l(2)mbn cells by immunostaining with an antibody to Dcp-1 (Fig. S3; Tenev et al., 2005). We observed colocalization between Dcp-1 and the mitochondrial markers ATPsynthase-α (ATPsyn-α; Fig. 4 A) and MitoTracker red (Fig. 4 B) but did not observe colocalization between Dcp-1 and markers for the endoplasmic reticulum or cis-Golgi (Fig. S3, A and B). Dcp-1 was also found to colocalize with β-Tubulin (Fig. S3 C). To confirm that Dcp-1 is located at the mitochondria, subcellular fractionation was performed on l(2)mbn cells subjected to nutrient-rich medium or 6 h of starvation (Fig. 4 C). Purity of the fractions was determined using Tubulin as a cytosolic (Fig. 4 C, abbreviated as C) marker and ATPsyn-α, voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC), and cytochrome c as the membrane-enriched (Fig. 4 C, abbreviated as M) markers. Using a previously described antibody (Fig. S3 E; Laundrie et al., 2003), we found that the proform (zymogen) of Dcp-1 was located only in the membrane-enriched fraction in nutrient-rich and starvation conditions, whereas the processed p10 subunit of Dcp-1 was found in both the membrane and cytosolic fractions (Fig. 4 C). Similar results were obtained after subcellular fractionation of ovaries (Fig. 4 D). To determine whether Dcp-1 is located inside the mitochondria or is associated with the surface of the outer mitochondrial membrane, a proteinase K protection assay was performed with or without hypotonic disruption of the mitochondria. Mitochondrial proteins within the mitochondria are resistant to proteinase K treatment, whereas proteins located on the surface of the outer mitochondrial membrane, but not embedded within the lipid bilayer of mitochondria, are sensitive to proteinase K (Smith et al., 1994; Setoguchi et al., 2006). VDAC, an embedded outer mitochondrial membrane protein, and ATPsyn-α, a mitochondrial matrix protein, remained intact upon proteinase K treatment as expected but were digested by proteinase K after hypotonic disruption of the mitochondria (Fig. 4 E). In addition, Pink1, a mitochondrial protein associated with the outer mitochondrial membrane, was degraded after proteinase K treatment as expected (Fig. 4 F). Examination of Dcp-1 showed that it was digested only after hypotonic disruption of the mitochondria, indicating that Dcp-1 is internalized within the mitochondria (Fig. 4, E and F). We speculate that the proform of Dcp-1 translocates into the mitochondria where a fraction of it is processed into its active form, and this active form either remains in the mitochondria or translocates back into the cytosol. Together, these data demonstrate that pro–Dcp-1 localizes within mitochondria.
Figure 4.
Dcp-1 is partially localized within mitochondria. (A and B) l(2)mbn cells were labeled with antibodies to Dcp-1 and ATPsyn-α (A) or MitoTracker red (MTR; B). Merged images show colocalization between Dcp-1 and the mitochondria. Boxes represent zoomed images. Bars: (main images) 5 µm; (zoomed images) 1.25 µm. (C) Western blot from l(2)mbn cells subjected to nutrient-rich or starvation conditions for 6 h. Cells were separated into cytosolic (C) and mitochondrial enriched (M) fractions. (D) Ovaries from fed w1118 flies were separated into cytosolic and membrane-enriched fractions and probed with antibodies to VDAC, Tubulin, ATPsyn-α, and Dcp-1. (E and F) Intact and lysed mitochondria (E) or intact mitochondria isolated from l(2)mbn cells (F) were treated with proteinase K (PK). The effects of proteinase K treatment were assessed by antibodies to VDAC, ATPsyn-α, Pink1, and Dcp-1. (G) Control and Dcp-1 RNAi–treated cells were subjected to nutrient-rich or starvation conditions and stained with NAO. Mean fluorescence was measured by flow cytometry. Graph represents ± SEM of three independent experiments (n = 3).
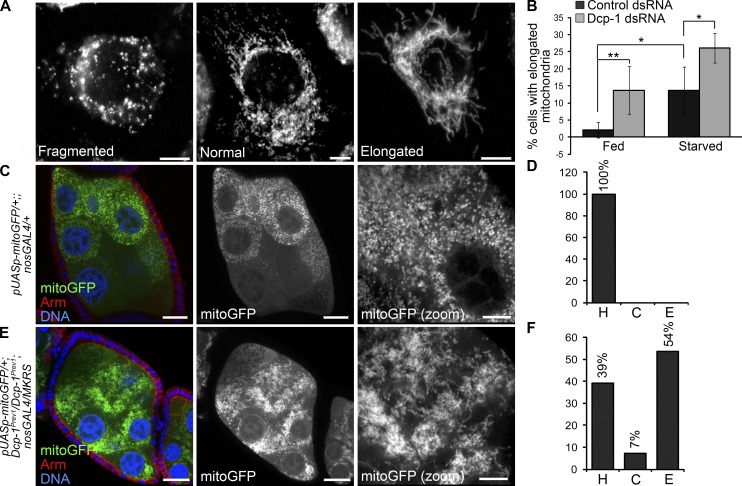
Loss of Dcp-1 alters morphology of the mitochondrial network
To examine a potential role of Dcp-1 at the mitochondria, we first analyzed whether loss of Dcp-1 alters mitochondrial mass. No changes in mitochondrial mass as detected by 10-N-nonyl acridine orange (NAO), a fluorescent dye that binds mitochondrial cardiolipin independently of mitochondrial membrane potential (Maftah et al., 1989), were detected in nutrient-rich or starvation conditions (Fig. 4 G). Next, we determined whether loss of Dcp-1 alters mitochondrial morphology. Mitochondria were labeled with ATPsyn-α and were scored as having a fragmented, a normal (containing both short and elongated mitochondria), or an elongated morphology (Fig. 5 A). The majority of control cells in nutrient-rich media contained mitochondria with a normal morphology, and starvation led to an increase in the percentage of cells with elongated mitochondria (Fig. 5 B). Treatment with Dcp-1 RNAi resulted in a significant increase in cells that contained elongated mitochondria in both nutrient-rich and starvation media (Fig. 5 B). Given that the changes observed in mitochondrial morphology after Dcp-1 RNAi were not associated with changes in mitochondrial mass under the conditions tested (Fig. 4 G) suggests that Dcp-1 may play a role in maintaining the mitochondrial network under fed and starvation conditions.
Figure 5.
Loss of Dcp-1 promotes mitochondrial elongation. (A) l(2)mbn cells were labeled with the ATPsyn-α, and mitochondrial morphology was scored as fragmented, normal, or elongated. (B) Cells were treated with control or Dcp-1 dsRNA and subjected to nutrient-rich media or 1 h of starvation. Quantifications represent the percentage of cells with elongated mitochondria divided by the total number of cells examined. At least 100 cells were examined manually in three independent experiments (n = 3). Error bars represent the mean ± SD. Statistical significance was determined using one-way ANOVA with a Bonferroni post test (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01). (C) Mitochondrial targeted GFP (mitoGFP) was expressed in the germline using the nosGAL4 driver. Staining shows mitoGFP, Armadillo, and DNA. (D) Mitochondria were scored as healthy (H), clustered (C), or elongated and overly connected (E). All of mitochondria from fed UASp-mitoGFP/+;nosGAL4/+ flies were scored as healthy. n = 15 egg chambers manually scored. (E) mitoGFP was expressed in Dcp-1Prev1 flies using the nosGAL4 driver. (F) 54% of egg chambers from UASp-mitoGFP/+;Dcp-1Prev1/Dcp-1Prev1;nosGAL4/+ flies contained elongated mitochondria, 39% contained mitochondria that were scored as healthy, and 7% contained clustered mitochondria. n = 28 egg chambers manually scored. Bars: (A) 5 µm; (C and E, main images) 25 µm; (C and E, zoomed images) 10 µm.
To determine whether Dcp-1 alters mitochondrial morphology in vivo, we expressed mitochondrial targeting GFP (mitoGFP) in the germline of Dcp-1Prev1 flies. All fed control flies contained short, tubular mitochondria that were dispersed throughout the entire nurse cell (Fig. 5 C) and were scored as healthy (Fig. 5 D, abbreviated as H). Starvation induces a series of mitochondrial events in degenerating midstage egg chambers, including mitochondrial remodeling and clustering, uptake by the follicle cells, and finally, degradation within the follicle cells (Tanner et al., 2011). Fed Dcp-1Prev1 flies expressing mitoGFP in the germline contained mitochondria with an altered morphology even in the absence of starvation. 54% of midstage egg chambers from Dcp-1Prev1 flies contained mitochondria that were elongated and overly connected (Fig. 5, E and F, abbreviated as E), whereas only 39% of midstage egg chambers contained mitochondria that were healthy (Fig. 5 F, abbreviated as H). To control for the different genetic backgrounds between wild-type and Dcp-1Prev1 flies with respect to the mitochondrial phenotypes, Dcp-1 was overexpressed in the germline of Dcp-1Prev1 flies to determine whether the mitochondrial phenotype could be rescued. Indeed, 94% of midstage egg chambers from Dcp-1Prev1 flies overexpressing wild-type Dcp-1 showed healthy mitochondria compared with only 33% of midstage egg chambers from Dcp-1Prev1 flies (Fig. S4, A–C), indicating that the mitochondrial phenotype is caused by the Dcp-1Prev1 mutation. These data demonstrate that Dcp-1 plays a role in the regulation of mitochondrial network morphology even in the absence of a starvation signal, underscoring a novel nonapoptotic role of an effector caspase in regulating mitochondrial dynamics under both fed and starvation conditions.
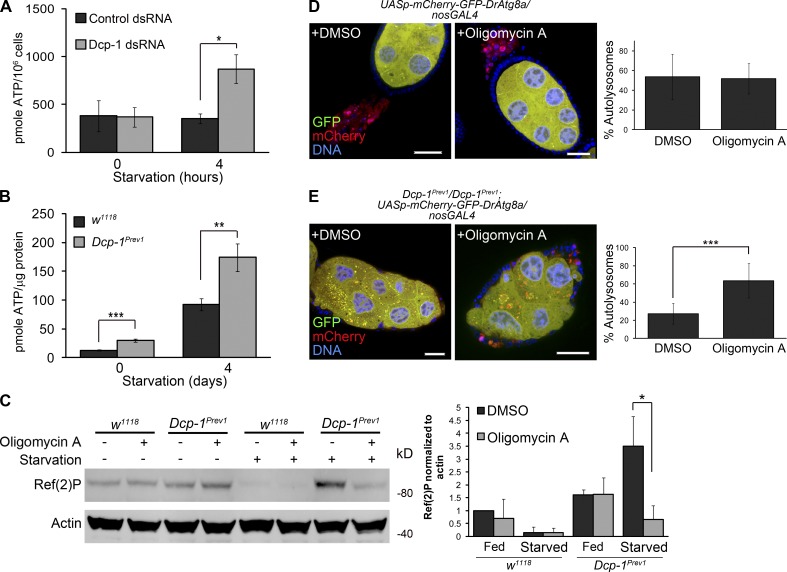
High ATP levels in Dcp-1Prev1 flies suppress autophagic flux
Loss of Dcp-1 promotes elongation of the mitochondrial network, and mitochondrial elongation has been shown to sustain ATP levels after starvation to promote cell survival (Gomes et al., 2011). In addition, the cellular energy sensor AMP-activated protein kinase is activated when the ratio of ATP/AMP falls, for example, during periods of starvation (Salt et al., 1998; Gleason et al., 2007), thus stimulating energy producing pathways such as autophagy (Kim et al., 2011). Therefore, we determined whether Dcp-1 also alters ATP levels as a mechanism to induce autophagic flux. Cells treated with Dcp-1 RNAi showed a significant increase in ATP levels within 4 h of starvation (Fig. 6 A), suggesting that at least under starvation in vitro, the elongated mitochondrial phenotype in Dcp-1 RNAi-treated cells is associated with increased ATP levels. To confirm this in vivo, we examined ovaries from wild-type and Dcp-1Prev1 flies subjected to fed or starvation conditions and found ATP levels to be significantly increased in ovaries of Dcp-1Prev1 flies under both conditions tested (Fig. 6 B). We reasoned that the increased ATP levels in Dcp-1Prev1 flies may inhibit autophagic flux after starvation. Reduction of ATP with oligomycin A, an inhibitor of the mitochondrial ATP synthase, induces autophagy in the IPLB-LdFB insect cell line (Tettamanti et al., 2006), and so, we tested whether oligomycin A would induce autophagy in Drosophila ovaries. Although oligomycin A did not alter Ref(2)P levels under fed conditions, ovaries from starved Dcp-1Prev1 flies treated with oligomycin A showed a significant reduction in Ref(2)P protein compared with those treated with DMSO (Fig. 6 C). In addition, starved oligomycin A–treated Dcp-1Prev1 flies expressing GFP-mCherry-DrAtg8a in the germline showed an increase in the percentage of autolysosomes in degenerating midstage egg chambers compared with those treated with DMSO (red puncta; Fig. 6 E), whereas we observed no additional increase in the percentage of autolysosomes in starved control flies treated with oligomycin A (Fig. 6 D). This suggests that high ATP levels are sufficient to block autophagic flux in Dcp-1Prev1 flies after starvation. Collectively, our data demonstrate that Dcp-1 controls autophagic flux by a mechanism involving the regulation of the mitochondrial network and maintenance of ATP levels.
Figure 6.
Dcp-1 alters ATP levels that in turn regulate autophagy. (A) Total cellular ATP levels were measured in l(2)mbn cells treated with control or Dcp-1 dsRNA. Data represent ± SEM of three independent experiments (n = 3). Statistical significance was determined using a two-tailed Students t test (*, P = 0.02). (B) Total cellular ATP levels were measured in ovaries from fed or starved w1118 and Dcp-1Prev1 flies. Data represent ± SEM of five independent experiments (n = 5). Statistical significance was determined using a two-tailed Student’s t test (**, P = 0.014; ***, P < 0.001). (C) Fed or starved w1118 and Dcp-1Prev1 flies were treated with DMSO or 25 µg/ml oligomycin A, and Ref(2)P levels were assessed by immunoblot analysis. Actin served as a loading control. Densitometry was performed to quantitate protein levels relative to actin. Graph represents ± SD from three independent experiments (n = 3). Statistical significance was determined using a two-tailed Student’s t test (*, P = 0.02). (D and E) Control UASp-GFP-mCherry-DrAtg8a/+;nosGAL4/+ flies (D) and Dcp-1Prev1/Dcp-1Prev1;UASp-GFP-mCherry-DrAtg8a/nosGAL4 flies (E) were subjected to starvation conditions supplemented with DMSO or 25 µg/ml oligomycin A. Bars, 25 µm. Quantifications show percentage of autolysosomes (autolysosomes/total autophagic structures). At least eight egg chambers were manually quantitated per genotype per condition (n = 8). Statistical testing was determined using a two-tailed Student’s t test. ***, P = 0.0002.
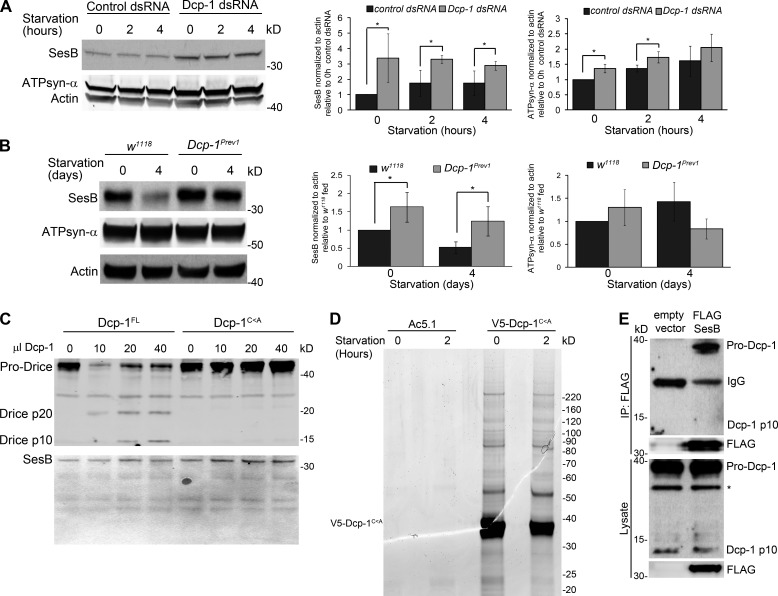
Dcp-1 negatively regulates the levels of the ANT SesB
We next determined the molecular mechanism by which Dcp-1 could regulate ATP levels to induce autophagy. Drosophila SesB encodes an ANT that functions to exchange ATP for ADP across the mitochondrial inner membrane (Terhzaz et al., 2010). RNAi of SesB in malpighian tubules significantly decreased ATP levels and altered mitochondrial morphology from a threadlike appearance to a short and globular morphology (Terhzaz et al., 2010). Treatment of l(2)mbn cells with Dcp-1 RNAi resulted in a significant increase in the levels of SesB protein under both fed and starvation conditions (Fig. 7 A). This observed increase in SesB protein was not caused by an increase in mitochondrial mass as measured by NAO (Fig. 4 G) nor could it be fully explained by alterations in SesB transcript levels (Fig. S5 A), which were unaltered in fed conditions, increased 12.4-fold after 2 h of starvation, and returned to levels comparable with fed conditions by 4 h of starvation. To determine whether the effect on SesB protein was also observed in vivo, we examined ovaries from fed and nutrient-deprived wild-type and Dcp-1Prev1 flies. We observed decreased SesB levels after starvation in wild-type flies (Fig. 7 B), whereas ovaries from fed or nutrient-deprived Dcp-1Prev1 flies contained increased SesB levels, indicating that Dcp-1 may be required to negatively regulate the levels of SesB and, thus, ATP. We also observed a significant increase in ATPsyn-α levels under fed and 2 h of starvation in vitro (Fig. 7 A) but did not detect a significant change in ATPsyn-α levels in vivo (Fig. 7 B). Given the consistent changes observed in SesB, we next tested whether SesB is a direct target of Dcp-1’s proteolytic activity using in vitro cleavage assays. Catalytically active Dcp-1 (Dcp-1FL) and inactive Dcp-1 (Dcp-1C<A) were expressed in l(2)mbn cells and purified by Ni2+–nitriloacetic acid (NTA) columns. Only Dcp-1FL was able to cleave in vitro translated Drice (Fig. 7 C), another Drosophila effector caspase and known substrate of Dcp-1 (Song et al., 2000). Treatment of in vitro translated SesB with Dcp-1FL or Dcp-1C<A failed to induce cleavage of SesB (Fig. 7 C), indicating that Dcp-1 does not directly cleave SesB but rather affects its stability. To test whether Dcp-1 directly interacts with SesB as a mechanism to regulate its stability, an immunoaffinity purification (immunoprecipitation [IP]) and tandem mass spectrometry (MS; MS/MS) fragmentation assay were performed. To prevent the proteolytic cleavage of Dcp-1’s substrates and allow for their identification, we overexpressed catalytically inactive V5-tagged Dcp-1C<A in l(2)mbn cells and subjected cells to nutrient-full medium or 2 h of starvation. Dcp-1 was immunoprecipitated with an anti-V5 antibody (Fig. 7 D), and immunoprecipitates were analyzed by liquid chromatography–MS/MS for protein detection and identification. Four unique peptides corresponding to SesB were identified in the Dcp-1 immunoprecipitate, but not in the vector control, in two independent replicates, indicating that SesB is a binding partner of Dcp-1 (Table S2). To confirm the interaction between Dcp-1 and SesB, we expressed FLAG-tagged SesB in l(2)mbn cells and found that FLAG-SesB immunoprecipitated endogenous pro–Dcp-1 (Fig. 7 E). Notably, no processed Dcp-1 was detected (Fig. 7 E), and we found that FLAG-SesB was mitochondrial localized (Fig. S5 B), further indicating that the interaction between Dcp-1 and SesB takes place in the mitochondria and occurs in a nonproteolytic manner. All together, these data show that pro–Dcp-1 interacts with SesB and affects its stability in a nonproteolytic manner.
Figure 7.
Dcp-1 regulates levels of SesB but SesB is not a direct target of Dcp-1’s proteolytic activity. (A) A representative Western blot showing SesB and ATPsyn-α levels from fed or starved l(2)mbn cells treated with control or Dcp-1 RNAi. Actin served as a loading control. Densitometry was performed to quantitate protein levels relative to actin. Graphs represent ± SD from three independent experiments (n = 3). Statistical significance was determined using a two-tailed Student’s t test (*, P < 0.05). (B) A representative Western blot of ovaries from fed or starved w1118 or Dcp-1Prev1 flies. SesB and ATPsyn-α were detected by immunoblotting. Actin served as a loading control. Densitometry was performed to quantitate protein levels relative to actin. Graphs represent ± SD from three independent experiments (n = 3). Statistical significance was determined using a two-tailed Student’s t test (*, P < 0.05). (C) Purified catalytically active Dcp-1FL, but not catalytically inactive Dcp-1C<A, cleaved in vitro translated Drice. Cleavage of in vitro translated SesB was not detected. (D) V5-tagged Dcp-1C<A or V5 vector only control was expressed in l(2)mbn cells and subjected to nutrient-full or starvation conditions for 2 h. After IP with anti-V5 antibodies, lysates were separated by SDS-PAGE. Proteins were visualized with colloidal Coomassie stain. (E) FLAG-SesB or a vector only control was expressed in l(2)mbn cells and was immunoprecipitated with FLAG-agarose. Immunoblots show the interaction between FLAG-SesB and endogenous pro–Dcp-1. The asterisk represents a nonspecific band.
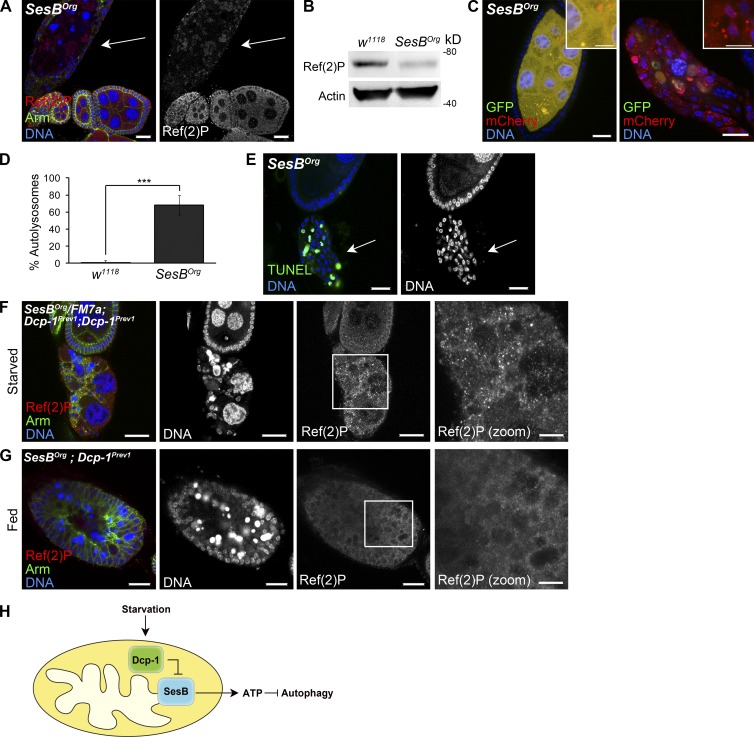
SesB is a negative regulator of autophagic flux and interacts genetically with Dcp-1
The loss of SesB after starvation suggests that SesB may negatively regulate autophagy. To test this, we examined ovaries from SesB hypomorphic flies (SesBOrg) that were shown to have reduced ANT activity (Rikhy et al., 2003). Consistent with this previous study, ovaries from SesBOrg flies had reduced ATP levels compared with ovaries from wild-type flies (Fig. S5 C). Although fed wild-type flies rarely contain degenerating midstage egg chambers (Table S1), fed SesBOrg flies contained an increase in degenerating midstage egg chambers (Table S1) that had increased LTR staining (Fig. S5 F) and reduced Ref(2)P (Fig. 8, A and B). Loss of SesB resulted in a similar phenotype in the larval fat body (Fig. S2). In addition, overexpression of GFP-mCherry-DrAtg8a in the germline of fed SesBOrg flies revealed an increase in the percentage of autolysosomes in both nondegenerating (Fig. 8, C [left] and D) and degenerating (Fig. 8 C, right) midstage egg chambers, confirming that there is increased autophagic flux in SesBOrg flies. Degenerating midstage egg chambers from SesBOrg flies also stained positively for TUNEL (Fig. 8 E), suggesting that SesB is normally required to suppress autophagic flux and DNA fragmentation during Drosophila oogenesis.
Figure 8.
SesB hypomorphic flies have an enhanced autophagy phenotype, and epistasis analysis indicates that SesB acts downstream of Dcp-1. (A) Ovaries from fed SesBOrg flies show reduced Ref(2)P staining in degenerating midstage egg chamber (arrow). (B) Ovaries from fed w1118 and SesBOrg were analyzed by Western blotting using Ref(2)P. Actin served as a loading control. Results are representative of three independent experiments (n = 3). (C) SesBOrg flies expressing GFP-mCherry-DrAtg8a in the germline showed increased autophagosomes and autolysosomes in nondegenerating (left) and degenerating (right) midstage egg chambers. Insets show autophagosomes and autolysosomes (left) and autolysosomes (right) in SesBOrg midstage egg chambers. (D) Quantitation of percentages of autolysosomes (autolysosomes/total autophagic structures) in nondegenerating ovaries from fed w1118 and SesBOrg flies. 10 egg chambers were manually examined per genotype. Error bars represent the means ± SD. Statistical significance was determined using a two-tailed Student’s t test (***, P < 0.0001). (E) Degenerating midstage egg chambers (arrows) from fed SesBOrg flies are TUNEL positive. (F) Degenerating midstage egg chambers from starved control SesBOrg/FM7a;Dcp-1Prev1/Dcp-1Prev1 flies contained persisting nurse cell nuclei and increased Ref(2)P. n = 117 ovarioles examined. Box represents zoomed image. (G) Degenerating midstage egg chambers from fed SesBOrg;Dcp-1Prev1 flies contained condensed and fragmented nurse cell nuclei and low levels of Ref(2)P. Box represents zoomed image. n = 156 ovarioles examined. (H) In response to starvation, Dcp-1 acts to negatively regulate the levels of SesB. SesB is a negative regulator of autophagy, and reduced SesB levels mediated by Dcp-1 lead to decreased ATP and induction of autophagic flux. Bars: (A, C [main images], E, F [main images], and G [main images]) 25 µm; (C, insets) 12.5 µm; (F and G [zoomed images]) 10 µm.
To determine the epistatic relationship between Dcp-1 and SesB, we examined fed and nutrient-deprived SesBOrg;Dcp-1Prev1 double mutant flies. Because of the high levels of SesB in Dcp-1Prev1 flies, we reasoned that by reducing SesB in the Dcp-1Prev1 background, a SesBOrg phenotype would result. Degenerating midstage egg chambers from nutrient-deprived control SesBOrg/FM7a;Dcp-1Prev1/Dcp-1Prev1 flies contained persisting nurse cell nuclei and an accumulation of Ref(2)P (Fig. 8 F). In contrast, ovarioles from fed SesBOrg/SesBOrg;Dcp-1Prev1/Dcp-1Prev1 flies arrested during midoogenesis, and these midstage egg chambers contained condensed and fragmented nurse cell nuclei and reduced Ref(2)P levels (Fig. 8 G), similar to the SesBOrg phenotype. These data place Dcp-1 upstream of SesB, suggesting that Dcp-1 may promote autophagy by inhibiting SesB activity. All together, these data demonstrate that SesB is a novel negative regulator of autophagic flux during Drosophila midoogenesis, and its levels are reduced after starvation in a Dcp-1–dependent manner.
Discussion
Our results reveal that starvation-induced autophagic flux occurs in both midstage egg chambers that have not entered the degeneration process as well as in those that are undergoing cell death. Furthermore, we find that the effector caspase Dcp-1 is required for autophagic flux in degenerating midstage egg chambers in addition to its role in cell death. We find that one mechanism of Dcp-1–induced autophagic flux is mediated through SesB. In humans, there are four mitochondrial ANT isoforms, each with a tissue-specific distribution and different roles in apoptosis. ANT1 and ANT3 were proposed to be proapoptotic, whereas ANT2 and ANT4 were shown to be antiapoptotic (Brenner et al., 2011). However, the roles of mammalian ANT proteins in autophagy have yet to be characterized. Our data show that reduced Dcp-1 leads to increased levels of SesB protein in fed and starvation conditions during Drosophila oogenesis and in Drosophila cultured cells. We detected no significant change in SesB transcript levels in fed conditions or after 4 h of starvation, but a significant increase was observed in cells after 2 h of starvation. This finding suggests that a transcription-related mechanism may play some role in the observed cellular response but is not sufficient to account for all of the observed changes in protein levels. Although Dcp-1 does not cleave SesB, the proform of Dcp-1 interacts with SesB, and we predict that this interaction regulates the stability of SesB. We find that SesB is required to suppress autophagic flux during midoogenesis even under nutrient-rich conditions, and reduction of SesB in Dcp-1Prev1 flies rescues the autophagic defect after starvation. This is the first study to our knowledge showing that an ANT functions as a negative regulator of autophagy.
The Drosophila genome encodes seven caspases, and to date, only the initiator caspase Dronc and the effector caspase Drice have been shown to localize to the mitochondria (Dorstyn et al., 2002). In mammalian cells, caspases have been detected at the mitochondria during apoptosis (Krajewski et al., 1999; Susin et al., 1999; Chandra and Tang, 2003); however, the role of caspases at the mitochondria, especially under nonapoptotic conditions, is poorly understood. Our results demonstrate that Dcp-1 localizes to the mitochondria where it functions to maintain the mitochondrial network morphology. Under nutrient-rich conditions, nondegenerating midstage egg chambers from Dcp-1Prev1 flies contained mitochondria that appeared elongated and overly connected, and ovaries contained increased ATP levels, indicating that Dcp-1 normally functions to negatively regulate mitochondrial dynamics and ATP levels. Consistent with our findings, overexpression of the caspase inhibitor p35 in the amnioserosa suppressed the transition of mitochondria from a tubular to a fragmented state during delamination (Muliyil et al., 2011), further suggesting that inhibition of caspases hinders normal mitochondrial dynamics.
Dcp-1 acts to finely tune the apoptotic process, and cell death only occurs when caspase activity reaches a certain apoptotic threshold (Florentin and Arama, 2012). Effector caspases involved in nonapoptotic processes may be restricted in time or space to regulate caspase activity (Kaplan et al., 2010; Florentin and Arama, 2012). As Dcp-1 functions not only in autophagy and apoptosis but also at the mitochondria to regulate mitochondrial morphology and ATP levels, one question that remains is to how the activity of Dcp-1 is regulated. As Dcp-1 has autocatalytic activity (Song et al., 1997), perhaps Dcp-1 is sequestered in mitochondria to prevent its full activation. Mitochondrial localized mammalian pro–Caspase 3 and 9 are S-nitrosylated in their catalytic active site, leading to the inhibition of their activity (Mannick et al., 2001). Perhaps mitochondrial Dcp-1 is also S-nitrosylated, serving to limit Dcp-1’s activity. In addition, mammalian Hsp60 and Hsp10 were shown to interact with mitochondrial localized pro–Caspase 3 in which they function to accelerate pro–Caspase 3 activation after the induction of apoptosis (Samali et al., 1999). Perhaps Dcp-1 associates with Drosophila Hsp60 or Hsp10 in the mitochondria to regulate its mitochondrial related functions. However, further studies are required to identify upstream regulators of Dcp-1 that regulate its mitochondrial, autophagic, and apoptotic functions.
Effector caspases are the main executioners of apoptotic cell death; however, it is becoming increasingly evident that caspases have nonapoptotic functions in differentiation, proliferation, cytokine production, and cell survival (Kuranaga and Miura, 2007; Galluzzi et al., 2012). For example, Caspase 3 was shown to regulate tumor cell repopulation in vitro and in vivo (Huang et al., 2011), and it was also shown to be required for skeletal muscle (Fernando et al., 2002) and macrophage differentiation (Sordet et al., 2002). In Drosophila, the initiator caspase Dronc maintains neural stem cell homeostasis by binding to Numb in a noncatalytic, nonapoptotic manner to regulate its activity (Ouyang et al., 2011). In addition, Dcp-1 is required for neuromuscular degeneration in a nonapoptotic manner (Keller et al., 2011). Our results show that Dcp-1 also has a nonapoptotic role during oogenesis, in which it is required to maintain mitochondrial physiology under basal conditions. Loss of Dcp-1 alters this physiology, leading to increased SesB and ATP levels that in part prevent the induction of autophagic flux after starvation. These data support the notion that caspases play a much more diverse role than previously known and that the underlying mechanisms should be better understood to appreciate the full impact of apoptosis pathway modulation for treatment in human pathologies.
Materials and methods
Fly strains
w1118 was used at the wild-type control strain in this study. Other fly strains used are as follows: nanos-GAL4::VP16 (abbreviated as nosGAL4, a driver containing the Gal4-VP16 transactivator under the control of the nanos promoter; Rørth, 1998), UASp-mitoGFP (expresses the COX VIII mitochondrial targeting sequence fused to EGFP under the UASp promoter; Cox and Spradling, 2003), Dcp-1Prev1 (contains a 40-bp partial P element insertion in the coding region of Dcp-1, resulting in a frame shift in Dcp-1 and an in-frame stop codon within the 40-bp insertion; Laundrie et al., 2003), and UASp-FL-Dcp-1 (drives expression of full-length Dcp-1 under the UASp promoter; Peterson et al., 2003) were gifts from K. McCall (Boston University, Boston, MA). Atg7d77 (P element excision removing CG5335 and exons 5 and 6 and most of exon 4 from Atg7) and Atg7d14 (P element excision removing the transcription and translation start sites and the majority of the Atg7 coding region) were gifts from T. Neufeld (University of Minnesota, Minneapolis MN; Juhász et al., 2007). UASp-GFP-mCherry-DrAtg8a (drives expression of GFP-mCherry-DrAtg8a under the UASp promoter) was a gift from T.E. Rusten (Centre for Cancer Biomedicine, Oslo University Hospital, Montebello, Oslo, Norway; Nezis et al., 2010), and SesBOrg hypomorphic flies, which contain a glutamate to lysine change at amino acid 266 that disrupts normal SesB activity, were obtained from the Bloomington Stock Center (stock 27590).
Cell culture conditions
Drosophila l(2)mbn cells were grow in Schneider’s medium (Invitrogen) supplemented with 10% FBS in 25-cm2 suspension cell flasks (Sarstedt) at 25°C. Drosophila S2-RFP-GFP-Atg8a cells were grown in ESF921 medium (Expression Systems) in the presence of 50 µg/ml Zeocin. All experiments were performed 3–4 d after passage.
Construction of RFP-GFP-ATG8a plasmid and creation of S2-RFP-GFP-Atg8a stable cell line
ATG8a was amplified using the primers 5′-TGACCTAGCTAGATCTAAGTTCCAATACAAGGAGGA-3′ and 5′-TGACCTAGCTGAATTCTTAGTTAATTTTGGCCATGCC-3′. Atg8a was cloned into the BglII–EcoRI sites of mRFP-EGFP-LC3 (Kimura et al., 2007). The cytomegalovirus promoter from this construct was removed using AseI–NheI digestion and replaced with the actin promoter amplified from pAFW (Drosophila Genomics Resource Center) using the primers 5′-TGACGATCGCATTAATCAGCATGCAATTCTATATTCT-3′ and 5′-TGACGATCGCGCTAGCGGCCTCGATATCTGGATCCGG-3′. The Pactin-RFP-GFP-ATG8a fragment (AseI–MluI digest) was then subcloned in the HindIII site of the previously described p2ZOp2F vector (Hegedus et al., 1998), which contains Zeocin as a selection agent for transfection in Drosophila cell lines. For transfections, 1 µg Pactin-RFP-GFP-ATG8a was added to 10 µl Cellfectin (Invitrogen) plus 100 µl Grace’s medium (Invitrogen) and incubated for ≥30 min. 3.75 × 106 S2 cells in 400 µl Grace’s media were incubated with transfection medium overnight. 1 ml ESF921 medium (Expression Systems) was added back to the cells, and the cells were incubated for an additional 3 d before adding Zeocin at a concentration of 0.6–0.8 mg/ml. The media were replaced every 4 d until the negative control showed 0% viability (∼3 wk). Transfected cells were maintained in ESF921 + 0.1 mg/ml Zeocin.
Double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) synthesis
Each PCR primer for RT-PCR was designed to contain a 5′ T7 RNA polymerase binding site (5′-TAATACGACTCACTATAGG-3′) followed by sequences specific for the target gene. The ampicillin resistance gene was used as a control dsRNA and was amplified using the primers 5′-TAATACGACTCACTATAGGATTGGACTACGATACGGGAGGGCTT-3′ and 5′-TAATACGACTCACTATAGGATTGGGCTATGTGGCGCGGTATTAT-3′. Dcp-1 was amplified using the primers 5′-TAATACGACTCACTATAGGACAAAAGCTGGCTGAGAAGC-3′ and 5′-TAATACGACTCACTATAGGCAGCCATTATAAAGCTGCCC-3′. The PCR products were generated by RT-PCR using SuperScript One-Step RT-PCR with Platinum Taq (Invitrogen). RT-PCR products were ethanol precipitated and used as a template for in vitro transcription reactions using T7 RiboMAX Express RNAi System (Promega). Quality of the RNA was analyzed by gel electrophoresis. dsRNA was quantitated using PicoGreen and adjusted to 200–400 ng/µl with nuclease-free water.
RNAi
For RNAi, cells were washed and resuspended in ESF921 medium to a concentration of 2 × 106 cells/ml. 333 µl of adjusted cells was plated in each well of a 24-well plate. 5–10 µg dsRNA was added per well and incubated at 25°C for 1 h. After incubation, 667 µl Schneider’s + 10% FBS was added back to each well and was incubated for an additional 72 h at 25°C.
Immunofluorescence experiments
Flies were conditioned on wet yeast paste for 2 d (fed) and then transferred to a vial containing 10% sucrose for 4 d for amino acid starvation. Ovaries were dissected in PBS and fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde. Ovaries were washed with PBS-T (PBS + 0.3% Triton X-100), permeabilized with 0.5% Triton X-100, and blocked with 2% BSA in PBS-T. For in vitro experiments, 200 µl cells was plated into an 8-well CC2-coated chamber slide and incubated for ≥30 min to let the cells adhere. For starvation treatments, media were replaced with 2 mg/ml glucose/PBS. For MitoTracker experiments, 500 nm MitoTracker red CMXRos (Invitrogen) was added to each well and incubated for 30 min in the dark at 25°C. Media were removed and fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 20 min. Cells were washed with PBS-T and permeabilized with 0.5% Triton X-100.
Primary antibodies included rabbit anti-Ref(2)P (1:5,000; T.E. Rusten), mouse anti-Armadillo (1:100; N2 7A1; Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank) mouse anti–ATPsyn-α (1:500; MitoSciences), guinea pig anti–Dcp-1 (1:500;Tenev et al., 2005), mouse anti–β-Tubulin (1:1,000; E7; Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank), mouse anti–protein disulfide isomerase (1:100; Abcam), and rabbit anti-GM130 (1:100; Abcam) were diluted in 0.5% BSA + PBS-T. Secondary antibodies included Alexa Fluor 488– and Alexa Fluor 546–conjugated antibodies (1:1,000; Invitrogen). For Draq5 DNA stain, Draq5 was diluted in PBS (1:500) with 100 µg/ml RNase A for 10 min at room temperature. Samples were mounted with SlowFade gold antifade reagent (Invitrogen) and viewed with a microscope (Confocal C1; Nikon) equipped with a Plan Apochromat 60×/1.45 NA oil immersion objective (Nikon) or a 20×/0.75 NA objective lens. Images were acquired at room temperature using EZ-C1 version 3.00 software (Nikon). Images were scanned with the same pinhole and laser brightness settings. Brightness and contrast were adjusted using Photoshop (CS4; Adobe) and was applied to the whole image.
LTR and TUNEL analysis
For LTR staining of ovaries, ovaries from fed, and amino acid–starved flies were dissected in PBS and incubated in 50 µm LTR DND-99 for 3 min, washed three times with PBS, and fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 20 min. Ovaries were washed three times with PBS-T (PBS + 0.3% Triton X-100), incubated in 1:500 Draq5 + 100 µg/ml RNase A for 10 min at room temperature, and mounted in SlowFade gold reagent. For LTR of fat bodies, second instar larvae were transferred to a cornmeal/dextrose fly food agar plate supplemented with yeast paste 48 h after hatching. 12–24 h later, fed larvae were dissected or were transferred to a plate containing 20% sucrose for 1–4 h before dissecting. Fat bodies were dissected in PBS and transferred to 0.8 µm LTR (Invitrogen) for 5 min at room temperature in the dark. Tissues were then incubated with 1:500 Draq5 + 100 µg/ml RNase A for 10 min at room temperature, washed three times in PBS, and mounted with SlowFade at room temperature.
For TUNEL analysis, ovaries were dissected in PBS and fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde. Ovaries were washed two times with PBS, permeabilized with 0.2% Triton X-100 for 5 min, and washed two additional times with PBS. The TUNEL assay was performed using the fluorometric TUNEL system (DeadEnd; Promega) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Ovaries were incubated with 1:500 Draq5 + 100 µg/ml RNase A for 10 min at room temperature and viewed by confocal microscopy.
Mitochondrial scoring
For in vitro experiments, mitochondrial morphology was first assessed under basal conditions by two independent researchers, and a classification scheme (fragmented, normal, and elongated) was devised and agreed upon by both researchers. For in vivo experiments, mitochondria were assessed in both fed and nutrient-deprived control flies, and a scoring scheme (healthy, clustered, or elongated and overly connected) was devised based on similar observations made in healthy and degenerating midstage egg chambers (scored as healthy, normally degenerating, or abnormal) described in Tanner et al. (2011).
Protein extraction and Western blot analysis
For ovary lysates, ovaries were dissected and placed immediately on dry ice. Cell and ovary lysates were extracted using radioimmunoprecipitation assay lysis buffer (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc.) plus complete protease inhibitors (Roche). Protein was quantitated using the Bicinchoninic Acid Protein Assay (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Proteins were separated on a 4–12% NuPAGE Bis-Tris gel (Invitrogen) and transferred to polyvinylidene fluoride membranes. Membranes were blocked in milk or Odyssey blocking buffer and incubated in primary antibodies overnight at 4°C. Primary antibodies included rabbit anti-Ref(2)P (1:10,000), mouse anti-actin (1:500; JLA20; Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank), mouse anti-Tubulin (1:1,000; E7), mouse anti–ATPsyn-α (1:1,000), mouse anti-Porin (1:1,000; MitoSciences), mouse anti-ANT (1:500; MitoSciences), rabbit anti–Dcp-1 (1:500; Laundrie et al., 2003), guinea pig anti–Dcp-1 (1:500; Tenev et al., 2005), rabbit anti-Pink1 (1:500; Abcam), and rabbit anti-Atg8a (1:1,000; Barth et al., 2011). Membranes were incubated with HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies or infrared-labeled secondary antibodies and were detected using the ECL Enhanced Western Blotting System (GE Healthcare) or the Odyssey System (LI-COR Biosciences). Densitometry was performed using ImageQuant 5.1 software (GE Healthcare).
Isolation of crude mitochondrial and cytosolic fractions
Approximately 5 × 107 cells were collected by centrifugation at 800 rpm for 10 min, resuspended in cold SEM-P (10 mM MOPS, pH 7.5, 320 mM sucrose, and 1 mM EDTA with complete protease inhibitor cocktail [Roche]), and ground using a dounce homogenizer. Lysates were centrifuged twice at 3,000 rpm to remove cell debris, and supernatants were collected. The membrane fraction (pellet) was separated from the cytosolic fraction (supernatant) by centrifugation at 12,000 rpm. The pellets were washed once with 500 µl SEM-P and finally resuspended in 50 µl SEM-P. Protein concentrations were determined using the Bicinchoninic Acid Protein Assay. Aliquots of 50 µg protein were either spun down (membrane fraction) or TCA precipitated (cytosolic fraction) and analyzed by Western blotting.
Proteinase K protection assay
For mitochondrial lysis, mitochondria were resuspended in the appropriate amount of swelling buffer (50 mM Tris, pH 7.5) for 30 min on ice with vigorous vortexing. Intact and lysed mitochondria were incubated in 20 µg/ml proteinase K (Roche). Proteinase K was inactivated by adding PMSF (Fluka) to a final concentration of 1 mM. Intact mitochondria were spun down at 4°C and 12,000 rpm for 20 min while lysed samples were TCA precipitated.
Oligomycin A treatment
3–5-d-old flies were transferred to a vial containing wet yeast paste supplemented with 200 µl of 25-µg/ml Oligomycin A or DMSO added directly to the top of the yeast paste. After 2 d of treatment, flies were transferred to a vial containing a Kimwipe soaked with 10% sucrose supplemented with 25 µg/ml Oligomycin A or DMSO for 4 d.
Mitochondrial mass analysis and determination of ATP levels
RNAi-treated cells were transferred from Schneider + 10% FBS to 2 mg/ml glucose/PBS starvation media plus 10 µg dsRNA for 1–24 h. For mitochondrial mass measurements, cells were incubated with 10 µM NAO for 10 min at 25°C in the dark. Cells were resuspended and put on ice to be analyzed by flow cytometry (FACSCalibur; BD). A minimum of 30,000 cells was acquired for triplicate samples per experiment. The mean fluorescence was analyzed using FlowJo Software version 5.7.2 (Tree Star, Inc.).
ATP levels from l(2)mbn cells or Drosophila ovaries were measured using the ATP Determination Kit (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Luminescence was measured using a plate reader (Wallac 1420 Victor; PerkinElmer).
Generation of constructs and in vitro synthesis
Drice (Tenev et al., 2005) was PCR amplified using primers containing AttB1 and AttB2 sequences. SesB was amplified from a full-length cDNA construct (Drosophila Genomics Resource Center) using primers containing AttB1 and AttB2 sequences. PCR products were cloned into the pDONR221 Gateway Entry Vector (Life Technologies) and were sequenced verified. The entry clones were then shuttled into the pEXP2-DEST and pEXP1-DEST expression vectors, respectively, for in vitro translation experiments. Sequences used for plasmid construction can be found in Table S1. SesB and Drice were synthesized using the Expressway Mini Expression Module (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. 1 µg of template DNA was used for every 100 µl of synthesis reaction in a 6-h reaction. PCR primers were used as follows: Drice AttB1, 5′-GGGGACAAGTTTGTACAAAAAAGCAGGCTTCACCATGGACGCCACTAACAATGGAGAAT-3′; Drice AttB2, 5′-GGGGACCACTTTGTACAAGAAAGCTGGGTCTCAAACCCGTCCGGCTGGT-3′; SesB AttB1, 5′-GGGGACAAGTTTGTACAAAAAAGCAGGCTTCACCATGGGCAAGGATTTCGATGCTGTT-3′; and SesB AttB2, 5′-GGGGACCACTTTGTACAAGAAAGCTGGGTCCAAGACCTTCTTGATCTCAT-3′.
Transfection and purification of Dcp-1 and in vitro cleavage assays
For transfection experiments, 0.5 µg His-V5–Dcp-1FL or His-V5–Dcp-1C<A plasmid DNA (Tenev et al., 2005) was added to 10 µl Cellfectin plus 100 µl Grace’s medium and incubated for ≥30 min. 3.75 × 106 cells in 400 µl Grace’s media were incubated with transfection medium overnight before receiving 1 ml Schneider’s medium + 10% FBS. Cells were incubated for an additional 3 d before Ni-NTA purification. Purification of His-V5–Dcp-1FL or His-V5–Dcp-1C<A was performed using Ni-NTA spin columns (HisPur; Thermo Fisher Scientific). Cells were resuspended in 400 µl equilibration buffer (PBS and 10 mM imidazole) with 1% Triton X-100, incubated in a rotary shaker at 4°C for 10 min, and centrifuged at 15,0000 rpm at 4°C for 15 min to remove insoluble material. Subsequent steps were performed according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Eluted Dcp-1FL and Dcp-1C<A were checked for caspase activity using the Caspase-Glo 3/7 Assay kit (Promega) according the manufacturer’s instructions. The elutions were immediately used for in vitro cleavage assays. The caspase reaction buffer used in this experiment was as previously described (Tenev et al., 2005) and consisted of 10 mM Tris, pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 2 mM DTT, and 0.1% Triton X-100. A 100-µl reaction volume was set up consisting of increasing volumes of Ni-NTA–purified Dcp-1FL or Dcp-1C<A (10, 20, and 40 µl) and 5 µl of in vitro translated SesB or Drice. The reaction mixture was incubated at 25°C overnight and precipitated with 400 µl acetone for Western blot analysis.
Quantitative RT-PCR (QRT-PCR) analysis
RNAi-treated cells were subjected to nutrient-full or starvation conditions for 2 or 4 h and were collected and pelleted at 850 rpm for 5 min. Cell pellets were lysed in 1 ml TRIZOL (Invitrogen), and total RNA was extracted according to the manufacturer’s instructions. RNA was treated with DNase, and QRT-PCR was performed using the One-Step SYBR green RT-PCR reagent kit (Applied Biosystems) on a 7900 Sequence Detection System (Applied Biosystems). Expression levels were calculated using the comparative threshold method with Drosophila rp49 as the reference gene. QRT-PCR primers are as follows: rp49, 5′-ATACAGGCCCAAGATCGTGA-3′ and 5′-GCACTCTGTTGTCGATACCCTT-3′, and SesB, 5′-AAGGATTTCGATGCTGTTGG-3′ and 5′-CTCCTTTGGAATGCGGATAA-3′.
IP and MS/MS analysis
For large-scale IP experiments, 96 ml V5–Dcp-1C196A or V5 vector control–transfected l(2)mbn cells were centrifuged at 800 rpm for 10 min. Nutrient-full medium was replaced with either new 10% FBS/Schneider medium (fed) or 2 mg/ml glucose/PBS for 2-h starvation treatment. Cells were centrifuged at 800 rpm for 10 min and cross-linked with 0.25% paraformaldehyde at 25°C for 40 min. 1.25 M glycine (final = 0.125 M) was added and incubated for 5 min at room temperature to stop the cross-linking reaction. Samples were then centrifuged at 800 rpm for 10 min and lysed (20 mM Tris, pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, 1% NP-40, 10 mM β-glycerophosphate, 2 mM sodium orthovanadate, 1 mM 4-(2-aminoethyl) benzenesulfonyl fluoride hydrochloride, 10 µg/ml pepstatin A, 10 µg/ml leupeptin, and 10 µg/ml aprotinin). Cells were disrupted by passing through a 21-gauge syringe five times, and lysates were incubated at 4°C for 30 min. Cells were spun down, and supernatants were incubated with a 50% slurry of Sepharose 4B (Sigma-Aldrich) for 1 h at 4°C. Sepharose 4B was removed by centrifugation, and supernatants were incubated with a 50% slurry of anti-V5 affinity agarose resin for 3 h at 4°C. Anti-V5 resins were recovered by centrifugation and washed 5× with cold lysis buffer and 2× lysis buffer with 500 mM NaCl. Bound proteins were eluted by 0.5 M formic acid. Eluates were boiled for 20 min at 95°C to reverse the formaldehyde cross-links. Eluates were then vacuum dried, resuspended in protein sample buffer (Invitrogen), and separated by SDS-PAGE using a 10% NuPAGE gel (Invitrogen) and MES buffer. Protein bands were visualized with the colloidal Coomassie stain, and each lane was cut into 16 equal sections. Gel slices were transferred into a 96-well plate, reduced with 10 mM DTT, S-alkylated with 100 mM iodoacetamide, and then subjected to in-gel trypsin digestion with 20 µl of 20-ng/µl trypsin per well overnight at 37°C. Peptide mixtures were subjected to liquid chromatography MS/MS analysis on a Finnigan LCQ (PTRL West) or a 4000 QTRAP (Applied Biosystems) ion trap mass spectrometer via reversed phase HPLC nanoelectrospray ionization. All MS–MS spectra were queried against the Drosophila Ensembl sequence databases (Flicek et al., 2014) using the Mascot (Matrix Science) or X!Tandem (Craig and Beavis, 2004) algorithms. Candidate interacting proteins were identified as described in Mead et al. (2010). In brief, putative interacting proteins were identified by at least two peptides each having an X!Tandem log(e) score less than −3 and were identified in at least two experimental samples (V5–Dcp-1C<A) and not in the negative control (V5 vector only).
Statistics
In each graph, data represent ± SEM or SD of n independent experiments. As indicated in the legends, statistical significance was calculated by analysis of variance (ANOVA) plus a Dunnett or Bonferroni post test, or a two-tailed Student’s t test between the indicated samples was used. P-values are shown in the legends.
Online supplemental material
Fig. S1 shows that Dcp-1Prev1 flies have reduced autolysosomes in nondegenerating midstage egg chambers after starvation. Fig. S2 shows LTR and Atg8a antibody staining in fat bodies of Dcp-1Prev1, CG-GAL4/+;UASDcp-1/+, SesBOrg, and control flies. Fig. S3 shows a lack of colocalization between Dcp-1 and the ER or Golgi but does show localization between Dcp-1 and β-Tubulin. Fig. S4 shows that overexpression of Dcp-1 can rescue the Dcp-1Prev1 mitochondrial phenotype. Fig. S5 shows SesB QRT-PCR analysis, FLAG-SesB localization to mitochondria, and that ovaries from SesBOrg flies have reduced ATP and contain increased LTR staining in degenerating midstage egg chambers. Table S1 shows quantification of TUNEL-positive germaria and midstage egg chambers. Table S2 shows identification of SesB by MS. Online supplemental material is available at http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201303144/DC1.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank E. Verheyen, M. Jardon, A. Kyle, C. Lebovitz, and S. Bortnik for helpful comments and suggestions on the manuscript and K. McCall, T.E. Rusten, P. Meier, and K. Kohler for reagents used in this study. The authors thank M. Sun and M. Kuzyk for assistance with processing the MS raw data.
This work was supported by a National Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada Discovery Grant (RGPIN/371368-2009) and Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) Operating Grant (MOP-78882) to S.M. Gorski. S.M. Gorski is supported in part by a CIHR New Investigator Salary Award.
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Footnotes
Abbreviations used in this paper:
- ANOVA
- analysis of variance
- ANT
- adenine nucleotide translocase
- Dcp-1
- Drosophila caspase 1
- dsRNA
- double-stranded RNA
- IP
- immunoprecipitation
- LTR
- LysoTracker red
- MS
- mass spectrometry
- NAO
- 10-N-nonyl acridine orange
- NTA
- nitriloacetic acid
- QRT-PCR
- quantitative RT-PCR
- SesB
- stress-sensitive B
- VDAC
- voltage-dependent anion channel
References
- Barth J.M., Szabad J., Hafen E., Köhler K. 2011. Autophagy in Drosophila ovaries is induced by starvation and is required for oogenesis. Cell Death Differ. 18:915–924 10.1038/cdd.2010.157 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett B.J., Isakson P., Lewerenz J., Sanchez H., Kotzebue R.W., Cumming R.C., Harris G.L., Nezis I.P., Schubert D.R., Simonsen A., Finley K.D. 2011. p62, Ref(2)P and ubiquitinated proteins are conserved markers of neuronal aging, aggregate formation and progressive autophagic defects. Autophagy. 7:572–583 10.4161/auto.7.6.14943 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry D.L., Baehrecke E.H. 2007. Growth arrest and autophagy are required for salivary gland cell degradation in Drosophila. Cell. 131:1137–1148 10.1016/j.cell.2007.10.048 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner C., Subramaniam K., Pertuiset C., Pervaiz S. 2011. Adenine nucleotide translocase family: four isoforms for apoptosis modulation in cancer. Oncogene. 30:883–895 10.1038/onc.2010.501 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bursch W., Ellinger A., Kienzl H., Török L., Pandey S., Sikorska M., Walker R., Hermann R.S. 1996. Active cell death induced by the anti-estrogens tamoxifen and ICI 164 384 in human mammary carcinoma cells (MCF-7) in culture: the role of autophagy. Carcinogenesis. 17:1595–1607 10.1093/carcin/17.8.1595 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandra D., Tang D.G. 2003. Mitochondrially localized active caspase-9 and caspase-3 result mostly from translocation from the cytosol and partly from caspase-mediated activation in the organelle. Lack of evidence for Apaf-1-mediated procaspase-9 activation in the mitochondria. J. Biol. Chem. 278:17408–17420 10.1074/jbc.M300750200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y., Azad M.B., Gibson S.B. 2009. Superoxide is the major reactive oxygen species regulating autophagy. Cell Death Differ. 16:1040–1052 10.1038/cdd.2009.49 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho D.-H., Jo Y.K., Hwang J.J., Lee Y.M., Roh S.A., Kim J.C. 2009. Caspase-mediated cleavage of ATG6/Beclin-1 links apoptosis to autophagy in HeLa cells. Cancer Lett. 274:95–100 10.1016/j.canlet.2008.09.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R.T., Spradling A.C. 2003. A Balbiani body and the fusome mediate mitochondrial inheritance during Drosophila oogenesis. Development. 130:1579–1590 10.1242/dev.00365 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig R., Beavis R.C. 2004. TANDEM: matching proteins with tandem mass spectra. Bioinformatics. 20:1466–1467 10.1093/bioinformatics/bth092 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denton D., Shravage B., Simin R., Mills K., Berry D.L., Baehrecke E.H., Kumar S. 2009. Autophagy, not apoptosis, is essential for midgut cell death in Drosophila. Curr. Biol. 19:1741–1746 10.1016/j.cub.2009.08.042 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorstyn L., Read S., Cakouros D., Huh J.R., Hay B.A., Kumar S. 2002. The role of cytochrome c in caspase activation in Drosophila melanogaster cells. J. Cell Biol. 156:1089–1098 10.1083/jcb.200111107 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond-Barbosa D., Spradling A.C. 2001. Stem cells and their progeny respond to nutritional changes during Drosophila oogenesis. Dev. Biol. 231:265–278 10.1006/dbio.2000.0135 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg-Lerner A., Bialik S., Simon H.-U., Kimchi A. 2009. Life and death partners: apoptosis, autophagy and the cross-talk between them. Cell Death Differ. 16:966–975 10.1038/cdd.2009.33 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Érdi B., Nagy P., Zvara A., Varga A., Pircs K., Ménesi D., Puskás L.G., Juhász G. 2012. Loss of the starvation-induced gene Rack1 leads to glycogen deficiency and impaired autophagic responses in Drosophila. Autophagy. 8:1124–1135 10.4161/auto.20069 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernando P., Kelly J.F., Balazsi K., Slack R.S., Megeney L.A. 2002. Caspase 3 activity is required for skeletal muscle differentiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 99:11025–11030 10.1073/pnas.162172899 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filkins J.P. 1970. Lysosomes and hepatic regression during fasting. Am. J. Physiol. 219:923–927 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flicek P., Amode M.R., Barrell D., Beal K., Billis K., Brent S., Carvalho-Silva D., Clapham P., Coates G., Fitzgerald S., et al. 2014. Ensembl 2014. Nucleic Acids Res. 42(D1, Database issue):D749–D755 10.1093/nar/gkt1196 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florentin A., Arama E. 2012. Caspase levels and execution efficiencies determine the apoptotic potential of the cell. J. Cell Biol. 196:513–527 10.1083/jcb.201107133 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galluzzi L., Kepp O., Trojel-Hansen C., Kroemer G. 2012. Non-apoptotic functions of apoptosis-regulatory proteins. EMBO Rep. 13:322–330 10.1038/embor.2012.19 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giorgi F., Deri P. 1976. Cell death in ovarian chambers of Drosophila melanogaster. J. Embryol. Exp. Morphol. 35:521–533 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleason C.E., Lu D., Witters L.A., Newgard C.B., Birnbaum M.J. 2007. The role of AMPK and mTOR in nutrient sensing in pancreatic beta-cells. J. Biol. Chem. 282:10341–10351 10.1074/jbc.M610631200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomes L.C., Di Benedetto G., Scorrano L. 2011. During autophagy mitochondria elongate, are spared from degradation and sustain cell viability. Nat. Cell Biol. 13:589–598 10.1038/ncb2220 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegedus D.D., Pfeifer T.A., Hendry J., Theilmann D.A., Grigliatti T.A. 1998. A series of broad host range shuttle vectors for constitutive and inducible expression of heterologous proteins in insect cell lines. Gene. 207:241–249 10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00636-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou Y.-C.C., Chittaranjan S., Barbosa S.G., McCall K., Gorski S.M. 2008. Effector caspase Dcp-1 and IAP protein Bruce regulate starvation-induced autophagy during Drosophila melanogaster oogenesis. J. Cell Biol. 182:1127–1139 10.1083/jcb.200712091 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Høyer-Hansen M., Jäättelä M. 2008. Autophagy: an emerging target for cancer therapy. Autophagy. 4:574–580 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang Q., Li F., Liu X., Li W., Shi W., Liu F.F., O’Sullivan B., He Z., Peng Y., Tan A.C., et al. 2011. Caspase 3-mediated stimulation of tumor cell repopulation during cancer radiotherapy. Nat. Med. 17:860–866 10.1038/nm.2385 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juhász G., Érdi B., Sass M., Neufeld T.P. 2007. Atg7-dependent autophagy promotes neuronal health, stress tolerance, and longevity but is dispensable for metamorphosis in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 21:3061–3066 10.1101/gad.1600707 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanzawa T., Kondo Y., Ito H., Kondo S., Germano I. 2003. Induction of autophagic cell death in malignant glioma cells by arsenic trioxide. Cancer Res. 63:2103–2108 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan Y., Gibbs-Bar L., Kalifa Y., Feinstein-Rotkopf Y., Arama E. 2010. Gradients of a ubiquitin E3 ligase inhibitor and a caspase inhibitor determine differentiation or death in spermatids. Dev. Cell. 19:160–173 10.1016/j.devcel.2010.06.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller L.C., Cheng L., Locke C.J., Müller M., Fetter R.D., Davis G.W. 2011. Glial-derived prodegenerative signaling in the Drosophila neuromuscular system. Neuron. 72:760–775 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.09.031 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J., Kundu M., Viollet B., Guan K.-L. 2011. AMPK and mTOR regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of Ulk1. Nat. Cell Biol. 13:132–141 10.1038/ncb2152 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmelman A.C. 2011. The dynamic nature of autophagy in cancer. Genes Dev. 25:1999–2010 10.1101/gad.17558811 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura S., Noda T., Yoshimori T. 2007. Dissection of the autophagosome maturation process by a novel reporter protein, tandem fluorescent-tagged LC3. Autophagy. 3:452–460 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo Y., Kanzawa T., Sawaya R., Kondo S. 2005. The role of autophagy in cancer development and response to therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 5:726–734 10.1038/nrc1692 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krajewski S., Krajewska M., Ellerby L.M., Welsh K., Xie Z., Deveraux Q.L., Salvesen G.S., Bredesen D.E., Rosenthal R.E., Fiskum G., Reed J.C. 1999. Release of caspase-9 from mitochondria during neuronal apoptosis and cerebral ischemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 96:5752–5757 10.1073/pnas.96.10.5752 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuranaga E., Miura M. 2007. Nonapoptotic functions of caspases: caspases as regulatory molecules for immunity and cell-fate determination. Trends Cell Biol. 17:135–144 10.1016/j.tcb.2007.01.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laundrie B., Peterson J.S., Baum J.S., Chang J.C., Fileppo D., Thompson S.R., McCall K. 2003. Germline cell death is inhibited by P-element insertions disrupting the dcp-1/pita nested gene pair in Drosophila. Genetics. 165:1881–1888 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maftah A., Petit J.M., Ratinaud M.H., Julien R. 1989. 10-N nonyl-acridine orange: a fluorescent probe which stains mitochondria independently of their energetic state. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 164:185–190 10.1016/0006-291X(89)91700-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maiuri M.C., Criollo A., Tasdemir E., Vicencio J.M., Tajeddine N., Hickman J.A., Geneste O., Kroemer G. 2007. BH3-only proteins and BH3 mimetics induce autophagy by competitively disrupting the interaction between Beclin 1 and Bcl-2/Bcl-X(L). Autophagy. 3:374–376 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannick J.B., Schonhoff C., Papeta N., Ghafourifar P., Szibor M., Fang K., Gaston B. 2001. S-Nitrosylation of mitochondrial caspases. J. Cell Biol. 154:1111–1116 10.1083/jcb.200104008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mead C.L., Kuzyk M.A., Moradian A., Wilson G.M., Holt R.A., Morin G.B. 2010. Cytosolic protein interactions of the schizophrenia susceptibility gene dysbindin. J. Neurochem. 113:1491–1503 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muliyil S., Krishnakumar P., Narasimha M. 2011. Spatial, temporal and molecular hierarchies in the link between death, delamination and dorsal closure. Development. 138:3043–3054 10.1242/dev.060731 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nezis I.P., Simonsen A., Sagona A.P., Finley K., Gaumer S., Contamine D., Rusten T.E., Stenmark H., Brech A. 2008. Ref(2)P, the Drosophila melanogaster homologue of mammalian p62, is required for the formation of protein aggregates in adult brain. J. Cell Biol. 180:1065–1071 10.1083/jcb.200711108 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nezis I.P., Lamark T., Velentzas A.D., Rusten T.E., Bjørkøy G., Johansen T., Papassideri I.S., Stravopodis D.J., Margaritis L.H., Stenmark H., Brech A. 2009. Cell death during Drosophila melanogaster early oogenesis is mediated through autophagy. Autophagy. 5:298–302 10.4161/auto.5.3.7454 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nezis I.P., Shravage B.V., Sagona A.P., Lamark T., Bjørkøy G., Johansen T., Rusten T.E., Brech A., Baehrecke E.H., Stenmark H. 2010. Autophagic degradation of dBruce controls DNA fragmentation in nurse cells during late Drosophila melanogaster oogenesis. J. Cell Biol. 190:523–531 10.1083/jcb.201002035 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang Y., Petritsch C., Wen H., Jan L., Jan Y.N., Lu B. 2011. Dronc caspase exerts a non-apoptotic function to restrain phospho-Numb-induced ectopic neuroblast formation in Drosophila. Development. 138:2185–2196 10.1242/dev.058347 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattingre S., Tassa A., Qu X., Garuti R., Liang X.H., Mizushima N., Packer M., Schneider M.D., Levine B. 2005. Bcl-2 antiapoptotic proteins inhibit Beclin 1-dependent autophagy. Cell. 122:927–939 10.1016/j.cell.2005.07.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J.S., Barkett M., McCall K. 2003. Stage-specific regulation of caspase activity in Drosophila oogenesis. Dev. Biol. 260:113–123 10.1016/S0012-1606(03)00240-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinowitz J.D., White E. 2010. Autophagy and metabolism. Science. 330:1344–1348 10.1126/science.1193497 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rikhy R., Ramaswami M., Krishnan K.S. 2003. A temperature-sensitive allele of Drosophila sesB reveals acute functions for the mitochondrial adenine nucleotide translocase in synaptic transmission and dynamin regulation. Genetics. 165:1243–1253 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rørth P. 1998. Gal4 in the Drosophila female germline. Mech. Dev. 78:113–118 10.1016/S0925-4773(98)00157-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubinstein A.D., Eisenstein M., Ber Y., Bialik S., Kimchi A. 2011. The autophagy protein Atg12 associates with antiapoptotic Bcl-2 family members to promote mitochondrial apoptosis. Mol. Cell. 44:698–709 10.1016/j.molcel.2011.10.014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salt I.P., Johnson G., Ashcroft S.J., Hardie D.G. 1998. AMP-activated protein kinase is activated by low glucose in cell lines derived from pancreatic beta cells, and may regulate insulin release. Biochem. J. 335:533–539 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samali A., Cai J., Zhivotovsky B., Jones D.P., Orrenius S. 1999. Presence of a pre-apoptotic complex of pro-caspase-3, Hsp60 and Hsp10 in the mitochondrial fraction of jurkat cells. EMBO J. 18:2040–2048 10.1093/emboj/18.8.2040 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherz-Shouval R., Shvets E., Fass E., Shorer H., Gil L., Elazar Z. 2007. Reactive oxygen species are essential for autophagy and specifically regulate the activity of Atg4. EMBO J. 26:1749–1760 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601623 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R.C., Schuldiner O., Neufeld T.P. 2004. Role and regulation of starvation-induced autophagy in the Drosophila fat body. Dev. Cell. 7:167–178 10.1016/j.devcel.2004.07.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R.C., Juhász G., Neufeld T.P. 2007. Direct induction of autophagy by Atg1 inhibits cell growth and induces apoptotic cell death. Curr. Biol. 17:1–11 10.1016/j.cub.2006.10.053 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setoguchi K., Otera H., Mihara K. 2006. Cytosolic factor- and TOM-independent import of C-tail-anchored mitochondrial outer membrane proteins. EMBO J. 25:5635–5647 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601438 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M., Hicks S., Baker K., McCauley R. 1994. Rupture of the mitochondrial outer membrane impairs porin assembly. J. Biol. Chem. 269:28460–28464 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song Z., McCall K., Steller H. 1997. DCP-1, a Drosophila cell death protease essential for development. Science. 275:536–540 10.1126/science.275.5299.536 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song Z., Guan B., Bergman A., Nicholson D.W., Thornberry N.A., Peterson E.P., Steller H. 2000. Biochemical and genetic interactions between Drosophila caspases and the proapoptotic genes rpr, hid, and grim. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20:2907–2914 10.1128/MCB.20.8.2907-2914.2000 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sordet O., Rébé C., Plenchette S., Zermati Y., Hermine O., Vainchenker W., Garrido C., Solary E., Dubrez-Daloz L. 2002. Specific involvement of caspases in the differentiation of monocytes into macrophages. Blood. 100:4446–4453 10.1182/blood-2002-06-1778 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Susin S.A., Lorenzo H.K., Zamzami N., Marzo I., Brenner C., Larochette N., Prévost M.-C., Alzari P.M., Kroemer G. 1999. Mitochondrial release of caspase-2 and -9 during the apoptotic process. J. Exp. Med. 189:381–394 10.1084/jem.189.2.381 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner E.A., Blute T.A., Brachmann C.B., McCall K. 2011. Bcl-2 proteins and autophagy regulate mitochondrial dynamics during programmed cell death in the Drosophila ovary. Development. 138:327–338 10.1242/dev.057943 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenev T., Zachariou A., Wilson R., Ditzel M., Meier P. 2005. IAPs are functionally non-equivalent and regulate effector caspases through distinct mechanisms. Nat. Cell Biol. 7:70–77 10.1038/ncb1204 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terhzaz S., Cabrero P., Chintapalli V.R., Davies S.-A., Dow J.A.T. 2010. Mislocalization of mitochondria and compromised renal function and oxidative stress resistance in Drosophila SesB mutants. Physiol. Genomics. 41:33–41 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00147.2009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tettamanti G., Malagoli D., Marchesini E., Congiu T., de Eguileor M., Ottaviani E. 2006. Oligomycin A induces autophagy in the IPLB-LdFB insect cell line. Cell Tissue Res. 326:179–186 10.1007/s00441-006-0206-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirawan E., Vande Walle L., Kersse K., Cornelis S., Claerhout S., Vanoverberghe I., Roelandt R., De Rycke R., Verspurten J., Declercq W., et al. 2010. Caspase-mediated cleavage of Beclin-1 inactivates Beclin-1-induced autophagy and enhances apoptosis by promoting the release of proapoptotic factors from mitochondria. Cell Death Dis. 1:e18 10.1038/cddis.2009.16 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong E., Cuervo A.M. 2010. Autophagy gone awry in neurodegenerative diseases. Nat. Neurosci. 13:805–811 10.1038/nn.2575 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H., Wang M.C., Bohmann D. 2009. JNK protects Drosophila from oxidative stress by transcriptionally activating autophagy. Mech. Dev. 126:624–637 10.1016/j.mod.2009.06.1082 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yousefi S., Perozzo R., Schmid I., Ziemiecki A., Schaffner T., Scapozza L., Brunner T., Simon H.-U. 2006. Calpain-mediated cleavage of Atg5 switches autophagy to apoptosis. Nat. Cell Biol. 8:1124–1132 10.1038/ncb1482 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu Y., Zhao L., Liu L., Gao P., Tian W., Wang X., Jin H., Xu H., Chen Q. 2010. Beclin 1 cleavage by caspase-3 inactivates autophagy and promotes apoptosis. Protein Cell. 1:468–477 10.1007/s13238-010-0048-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.