Abstract
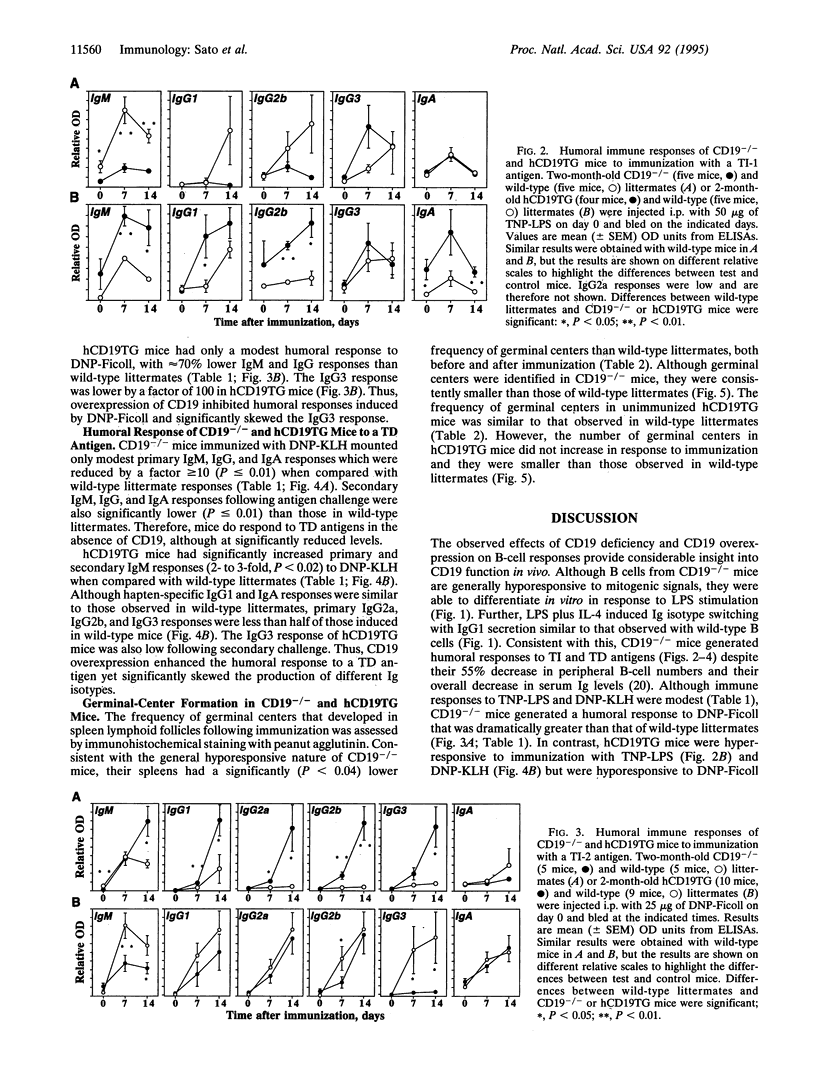
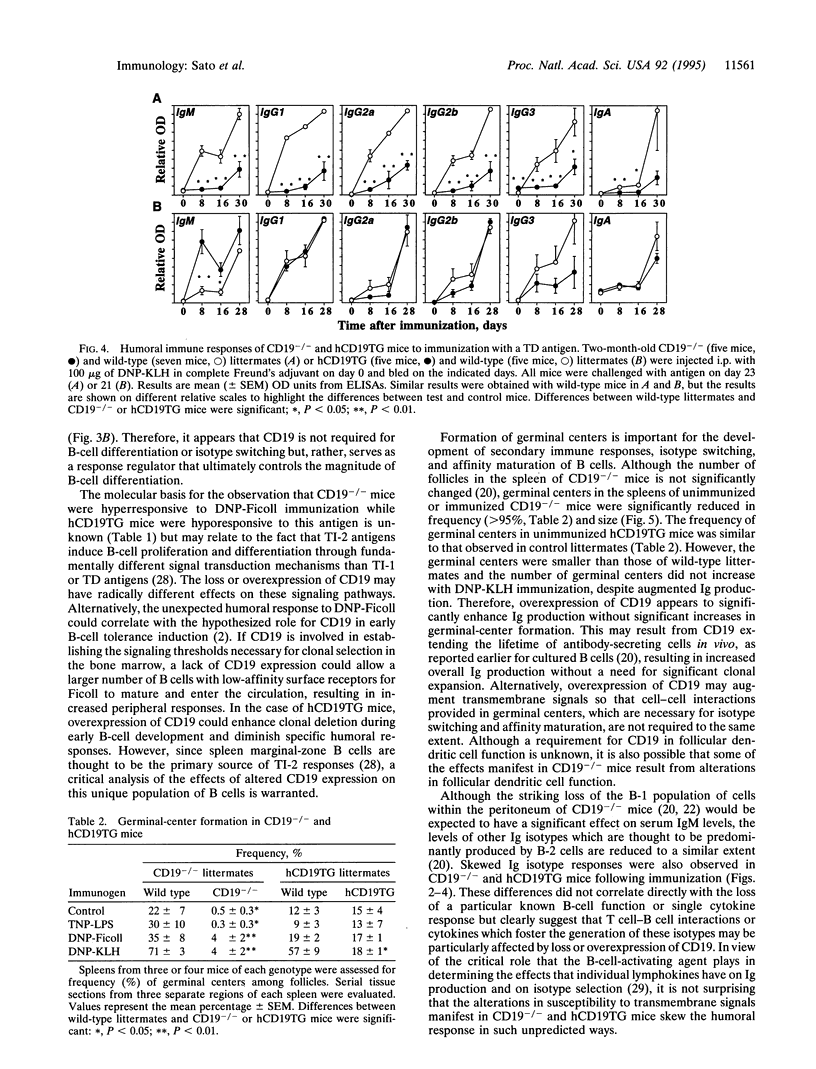
The phenotypes of CD19-deficient (CD19-/-) mice, and human CD19-transgenic (hCD19TG) mice that overexpress CD19 indicate that CD19 is a response regulator of B-lymphocyte surface receptor signaling. To further characterize the function of CD19 during B-cell differentiation, humoral immune responses to a T-cell-independent type 1 [trinitrophenyl-lipopolysaccharide (TNP-LPS)], a T-cell-independent type 2 [dinitrophenyl (DNP)-Ficoll], and a T-cell-dependent [DNP-keyhole limpet hemocyanin (KLH)] antigen were assessed in CD19-/- and hCD19TG mice. B cells from CD19-/- mice differentiated and underwent immunoglobulin isotype switching in vitro in response to mitogens and cytokines. In vivo, CD19-/- mice generated humoral responses to TNP-LPS and DNP-KLH that were dramatically lower than those of wild-type littermates. Surprisingly, the humoral response to DNP-Ficoll was significantly greater in CD19-/- mice. In contrast, hCD19TG mice were hyperresponsive to TNP-LPS and DNP-KLH immunization but were hyporesponsive to DNP-Ficoll. These results demonstrate that CD19 is not required for B-cell differentiation and isotype switching but serves as a response regulator which modulates B-cell differentiation. Since humoral responses to both T-cell-dependent and T-cell-independent antigens were similarly affected by alterations in CD19 expression, these differences are most likely to result from intrinsic changes in B-cell function rather than from the selective disruption of B-cell interactions with T cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrett T. B., Shu G. L., Draves K. E., Pezzutto A., Clark E. A. Signaling through CD19, Fc receptors or transforming growth factor-beta: each inhibits the activation of resting human B cells differently. Eur J Immunol. 1990 May;20(5):1053–1059. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury L. E., Kansas G. S., Levy S., Evans R. L., Tedder T. F. The CD19/CD21 signal transducing complex of human B lymphocytes includes the target of antiproliferative antibody-1 and Leu-13 molecules. J Immunol. 1992 Nov 1;149(9):2841–2850. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter R. H., Fearon D. T. CD19: lowering the threshold for antigen receptor stimulation of B lymphocytes. Science. 1992 Apr 3;256(5053):105–107. doi: 10.1126/science.1373518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter R. H., Tuveson D. A., Park D. J., Rhee S. G., Fearon D. T. The CD19 complex of B lymphocytes. Activation of phospholipase C by a protein tyrosine kinase-dependent pathway that can be enhanced by the membrane IgM complex. J Immunol. 1991 Dec 1;147(11):3663–3671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel P., Zhou L. J., Ord D. C., Sato S., Koller B., Tedder T. F. Abnormal B lymphocyte development, activation, and differentiation in mice that lack or overexpress the CD19 signal transduction molecule. Immunity. 1995 Jul;3(1):39–50. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(95)90157-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T., Carter R. H. The CD19/CR2/TAPA-1 complex of B lymphocytes: linking natural to acquired immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1995;13:127–149. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.13.040195.001015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Förster I., Rajewsky K. Expansion and functional activity of Ly-1+ B cells upon transfer of peritoneal cells into allotype-congenic, newborn mice. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Apr;17(4):521–528. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy R. R., Carmack C. E., Li Y. S., Hayakawa K. Distinctive developmental origins and specificities of murine CD5+ B cells. Immunol Rev. 1994 Feb;137:91–118. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1994.tb00660.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haughton G., Arnold L. W., Whitmore A. C., Clarke S. H. B-1 cells are made, not born. Immunol Today. 1993 Feb;14(2):84–91. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90064-R. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A. Toward a layered immune system. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):953–954. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90748-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kansas G. S., Tedder T. F. Transmembrane signals generated through MHC class II, CD19, CD20, CD39, and CD40 antigens induce LFA-1-dependent and independent adhesion in human B cells through a tyrosine kinase-dependent pathway. J Immunol. 1991 Dec 15;147(12):4094–4102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantor A. B. The development and repertoire of B-1 cells (CD5 B cells). Immunol Today. 1991 Nov;12(11):389–391. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90136-H. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mond J. J., Lees A., Snapper C. M. T cell-independent antigens type 2. Annu Rev Immunol. 1995;13:655–692. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.13.040195.003255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadler L. M., Anderson K. C., Marti G., Bates M., Park E., Daley J. F., Schlossman S. F. B4, a human B lymphocyte-associated antigen expressed on normal, mitogen-activated, and malignant B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):244–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pezzutto A., Dörken B., Rabinovitch P. S., Ledbetter J. A., Moldenhauer G., Clark E. A. CD19 monoclonal antibody HD37 inhibits anti-immunoglobulin-induced B cell activation and proliferation. J Immunol. 1987 May 1;138(9):2793–2799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickert R. C., Rajewsky K., Roes J. Impairment of T-cell-dependent B-cell responses and B-1 cell development in CD19-deficient mice. Nature. 1995 Jul 27;376(6538):352–355. doi: 10.1038/376352a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigley K. P., Callard R. E. Inhibition of B cell proliferation with anti-CD19 monoclonal antibodies: anti-CD19 antibodies do not interfere with early signaling events triggered by anti-IgM or interleukin 4. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Mar;21(3):535–540. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijkers G. T., Griffioen A. W., Zegers B. J., Cambier J. C. Ligation of membrane immunoglobulin leads to inactivation of the signal-transducing ability of membrane immunoglobulin, CD19, CD21, and B-cell gp95. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8766–8770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolink A., Melchers F. Molecular and cellular origins of B lymphocyte diversity. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1081–1094. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90032-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snapper C. M., Mond J. J. Towards a comprehensive view of immunoglobulin class switching. Immunol Today. 1993 Jan;14(1):15–17. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90318-F. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tedder T. F., Isaacs C. M. Isolation of cDNAs encoding the CD19 antigen of human and mouse B lymphocytes. A new member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 15;143(2):712–717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tedder T. F., Zhou L. J., Engel P. The CD19/CD21 signal transduction complex of B lymphocytes. Immunol Today. 1994 Sep;15(9):437–442. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(94)90274-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuveson D. A., Carter R. H., Soltoff S. P., Fearon D. T. CD19 of B cells as a surrogate kinase insert region to bind phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Science. 1993 May 14;260(5110):986–989. doi: 10.1126/science.7684160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uckun F. M., Burkhardt A. L., Jarvis L., Jun X., Stealey B., Dibirdik I., Myers D. E., Tuel-Ahlgren L., Bolen J. B. Signal transduction through the CD19 receptor during discrete developmental stages of human B-cell ontogeny. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 5;268(28):21172–21184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uckun F. M., Ledbetter J. A. Immunobiologic differences between normal and leukemic human B-cell precursors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8603–8607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weng W. K., Jarvis L., LeBien T. W. Signaling through CD19 activates Vav/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway and induces formation of a CD19/Vav/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase complex in human B cell precursors. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 23;269(51):32514–32521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou L. J., Ord D. C., Hughes A. L., Tedder T. F. Structure and domain organization of the CD19 antigen of human, mouse, and guinea pig B lymphocytes. Conservation of the extensive cytoplasmic domain. J Immunol. 1991 Aug 15;147(4):1424–1432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou L. J., Smith H. M., Waldschmidt T. J., Schwarting R., Daley J., Tedder T. F. Tissue-specific expression of the human CD19 gene in transgenic mice inhibits antigen-independent B-lymphocyte development. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;14(6):3884–3894. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.6.3884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Noesel C. J., Lankester A. C., van Lier R. A. Dual antigen recognition by B cells. Immunol Today. 1993 Jan;14(1):8–11. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90316-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]