Abstract
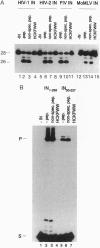
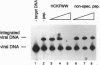
Integration of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) DNA into the human genome requires the virus-encoded integrase (IN) protein, and therefore the IN protein is a suitable target for antiviral strategies. To find a potent HIV IN inhibitor, we screened a "synthetic peptide combinatorial library." We identified a hexapeptide with the sequence HCKFWW that inhibits IN-mediated 3'-processing and integration with an IC50 of 2 microM. The peptide is active on IN proteins from other retroviruses such as HIV-2, feline immunodeficiency virus, and Moloney murine leukemia virus, supporting the notion that a conserved region of IN is targeted. The hexapeptide was also tested in the disintegration reaction. This phosphoryl-transfer reaction can be carried out by the catalytic core of IN alone, and the peptide HCKFWW was found to inhibit this reaction, suggesting that the hexapeptide acts at or near the catalytic site of IN. Identification of an IN hexapeptide inhibitor provides proof of concept for the approach, and, moreover, this peptide may be useful for structure-function analysis of IN.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ariyoshi M., Vassylyev D. G., Iwasaki H., Nakamura H., Shinagawa H., Morikawa K. Atomic structure of the RuvC resolvase: a holliday junction-specific endonuclease from E. coli. Cell. 1994 Sep 23;78(6):1063–1072. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90280-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowerman B., Brown P. O., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. A nucleoprotein complex mediates the integration of retroviral DNA. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):469–478. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. O., Bowerman B., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Correct integration of retroviral DNA in vitro. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):347–356. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P. O., Bowerman B., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Retroviral integration: structure of the initial covalent product and its precursor, and a role for the viral IN protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2525–2529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushman F. D., Craigie R. Activities of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) integration protein in vitro: specific cleavage and integration of HIV DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1339–1343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushman F. D., Engelman A., Palmer I., Wingfield P., Craigie R. Domains of the integrase protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 responsible for polynucleotidyl transfer and zinc binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3428–3432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow S. A., Vincent K. A., Ellison V., Brown P. O. Reversal of integration and DNA splicing mediated by integrase of human immunodeficiency virus. Science. 1992 Feb 7;255(5045):723–726. doi: 10.1126/science.1738845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushman M., Sherman P. Inhibition of HIV-1 integration protein by aurintricarboxylic acid monomers, monomer analogs, and polymer fractions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 May 29;185(1):85–90. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80958-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. F., 2nd, Hostomska Z., Hostomsky Z., Jordan S. R., Matthews D. A. Crystal structure of the ribonuclease H domain of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Science. 1991 Apr 5;252(5002):88–95. doi: 10.1126/science.1707186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyda F., Hickman A. B., Jenkins T. M., Engelman A., Craigie R., Davies D. R. Crystal structure of the catalytic domain of HIV-1 integrase: similarity to other polynucleotidyl transferases. Science. 1994 Dec 23;266(5193):1981–1986. doi: 10.1126/science.7801124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman A., Bushman F. D., Craigie R. Identification of discrete functional domains of HIV-1 integrase and their organization within an active multimeric complex. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3269–3275. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05996.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fayet O., Ramond P., Polard P., Prère M. F., Chandler M. Functional similarities between retroviruses and the IS3 family of bacterial insertion sequences? Mol Microbiol. 1990 Oct;4(10):1771–1777. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00555.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fesen M. R., Kohn K. W., Leteurtre F., Pommier Y. Inhibitors of human immunodeficiency virus integrase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2399–2403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fesen M. R., Pommier Y., Leteurtre F., Hiroguchi S., Yung J., Kohn K. W. Inhibition of HIV-1 integrase by flavones, caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) and related compounds. Biochem Pharmacol. 1994 Aug 3;48(3):595–608. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(94)90291-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara T., Mizuuchi K. Retroviral DNA integration: structure of an integration intermediate. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):497–504. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90071-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazuda D. J., Hastings J. C., Wolfe A. L., Emini E. A. A novel assay for the DNA strand-transfer reaction of HIV-1 integrase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Mar 25;22(6):1121–1122. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.6.1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghten R. A. Peptide libraries: criteria and trends. Trends Genet. 1993 Jul;9(7):235–239. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(93)90087-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghten R. A., Pinilla C., Blondelle S. E., Appel J. R., Dooley C. T., Cuervo J. H. Generation and use of synthetic peptide combinatorial libraries for basic research and drug discovery. Nature. 1991 Nov 7;354(6348):84–86. doi: 10.1038/354084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalpana G. V., Goff S. P. Genetic analysis of homomeric interactions of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 integrase using the yeast two-hybrid system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 15;90(22):10593–10597. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.22.10593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzman M., Katz R. A., Skalka A. M., Leis J. The avian retroviral integration protein cleaves the terminal sequences of linear viral DNA at the in vivo sites of integration. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5319–5327. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5319-5327.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan E., Mack J. P., Katz R. A., Kulkosky J., Skalka A. M. Retroviral integrase domains: DNA binding and the recognition of LTR sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 25;19(4):851–860. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.4.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaFemina R. L., Callahan P. L., Cordingley M. G. Substrate specificity of recombinant human immunodeficiency virus integrase protein. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5624–5630. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5624-5630.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaFemina R. L., Graham P. L., LeGrow K., Hastings J. C., Wolfe A., Young S. D., Emini E. A., Hazuda D. J. Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus integrase by bis-catechols. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1995 Feb;39(2):320–324. doi: 10.1128/aac.39.2.320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam K. S., Salmon S. E., Hersh E. M., Hruby V. J., Kazmierski W. M., Knapp R. J. A new type of synthetic peptide library for identifying ligand-binding activity. Nature. 1991 Nov 7;354(6348):82–84. doi: 10.1038/354082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazumder A., Cooney D., Agbaria R., Gupta M., Pommier Y. Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 integrase by 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidylate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 21;91(13):5771–5775. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.13.5771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazumder A., Gupta M., Perrin D. M., Sigman D. S., Rabinovitz M., Pommier Y. Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 integrase by a hydrophobic cation: the phenanthroline-cuprous complex. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1995 Jan;11(1):115–125. doi: 10.1089/aid.1995.11.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice P., Mizuuchi K. Structure of the bacteriophage Mu transposase core: a common structural motif for DNA transposition and retroviral integration. Cell. 1995 Jul 28;82(2):209–220. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90308-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauer M., Billich A. The N-terminal region of HIV-1 integrase is required for integration activity, but not for DNA-binding. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Jun 30;185(3):874–880. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)91708-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. K., Smith G. P. Searching for peptide ligands with an epitope library. Science. 1990 Jul 27;249(4967):386–390. doi: 10.1126/science.1696028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman P. A., Fyfe J. A. Human immunodeficiency virus integration protein expressed in Escherichia coli possesses selective DNA cleaving activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5119–5123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson M., Haggerty S., Lamonica C. A., Meier C. M., Welch S. K., Wasiak A. J. Integration is not necessary for expression of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 protein products. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2421–2425. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2421-2425.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vink C., Banks M., Bethell R., Plasterk R. H. A high-throughput, non-radioactive microtiter plate assay for activity of the human immunodeficiency virus integrase protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Jun 11;22(11):2176–2177. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.11.2176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vink C., Oude Groeneger A. M., Plasterk R. H. Identification of the catalytic and DNA-binding region of the human immunodeficiency virus type I integrase protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Mar 25;21(6):1419–1425. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.6.1419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vink C., Plasterk R. H. The human immunodeficiency virus integrase protein. Trends Genet. 1993 Dec;9(12):433–438. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(93)90107-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vink C., van der Linden K. H., Plasterk R. H. Activities of the feline immunodeficiency virus integrase protein produced in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1994 Mar;68(3):1468–1474. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.3.1468-1474.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vora A. C., Fitzgerald M. L., Grandgenett D. P. Removal of 3'-OH-terminal nucleotides from blunt-ended long terminal repeat termini by the avian retrovirus integration protein. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5656–5659. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5656-5659.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Gent D. C., Elgersma Y., Bolk M. W., Vink C., Plasterk R. H. DNA binding properties of the integrase proteins of human immunodeficiency viruses types 1 and 2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 25;19(14):3821–3827. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.14.3821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Gent D. C., Vink C., Groeneger A. A., Plasterk R. H. Complementation between HIV integrase proteins mutated in different domains. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3261–3267. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05995.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Ent F. M., Vink C., Plasterk R. H. DNA substrate requirements for different activities of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 integrase protein. J Virol. 1994 Dec;68(12):7825–7832. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.12.7825-7832.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]