SUMMARY
Epigenetic alterations, particularly in DNA methylation, are ubiquitous in cancer, yet the molecular origins and the consequences of these alterations are poorly understood. The DNA binding protein CTCF regulates a diverse array of epigenetic processes and is frequently altered by hemizygous deletion or mutation in human cancer. To date, a causal role for CTCF in cancer has not been established. Here we show that Ctcf hemizygous knockout mice are markedly susceptible to spontaneous, radiation, and chemically induced cancer in a broad range of tissues. Ctcf+/− tumors are characterized by increased aggressiveness including invasion, metastatic dissemination, and mixed epithelial/mesenchymal differentiation. Molecular analysis of Ctcf+/− tumors indicates that Ctcf is haploinsufficient for tumor suppression. Tissues with hemizygous loss of CTCF exhibit increased variability in CpG methylation genome-wide. These findings establish CTCF as a prominent tumor suppressor gene and point to CTCF mediated epigenetic stability as a major barrier to neoplastic progression.
INTRODUCTION
CTCF (CCCTC-binding factor) is a highly conserved 11 Zn finger DNA binding protein that utilizes different combinations of its Zn fingers to bind a large number of highly divergent target sequences throughout the genome (Kim et al., 2007; Nakahashi et al., 2013). CTCF establishes chromatin boundaries and mediates higher order chromatin organization (Phillips and Corces, 2009). Numerous epigenetic phenomena regulated by CTCF include X chromosome inactivation, imprinting, noncoding transcription, and RNA processing (Filippova, 2008; Ong and Corces, 2014). Further, CTCF binds to target DNA sequences in a DNA methylation-dependent manner and regulates spreading of DNA methylation (Mukhopadhyay et al., 2004; Wang et al., 2012; Zampieri et al., 2012).
Chromosomal deletion at 16q22.1 is well documented in several human cancers and is one of the most common genetic events in breast cancer, with frequencies ranging from 28–90%, depending on the study and molecular subtype (Filippova et al., 1998; Rakha et al., 2006). Extensive genetic and molecular analyses have implicated the involvement of several candidate tumor suppressor genes within 16q22.1 and multiple genes therein, however, with the exception of CDH1 (Berx et al., 1996), inactivating “second hit” mutations in other genes are rare, thus hampering efforts to confirm additional candidates. As CTCF maps to 16q22.1, we hypothesized that it might be a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor gene in which inactivation of just one allele would increase cancer risk (Payne and Kemp, 2005). To directly address this possibility, we examined the tumor predisposition of Ctcf hemizygous knockout mice.
RESULTS
Ctcf is a Tumor Suppressor Gene
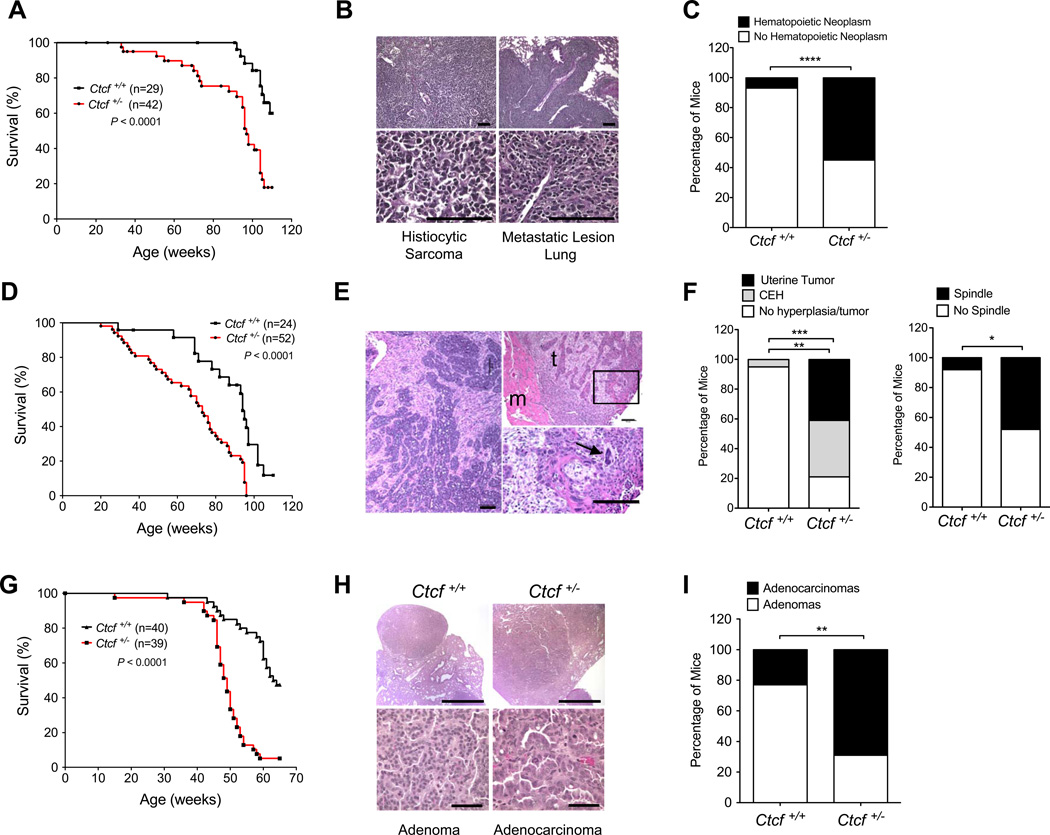
Ctcf nullizygous embryos failed to thrive due to cell death by apoptosis, demonstrating that CTCF is indispensable for development (Moore et al., 2012). C57BL6/129 (B6/129) F1 Ctcf+/− mice were born at the expected Mendelian frequency and displayed no overt developmental defects, excepting a slight reduction in mature B cells (data not shown). However, Ctcf heterozygous knockout mice were markedly predisposed to spontaneous tumor development in a broad range of tissues. By 100 weeks of age, 80% of Ctcf+/− mice succumbed to cancer, compared to only 40% of wild type littermates (Figure 1A). Ctcf+/− mice were also three times more likely to develop multiple tumors per mouse (Table S1). The tumor spectrum associated with Ctcf deficiency included benign and malignant uterine tumors, histiocytic sarcomas that presented as aggressive, metastatic disease, and diploid T-cell and T-cell infiltrating B-cell lymphomas (Figures S1 and S2). The latter findings indicate a role for CTCF in lymphocyte maturation and lymphomagenesis, consistent with the reported block in T cell development after conditional deletion of Ctcf (Heath et al., 2008) and DNA methylation profiling studies of B cell lymphomas (De et al., 2013).
Figure 1. Ctcf+/− mice are susceptible to tumor development.
A, Kaplan-Meier analysis of tumor-free survival of Ctcf+/− (n = 42) and Ctcf+/+ (n = 29) mice, P < 0.0001. B, H&E staining of spontaneous primary histiocytic sarcoma and corresponding lung metastasis from a Ctcf+/− mouse. Scale bars, 100 µm. C, Hematopoietic neoplasms by Ctcf genotype, **** P < 0.0001. D, Kaplan-Meier analysis of tumor-free survival of irradiated Ctcf+/− (n = 52) and Ctcf+/+ (n = 24) mice, P < 0.0001. E, H&E staining of DMBA-induced tumors from Ctcf+/− mice. Left, uterine endometrial adenocarcinoma with epithelial and mesenchymal components. Right, mammary gland adenocarcinoma with areas of spindle cell differentiation (t) and invasion of adjacent skeletal muscle (m); magnification of boxed region (bottom) reveals nuclear atypia (arrowhead). Scale bars, 100 µm. F, Frequency of endometrial lesions (left) and mammary gland histopathology (right) from DMBA-treated mice. Spindle indicates prominent neoplastic spindle cells intermixed within the tumor, ** P < 0.01, * P < 0.05. G, Kaplan-Meier analysis of tumor-free survival in urethane-treated Ctcf+/− (n = 39) and Ctcf+/+ (n = 40) mice, P < 0.0001. H, H&E staining of urethane-induced lung tumors. Scale bars, 1 mm (top) and 50 µm (bottom). I, Distribution of adenomas/adenocarcinomas in each genotype, ** P = 0.002. See also Figure S1.
To determine if CTCF functions to suppress ionizing radiation (IR) induced carcinogenesis, we subjected a second cohort of mice to 4 Gy IR at two weeks of age. Irradiated Ctcf+/− mice developed tumors earlier than their wild type littermates (Figure 1D) and displayed a broader range of neoplasms including thymic and splenic lymphomas, and benign, malignant, and metastatic tumors of the lung, liver, pituitary, ovary, gastrointestinal tract, bone, adrenal cortex, Harderian gland, mammary gland, and thyroid gland (Table S2 and Figure S1).
Ctcf+/− mice were also predisposed to chemically induced cancers, particularly of the uterus. Approximately 80% of DMBA treated Ctcf+/− female mice developed uterine lesions, ranging from cystic endometrial hyperplasias (CEH) to leiomyomas/sarcomas and highly aggressive endometrial adenocarcinomas, as compared to only a 5% incidence of CEH in wild type mice (Figures 1 E,F and S1). DMBA treated female mice also developed mammary gland tumors that, on a wild type background, were typically adeno- or adenosquamous carcinomas. In contrast, Ctcf+/− mice exhibited a broader histopathological spectrum, ranging from adenosquamous carcinomas to more primitive appearing tumors with mixed luminal epithelial and mesenchymal components. Importantly, tumor cells also exhibited a pleomorphic spindle morphology consistent with myoepithelial derivation and/or epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Cells with spindle morphology showed reduced E-cadherin and increased vimentin staining, suggesting that Ctcf hemizygosity affects transdifferentiation of these tumors (Figure S1). DMBA treated Ctcf+/− female mice also developed tumors of the lung, gastrointestinal tract, skin, and ovary (Table S3). Thus, hemizygous deletion of Ctcf sensitizes a broad spectrum of cell lineages and tissues to spontaneous, radiation, and chemically induced cancers, establishing CTCF as a pan-tissue tumor suppressor.
CTCF Suppresses Kras-Driven Lung Cancer
To address the interaction between an epigenetic regulator and a genetic driver of cancer, we next asked if reduction of Ctcf cooperates with mutated Kras in a model of urethane induced non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC). These tumors closely resemble human NSCLC in morphologic and molecular characteristics, and over 80% harbor activating mutations in the Kras oncogene (Gurley et al., 2014). Urethane treated Ctcf+/− mice developed more lung tumors that were significantly larger compared to wild type mice (Figure S1). This enhanced lung tumor burden led to earlier mortality (Figure 1G). The majority of lung tumors from wild type mice were benign adenomas (17/22, 77%) with low mitotic activity, uniform small nuclei, and well defined boundaries. In contrast, 69% (22/32) of Ctcf+/− lung tumors were classified as malignant adenocarcinomas with abundant mitotic activity, large and irregularly shaped nuclei, disorganized growth patterns, and frequent invasion into local parenchyma and airways (Figure 1H,I). Lung tumors from Ctcf+/− mice exhibited increased proliferation as measured by BrdU labeling (Figure S1), while apoptosis was negligible in both genotypes (not shown). Thus, reduction of Ctcf accelerated the development of Kras- driven cancer, arguing that epigenetic events regulated by CTCF play a significant role in suppressing RAS mediated tumorigenesis.
Ctcf is Haploinsufficient for Tumor Suppression
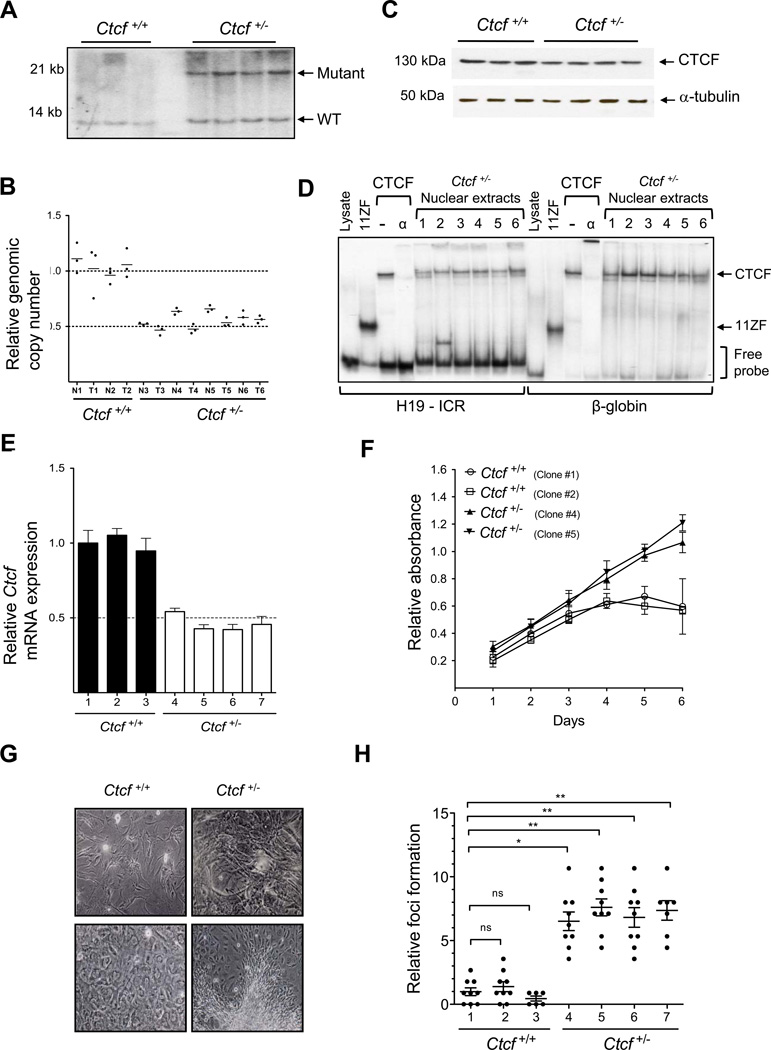
Many tumor suppressor genes are recessive and require a second “hit” for abrogation of function (Payne and Kemp, 2005). However, complete loss of Ctcf leads to apoptotic cell death (Moore et al., 2012) and therefore is unlikely to provide a selective advantage. Southern blot analysis and Q-PCR showed retention of the wild type Ctcf allele in 100% (4/4) of lung tumors (Figure 2A,B). RT-PCR and immunoblot analysis showed full-length Ctcf mRNA transcript and CTCF protein were maintained in both tumors and normal tissue (Figure 2C and not shown). Sequencing of Ctcf cDNA from 19 representative tumors from spontaneous, irradiated, and urethane-treated Ctcf+/− mice revealed no mutations throughout the entire coding region (Table S4). No mutations or deletions in Ctcf were observed in five tumors from Ctcf wild type mice. Gel mobility shift analysis of CTCF DNA binding activity in nuclear extracts confirmed retention of functional CTCF in 6/6 (100%) of Ctcf+/− tumors (Figure 2D).
Figure 2. Ctcf is haploinsufficient for tumor suppression.
A, Southern blot analysis of lung tumors from Ctcf+/+ (lanes 1–3) and Ctcf+/− (lanes 4–7) mice. B, qPCR analysis of genomic DNA from normal lung (N) and lung tumors (T) from each genotype. C, Immunoblot analysis of CTCF protein in lung tumors from Ctcf+/+ (lanes 1–3) and Ctcf+/− (lanes 4–7) mice. α-tubulin served as loading control. D, Gel shift analysis of nuclear extracts from Ctcf+/− lung tumors show CTCF binding at both the H19/Igf2 ICR and β-globin insulator FII loci. Positions of protein-DNA complexes with 11ZF CTCF DNA binding domain (11ZF) or full length CTCF protein (CTCF) are indicated. α-CTCF antibody (α) was used to super-shift CTCF-DNA complexes. E, qRT-PCR analysis of Ctcf mRNA in Ctcf+/+ (n=3) and Ctcf+/− (n=4) MEFs, mean +/− s.e.m. F, Proliferation of Ctcf+/+ and Ctcf+/− MEFS. Assays performed in triplicate for two clones, each genotype; mean +/− s.d. G, Foci formation in MEFS cultured from Ctcf+/− compared to Ctcf+/+ mice. H, Increased foci formation in Ctcf+/− MEFs; mean +/− s.e.m., *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.
As ectopic expression of CTCF inhibits cell growth (Rasko et al., 2001), we next asked if Ctcf had a gene dosage dependent effect on cell proliferation. Mouse embryo derived fibroblasts (MEFs) from wild type mice stopped proliferating at confluence, forming a uniform monolayer with a flattened morphology. In contrast, Ctcf+/− MEFs that showed a 50% reduction in Ctcf mRNA transcript levels (Figure 2E), continued to proliferate after reaching confluence, piling up and forming foci indicating loss of contact inhibition (Figure 2F–H).
Collectively, the increased tumor predisposition of Ctcf+/− mice, the retention of the wild-type Ctcf allele, mRNA, and protein expression in tumors, and the cell autonomous loss of contact inhibition of Ctcf+/− cells establish this gene as a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor, where loss of a single allele significantly increases cancer risk.
Ctcf Hemizygosity Causes DNA Methylation Instability In Vivo
CTCF can affect cytosine methylation both locally, through binding to chromatin boundaries, and distally, through its long-range effects on DNA looping and three-dimensional chromatin architecture (Zampieri et al., 2012; Wang et al., 2012). Aberrant methylation at CTCF binding sites in several tumor suppressor genes and imprinted loci has been reported in human cancer (Filippova, 2008). To determine if hemizygous loss of Ctcf affects DNA methylation in vivo, we examined the methylation status of known CTCF binding sites at the promoters of three tumor suppressor genes, (p16Ink4a, p19Arf, and Mlh1), as well as at the imprinting control regions (ICRs) of three imprinted loci, (Igf2/H19, KvDMR1, and Rasgrf1). Bisulfite conversion and sequencing analysis of wild type and Ctcf+/− MEFs, as well as paired normal lung and lung tumor tissue samples from three wild type and four Ctcf+/− mice revealed that of the six loci examined, one, the Igf2/H19 ICR, showed differences in DNA methylation. The maternally inherited Igf2/H19 ICR allele is normally unmethylated and bound by CTCF, while the paternal ICR is methylated and does not bind CTCF (Bell and Felsenfeld, 2000). Both normal lung and MEFs from wild type mice showed the expected pattern of 50% methylated CpGs at two CTCF binding sites analyzed within the Igf2/H19 ICR. In contrast Ctcf+/− lung tissue and MEFs exhibited between 80–90% CpG methylation at these sites (Figure S3).
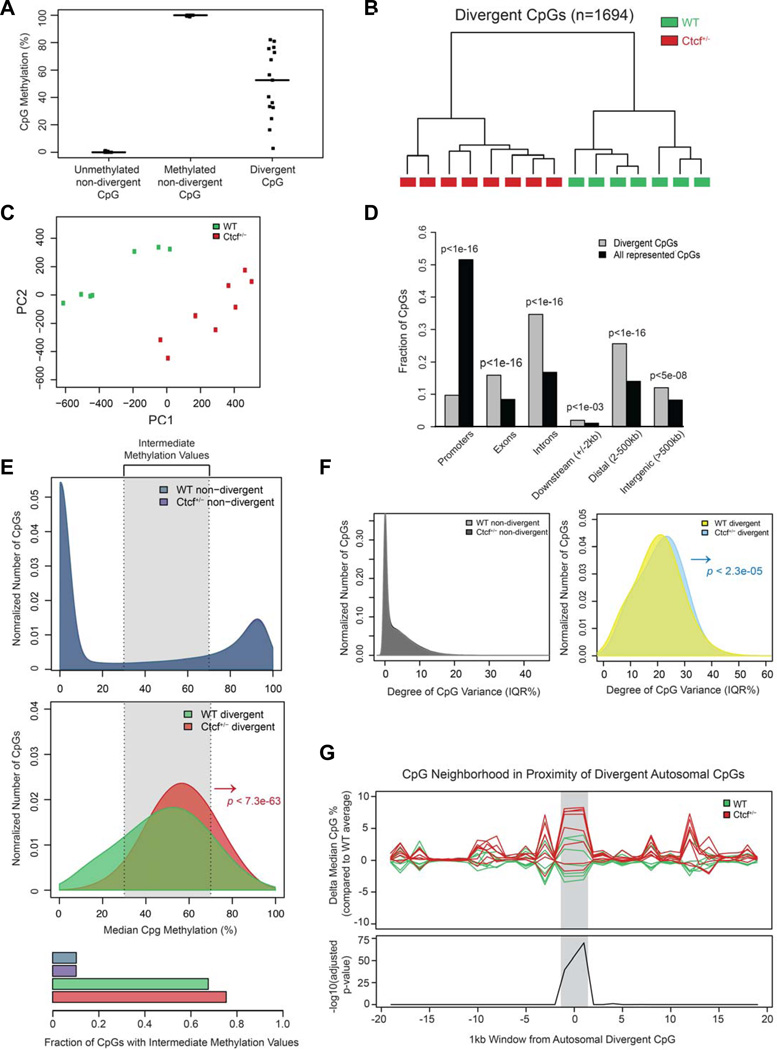
To explore the effect of hemizygous deletion of Ctcf on DNA methylation genome-wide, we profiled non-cancerous murine lung tissue. We examined 1.75M CpGs by enhanced reduced representation bisulfite sequencing (ERRBS), a method based on bisulfite conversion of DNA followed by deep sequencing of MspI fragments with size-based enrichment for genes and regulatory regions (Akalin et al., 2012). We first performed an unsupervised analysis based on the CpGs with the greatest degree of divergence among the 15 lung samples examined (n=1694 CpGs, interquartile range (IQR) >25%) (Figure 3A and Table S5). This unbiased analysis yielded two main clusters, corresponding precisely to the seven and eight samples from Ctcf+/+ and Ctcf+/− mice, respectively (Figures 3B,C and S3C). This suggests that the most prominent differences in DNA methylation between these tissues are directly attributed to Ctcf hemizygosity. Outside of these divergent CpGs, the overall CpG methylation patterns were remarkably stable and consistent between genotypes (Figure S3D), implying that CTCF regulation of DNA methylation occurs primarily at specific loci. The divergent CpGs were non-randomly distributed in the genome with preferential localization within introns, exons, and intergenic regions and depletion from promoter regions (Figure 3D).
Figure 3. Aberrant DNA methylation in non-cancerous lung tissue from Ctcf+/− mice.
A, Examples of non-divergent and divergent CpGs within 15 lung samples. B, Hierarchical clustering of divergent autosomal CpG methylation values. C, Principle component analysis (PCA) plot for divergent autosomal CpG methylation values. D, Genomic distribution of divergent autosomal CpGs vs. all represented CpGs. E, Density plots of median CpG methylation values according to Ctcf genotype; non-divergent autosomal CpGs (top) and divergent autosomal CpGs (middle), P<7.3e-63). Divergent CpGs tend to have intermediate methylation values (bottom). F, Density plots of CpG methylation variance according to Ctcf genotype; non-divergent autosomal CpGs (left) and divergent autosomal CpGs (right), P<2.3e-05). G, CpG methylation values within 1kb intervals up- and downstream of divergent CpGs. The differences of median CpG methylation values for each sample relative to the median of all seven wild type CpG methylation values and associated P values are plotted. Shaded area indicates region with significant difference between genotypes, P<1e-25, ANOVA.
The divergent CpGs exhibited intermediate methylation levels (ranging from 30 to 70%), contrasting with the classical bimodal distribution among the non-variable CpGs (Figures 3E). This indicates a high degree of intra-sample heterogeneity among these divergent CpGs which might represent hotspots for epigenetic hypervariability in lung tissue. Divergent CpGs from Ctcf+/− lungs were significantly shifted towards cytosine hypermethylation (Figure 3E, middle panel) and showed increased variance in methylation (Figure 3F), further evidence that Ctcf hemizygosity destabilized the regulation of DNA methylation. While DNA methylation changes between genotypes occurred primarily at the set of divergent CpGs, a modest overall gain in genome-wide DNA methylation was also observed in Ctcf+/− lung (Figure S3E).
Although the methylation differences between Ctcf genotypes were striking, these changes would unlikely have biological relevance if they were limited to individual CpGs. Hence, to test whether CTCF also affects regions surrounding the divergent CpGs, the median methylation values within each lung sample, relative to the average wild type methylation values were determined for all CpGs occurring within 1kb windows extending up- and downstream of the divergent CpGs. We found significant hypermethylation in Ctcf+/− samples that extended to ~2kb regions surrounding divergent CpGs (Figure 3G). Interestingly, several cancer associated genes such as Trp53, Dnmt3A, RunX1, Alk, Card11, Kit, Mpo, Pou2F2, Spen, ZfhX3, and Arid1A, including Ctcf itself, contain divergent CpGs either within or in close proximity to the gene. Ctcf+/− lung cytosine methylation patterns therefore reflect discrete regional increases in methylation diversity, with a significant tendency of these regions to shift towards a hypermethylated state, suggesting a role for CTCF in maintaining stability of cytosine methylation patterning in vivo.
CTCF Mutation and Copy Number Variation in Human Breast and Endometrial Cancer
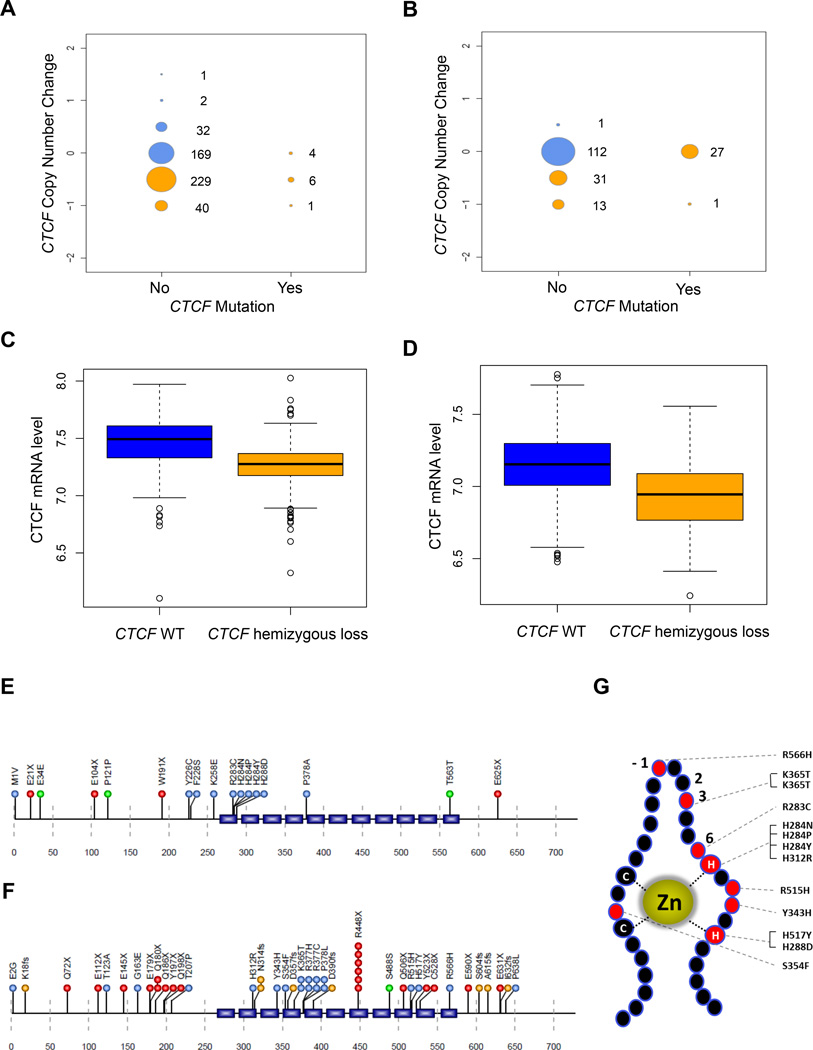
The functions of tumor suppressor genes are typically well conserved between mice and humans. Our mouse model results, together with the frequent 16q22.1 deletions reported in breast and other cancers (Rakha et al., 2006) predict that CTCF is a tumor suppressor in human cancer. Indeed, analysis of The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) data revealed reduced gene copy number of CTCF in 276/484 (57%) of breast tumors (Figure 4A). Tumors with reduced CTCF DNA copy number showed significantly reduced levels of CTCF mRNA (Figure 4C). In addition, point mutations in CTCF were identified in 21 out of 772 tumors with 17 of these mapping to the protein sequence (Figure 4E). CTCF mutations predominantly occurred in the estrogen receptor (ER) positive luminal A subtype, where the frequency was 4% (The Cancer Genome Atlas Network, 2012). Although complete loss of CTCF function is incompatible with cell survival, seven breast tumors showed evidence of both CTCF copy number reduction and mutation (Figures 4, S4 and Table S6). One had a truncating ‘loss of function’ mutation (E21X), possibly indicating two separate subclonal events. The other 6 mutations were either silent or missense mutations and clustered in the CTCF Zn finger (ZF) DNA binding domain, particularly in ZF1. Previous analysis of similar mutations (R283C and H284N/P/Y) that disrupt either DNA sequence recognition or zinc coordination showed that these mutations selectively impaired CTCF binding to some but not all DNA target sites, consistent with the multivalent nature of this 11 Zn finger protein (Filippova et al., 2002; Nakahashi et al., 2013).
Figure 4. CTCF hemizygous deletion and mutation in human breast and endometrial cancer.
A,B, Size plots for breast invasive carcinoma (A) and uterine corpus endometrioid carcinoma (B) indicating the total number of samples with either copy number change or mutation (yellow) or samples diploid for CTCF (blue). Copy number values are presented in discrete increments of 0.5. C,D Relative CTCF mRNA levels in breast (n=856, P < 10e-16) (C) and endometrial (n=362, P < 7.15e-12) (D) tumors are plotted according to CTCF DNA copy number. E,F, Somatic mutations within the CTCF protein coding sequence are plotted based on amino acid position (Uniprot Identifier P49711) for breast carcinoma (E) and endometrioid carcinoma (F). Synonymous (green), missense (blue), frameshift InDels (gold), and nonsense (red) mutations are shown. Blue rectangles indicate 11 ZN finger domains. G, Rendition of a typical C2-H2 type zinc finger (ZF) showing composite of missense mutations from endometrial and breast cancers. Amino acids at positions −1, 2, 3, and 6 that contact DNA directly and histidine (H) and cysteine (C) residues that coordinate Zn are indicated.
Hemizygous deletions of CTCF were also observed in uterine endometrial cancer (45/185, 24%) which again correlated with significantly reduced levels of CTCF mRNA (Figure 4B,D). Point mutations were also frequent, (53/248, 21%), primarily in the type 1 endometrioid subtype (Kandoth et al., 2013). 48/53 of these tumor-specific mutations mapped to the CTCF protein sequence and included missense mutations localized to the ZF domain and predicted to alter DNA sequence recognition, as well as truncating and frameshift mutations predicted to delete some or all of the ZFs (Figures 4F,G and S4). Only one tumor with a missense mutation (R377C in the ZF domain) showed evidence of both copy number loss and mutation (Table S6). Overall, CTCF is ranked as the 4th and 16th most significantly mutated gene in endometrial and breast cancer respectively, comparable to well-known cancer genes such as PTEN, TP53, PIK3CA, and FBXW7 (Figure S4).
CTCF Mutational Status Correlates with Whole-Genome Methylation Patterns in Human Tumors
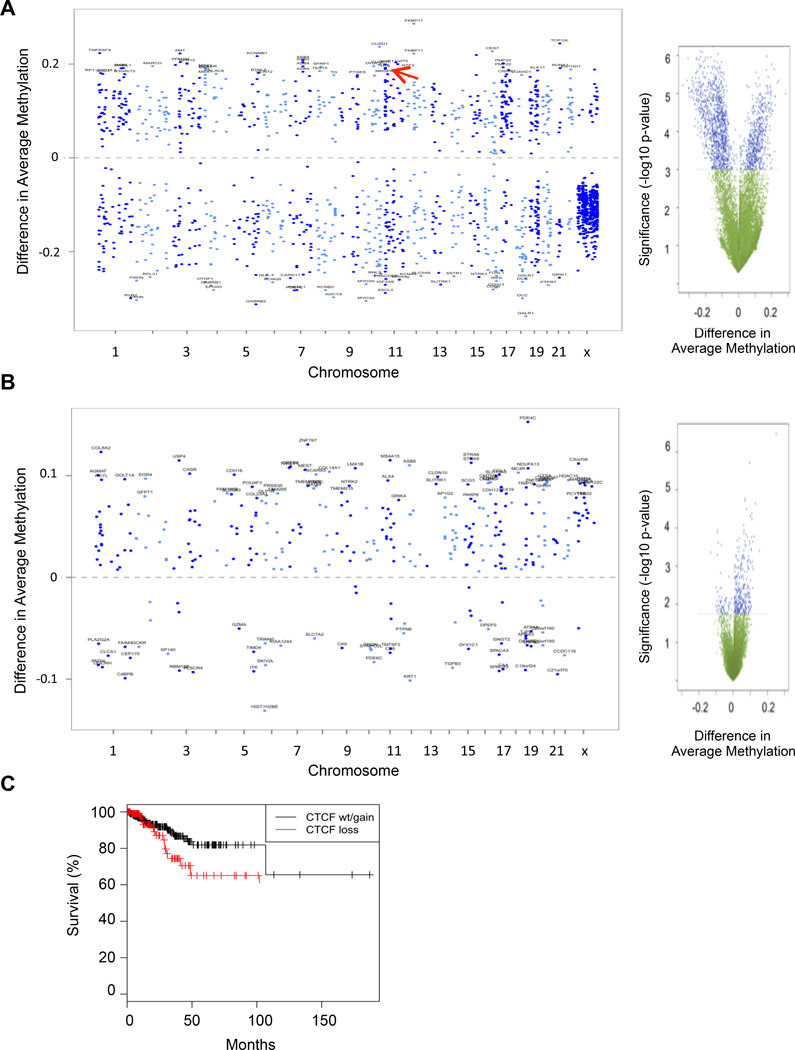
As our mouse model demonstrated that a 50% reduction in Ctcf gene dosage altered DNA methylation patterns genome-wide, we next asked if DNA methylation was altered in human tumors with CTCF hemizygous deletions or mutations. We analyzed Illumina Infinium DNA methylation data generated by the TCGA, a platform which assays methylation status of 27,000 CpGs (Kandoth et al., 2013). Endometrial adenocarcinomas with CTCF copy number aberrations (CNA) or point mutations exhibited significantly distinct methylation patterns, with a subset of CpGs showing either an increase or decrease in methylation compared to CTCF diploid tumors (Figure 5 A,B, and Table S7). CTCF CNA tumors tended to have a greater number of CpG methylation differences as compared to tumors with CTCF point mutations. This could reflect a broader destabilization associated with loss of additional genes on chromosome 16q in the CNA tumors, as, for example, seen for CpGs located on chromosome 16 itself, and/or a more restrictive phenotype associated with individual CTCF point mutations. In either case, these hyper- and hypomethylated CpGs were distributed across the genome. Interestingly, of the 16 CpGs assayed at the H19 locus, 12 showed a significant increase in methylation in CTCF CNA tumors (Table S7), a finding that is consistent with the increased methylation seen at the Igf2/H19 ICR in murine Ctcf+/− tissues (Figure S3B). Likewise, in luminal A breast cancer, a subset of CpGs showed significantly altered methylation in CTCF CNA or mutant tumors compared to CTCF wild type tumors (Figure S5 and Tables S7).
Figure 5. CTCF status correlates with genome wide DNA methylation patterns and patient survival in endometrial cancer.
A, Chromosomal plot of significantly differentially methylated CpGs between CTCF CNA (n = 45) vs. CTCF diploid (n = 114) endometrial tumors, P < 0.001. Positive and negative differences indicate methylation probes with increased or decreased methylation in the CTCF CNA tumors, respectively. The H19 locus is indicated with a red arrow. Right, volcano plot of permutation-based significance (blue, P < 0.001) as a function of differences in average DNA methylation between CTCF CNA vs. wild type endometrial tumors (beta-value differentials). B, Chromosomal plot of significantly differentially methylated CpGs (P < 0.018) between CTCF mutant (n = 45) vs. CTCF diploid (n = 114) endometrial tumors. Note, COL14A1 at chr8 with a differential methylation value of 0.25 was deleted for clarity (see Table S8). Right, volcano plot of permutation-based significance (blue, P < 0.018) as a function of differences in average DNA methylation between CTCF mutant vs. wild type tumors (beta-value differentials). C, Kaplan Meier survival plot of patients with endometrial cancer (n=492) stratified by CTCF copy number (P < 0.05, log-rank test).
The accelerated cancer associated mortality and increased aggressiveness of tumors in Ctcf+/− mice prompted us to ask if CTCF copy number in human tumors was associated with survival. In the TCGA breast cancer cohort, which included all subtypes, we observed no significant association with overall survival (not shown) while in endometrial cancer, reduction of CTCF copy number was associated with poor survival (Figure 5C). Although a careful analysis of different tumor subtypes with and without CTCF mutation or copy number variation will be required, this data suggest that in addition to a distinct epigenetic profile, CTCF hemizygous loss in human tumors might also correlate with a distinct clinical outcome.
DISCUSSION
Here we have shown that the chromatin organizer CTCF is a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor in vivo, where loss of just one allele enhances both tumor formation and malignant progression. Ctcf+/− mice were predisposed to spontaneous, ionizing radiation, and chemically induced tumors of epithelial, mesenchymal, and hematopoietic origin indicating a broad role for CTCF in tumor suppression. Furthermore, tumors from Ctcf hemizygous mice were more aggressive, with frequent local invasion, metastatic dissemination, features of EMT, and mixed lineage differentiation indicating reduction of Ctcf enhances malignant progression.
Our functional studies in mice, when viewed together with frequent CTCF hemizygous deletions or point mutations found in human tumors, implicate CTCF as a major tumor suppressor gene in human cancer. Indeed, analysis of 4,742 tumors across 21 cancer types revealed that CTCF was one of the most significantly mutated genes (Lawrence et al., 2014).
Estrogen signaling is a significant risk factor for both estrogen receptor positive luminal A breast cancer and type 1 endometrial cancer. The particularly high frequency of CTCF aberrations in these tumors, together with the susceptibility of Ctcf+/− mice to endometrial tumors and pleomorphic breast tumors suggests a prominent role for CTCF in hormone-driven cancers. Given that CTCF is a negative regulator of FOXA1-chromatin interactions that are required for estrogen receptor activity (Hurtado et al., 2011), it is possible that CTCF disruption contributes to tumor development by enhancing the promoting effects of estrogen.
Our study also has implications for understanding the origins of DNA methylation alterations in cancer. That hemizygous loss of Ctcf destabilized DNA methylation at epigenetically variable CpGs in normal tissue and enhanced cancer progression, suggests that epigenetic instability may both precede and accelerate the evolution of cancer. Indeed, human endometrial and breast tumors with genetic disruption of CTCF exhibited a distinct pattern of DNA methylation relative to CTCF intact tumors. Whether these methylation changes are a direct consequence of CTCF disruption remains unclear; however the impact of Ctcf hemizygosity on DNA methylation profiles that we observed in mice suggests this as a strong possibility. Overall, our data support a model wherein CTCF hemizygous deletion or mutation leads to epigenetic instability that in turn enhances phenotypic plasticity and thereby accelerates the emergence, adaptation, and evolution of neoplastic lesions. Our findings further suggest that human tumors with CTCF disruption might manifest as discrete epigenetic subtypes with clinically distinct outcomes and potentially unique therapeutic opportunities.
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
Tumor Induction and Analysis
All experiments with mice were approved by the FHCRC animal care and use committee and performed according to IACUC regulations. Experimental mice were generated by crossing 129/sv Ctcf+/− mice to C57BL6 Ctcf+/+ mice. Isogenic C57BL6/129 F1 Ctcf+/− and Ctcf+/+ offspring were genotyped (Moore et al., 2012), maintained on standard lab chow and water ad libitum, and housed in a 12 h light-dark cycle. A second cohort was generated and mice were exposed at two weeks of age to 400 cGy ionizing radiation (137Cesium at 500cGy/min). A third cohort was given 1 mg of 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene (DMBA) dissolved in 200ul of sesame oil by gavage once a week for six weeks. A fourth was injected at 14–15 days of age with a single dose of urethane (1 mg/g body weight, i.p.). Eight urethane treated mice of each genotype were injected with BrdU (100mg/kg, Sigma) 1 h before sacrifice. For all experiments, mice were observed on a daily basis through 24 months and euthanized when moribund. Mice were necropsied, and all grossly visible tumors and surrounding normal tissues were fixed in formalin or frozen.
Statistical Analysis
Tumor development and patient survival data were analyzed using Kaplan Meier survival plots with log rank test for significance. The mean tumor multiplicity and tumor incidence at each anatomic site were compared between the genotypes using the Mann-Whitney non-parametric test and Fisher’s exact test respectively. Significant differences in foci formation were assessed via a Kruskal Wallis test with Dennett’s post-test for multiple comparisons. CTCF mRNA expression was compared to DNA copy number using Wilcoxon rank sum test. Data are presented as either mean +/− s.d. or mean +/− s.e.m. as indicated and asterisks depicted in figures represent statistical significance.
Molecular Biology Protocols
See Supplemental Experimental Procedures for detailed protocols on immunohistochemistry, immunophenotyping and cell cycle analysis of lymphomas, Southern blotting, qRT-PCR, DNA sequencing, electrophoretic mobility shift assay, bisulfite sequencing analysis of DNA methylation, and experiments on MEFs.
Enhanced Reduced Representation Bisulfite Sequencing (ERRBS)
Genome-wide methylation analysis was performed on non-cancerous murine lung tissue at approximately 48 weeks after urethane treatment, at which time no histological differences were seen in normal lungs between Ctcf genotypes. 500ng of DNA from 8 Ctcf+/− mice (4 male, 4 female) and 7 wild-type mice (3 male, 4 female) was processed by the ERRBS protocol (Akalin et al., 2012) as described in Supplemental Experimental Procedures.
The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) Analysis
Mutation Annotation Format (MAF) files containing somatic mutation calls for breast invasive carcinoma and uterine corpus endometrioid carcinoma were downloaded from the TCGA Data Coordination Center (DCC). The GISTIC2 algorithm was used to identify samples with significant somatic gains or losses of CTCF. Methylation beta-values were calculated as the fraction (ranging from 0 to 1) of methylated beads from the Illumina Infinium DNA methylation platform, taken from Level 3 TCGA data as described in Supplemental Experimental Procedures.
Supplementary Material
Highlights.
Mice with hemizygous loss of CTCF are cancer prone
CTCF reduction destabilizes DNA methylation and this occurs prior to tumor development
CTCF is frequently hemizygously deleted or mutated in human cancer
The epigenetic regulator CTCF is a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor gene
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by NIH grant numbers CA68360, ES007033, DA030326, U24CA143835, U01 CA141550, PHS NRSA T32 GM007270 from NIGMS. We thank S.Collins, C.Grandori, S.Henikoff, S. Tapscott, and F. Yang for comments on the manuscript.
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
ACCESSION NUMBERS
Data are deposited in NCBI’s Gene Expression Omnibus and are accessible through GEO accession number GSE48975.
Reference List
- Akalin A, Garrett-Bakelman FE, Kormaksson M, Busuttil J, Zhang L, Khrebtukova I, Milne TA, Huang Y, Biswas D, Hess JL, Allis CD, Roeder RG, Valk PJ, Lowenberg B, Delwel R, Fernandez HF, Paietta E, Tallman MS, Schroth GP, Mason CE, Melnick A, Figueroa ME. Base-pair resolution DNA methylation sequencing reveals profoundly divergent epigenetic landscapes in acute myeloid leukemia. PLoS Genet. 2012;8:e1002781. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell AC, Felsenfeld G. Methylation of a CTCF-dependent boundary controls imprinted expression of the Igf2 gene. Nature. 2000;405:482–485. doi: 10.1038/35013100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berx G, Cleton-Jansen AM, Strumane K, de Leeuw WJ, Nollet F, Van Roy F, Cornelisse C. E-cadherin is inactivated in a majority of invasive human lobular breast cancers by truncation mutations throughout its extracellular domain. Oncogene. 1996;13:1919–1925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De S, Shaknovich R, Riester M, Elemento O, Geng H, Kormaksson M, Jiang Y, Woolcock B, Johnson N, Polo JM, Cerchietti L, Gascoyne RD, Melnick A, Michor F. Aberration in DNA methylation in B-cell lymphomas has a complex origin and increases with disease severity. PLoS Genet. 2013;9:e1003137. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filippova GN. Genetics and epigenetics of the multifunctional protein CTCF. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2008;80:337–360. doi: 10.1016/S0070-2153(07)80009-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filippova GN, Lindblom A, Meincke LJ, Klenova EM, Neiman PE, Collins SJ, Doggett NA, Lobanenkov VV. A widely expressed transcription factor with multiple DNA sequence specificity, CTCF, is localized at chromosome segment 16q22.1 within one of the smallest regions of overlap for common deletions in breast and prostate cancers. Genes Chromosomes. Cancer. 1998;22:26–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filippova GN, Qi CF, Ulmer JE, Moore JM, Ward MD, Hu YJ, Loukinov DI, Pugacheva EM, Klenova EM, Grundy PE, Feinberg AP, Cleton-Jansen AM, Moerland EW, Cornelisse CJ, Suzuki H, Komiya A, Lindblom A, Dorion-Bonnet F, Neiman PE, Morse HC, III, Collins SJ, Lobanenkov VV. Tumor-associated zinc finger mutations in the CTCF transcription factor selectively alter tts DNA-binding specificity. Cancer Res. 2002;62:48–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurley KE, Moser AR, Kemp CJ. Induction of lung tumors in mice with urethane. In: Abate-Shen C, Politi K, Chodosh LA, Olive KP, editors. Mouse Models of Cancer. Cold Spring Harbor: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory; 2014. pp. 63–65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath H, Ribeiro de AC, Sleutels F, Dingjan G, van de Nobelen S, Jonkers I, Ling KW, Gribnau J, Renkawitz R, Grosveld F, Hendriks RW, Galjart N. CTCF regulates cell cycle progression of alphabeta T cells in the thymus. EMBO J. 2008;27:2839–2850. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2008.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurtado A, Holmes KA, Ross-Innes CS, Schmidt D, Carroll JS. FOXA1 is a key determinant of estrogen receptor function and endocrine response. Nat. Genet. 2011;43:27–33. doi: 10.1038/ng.730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandoth C, Schultz N, Cherniack AD, Akbani R, Liu Y, Shen H, Robertson AG, Pashtan I, Shen R, Benz CC, Yau C, Laird PW, Ding L, Zhang W, Mills GB, Kucherlapati R, Mardis ER, Levine DA. Integrated genomic characterization of endometrial carcinoma. Nature. 2013;497:67–73. doi: 10.1038/nature12113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim TH, Abdullaev ZK, Smith AD, Ching KA, Loukinov DI, Green RD, Zhang MQ, Lobanenkov VV, Ren B. Analysis of the vertebrate insulator protein CTCF-binding sites in the human genome. Cell. 2007;128:1231–1245. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.12.048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence MS, Stojanov P, Mermel CH, Robinson JT, Garraway LA, Golub TR, Meyerson M, Gabriel SB, Lander ES, Getz G. Discovery and saturation analysis of cancer genes across 21 tumour types. Nature. 2014;505:495–501. doi: 10.1038/nature12912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore JM, Rabaia NA, Smith LE, Fagerlie S, Gurley KE, Loukinov D, Disteche CM, Collins SJ, Kemp CJ, Lobanenkov VV, Filippova GN. Loss of maternal CTCF is associated with peri-implantation lethality of Ctcf null embryos. PLoS. ONE. 2012;7:1–9. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukhopadhyay R, Yu W, Whitehead J, Xu J, Lezcano M, Pack S, Kanduri C, Kanduri M, Ginjala V, Vostrov A, Quitschke W, Chernukhin I, Klenova E, Lobanenkov V, Ohlsson R. The binding sites for the chromatin insulator protein CTCF map to DNA methylation-free domains genome-wide. Genome Res. 2004;14:1594–1602. doi: 10.1101/gr.2408304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakahashi H, Kwon KR, Resch W, Vian L, Dose M, Stavreva D, Hakim O, Pruett N, Nelson S, Yamane A, Qian J, Dubois W, Welsh S, Phair RD, Pugh BF, Lobanenkov V, Hager GL, Casellas R. A genome-wide map of CTCF multivalency redefines the CTCF code. Cell Rep. 2013;3:1678–1689. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2013.04.024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ong CT, Corces VG. CTCF: an architectural protein bridging genome topology and function. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014;15:234–246. doi: 10.1038/nrg3663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne SR, Kemp CJ. Tumor suppressor genetics. Carcinogenesis. 2005;26:2031–2045. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgi223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips JE, Corces VG. CTCF: master weaver of the genome. Cell. 2009;137:1194–1211. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.06.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rakha EA, Green AR, Powe DG, Roylance R, Ellis IO. Chromosome 16 tumor-suppressor genes in breast cancer. Genes Chromosomes. Cancer. 2006;45:527–535. doi: 10.1002/gcc.20318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasko JE, Klenova EM, Leon J, Filippova GN, Loukinov DI, Vatolin S, Robinson AF, Hu YJ, Ulmer J, Ward MD, Pugacheva EM, Neiman PE, Morse HC, III, Collins SJ, Lobanenkov VV. Cell growth inhibition by the multifunctional multivalent zinc-finger factor CTCF. Cancer Res. 2001;61:6002–6007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- The Cancer Genome Atlas Network. Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 2012;490:61–70. doi: 10.1038/nature11412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H, Maurano MT, Qu H, Varley KE, Gertz J, Pauli F, Lee K, Canfield T, Weaver M, Sandstrom R, Thurman RE, Kaul R, Myers RM, Stamatoyannopoulos JA. Widespread plasticity in CTCF occupancy linked to DNA methylation. Genome Res. 2012;22:1680–1688. doi: 10.1101/gr.136101.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zampieri M, Guastafierro T, Calabrese R, Ciccarone F, Bacalini MG, Reale A, Perilli M, Passananti C, Caiafa P. ADP-ribose polymers localized on Ctcf-Parp1-Dnmt1 complex prevent methylation of Ctcf target sites. Biochem. J. 2012;441:645–652. doi: 10.1042/BJ20111417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.