Abstract
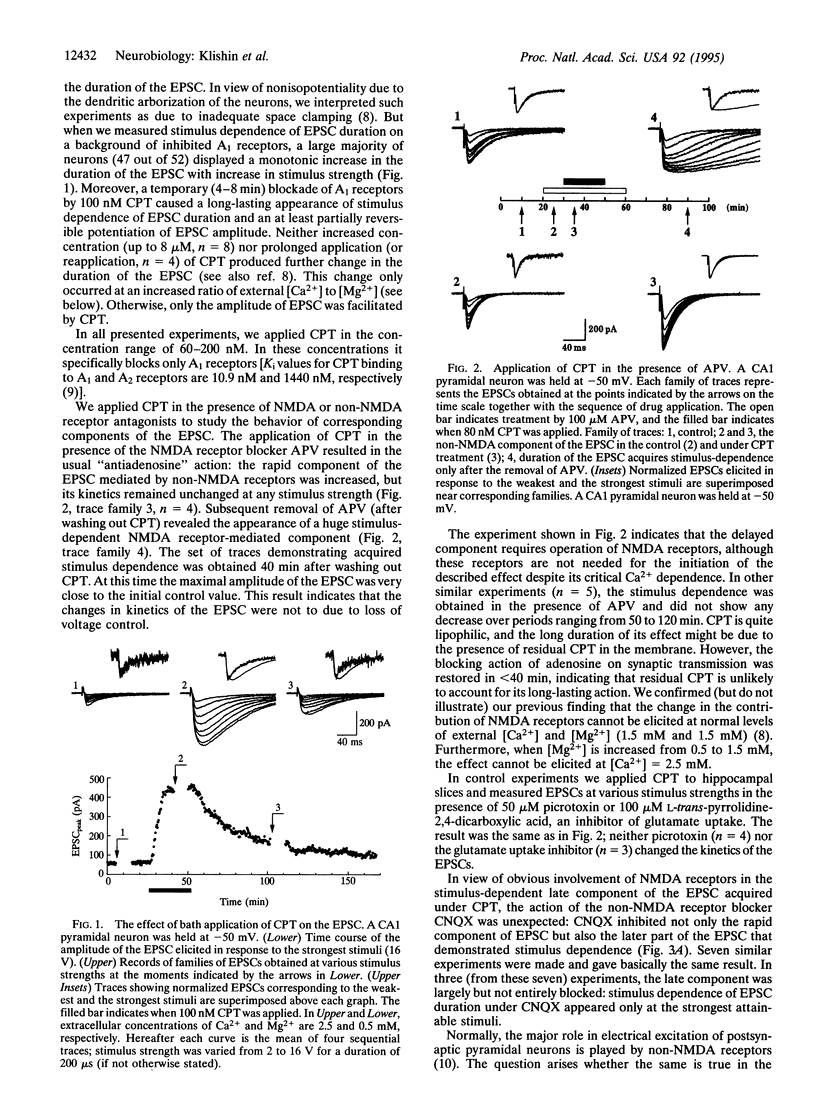
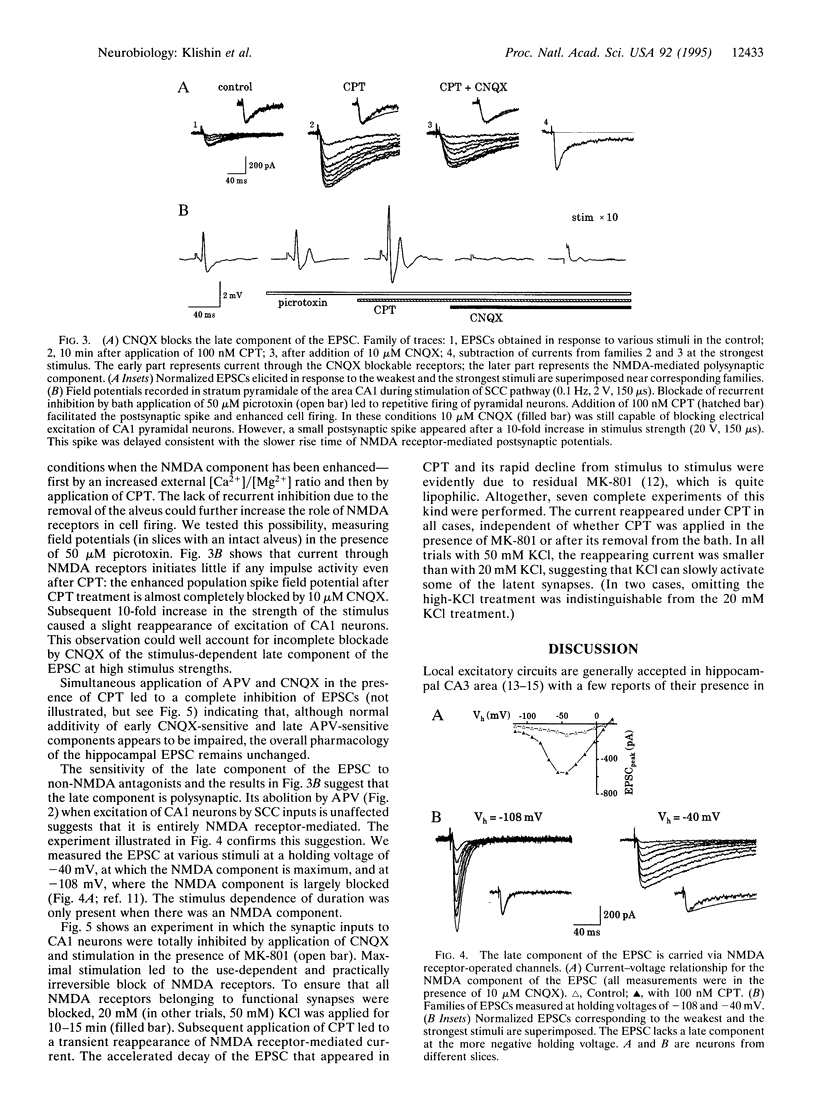
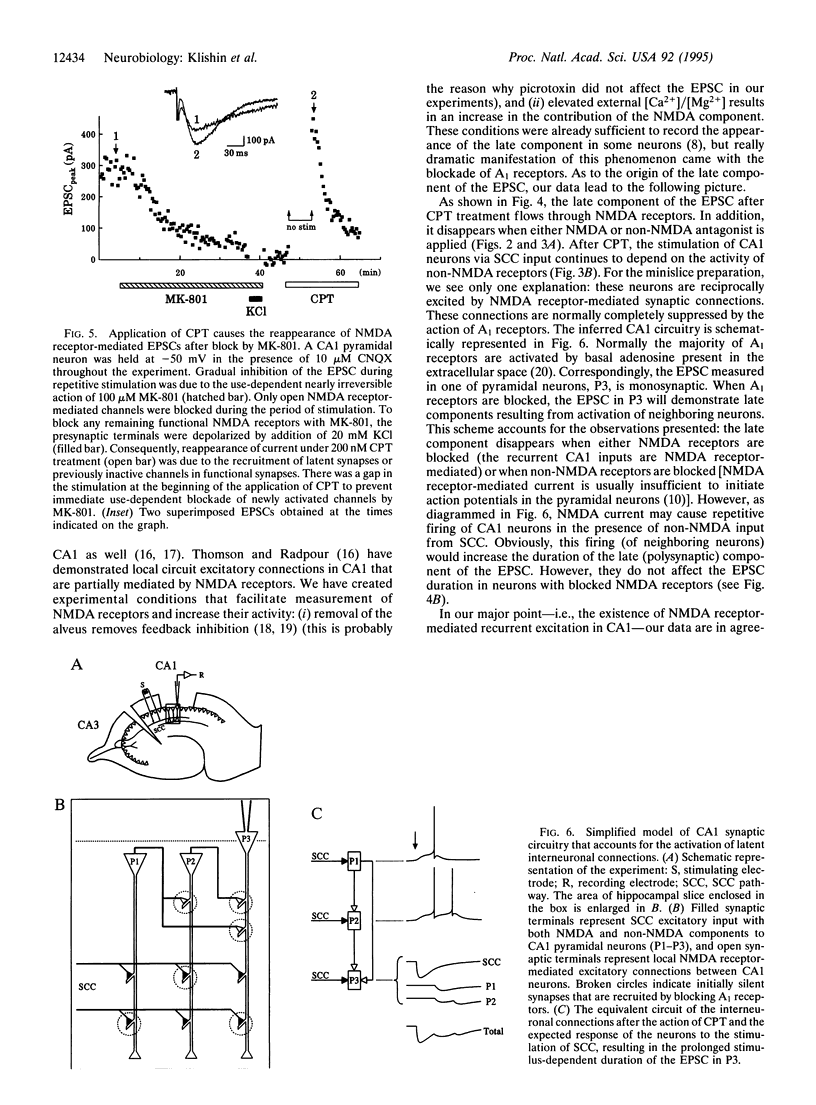
When performed at increased external [Ca2+]/[Mg2+] ratio (2.5 mM/0.5 mM), temporary block of A1 adenosine receptors in hippocampus [by 8-cyclopentyltheophylline (CPT)] leads to a dramatic and irreversible change in the excitatory postsynaptic current (EPSC) evoked by Schaffer collateral/commissural (SCC) stimulation and recorded by in situ patch clamp in CA1 pyramidal neurons. The duration of the EPSC becomes stimulus dependent, increasing with increase in stimulus strength. The later occurring component of the EPSC is carried through N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor-operated channels but disappears under either the NMDA antagonist 2-amino-5-phosphonovaleric acid (APV) or the non-NMDA antagonist 6-cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione (CNQX). These findings indicate that the late component of the SCC-evoked EPSC is polysynaptic: predominantly non-NMDA receptor-mediated SCC inputs excite CA1 neurons that recurrently excite each other by predominantly NDMA receptor-mediated synapses. These recurrent connections are normally silent but become active after CPT treatment, leading to enhancement of the late component of the EPSC. The activity of these connections is maintained for at least 2 hr after CPT removal. When all functional NMDA receptors are blocked by dizocilpine maleate (MK-801), subsequent application of CPT leads to a partial reappearance of NMDA receptor-mediated EPSCs evoked by SCC stimulation, indicating that latent NMDA receptors are recruited. Altogether, these findings indicate the existence of a powerful system of NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic contacts in SCC input to hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons and probably also in reciprocal connections between these neurons, which in the usual preparation are kept latent by activity of A1 receptors.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bekkers J. M., Stevens C. F. NMDA and non-NMDA receptors are co-localized at individual excitatory synapses in cultured rat hippocampus. Nature. 1989 Sep 21;341(6239):230–233. doi: 10.1038/341230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns R. F., Lu G. H., Pugsley T. A. Characterization of the A2 adenosine receptor labeled by [3H]NECA in rat striatal membranes. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Apr;29(4):331–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christian E. P., Dudek F. E. Electrophysiological evidence from glutamate microapplications for local excitatory circuits in the CA1 area of rat hippocampal slices. J Neurophysiol. 1988 Jan;59(1):110–123. doi: 10.1152/jn.1988.59.1.110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collingridge G. L., Herron C. E., Lester R. A. Synaptic activation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in the Schaffer collateral-commissural pathway of rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1988 May;399:283–300. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crépel V., Hammond C., Chinestra P., Diabira D., Ben-Ari Y. A selective LTP of NMDA receptor-mediated currents induced by anoxia in CA1 hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1993 Nov;70(5):2045–2055. doi: 10.1152/jn.1993.70.5.2045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunwiddie T. V., Hoffer B. J. Adenine nucleotides and synaptic transmission in the in vitro rat hippocampus. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 May;69(1):59–68. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb10883.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilers J., Augustine G. J., Konnerth A. Subthreshold synaptic Ca2+ signalling in fine dendrites and spines of cerebellar Purkinje neurons. Nature. 1995 Jan 12;373(6510):155–158. doi: 10.1038/373155a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch D. M., Nowlin N. L., Babb T. L. Demonstration of axonal projections of neurons in the rat hippocampus and subiculum by intracellular injection of HRP. Brain Res. 1983 Jul 25;271(2):201–216. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90283-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garaschuk O., Kovalchuk Y. u., Krishtal O. Adenosine-dependent enhancement by methylxanthines of excitatory synaptic transmission in hippocampus of rats. Neurosci Lett. 1992 Jan 20;135(1):10–12. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(92)90124-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene R. W., Haas H. L. The electrophysiology of adenosine in the mammalian central nervous system. Prog Neurobiol. 1991;36(4):329–341. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(91)90005-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hestrin S., Nicoll R. A., Perkel D. J., Sah P. Analysis of excitatory synaptic action in pyramidal cells using whole-cell recording from rat hippocampal slices. J Physiol. 1990 Mar;422:203–225. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp017980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hestrin S., Sah P., Nicoll R. A. Mechanisms generating the time course of dual component excitatory synaptic currents recorded in hippocampal slices. Neuron. 1990 Sep;5(3):247–253. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90162-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klishin A., Lozovaya N., Krishtal O. Persistently enhanced ratio of NMDA and non-NMDA components of rat hippocampal EPSC after block of A1 adenosine receptors at increased [Ca2+]o/[Mg2+]o. Neurosci Lett. 1994 Sep 26;179(1-2):132–136. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(94)90952-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao D., Hessler N. A., Malinow R. Activation of postsynaptically silent synapses during pairing-induced LTP in CA1 region of hippocampal slice. Nature. 1995 Jun 1;375(6530):400–404. doi: 10.1038/375400a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacVicar B. A., Dudek F. E. Local synaptic circuits in rat hippocampus: interactions between pyramidal cells. Brain Res. 1980 Feb 17;184(1):220–223. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90602-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles R., Wong R. K. Latent synaptic pathways revealed after tetanic stimulation in the hippocampus. Nature. 1987 Oct 22;329(6141):724–726. doi: 10.1038/329724a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak L., Bregestovski P., Ascher P., Herbet A., Prochiantz A. Magnesium gates glutamate-activated channels in mouse central neurones. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):462–465. doi: 10.1038/307462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proctor W. R., Dunwiddie T. V. Pre- and postsynaptic actions of adenosine in the in vitro rat hippocampus. Brain Res. 1987 Nov 17;426(1):187–190. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90441-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radpour S., Thomson A. M. Coactivation of Local Circuit NMDA Receptor Mediated epsps Induces Lasting Enhancement of Minimal Schaffer Collateral epsps in Slices of Rat Hippocampus. Eur J Neurosci. 1991;3(6):602–613. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1991.tb00846.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert P., Mitzdorf U. Analysis and quantitative evaluation of the depressive effect of adenosine on evoked potentials in hippocampal slices. Brain Res. 1979 Aug 17;172(1):186–190. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90910-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. M., Haas H. L., Gähwiler B. H. Comparison of the actions of adenosine at pre- and postsynaptic receptors in the rat hippocampus in vitro. J Physiol. 1992;451:347–363. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson A. M., Radpour S. Excitatory Connections Between CA1 Pyramidal Cells Revealed by Spike Triggered Averaging in Slices of Rat Hippocampus are Partially NMDA Receptor Mediated. Eur J Neurosci. 1991;3(6):587–601. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1991.tb00845.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zetterström T., Vernet L., Ungerstedt U., Tossman U., Jonzon B., Fredholm B. B. Purine levels in the intact rat brain. Studies with an implanted perfused hollow fibre. Neurosci Lett. 1982 Apr 16;29(2):111–115. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(82)90338-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



