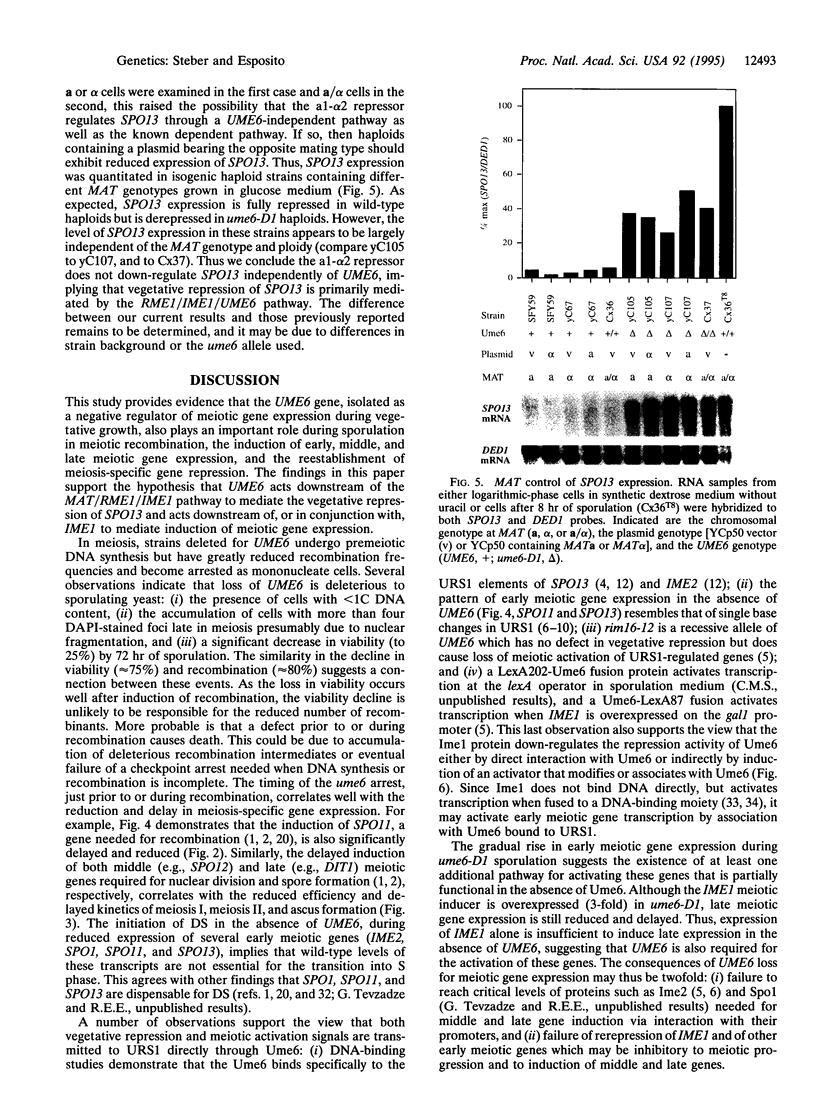
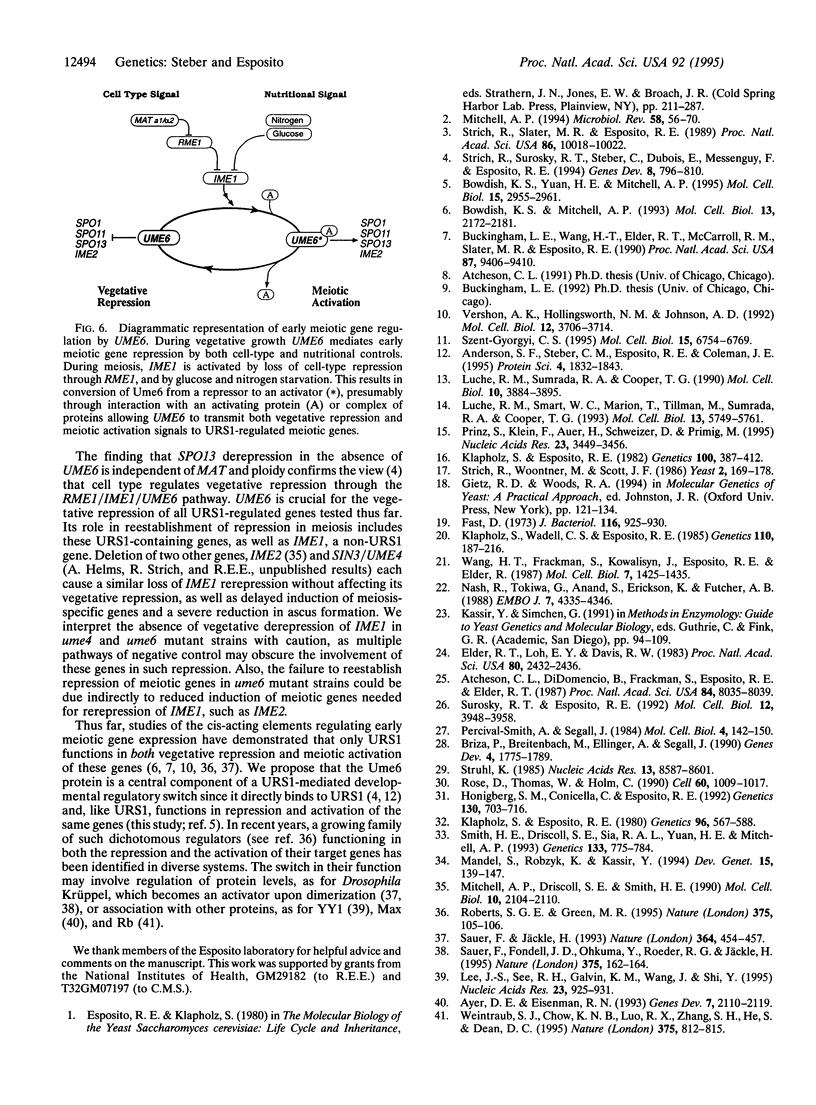
Abstract
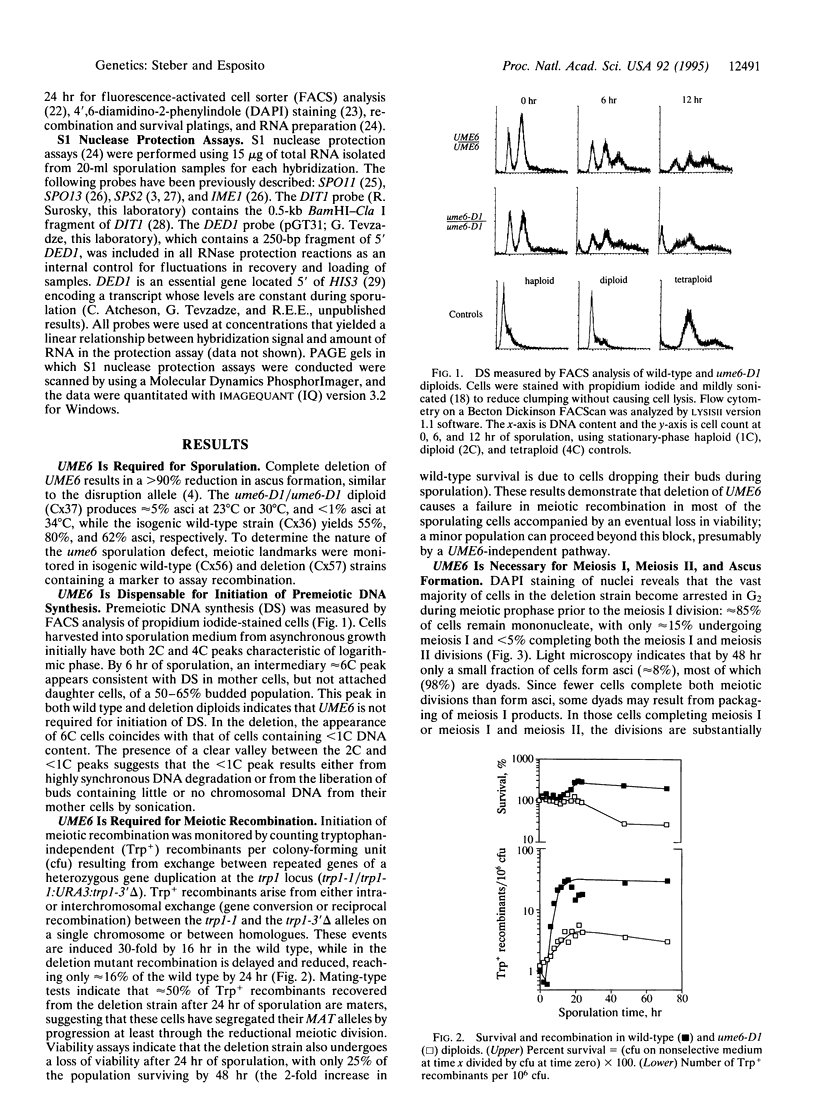
The UME6 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae was identified as a mitotic repressor of early meiosis-specific gene expression. It encodes a Zn2Cys6 DNA-binding protein which binds to URS1, a promoter element needed for both mitotic repression and meiotic induction of early meiotic genes. This paper demonstrates that a complete deletion of UME6 causes not only vegetative derepression of early meiotic genes during vegetative growth but also a significant reduction in induction of meiosis-specific genes, accompanied by a severe defect in meiotic progression. After initiating premeiotic DNA synthesis the vast majority of cells (approximately 85%) become arrested in prophase and fail to execute recombination; a minority of cells (approximately 15%) complete recombination and meiosis I, and half of these form asci. Quantitative analysis of the same early meiotic transcripts that are vegetatively derepressed in the ume6 mutant, SPO11, SPO13, IME2, and SPO1, indicates a low level of induction in meiosis above their vegetative derepressed levels. In addition, the expression of later meiotic transcripts, SPS2 and DIT1, is significantly delayed and reduced. The expression pattern of early meiotic genes in ume6-deleted cells is strikingly similar to that of early meiotic genes with promoter mutations in URS1. These results support the view that UME6 and URS1 are part of a developmental switch that controls both vegetative repression and meiotic induction of meiosis-specific genes.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S. F., Steber C. M., Esposito R. E., Coleman J. E. UME6, a negative regulator of meiosis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, contains a C-terminal Zn2Cys6 binuclear cluster that binds the URS1 DNA sequence in a zinc-dependent manner. Protein Sci. 1995 Sep;4(9):1832–1843. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560040918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atcheson C. L., DiDomenico B., Frackman S., Esposito R. E., Elder R. T. Isolation, DNA sequence, and regulation of a meiosis-specific eukaryotic recombination gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8035–8039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayer D. E., Eisenman R. N. A switch from Myc:Max to Mad:Max heterocomplexes accompanies monocyte/macrophage differentiation. Genes Dev. 1993 Nov;7(11):2110–2119. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.11.2110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowdish K. S., Mitchell A. P. Bipartite structure of an early meiotic upstream activation sequence from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2172–2181. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowdish K. S., Yuan H. E., Mitchell A. P. Positive control of yeast meiotic genes by the negative regulator UME6. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Jun;15(6):2955–2961. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.6.2955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briza P., Breitenbach M., Ellinger A., Segall J. Isolation of two developmentally regulated genes involved in spore wall maturation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1775–1789. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckingham L. E., Wang H. T., Elder R. T., McCarroll R. M., Slater M. R., Esposito R. E. Nucleotide sequence and promoter analysis of SPO13, a meiosis-specific gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9406–9410. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder R. T., Loh E. Y., Davis R. W. RNA from the yeast transposable element Ty1 has both ends in the direct repeats, a structure similar to retrovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2432–2436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fast D. Sporulation synchrony of Saccharomyces cerevisiae grown in various carbon sources. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):925–930. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.925-930.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honigberg S. M., Conicella C., Espositio R. E. Commitment to meiosis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: involvement of the SPO14 gene. Genetics. 1992 Apr;130(4):703–716. doi: 10.1093/genetics/130.4.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapholz S., Esposito R. E. A new mapping method employing a meiotic rec-mutant of yeast. Genetics. 1982 Mar;100(3):387–412. doi: 10.1093/genetics/100.3.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapholz S., Esposito R. E. Isolation of SPO12-1 and SPO13-1 from a natural variant of yeast that undergoes a single meiotic division. Genetics. 1980 Nov;96(3):567–588. doi: 10.1093/genetics/96.3.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapholz S., Waddell C. S., Esposito R. E. The role of the SPO11 gene in meiotic recombination in yeast. Genetics. 1985 Jun;110(2):187–216. doi: 10.1093/genetics/110.2.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. S., See R. H., Galvin K. M., Wang J., Shi Y. Functional interactions between YY1 and adenovirus E1A. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995 Mar 25;23(6):925–931. doi: 10.1093/nar/23.6.925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luche R. M., Smart W. C., Marion T., Tillman M., Sumrada R. A., Cooper T. G. Saccharomyces cerevisiae BUF protein binds to sequences participating in DNA replication in addition to those mediating transcriptional repression (URS1) and activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Sep;13(9):5749–5761. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.9.5749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luche R. M., Sumrada R., Cooper T. G. A cis-acting element present in multiple genes serves as a repressor protein binding site for the yeast CAR1 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):3884–3895. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.3884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel S., Robzyk K., Kassir Y. IME1 gene encodes a transcription factor which is required to induce meiosis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Dev Genet. 1994;15(2):139–147. doi: 10.1002/dvg.1020150204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell A. P. Control of meiotic gene expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Rev. 1994 Mar;58(1):56–70. doi: 10.1128/mr.58.1.56-70.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell A. P., Driscoll S. E., Smith H. E. Positive control of sporulation-specific genes by the IME1 and IME2 products in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2104–2110. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash R., Tokiwa G., Anand S., Erickson K., Futcher A. B. The WHI1+ gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae tethers cell division to cell size and is a cyclin homolog. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4335–4346. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03332.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Percival-Smith A., Segall J. Isolation of DNA sequences preferentially expressed during sporulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;4(1):142–150. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.1.142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prinz S., Klein F., Auer H., Schweizer D., Primig M. A DNA binding factor (UBF) interacts with a positive regulatory element in the promoters of genes expressed during meiosis and vegetative growth in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995 Sep 11;23(17):3449–3456. doi: 10.1093/nar/23.17.3449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts S. G., Green M. R. Transcription. Dichotomous regulators. Nature. 1995 May 11;375(6527):105–106. doi: 10.1038/375105a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose D., Thomas W., Holm C. Segregation of recombined chromosomes in meiosis I requires DNA topoisomerase II. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):1009–1017. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90349-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauer F., Fondell J. D., Ohkuma Y., Roeder R. G., Jäckle H. Control of transcription by Krüppel through interactions with TFIIB and TFIIE beta. Nature. 1995 May 11;375(6527):162–164. doi: 10.1038/375162a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauer F., Jäckle H. Dimerization and the control of transcription by Krüppel. Nature. 1993 Jul 29;364(6436):454–457. doi: 10.1038/364454a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. E., Driscoll S. E., Sia R. A., Yuan H. E., Mitchell A. P. Genetic evidence for transcriptional activation by the yeast IME1 gene product. Genetics. 1993 Apr;133(4):775–784. doi: 10.1093/genetics/133.4.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strich R., Slater M. R., Esposito R. E. Identification of negative regulatory genes that govern the expression of early meiotic genes in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):10018–10022. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.10018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strich R., Surosky R. T., Steber C., Dubois E., Messenguy F., Esposito R. E. UME6 is a key regulator of nitrogen repression and meiotic development. Genes Dev. 1994 Apr 1;8(7):796–810. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.7.796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strich R., Woontner M., Scott J. F. Mutations in ARS1 increase the rate of simple loss of plasmids in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast. 1986 Sep;2(3):169–178. doi: 10.1002/yea.320020305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Nucleotide sequence and transcriptional mapping of the yeast pet56-his3-ded1 gene region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 9;13(23):8587–8601. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.23.8587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surosky R. T., Esposito R. E. Early meiotic transcripts are highly unstable in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):3948–3958. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.3948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
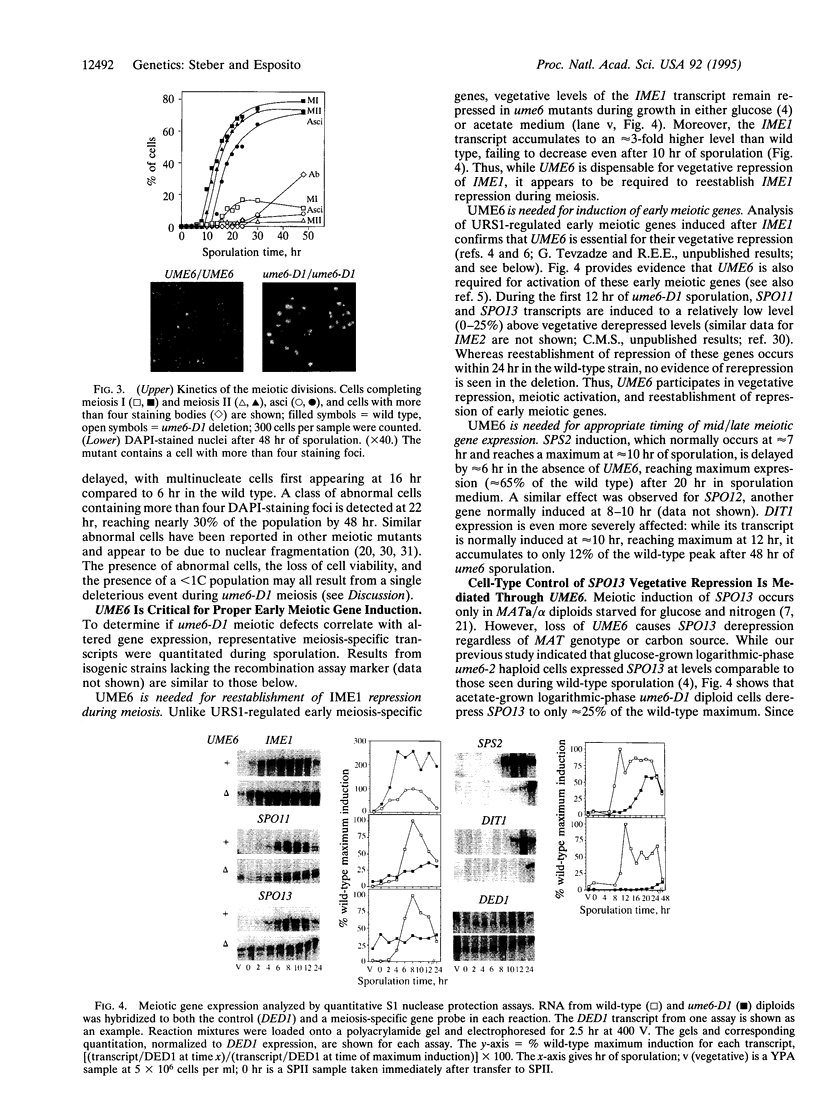
- Szent-Gyorgyi C. A bipartite operator interacts with a heat shock element to mediate early meiotic induction of Saccharomyces cerevisiae HSP82. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Dec;15(12):6754–6769. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.12.6754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vershon A. K., Hollingsworth N. M., Johnson A. D. Meiotic induction of the yeast HOP1 gene is controlled by positive and negative regulatory sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):3706–3714. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.3706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H. T., Frackman S., Kowalisyn J., Esposito R. E., Elder R. Developmental regulation of SPO13, a gene required for separation of homologous chromosomes at meiosis I. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1425–1435. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub S. J., Chow K. N., Luo R. X., Zhang S. H., He S., Dean D. C. Mechanism of active transcriptional repression by the retinoblastoma protein. Nature. 1995 Jun 29;375(6534):812–815. doi: 10.1038/375812a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]