Abstract
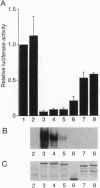
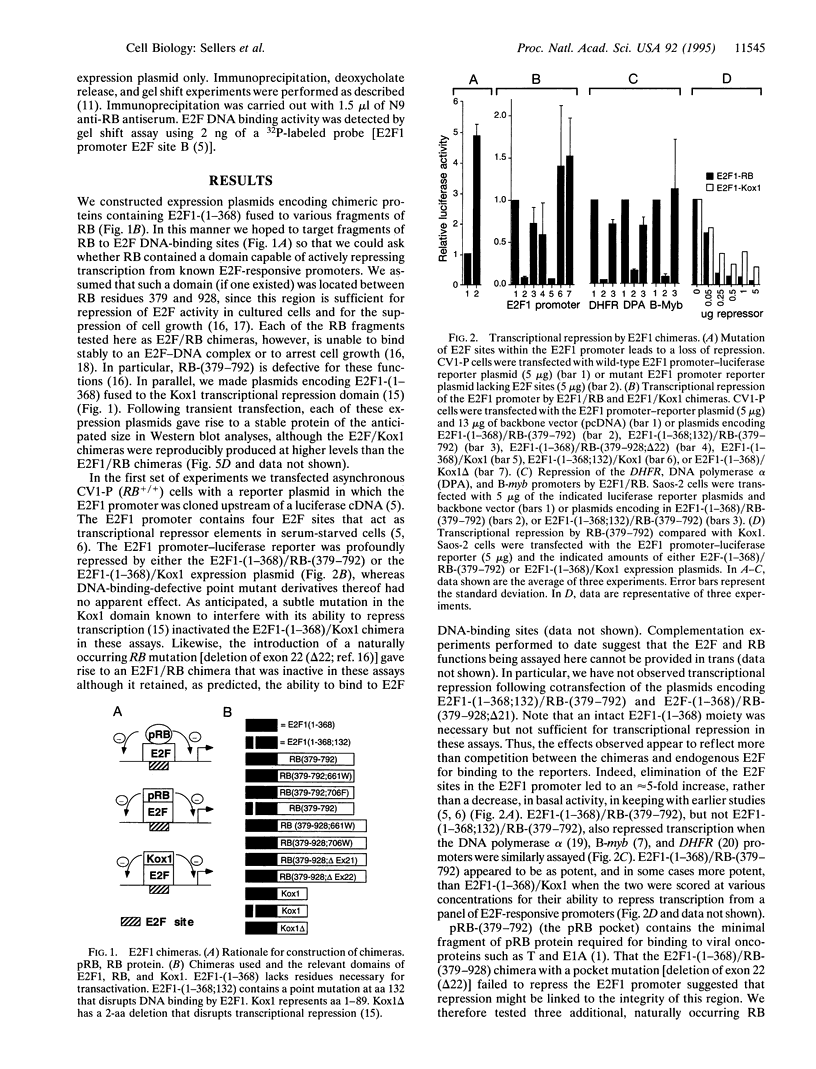
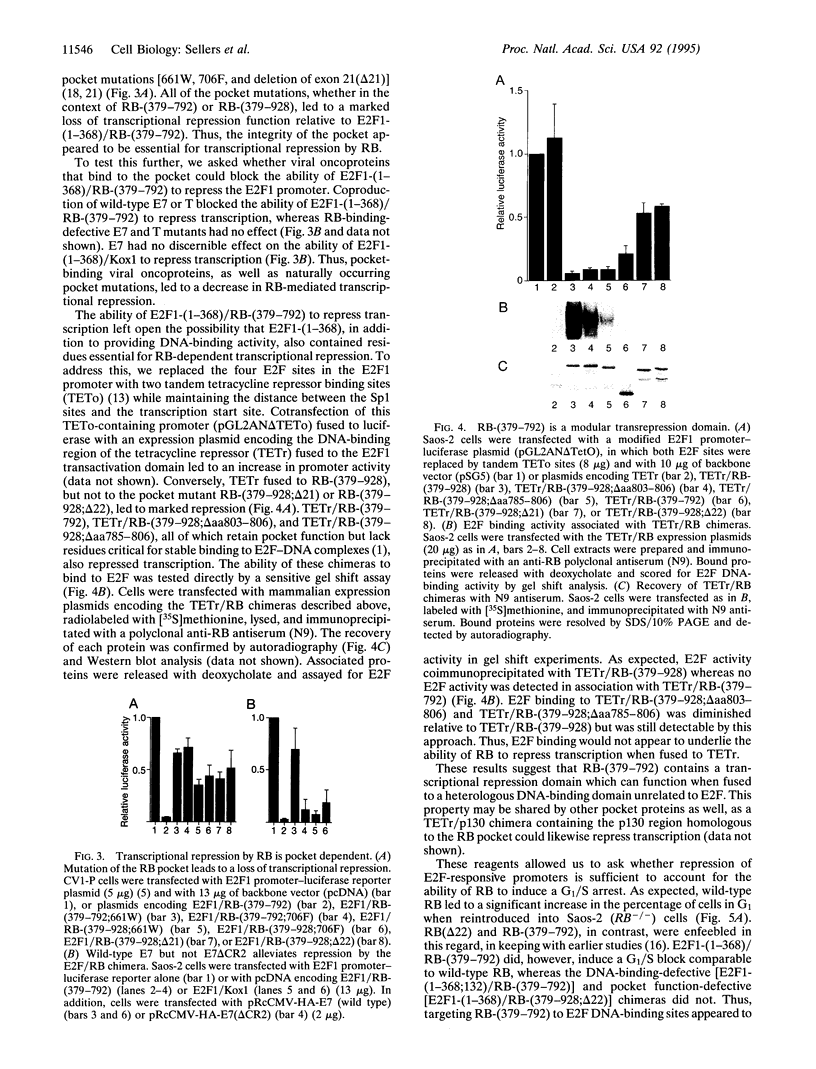
An intact T/E1A-binding domain (the pocket) is necessary, but not sufficient, for the retinoblastoma protein (RB) to bind to DNA-protein complexes containing E2F and for RB to induce a G1/S block. Indirect evidence suggests that the binding of RB to E2F may, in addition to inhibiting E2F transactivation function, generate a complex capable of functioning as a transrepressor. Here we show that a chimera in which the E2F1 transactivation domain was replaced with the RB pocket could, in a DNA-binding and pocket-dependent manner, mimic the ability of RB to repress transcription and induce a cell cycle arrest. In contrast, a transdominant negative E2F1 mutant that is capable of blocking E2F-dependent transactivation did not. Fusion of the RB pocket to a heterologous DNA-binding domain unrelated to E2F likewise generated a transrepressor protein when scored against a suitable reporter. These results suggest that growth suppression by RB is due, at least in part, to transrepression mediated by the pocket domain bound to certain promoters via E2F.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. D., Kaelin W. G., Jr Transcriptional control by E2F. Semin Cancer Biol. 1995 Apr;6(2):99–108. doi: 10.1006/scbi.1995.0013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adnane J., Shao Z., Robbins P. D. The retinoblastoma susceptibility gene product represses transcription when directly bound to the promoter. J Biol Chem. 1995 Apr 14;270(15):8837–8843. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.15.8837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arroyo M., Bagchi S., Raychaudhuri P. Association of the human papillomavirus type 16 E7 protein with the S-phase-specific E2F-cyclin A complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;13(10):6537–6546. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.10.6537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azizkhan J. C., Jensen D. E., Pierce A. J., Wade M. Transcription from TATA-less promoters: dihydrofolate reductase as a model. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 1993;3(4):229–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremner R., Cohen B. L., Sopta M., Hamel P. A., Ingles C. J., Gallie B. L., Phillips R. A. Direct transcriptional repression by pRB and its reversal by specific cyclins. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Jun;15(6):3256–3265. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.6.3256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chittenden T., Livingston D. M., DeCaprio J. A. Cell cycle analysis of E2F in primary human T cells reveals novel E2F complexes and biochemically distinct forms of free E2F. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):3975–3983. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.3975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodrich D. W., Wang N. P., Qian Y. W., Lee E. Y., Lee W. H. The retinoblastoma gene product regulates progression through the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):293–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90181-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossen M., Bujard H. Tight control of gene expression in mammalian cells by tetracycline-responsive promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5547–5551. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan K. L., Jenkins C. W., Li Y., Nichols M. A., Wu X., O'Keefe C. L., Matera A. G., Xiong Y. Growth suppression by p18, a p16INK4/MTS1- and p14INK4B/MTS2-related CDK6 inhibitor, correlates with wild-type pRb function. Genes Dev. 1994 Dec 15;8(24):2939–2952. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.24.2939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamel P. A., Gill R. M., Phillips R. A., Gallie B. L. Regions controlling hyperphosphorylation and conformation of the retinoblastoma gene product are independent of domains required for transcriptional repression. Oncogene. 1992 Apr;7(4):693–701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi R., Krummel B., Saiki R. K. A general method of in vitro preparation and specific mutagenesis of DNA fragments: study of protein and DNA interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7351–7367. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang P. S., Patrick D. R., Edwards G., Goodhart P. J., Huber H. E., Miles L., Garsky V. M., Oliff A., Heimbrook D. C. Protein domains governing interactions between E2F, the retinoblastoma gene product, and human papillomavirus type 16 E7 protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):953–960. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda M. A., Nevins J. R. Identification of distinct roles for separate E1A domains in disruption of E2F complexes. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;13(11):7029–7035. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.11.7029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaelin W. G., Jr, Krek W., Sellers W. R., DeCaprio J. A., Ajchenbaum F., Fuchs C. S., Chittenden T., Li Y., Farnham P. J., Blanar M. A. Expression cloning of a cDNA encoding a retinoblastoma-binding protein with E2F-like properties. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):351–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90108-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaelin W. G., Jr, Pallas D. C., DeCaprio J. A., Kaye F. J., Livingston D. M. Identification of cellular proteins that can interact specifically with the T/E1A-binding region of the retinoblastoma gene product. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):521–532. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90236-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koh J., Enders G. H., Dynlacht B. D., Harlow E. Tumour-derived p16 alleles encoding proteins defective in cell-cycle inhibition. Nature. 1995 Jun 8;375(6531):506–510. doi: 10.1038/375506a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li R., Botchan M. R. The acidic transcriptional activation domains of VP16 and p53 bind the cellular replication protein A and stimulate in vitro BPV-1 DNA replication. Cell. 1993 Jun 18;73(6):1207–1221. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90649-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuman E., Flemington E. K., Sellers W. R., Kaelin W. G., Jr Transcription of the E2F-1 gene is rendered cell cycle dependent by E2F DNA-binding sites within its promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;14(10):6607–6615. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.10.6607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson B. E., Nasheuer H. P., Wang T. S. Human DNA polymerase alpha gene: sequences controlling expression in cycling and serum-stimulated cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):2081–2095. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.2081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qin X. Q., Chittenden T., Livingston D. M., Kaelin W. G., Jr Identification of a growth suppression domain within the retinoblastoma gene product. Genes Dev. 1992 Jun;6(6):953–964. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.6.953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qin X. Q., Livingston D. M., Ewen M., Sellers W. R., Arany Z., Kaelin W. G., Jr The transcription factor E2F-1 is a downstream target of RB action. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Feb;15(2):742–755. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.2.742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz J. K., Devoto S. H., Smith E. J., Chellappan S. P., Jakoi L., Nevins J. R. Interactions of the p107 and Rb proteins with E2F during the cell proliferation response. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):1013–1020. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05742.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slansky J. E., Li Y., Kaelin W. G., Farnham P. J. A protein synthesis-dependent increase in E2F1 mRNA correlates with growth regulation of the dihydrofolate reductase promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1610–1618. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub S. J., Chow K. N., Luo R. X., Zhang S. H., He S., Dean D. C. Mechanism of active transcriptional repression by the retinoblastoma protein. Nature. 1995 Jun 29;375(6534):812–815. doi: 10.1038/375812a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub S. J., Prater C. A., Dean D. C. Retinoblastoma protein switches the E2F site from positive to negative element. Nature. 1992 Jul 16;358(6383):259–261. doi: 10.1038/358259a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu E. W., Clemens K. E., Heck D. V., Münger K. The human papillomavirus E7 oncoprotein and the cellular transcription factor E2F bind to separate sites on the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):2402–2407. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.2402-2407.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]