Abstract
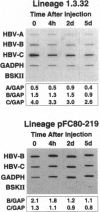
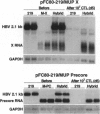
Using transgenic mice that replicate the hepatitis B virus (HBV) genome, we recently demonstrated that class I-restricted, hepatitis B surface antigen-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) can noncytolytically eliminate HBV pregenomic and envelope RNA transcripts from the hepatocyte. We now demonstrate that the steady-state content of these viral transcripts is profoundly reduced in the nucleus and cytoplasm of CTL-activated hepatocytes, but their transcription rates are only slightly reduced. Additionally, we demonstrate that transcripts covering the HBV X coding region are resistant to downregulation by the CTL. These results imply the existence of CTL-inducible hepatocellular factors that interact with a discrete element(s) between nucleotides 3157 and 1239 within the viral pregenomic and envelope transcripts and mediate their degradation, thus converting the hepatocyte from a passive victim to an active participant in the host response to HBV infection.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ando K., Moriyama T., Guidotti L. G., Wirth S., Schreiber R. D., Schlicht H. J., Huang S. N., Chisari F. V. Mechanisms of class I restricted immunopathology. A transgenic mouse model of fulminant hepatitis. J Exp Med. 1993 Nov 1;178(5):1541–1554. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.5.1541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohjanen P. R., Petryniak B., June C. H., Thompson C. B., Lindsten T. AU RNA-binding factors differ in their binding specificities and affinities. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):6302–6309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohjanen P. R., Petryniak B., June C. H., Thompson C. B., Lindsten T. An inducible cytoplasmic factor (AU-B) binds selectively to AUUUA multimers in the 3' untranslated region of lymphokine mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3288–3295. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caput D., Beutler B., Hartog K., Thayer R., Brown-Shimer S., Cerami A. Identification of a common nucleotide sequence in the 3'-untranslated region of mRNA molecules specifying inflammatory mediators. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1670–1674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisari F. V., Ferrari C. Hepatitis B virus immunopathogenesis. Annu Rev Immunol. 1995;13:29–60. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.13.040195.000333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilles P. N., Fey G., Chisari F. V. Tumor necrosis factor alpha negatively regulates hepatitis B virus gene expression in transgenic mice. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3955–3960. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3955-3960.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis P., Malter J. S. The adenosine-uridine binding factor recognizes the AU-rich elements of cytokine, lymphokine, and oncogene mRNAs. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):3172–3177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti L. G., Ando K., Hobbs M. V., Ishikawa T., Runkel L., Schreiber R. D., Chisari F. V. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes inhibit hepatitis B virus gene expression by a noncytolytic mechanism in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):3764–3768. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.3764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti L. G., Guilhot S., Chisari F. V. Interleukin-2 and alpha/beta interferon down-regulate hepatitis B virus gene expression in vivo by tumor necrosis factor-dependent and -independent pathways. J Virol. 1994 Mar;68(3):1265–1270. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.3.1265-1270.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti L. G., Matzke B., Schaller H., Chisari F. V. High-level hepatitis B virus replication in transgenic mice. J Virol. 1995 Oct;69(10):6158–6169. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.10.6158-6169.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilhot S., Guidotti L. G., Chisari F. V. Interleukin-2 downregulates hepatitis B virus gene expression in transgenic mice by a posttranscriptional mechanism. J Virol. 1993 Dec;67(12):7444–7449. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.12.7444-7449.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamasaki K., Nakata K., Nakao K., Mitsuoka S., Tsutsumi T., Kato Y., Shima M., Ishii N., Tamaoki T., Nagataki S. Interaction of interferon-alpha with interleukin-1 beta or tumor necrosis factor-alpha on hepatitis B virus enhancer activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Mar 16;183(2):904–909. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)90569-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi Y., Koike K. Interferon inhibits hepatitis B virus replication in a stable expression system of transfected viral DNA. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):2936–2940. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.2936-2940.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs M. V., Weigle W. O., Noonan D. J., Torbett B. E., McEvilly R. J., Koch R. J., Cardenas G. J., Ernst D. N. Patterns of cytokine gene expression by CD4+ T cells from young and old mice. J Immunol. 1993 Apr 15;150(8 Pt 1):3602–3614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J., Liang T. J. A novel hepatitis B virus (HBV) genetic element with Rev response element-like properties that is essential for expression of HBV gene products. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;13(12):7476–7486. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.12.7476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang Z. M., Yen T. S. Hepatitis B virus RNA element that facilitates accumulation of surface gene transcripts in the cytoplasm. J Virol. 1994 May;68(5):3193–3199. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.5.3193-3199.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jochum C., Voth R., Rossol S., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H., Hess G., Will H., Schröder H. C., Steffen R., Müller W. E. Immunosuppressive function of hepatitis B antigens in vitro: role of endoribonuclease V as one potential trans inactivator for cytokines in macrophages and human hepatoma cells. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):1956–1963. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.1956-1963.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karupiah G., Blanden R. V., Ramshaw I. A. Interferon gamma is involved in the recovery of athymic nude mice from recombinant vaccinia virus/interleukin 2 infection. J Exp Med. 1990 Nov 1;172(5):1495–1503. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.5.1495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn N. J., Woodworth-Gutai M., Gross K. W., Held W. A. Subfamilies of the mouse major urinary protein (MUP) multi-gene family: sequence analysis of cDNA clones and differential regulation in the liver. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 10;12(15):6073–6090. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.15.6073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann-Grube F., Assmann U., Löliger C., Moskophidis D., Löhler J. Mechanism of recovery from acute virus infection. I. Role of T lymphocytes in the clearance of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus from spleens of mice. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):608–615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann-Grube F., Moskophidis D., Löhler J. Recovery from acute virus infection. Role of cytotoxic T lymphocytes in the elimination of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus from spleens of mice. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;532:238–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb36343.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malter J. S. Identification of an AUUUA-specific messenger RNA binding protein. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):664–666. doi: 10.1126/science.2814487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestan J., Digel W., Mittnacht S., Hillen H., Blohm D., Möller A., Jacobsen H., Kirchner H. Antiviral effects of recombinant tumour necrosis factor in vitro. 1986 Oct 30-Nov 5Nature. 323(6091):816–819. doi: 10.1038/323816a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriyama T., Guilhot S., Klopchin K., Moss B., Pinkert C. A., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L., Kanagawa O., Chisari F. V. Immunobiology and pathogenesis of hepatocellular injury in hepatitis B virus transgenic mice. Science. 1990 Apr 20;248(4953):361–364. doi: 10.1126/science.1691527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller W. E., Slor H., Pfeifer K., Hühn P., Bek A., Orsulic S., Ushijima H., Schröder H. C. Association of AUUUA-binding protein with A+U-rich mRNA during nucleo-cytoplasmic transport. J Mol Biol. 1992 Aug 5;226(3):721–733. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90628-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raj N. B., Pitha P. M. 65-kDa protein binds to destabilizing sequences in the IFN-beta mRNA coding and 3' UTR. FASEB J. 1993 May;7(8):702–710. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.8.8500695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standring D. N., Rutter W. J., Varmus H. E., Ganem D. Transcription of the hepatitis B surface antigen gene in cultured murine cells initiates within the presurface region. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):563–571. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.563-571.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan W., Schwartz S. The Rev protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 counteracts the effect of an AU-rich negative element in the human papillomavirus type 1 late 3' untranslated region. J Virol. 1995 May;69(5):2932–2945. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.5.2932-2945.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tur-Kaspa R., Teicher L., Laub O., Itin A., Dagan D., Bloom B. R., Shafritz D. A. Alpha interferon suppresses hepatitis B virus enhancer activity and reduces viral gene transcription. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1821–1824. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1821-1824.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vakalopoulou E., Schaack J., Shenk T. A 32-kilodalton protein binds to AU-rich domains in the 3' untranslated regions of rapidly degraded mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3355–3364. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. H., Goeddel D. V. Tumour necrosis factors alpha and beta inhibit virus replication and synergize with interferons. 1986 Oct 30-Nov 5Nature. 323(6091):819–822. doi: 10.1038/323819a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]