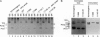Abstract
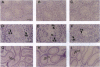
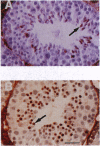
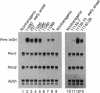
Translational control is a major form of regulating gene expression during gametogenesis and early development in many organisms. We sought to determine whether the translational repression of the protamine 1 (Prm1) mRNA is necessary for normal spermatid differentiation in mice. To accomplish this we generated transgenic animals that carry a Prm1 transgene lacking its normal 3' untranslated region. Premature translation of Prm1 mRNA caused precocious condensation of spermatid nuclear DNA, abnormal head morphogenesis, and incomplete processing of Prm2 protein. Premature accumulation of Prm1 within syncytial spermatids in mice hemizygous for the transgene caused dominant male sterility, which in some cases was accompanied by a complete arrest in spermatid differentiation. These results demonstrate that correct temporal synthesis of Prm1 is necessary for the transition from nucleohistones to nucleoprotamines.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balhorn R., Weston S., Thomas C., Wyrobek A. J. DNA packaging in mouse spermatids. Synthesis of protamine variants and four transition proteins. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Feb;150(2):298–308. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90572-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellvé A. R. Purification, culture, and fractionation of spermatogenic cells. Methods Enzymol. 1993;225:84–113. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(93)25009-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun R. E., Behringer R. R., Peschon J. J., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. Genetically haploid spermatids are phenotypically diploid. Nature. 1989 Jan 26;337(6205):373–376. doi: 10.1038/337373a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun R. E., Peschon J. J., Behringer R. R., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. Protamine 3'-untranslated sequences regulate temporal translational control and subcellular localization of growth hormone in spermatids of transgenic mice. Genes Dev. 1989 Jun;3(6):793–802. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.6.793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun R. E. Temporal translational regulation of the protamine 1 gene during mouse spermatogenesis. Enzyme. 1990;44(1-4):120–128. doi: 10.1159/000468752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinster R. L., Chen H. Y., Trumbauer M. E., Yagle M. K., Palmiter R. D. Factors affecting the efficiency of introducing foreign DNA into mice by microinjecting eggs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4438–4442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell K. A., Handel M. A. Protamine transcript sharing among postmeiotic spermatids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2407–2411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carré-Eusèbe D., Lederer F., Lê K. H., Elsevier S. M. Processing of the precursor of protamine P2 in mouse. Peptide mapping and N-terminal sequence analysis of intermediates. Biochem J. 1991 Jul 1;277(Pt 1):39–45. doi: 10.1042/bj2770039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chauvière M., Martinage A., Debarle M., Alimi E., Sautière P., Chevaillier P. Purification et caractérisation des précurseurs de la protamine mP2 de Souris. C R Acad Sci III. 1991;313(2):107–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeNoto F. M., Moore D. D., Goodman H. M. Human growth hormone DNA sequence and mRNA structure: possible alternative splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 11;9(15):3719–3730. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.15.3719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fajardo M. A., Butner K. A., Lee K., Braun R. E. Germ cell-specific proteins interact with the 3' untranslated regions of Prm-1 and Prm-2 mRNA. Dev Biol. 1994 Dec;166(2):643–653. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1994.1344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawcett D. W., Anderson W. A., Phillips D. M. Morphogenetic factors influencing the shape of the sperm head. Dev Biol. 1971 Oct;26(2):220–251. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(71)90124-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kierszenbaum A. L., Tres L. L. Structural and transcriptional features of the mouse spermatid genome. J Cell Biol. 1975 May;65(2):258–270. doi: 10.1083/jcb.65.2.258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleene K. C., Distel R. J., Hecht N. B. Translational regulation and deadenylation of a protamine mRNA during spermiogenesis in the mouse. Dev Biol. 1984 Sep;105(1):71–79. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90262-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleene K. C., Flynn J. Translation of mouse testis poly(A)+ mRNAs for testis-specific protein, protamine 1, and the precursor for protamine 2. Dev Biol. 1987 Sep;123(1):125–135. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90434-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon Y. K., Hecht N. B. Cytoplasmic protein binding to highly conserved sequences in the 3' untranslated region of mouse protamine 2 mRNA, a translationally regulated transcript of male germ cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3584–3588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loir M., Lanneau M. Structural function of the basic nuclear proteins in ram spermatids. J Ultrastruct Res. 1984 Mar;86(3):262–272. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(84)90106-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONESI V. RIBONUCLEIC ACID SYNTHESIS DURING MITOSIS AND MEIOSIS IN THE MOUSE TESTIS. J Cell Biol. 1964 Sep;22:521–532. doi: 10.1083/jcb.22.3.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay D. J., Renaux B. S., Dixon G. H. The amino acid sequence of human sperm protamine P1. Biosci Rep. 1985 May;5(5):383–391. doi: 10.1007/BF01116555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meistrich M. L., Reid B. O., Barcellona W. J. Changes sperm culei during sperimogensis and epidymal maturation. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Apr;99(1):72–78. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90681-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OAKBERG E. F. A description of spermiogenesis in the mouse and its use in analysis of the cycle of the seminiferous epithelium and germ cell renewal. Am J Anat. 1956 Nov;99(3):391–413. doi: 10.1002/aja.1000990303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panyim S., Chalkley R. High resolution acrylamide gel electrophoresis of histones. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Mar;130(1):337–346. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peschon J. J., Behringer R. R., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. Spermatid-specific expression of protamine 1 in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5316–5319. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platz R. D., Meistrich M. L., Grimes S. R., Jr Low-molecular-weight basic proteins in spermatids. Methods Cell Biol. 1977;16:297–316. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60107-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanker L. H., Wyrobek A., McKeown C., Balhorn R. Identification of the binding site of two monoclonal antibodies to human protamine. Mol Immunol. 1993 Dec;30(18):1633–1638. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(93)90436-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yelick P. C., Kwon Y. H., Flynn J. F., Borzorgzadeh A., Kleene K. C., Hecht N. B. Mouse transition protein 1 is translationally regulated during the postmeiotic stages of spermatogenesis. Mol Reprod Dev. 1989;1(3):193–200. doi: 10.1002/mrd.1080010307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambrowicz B. P., Harendza C. J., Zimmermann J. W., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. Analysis of the mouse protamine 1 promoter in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5071–5075. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]