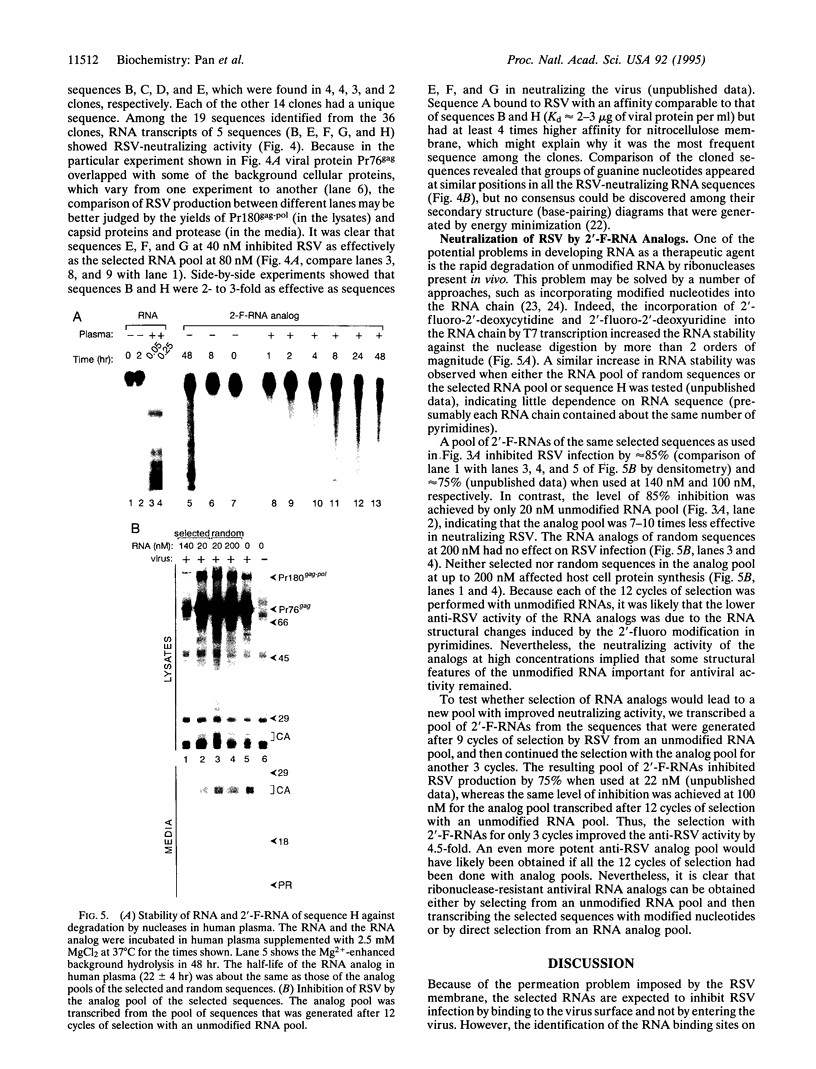
Abstract
RNA and ribonuclease-resistant RNA analogs that bound and neutralized Rous sarcoma virus (RSV) were isolated from a large pool of random sequences by multiple cycles of in vitro selection using infectious viral particles. The selected RNA pool of RSV-binding sequences at a concentration of 0.16 microM completely neutralized the virus. Of 19 sequences cloned from the selected pool, 5 inhibited RSV infection. The selected RNA and RNA analogs were shown to neutralize RSV by interacting with the virus, rather than by adversely affecting the host cells. The selection of the anti-RSV RNA and RNA analogs by intact virions immediately suggests the potential application of this approach to develop RNA and RNA analogs as inhibitors of other viruses such as human immunodeficiency virus.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bova C. A., Olsen J. C., Swanstrom R. The avian retrovirus env gene family: molecular analysis of host range and antigenic variants. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):75–83. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.75-83.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven R. C., Leure-duPree A. E., Erdie C. R., Wilson C. B., Wills J. W. Necessity of the spacer peptide between CA and NC in the Rous sarcoma virus gag protein. J Virol. 1993 Oct;67(10):6246–6252. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.10.6246-6252.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davanloo P., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Cloning and expression of the gene for bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2035–2039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimmock N. J. Neutralization of animal viruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1993;183:1–149. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-77849-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorner A. J., Coffin J. M. Determinants for receptor interaction and cell killing on the avian retrovirus glycoprotein gp85. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):365–374. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90322-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellington A. D., Szostak J. W. In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature. 1990 Aug 30;346(6287):818–822. doi: 10.1038/346818a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illangasekare M., Sanchez G., Nickles T., Yarus M. Aminoacyl-RNA synthesis catalyzed by an RNA. Science. 1995 Feb 3;267(5198):643–647. doi: 10.1126/science.7530860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine D., Tuerk C., Gold L. SELEXION. Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment with integrated optimization by non-linear analysis. J Mol Biol. 1991 Dec 5;222(3):739–761. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90509-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M. I., Hoth D. F. Present status and future prospects for HIV therapies. Science. 1993 May 28;260(5112):1286–1293. doi: 10.1126/science.7684163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joyce G. F. Amplification, mutation and selection of catalytic RNA. Gene. 1989 Oct 15;82(1):83–87. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90033-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenan D. J., Tsai D. E., Keene J. D. Exploring molecular diversity with combinatorial shape libraries. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Feb;19(2):57–64. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Whole genome PCR: application to the identification of sequences bound by gene regulatory proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 25;17(10):3645–3653. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.10.3645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y., Qiu Q., Gill S. C., Jayasena S. D. Modified RNA sequence pools for in vitro selection. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Dec 11;22(24):5229–5234. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.24.5229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. P., McKeating J. A., Huang Y. X., Ashkenazi A., Ho D. D. Virions of primary human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolates resistant to soluble CD4 (sCD4) neutralization differ in sCD4 binding and glycoprotein gp120 retention from sCD4-sensitive isolates. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):235–243. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.235-243.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orloff S. L., Kennedy M. S., Belperron A. A., Maddon P. J., McDougal J. S. Two mechanisms of soluble CD4 (sCD4)-mediated inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infectivity and their relation to primary HIV-1 isolates with reduced sensitivity to sCD4. J Virol. 1993 Mar;67(3):1461–1471. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.3.1461-1471.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan T., Uhlenbeck O. C. In vitro selection of RNAs that undergo autolytic cleavage with Pb2+. Biochemistry. 1992 Apr 28;31(16):3887–3895. doi: 10.1021/bi00131a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieken W. A., Olsen D. B., Benseler F., Aurup H., Eckstein F. Kinetic characterization of ribonuclease-resistant 2'-modified hammerhead ribozymes. Science. 1991 Jul 19;253(5017):314–317. doi: 10.1126/science.1857967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prudent J. R., Uno T., Schultz P. G. Expanding the scope of RNA catalysis. Science. 1994 Jun 24;264(5167):1924–1927. doi: 10.1126/science.8009223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. E. Large-scale growth of Rous sarcoma virus. Methods Enzymol. 1979;58:393–403. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)58154-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuerk C., Gold L. Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science. 1990 Aug 3;249(4968):505–510. doi: 10.1126/science.2200121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varmus H. Retroviruses. Science. 1988 Jun 10;240(4858):1427–1435. doi: 10.1126/science.3287617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wills J. W., Craven R. C., Achacoso J. A. Creation and expression of myristylated forms of Rous sarcoma virus gag protein in mammalian cells. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4331–4343. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4331-4343.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M. On finding all suboptimal foldings of an RNA molecule. Science. 1989 Apr 7;244(4900):48–52. doi: 10.1126/science.2468181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Sijs I. H., Wiltink E. H. Antiviral drugs: present status and future prospects. Int J Biochem. 1994 May;26(5):621–630. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(94)90161-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]