Abstract
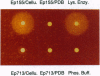
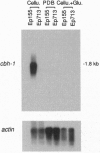
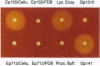
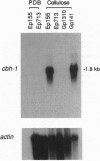
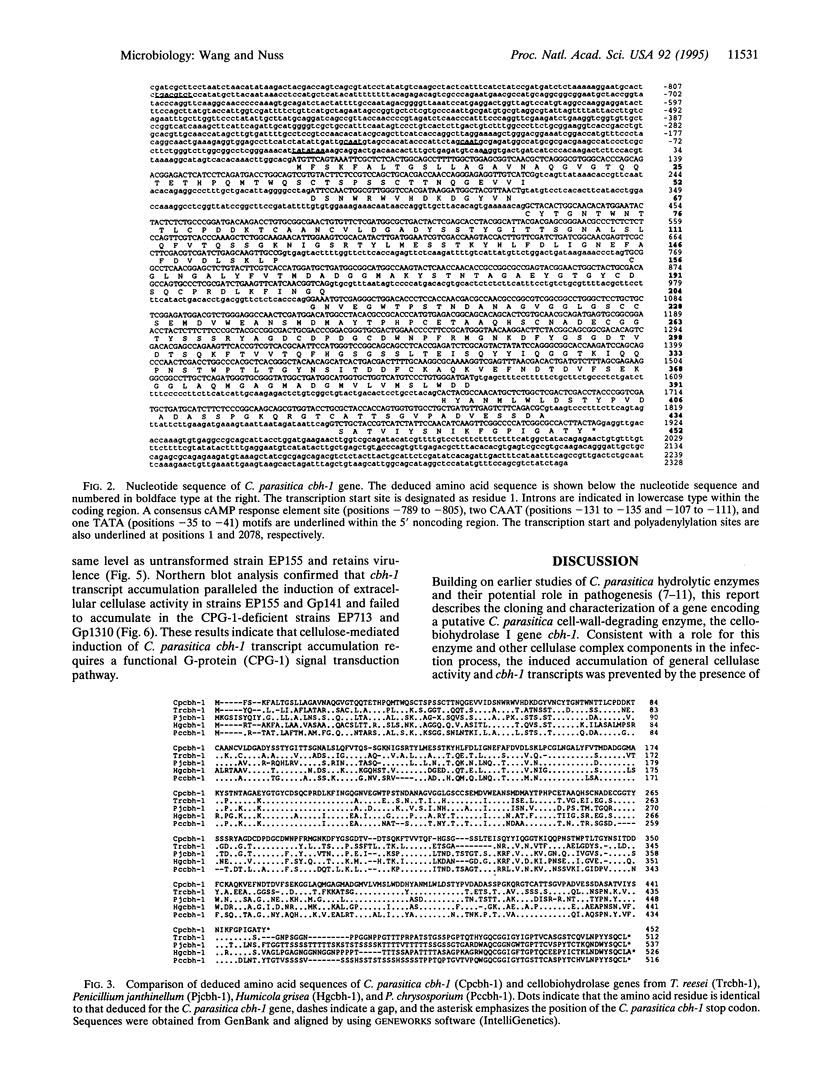
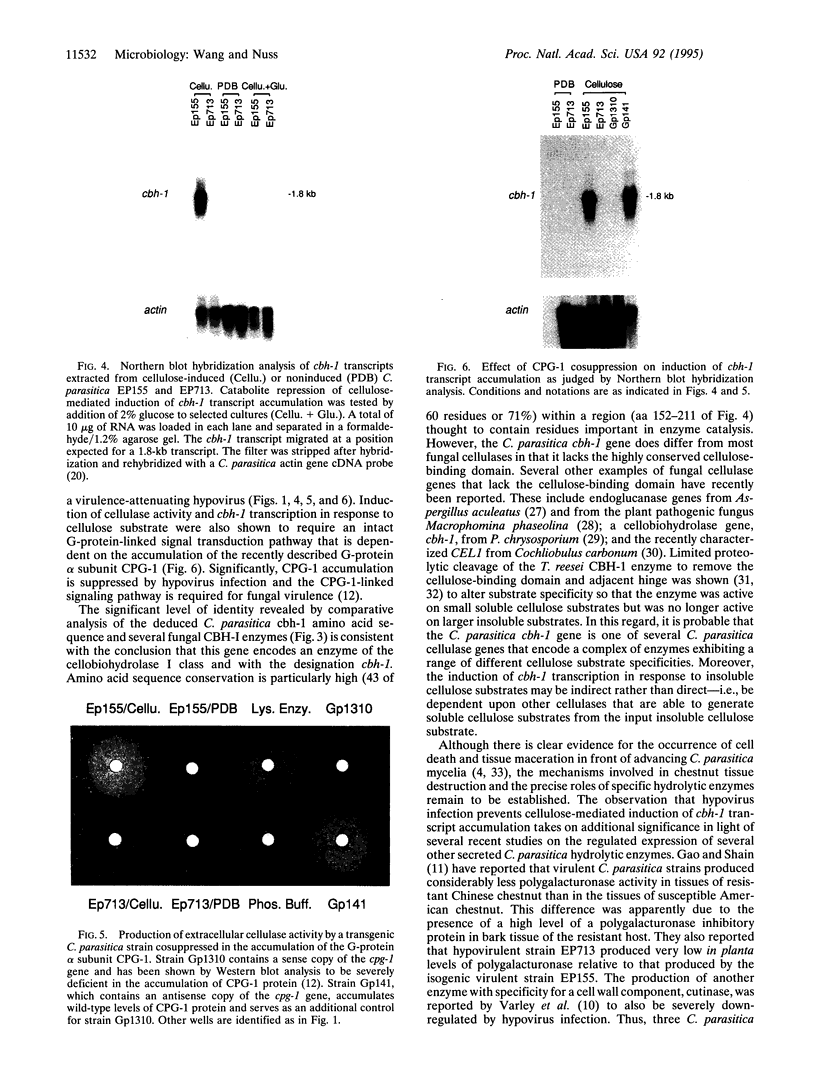
Extracellular cellulase activity is readily induced when the chestnut blight fungus Cryphonectria parasitica is grown on cellulose substrate as the sole carbon source. However, an isogenic C. parasitica strain rendered hypovirulent due to hypovirus infection failed to secrete detectable cellulase activity when grown under parallel conditions. Efforts to identify C. parasitica cellulase-encoding genes resulted in the cloning of a cellobiohydrolase (exoglucanase, EC 3.2.1.91) gene designated chb-1. Northern blot analysis revealed an increase in cbh-1 transcript accumulation in a virus-free virulent C. parasitica strain concomitant with the induction of extracellular cellulase activity. In contrast, induction of cbh-1 transcript accumulation was suppressed in an isogenic hypovirus-infected strain. Significantly, virus-free C. parasitica strains rendered hypovirulent by transgenic cosuppression of a GTP-binding protein alpha subunit were also found to be deficient in the induction of cbh-1 transcript accumulation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anagnostakis S. L. Biological control of chestnut blight. Science. 1982 Jan 29;215(4532):466–471. doi: 10.1126/science.215.4532.466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnett C. C., Berka R. M., Fowler T. Cloning and amplification of the gene encoding an extracellular beta-glucosidase from Trichoderma reesei: evidence for improved rates of saccharification of cellulosic substrates. Biotechnology (N Y) 1991 Jun;9(6):562–567. doi: 10.1038/nbt0691-562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carder J. H. Detection and quantitation of cellulase by Congo red staining of substrates in a cup-plate diffusion assay. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 15;153(1):75–79. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90063-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi G. H., Chen B., Nuss D. L. Virus-mediated or transgenic suppression of a G-protein alpha subunit and attenuation of fungal virulence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jan 3;92(1):305–309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.1.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi G. H., Larson T. G., Nuss D. L. Molecular analysis of the laccase gene from the chestnut blight fungus and selective suppression of its expression in an isogenic hypovirulent strain. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1992 Mar-Apr;5(2):119–128. doi: 10.1094/mpmi-5-119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi G. H., Pawlyk D. M., Rae B., Shapira R., Nuss D. L. Molecular analysis and overexpression of the gene encoding endothiapepsin, an aspartic protease from Cryphonectria parasitica. Gene. 1993 Mar 30;125(2):135–141. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90320-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covert S. F., Vanden Wymelenberg A., Cullen D. Structure, organization, and transcription of a cellobiohydrolase gene cluster from Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jul;58(7):2168–2175. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.7.2168-2175.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler T., Brown R. D., Jr The bgl1 gene encoding extracellular beta-glucosidase from Trichoderma reesei is required for rapid induction of the cellulase complex. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Nov;6(21):3225–3235. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01777.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilkes N. R., Henrissat B., Kilburn D. G., Miller R. C., Jr, Warren R. A. Domains in microbial beta-1, 4-glycanases: sequence conservation, function, and enzyme families. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Jun;55(2):303–315. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.2.303-315.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson T. G., Choi G. H., Nuss D. L. Regulatory pathways governing modulation of fungal gene expression by a virulence-attenuating mycovirus. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(12):4539–4548. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05555.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson T. G., Nuss D. L. Altered transcriptional response to nutrient availability in hypovirus-infected chestnut blight fungus. EMBO J. 1994 Dec 1;13(23):5616–5623. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06899.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ooi T., Shinmyo A., Okada H., Hara S., Ikenaka T., Murao S., Arai M. Cloning and sequence analysis of a cDNA for cellulase (FI-CMCase) from Aspergillus aculeatus. Curr Genet. 1990 Oct;18(3):217–222. doi: 10.1007/BF00318384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims P., James C., Broda P. The identification, molecular cloning and characterisation of a gene from Phanerochaete chrysosporium that shows strong homology to the exo-cellobiohydrolase I gene from Trichoderma reesei. Gene. 1988 Dec 30;74(2):411–422. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sposato P., Ahn J. H., Walton J. D. Characterization and disruption of a gene in the maize pathogen Cochliobolus carbonum encoding a cellulase lacking a cellulose binding domain and hinge region. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1995 Jul-Aug;8(4):602–609. doi: 10.1094/mpmi-8-0602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teeri T. T., Penttilä M., Keränen S., Nevalainen H., Knowles J. K. Structure, function, and genetics of cellulases. Biotechnology. 1992;21:417–445. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-7506-9115-4.50020-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomme P., Van Tilbeurgh H., Pettersson G., Van Damme J., Vandekerckhove J., Knowles J., Teeri T., Claeyssens M. Studies of the cellulolytic system of Trichoderma reesei QM 9414. Analysis of domain function in two cellobiohydrolases by limited proteolysis. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jan 4;170(3):575–581. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13736.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varley D. A., Podila G. K., Hiremath S. T. Cutinase in Cryphonectria parasitica, the chestnut blight fungus: suppression of cutinase gene expression in isogenic hypovirulent strains containing double-stranded RNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4539–4544. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton J. D. Deconstructing the Cell Wall. Plant Physiol. 1994 Apr;104(4):1113–1118. doi: 10.1104/pp.104.4.1113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H., Jones R. W. Cloning, characterization and functional expression of an endoglucanase-encoding gene from the phytopathogenic fungus Macrophomina phaseolina. Gene. 1995 May 26;158(1):125–128. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(95)00094-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Gogary S., Leite A., Crivellaro O., Eveleigh D. E., el-Dorry H. Mechanism by which cellulose triggers cellobiohydrolase I gene expression in Trichoderma reesei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6138–6141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]