Abstract
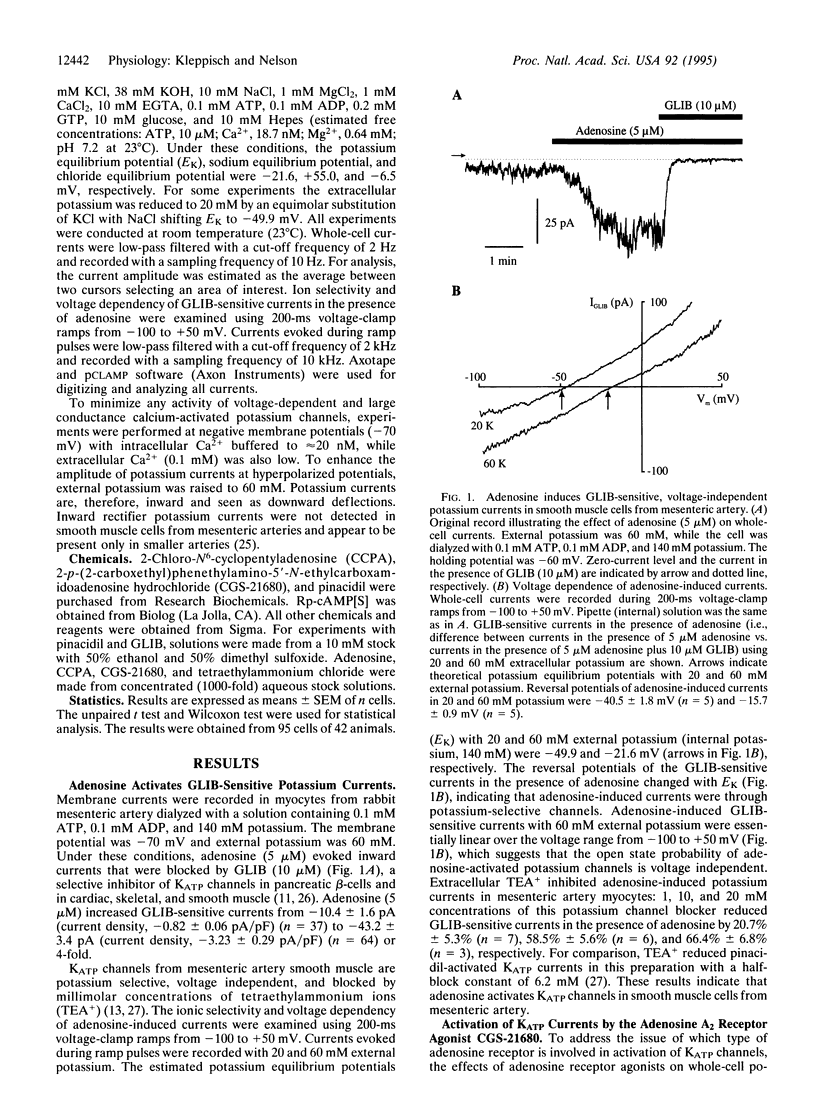
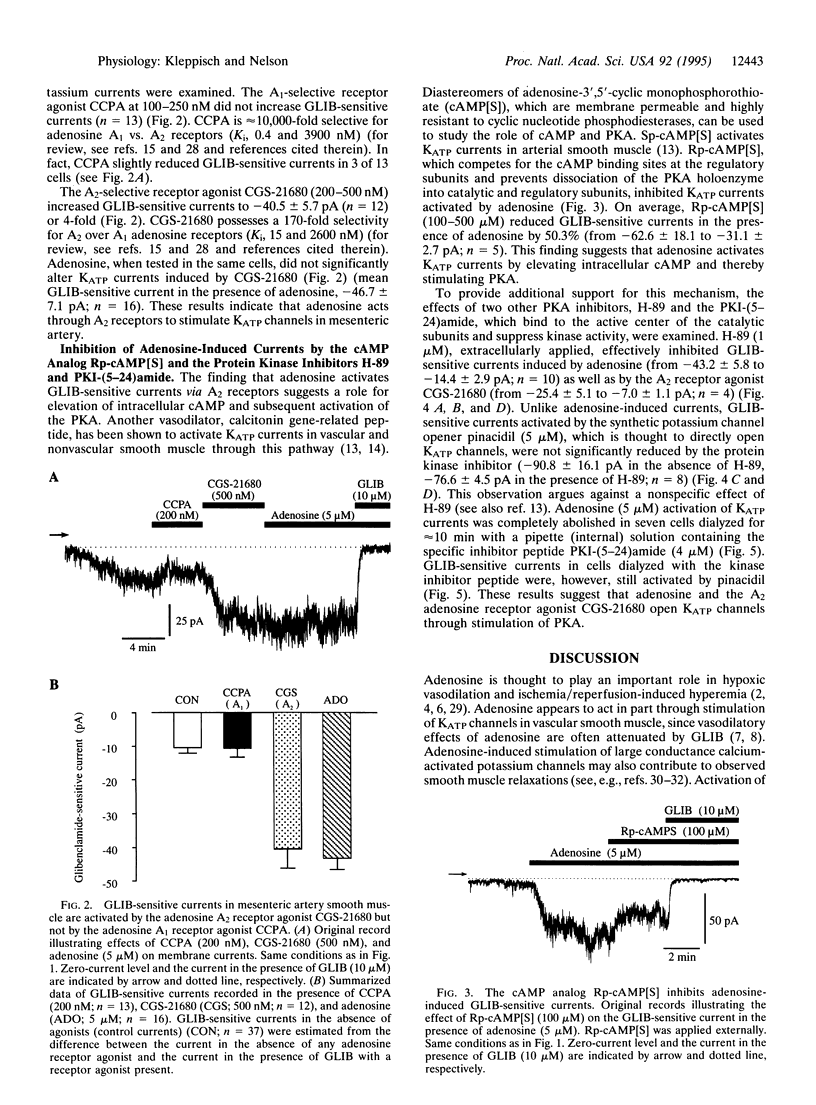
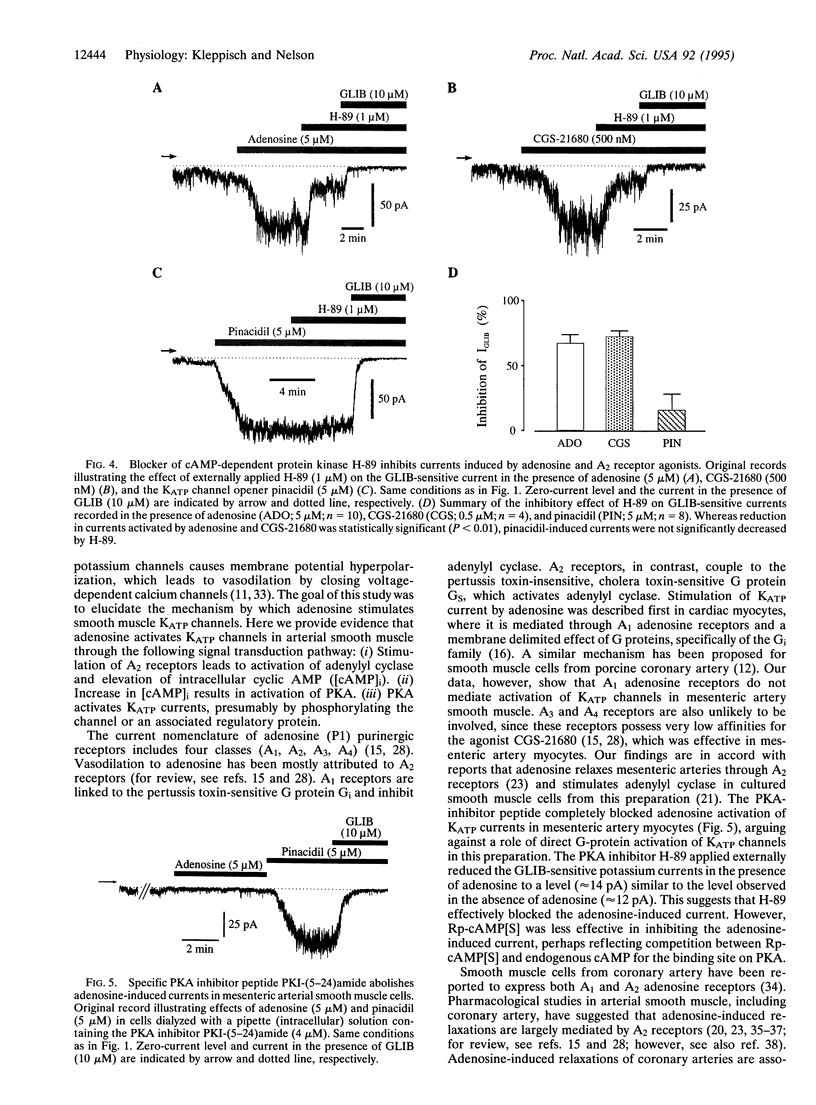
The mechanism by which the endogenous vasodilator adenosine causes ATP-sensitive potassium (KATP) channels in arterial smooth muscle to open was investigated by the whole-cell patch-clamp technique. Adenosine induced voltage-independent, potassium-selective currents, which were inhibited by glibenclamide, a blocker of KATP currents. Glibenclamide-sensitive currents were also activated by the selective adenosine A2-receptor agonist 2-p-(2-carboxethyl)-phenethylamino-5'-N- ethylcarboxamidoadenosine hydrochloride (CGS-21680), whereas 2-chloro-N6-cyclopentyladenosine (CCPA), a selective adenosine A1-receptor agonist, failed to induce potassium currents. Glibenclamide-sensitive currents induced by adenosine and CGS-21680 were largely reduced by blockers of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase (Rp-cAMP[S], H-89, protein kinase A inhibitor peptide). Therefore, we conclude that adenosine can activate KATP currents in arterial smooth muscle through the following pathway: (i) Adenosine stimulates A2 receptors, which activates adenylyl cyclase; (ii) the resulting increase intracellular cAMP stimulates protein kinase A, which, probably through a phosphorylation step, opens KATP channels.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abebe W., Makujina S. R., Mustafa S. J. Adenosine receptor-mediated relaxation of porcine coronary artery in presence and absence of endothelium. Am J Physiol. 1994 May;266(5 Pt 2):H2018–H2025. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1994.266.5.H2018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anand-Srivastava M. B., Franks D. J. Stimulation of adenylate cyclase by adenosine and other agonists in mesenteric artery smooth muscle cells in culture. Life Sci. 1985 Sep 2;37(9):857–867. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(85)90521-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashcroft S. J., Ashcroft F. M. Properties and functions of ATP-sensitive K-channels. Cell Signal. 1990;2(3):197–214. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(90)90048-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabell F., Weiss D. S., Price J. M. Inhibition of adenosine-induced coronary vasodilation by block of large-conductance Ca(2+)-activated K+ channels. Am J Physiol. 1994 Oct;267(4 Pt 2):H1455–H1460. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1994.267.4.H1455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collis M. G., Brown C. M. Adenosine relaxes the aorta by interacting with an A2 receptor and an intracellular site. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Dec 9;96(1-2):61–69. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90529-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushing D. J., Brown G. L., Sabouni M. H., Mustafa S. J. Adenosine receptor-mediated coronary artery relaxation and cyclic nucleotide production. Am J Physiol. 1991 Aug;261(2 Pt 2):H343–H348. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1991.261.2.H343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dart C., Standen N. B. Adenosine-activated potassium current in smooth muscle cells isolated from the pig coronary artery. J Physiol. 1993 Nov;471:767–786. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daut J., Standen N. B., Nelson M. T. The role of the membrane potential of endothelial and smooth muscle cells in the regulation of coronary blood flow. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 1994 Feb;5(2):154–181. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8167.1994.tb01156.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edvinsson L., Fredholm B. B. Characterization of adenosine receptors in isolated cerebral arteries of cat. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Dec;80(4):631–637. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10052.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards R. M., Stack E. J., Trizna W. Calcitonin gene-related peptide stimulates adenylate cyclase and relaxes intracerebral arterioles. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Jun;257(3):1020–1024. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feigl E. O. Coronary physiology. Physiol Rev. 1983 Jan;63(1):1–205. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1983.63.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa S., Satoh K., Taira N. Opening of ATP-sensitive K+ channels responsible for adenosine A2 receptor-mediated vasodepression does not involve a pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 May 19;236(2):255–262. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90596-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidday J. M., Park T. S. Adenosine-mediated autoregulation of retinal arteriolar tone in the piglet. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1993 Aug;34(9):2713–2719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu Z. F., Jensen R. T., Maton P. N. A primary role for protein kinase A in smooth muscle relaxation induced by adrenergic agonists and neuropeptides. Am J Physiol. 1992 Sep;263(3 Pt 1):G360–G364. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1992.263.3.G360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz F. G., Steinhausen M. Renovascular effects of adenosine receptor agonists. Ren Physiol. 1987;10(5):272–282. doi: 10.1159/000173135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson W. F. Arteriolar tone is determined by activity of ATP-sensitive potassium channels. Am J Physiol. 1993 Nov;265(5 Pt 2):H1797–H1803. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1993.265.5.H1797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson W. F., König A., Dambacher T., Busse R. Prostacyclin-induced vasodilation in rabbit heart is mediated by ATP-sensitive potassium channels. Am J Physiol. 1993 Jan;264(1 Pt 2):H238–H243. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1993.264.1.H238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson K. A., van Galen P. J., Williams M. Adenosine receptors: pharmacology, structure-activity relationships, and therapeutic potential. J Med Chem. 1992 Feb 7;35(3):407–422. doi: 10.1021/jm00081a001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch G. E., Codina J., Birnbaumer L., Brown A. M. Coupling of ATP-sensitive K+ channels to A1 receptors by G proteins in rat ventricular myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1990 Sep;259(3 Pt 2):H820–H826. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.259.3.H820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitazono T., Faraci F. M., Heistad D. D. Effect of norepinephrine on rat basilar artery in vivo. Am J Physiol. 1993 Jan;264(1 Pt 2):H178–H182. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1993.264.1.H178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kume H., Hall I. P., Washabau R. J., Takagi K., Kotlikoff M. I. Beta-adrenergic agonists regulate KCa channels in airway smooth muscle by cAMP-dependent and -independent mechanisms. J Clin Invest. 1994 Jan;93(1):371–379. doi: 10.1172/JCI116969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meno J. R., Ngai A. C., Ibayashi S., Winn H. R. Adenosine release and changes in pial arteriolar diameter during transient cerebral ischemia and reperfusion. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1991 Nov;11(6):986–993. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1991.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merkel L. A., Lappe R. W., Rivera L. M., Cox B. F., Perrone M. H. Demonstration of vasorelaxant activity with an A1-selective adenosine agonist in porcine coronary artery: involvement of potassium channels. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Feb;260(2):437–443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills I., Gewirtz H. Cultured vascular smooth muscle cells from porcine coronary artery possess A1 and A2 adenosine receptor activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 May 16;168(3):1297–1302. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91170-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narishige T., Egashira K., Akatsuka Y., Imamura Y., Takahashi T., Kasuya H., Takeshita A. Glibenclamide prevents coronary vasodilation induced by beta 1-adrenoceptor stimulation in dogs. Am J Physiol. 1994 Jan;266(1 Pt 2):H84–H92. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1994.266.1.H84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M. T., Huang Y., Brayden J. E., Hescheler J., Standen N. B. Arterial dilations in response to calcitonin gene-related peptide involve activation of K+ channels. Nature. 1990 Apr 19;344(6268):770–773. doi: 10.1038/344770a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M. T., Patlak J. B., Worley J. F., Standen N. B. Calcium channels, potassium channels, and voltage dependence of arterial smooth muscle tone. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jul;259(1 Pt 1):C3–18. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.259.1.C3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M. T., Quayle J. M. Physiological roles and properties of potassium channels in arterial smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1995 Apr;268(4 Pt 1):C799–C822. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1995.268.4.C799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parfenova H., Hsu P., Leffler C. W. Dilator prostanoid-induced cyclic AMP formation and release by cerebral microvascular smooth muscle cells: inhibition by indomethacin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1995 Jan;272(1):44–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park K. H., Rubin L. E., Gross S. S., Levi R. Nitric oxide is a mediator of hypoxic coronary vasodilatation. Relation to adenosine and cyclooxygenase-derived metabolites. Circ Res. 1992 Oct;71(4):992–1001. doi: 10.1161/01.res.71.4.992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennanen M. F., Bass B. L., Dziki A. J., Harmon J. W. Adenosine: differential effect on blood flow to subregions of the upper gastrointestinal tract. J Surg Res. 1994 May;56(5):461–465. doi: 10.1006/jsre.1994.1073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quayle J. M., Bonev A. D., Brayden J. E., Nelson M. T. Calcitonin gene-related peptide activated ATP-sensitive K+ currents in rabbit arterial smooth muscle via protein kinase A. J Physiol. 1994 Feb 15;475(1):9–13. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quayle J. M., McCarron J. G., Brayden J. E., Nelson M. T. Inward rectifier K+ currents in smooth muscle cells from rat resistance-sized cerebral arteries. Am J Physiol. 1993 Nov;265(5 Pt 1):C1363–C1370. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.265.5.C1363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quayle J. M., Standen N. B. KATP channels in vascular smooth muscle. Cardiovasc Res. 1994 Jun;28(6):797–804. doi: 10.1093/cvr/28.6.797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabouni M. H., Cushing D. J., Mustafa S. J. Adenosine receptor-mediated relaxation in coronary artery: evidence for a guanyl nucleotide-binding regulatory protein involvement. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Dec;251(3):943–948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawmiller D. R., Linden J., Berne R. M. Effects of xanthine amine congener on hypoxic coronary resistance and venous and epicardial adenosine concentrations. Cardiovasc Res. 1994 May;28(5):604–609. doi: 10.1093/cvr/28.5.604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scornik F. S., Codina J., Birnbaumer L., Toro L. Modulation of coronary smooth muscle KCa channels by Gs alpha independent of phosphorylation by protein kinase A. Am J Physiol. 1993 Oct;265(4 Pt 2):H1460–H1465. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1993.265.4.H1460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver P. J., Walus K., DiSalvo J. Adenosine-mediated relaxation and activation of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase in coronary arterial smooth muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Feb;228(2):342–347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. E., Phillis J. W. Adenosine deaminase reduces hypoxic and hypercapnic dilatation of rat pial arterioles: evidence for mediation by adenosine. Brain Res. 1991 Jul 12;553(2):305–308. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90839-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standen N. B., Quayle J. M., Davies N. W., Brayden J. E., Huang Y., Nelson M. T. Hyperpolarizing vasodilators activate ATP-sensitive K+ channels in arterial smooth muscle. Science. 1989 Jul 14;245(4914):177–180. doi: 10.1126/science.2501869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker A. L., Linden J. Cloned receptors and cardiovascular responses to adenosine. Cardiovasc Res. 1993 Jan;27(1):62–67. doi: 10.1093/cvr/27.1.62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang L., Bonev A. D., Mawe G. M., Nelson M. T. Protein kinase A mediates activation of ATP-sensitive K+ currents by CGRP in gallbladder smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1994 Sep;267(3 Pt 1):G494–G499. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1994.267.3.G494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Beckerath N., Cyrys S., Dischner A., Daut J. Hypoxic vasodilatation in isolated, perfused guinea-pig heart: an analysis of the underlying mechanisms. J Physiol. 1991 Oct;442:297–319. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



