Abstract
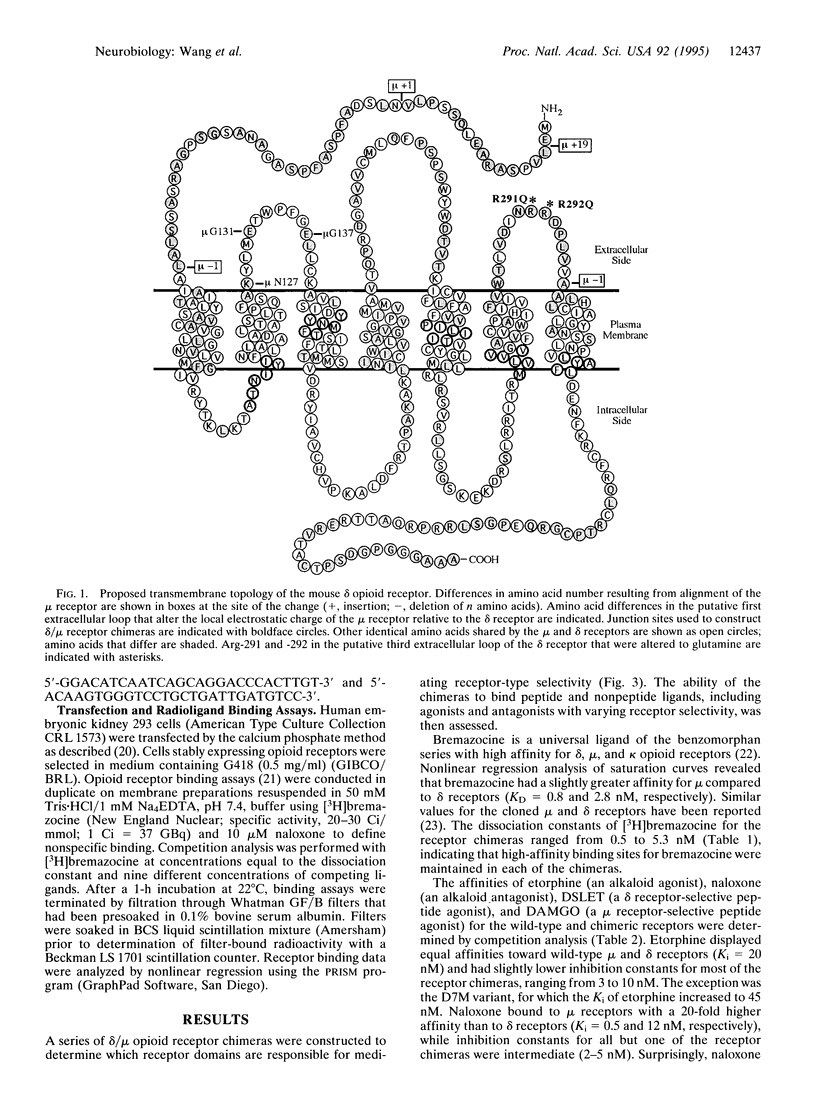
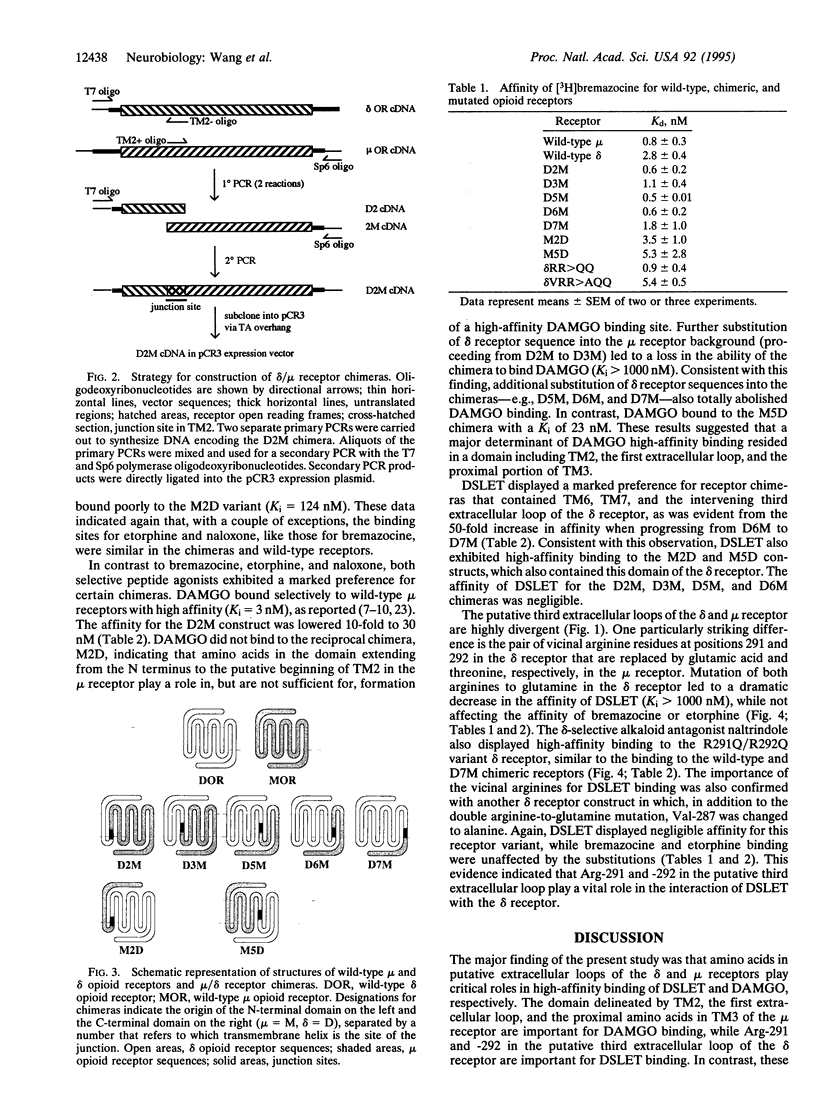
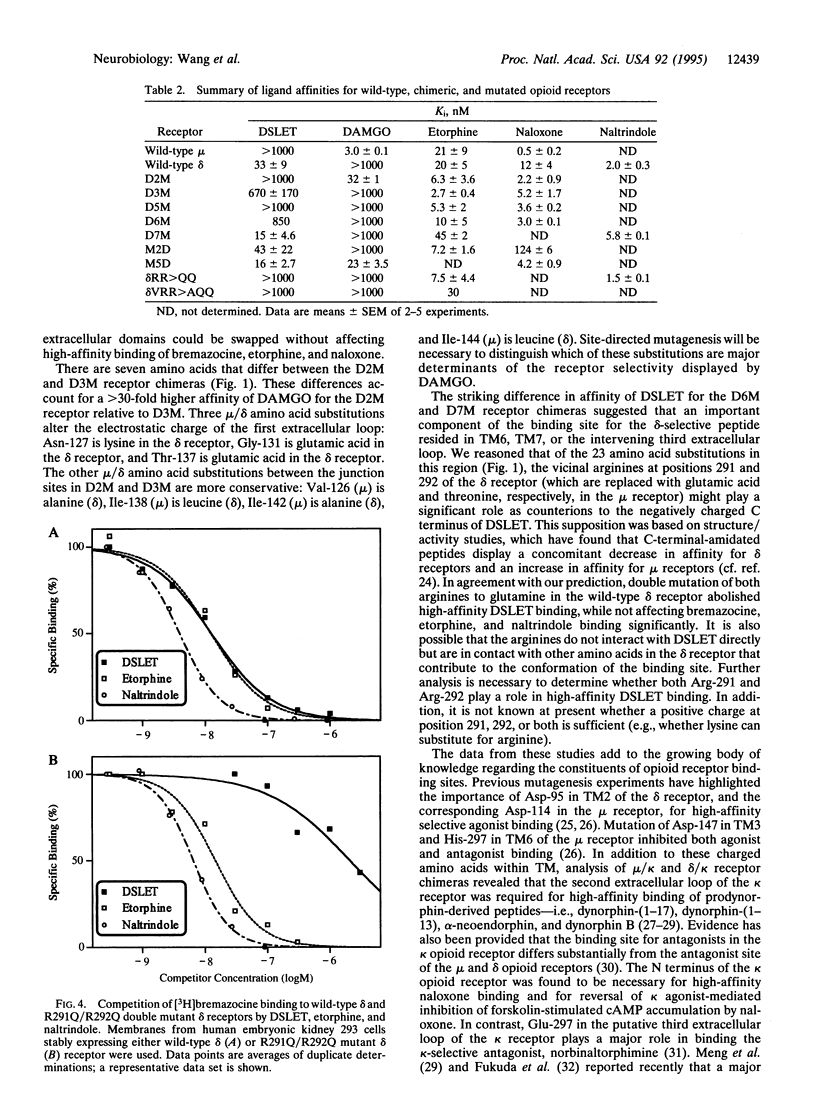
Opioid receptors are members of the guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein)-coupled receptor family. Three types of opioid receptors have been cloned and characterized and are referred to as the delta, kappa and mu types. Analysis of receptor chimeras and site-directed mutant receptors has provided a great deal of information about functionally important amino acid side chains that constitute the ligand-binding domains and G-protein-coupling domains of G-protein-coupled receptors. We have constructed delta/mu opioid receptor chimeras that were express in human embryonic kidney 293 cells in order to define receptor domains that are responsible for receptor type selectivity. All chimeric receptors and wild-type delta and mu opioid receptors displayed high-affinity binding of etorphine (an agonist), naloxone (an antagonist), and bremazocine (a mixed agonist/antagonist). In contrast, chimeras that lacked the putative first extracellular loop of the mu receptor did not bind the mu-selective peptide [D-Ala2,MePhe4,Gly5-ol]enkephalin (DAMGO). Chimeras that lacked the putative third extracellular loop of the delta receptor did not bind the delta-selective peptide, [D-Ser2,D-Leu5]enkephalin-Thr (DSLET). Point mutations in the putative third extracellular loop of the wild-type delta receptor that converted vicinal arginine residues to glutamine abolished DSLET binding while not affecting bremazocine, etorphine, and naltrindole binding. We conclude that amino acids in the putative first extracellular loop of the mu receptor are critical for high-affinity DAMGO binding and that arginine residues in the putative third extracellular loop of the delta receptor are important for high-affinity DSLET binding.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abood M. E., Noel M. A., Farnsworth J. S., Tao Q. Molecular cloning and expression of a delta-opioid receptor from rat brain. J Neurosci Res. 1994 Apr 15;37(6):714–719. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490370605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter B. D., Medzihradsky F. Go mediates the coupling of the mu opioid receptor to adenylyl cyclase in cloned neural cells and brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):4062–4066. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.4062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y., Mestek A., Liu J., Hurley J. A., Yu L. Molecular cloning and functional expression of a mu-opioid receptor from rat brain. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Jul;44(1):8–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans C. J., Keith D. E., Jr, Morrison H., Magendzo K., Edwards R. H. Cloning of a delta opioid receptor by functional expression. Science. 1992 Dec 18;258(5090):1952–1955. doi: 10.1126/science.1335167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda K., Kato S., Mori K. Location of regions of the opioid receptor involved in selective agonist binding. J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 24;270(12):6702–6709. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.12.6702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda K., Kato S., Mori K., Nishi M., Takeshima H. Primary structures and expression from cDNAs of rat opioid receptor delta- and mu-subtypes. FEBS Lett. 1993 Aug 2;327(3):311–314. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81011-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjorth S. A., Thirstrup K., Grandy D. K., Schwartz T. W. Analysis of selective binding epitopes for the kappa-opioid receptor antagonist nor-binaltorphimine. Mol Pharmacol. 1995 Jun;47(6):1089–1094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howells R. D., Gioannini T. L., Hiller J. M., Simon E. J. Solubilization and characterization of active opiate binding sites from mammalian brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Sep;222(3):629–634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieffer B. L., Befort K., Gaveriaux-Ruff C., Hirth C. G. The delta-opioid receptor: isolation of a cDNA by expression cloning and pharmacological characterization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):12048–12052. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.12048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kong H., Raynor K., Yano H., Takeda J., Bell G. I., Reisine T. Agonists and antagonists bind to different domains of the cloned kappa opioid receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 16;91(17):8042–8046. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.17.8042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kong H., Raynor K., Yasuda K., Moe S. T., Portoghese P. S., Bell G. I., Reisine T. A single residue, aspartic acid 95, in the delta opioid receptor specifies selective high affinity agonist binding. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 5;268(31):23055–23058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laugwitz K. L., Offermanns S., Spicher K., Schultz G. mu and delta opioid receptors differentially couple to G protein subtypes in membranes of human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells. Neuron. 1993 Feb;10(2):233–242. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90314-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meng F., Hoversten M. T., Thompson R. C., Taylor L., Watson S. J., Akil H. A chimeric study of the molecular basis of affinity and selectivity of the kappa and the delta opioid receptors. Potential role of extracellular domains. J Biol Chem. 1995 May 26;270(21):12730–12736. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.21.12730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meng F., Xie G. X., Thompson R. C., Mansour A., Goldstein A., Watson S. J., Akil H. Cloning and pharmacological characterization of a rat kappa opioid receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):9954–9958. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.9954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minami M., Onogi T., Nakagawa T., Katao Y., Aoki Y., Katsumata S., Satoh M. DAMGO, a mu-opioid receptor selective ligand, distinguishes between mu-and kappa-opioid receptors at a different region from that for the distinction between mu- and delta-opioid receptors. FEBS Lett. 1995 May 1;364(1):23–27. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)00340-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onogi T., Minami M., Katao Y., Nakagawa T., Aoki Y., Toya T., Katsumata S., Satoh M. DAMGO, a mu-opioid receptor selective agonist, distinguishes between mu- and delta-opioid receptors around their first extracellular loops. FEBS Lett. 1995 Jan 2;357(1):93–97. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)01341-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prather P. L., McGinn T. M., Erickson L. J., Evans C. J., Loh H. H., Law P. Y. Ability of delta-opioid receptors to interact with multiple G-proteins is independent of receptor density. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 19;269(33):21293–21302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raynor K., Kong H., Chen Y., Yasuda K., Yu L., Bell G. I., Reisine T. Pharmacological characterization of the cloned kappa-, delta-, and mu-opioid receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Feb;45(2):330–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisine T., Bell G. I. Molecular biology of opioid receptors. Trends Neurosci. 1993 Dec;16(12):506–510. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(93)90194-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Römer D., Büscher H., Hill R. C., Maurer R., Petcher T. J., Welle H. B., Bakel H. C., Akkerman A. M. Bremazocine: a potent, long-acting opiate kappa-agonist. Life Sci. 1980 Sep 15;27(11):971–978. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90107-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiller P. W., Nguyen T. M., Weltrowska G., Wilkes B. C., Marsden B. J., Lemieux C., Chung N. N. Differential stereochemical requirements of mu vs. delta opioid receptors for ligand binding and signal transduction: development of a class of potent and highly delta-selective peptide antagonists. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):11871–11875. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.11871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strader C. D., Fong T. M., Tota M. R., Underwood D., Dixon R. A. Structure and function of G protein-coupled receptors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:101–132. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.63.070194.000533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surratt C. K., Johnson P. S., Moriwaki A., Seidleck B. K., Blaschak C. J., Wang J. B., Uhl G. R. -mu opiate receptor. Charged transmembrane domain amino acids are critical for agonist recognition and intrinsic activity. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 12;269(32):20548–20553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. C., Mansour A., Akil H., Watson S. J. Cloning and pharmacological characterization of a rat mu opioid receptor. Neuron. 1993 Nov;11(5):903–913. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90120-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. B., Imai Y., Eppler C. M., Gregor P., Spivak C. E., Uhl G. R. mu opiate receptor: cDNA cloning and expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):10230–10234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.10230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. B., Johnson P. S., Wu J. M., Wang W. F., Uhl G. R. Human kappa opiate receptor second extracellular loop elevates dynorphin's affinity for human mu/kappa chimeras. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 21;269(42):25966–25969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W. W., Howells R. D. Sequence of the 5'-flanking region of the rat c-fos proto-oncogene. Gene. 1994 Jun 10;143(2):261–264. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90107-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xue J. C., Chen C., Zhu J., Kunapuli S. P., de Riel J. K., Yu L., Liu-Chen L. Y. The third extracellular loop of the mu opioid receptor is important for agonist selectivity. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jun 2;270(22):12977–12979. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xue J. C., Chen C., Zhu J., Kunapuli S., DeRiel J. K., Yu L., Liu-Chen L. Y. Differential binding domains of peptide and non-peptide ligands in the cloned rat kappa opioid receptor. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 2;269(48):30195–30199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasuda K., Raynor K., Kong H., Breder C. D., Takeda J., Reisine T., Bell G. I. Cloning and functional comparison of kappa and delta opioid receptors from mouse brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6736–6740. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]