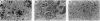Abstract
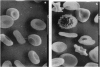
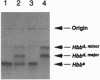
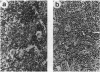
We have used a "plug and socket" targeting technique to generate a mouse model of beta 0-thalassemia in which both the b1 and b2 adult globin genes have been deleted. Mice homozygous for this deletion (Hbbth-3/Hbbth-3) die perinatally, similar to the most severe form of Cooley anemia in humans. Mice heterozygous for the deletion appear normal, but their hematologic indices show characteristics typical of severe thalassemia, including dramatically decreased hematocrit, hemoglobin, red blood cell counts, mean corpuscular volume, mean corpuscular hemoglobin, and mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration, as well as dramatically increased reticulocyte counts, serum bilirubin concentrations, and red cell distribution widths. Tissue and organ damage typical of beta-thalassemia, such as bone deformities and splenic enlargement due to increased hematopoiesis, are also seen in the heterozygous animals, as is spontaneous iron overload in the spleen, liver, and kidneys. The mice homozygous for the b1 and b2 deletions should be of great value in developing therapies for the treatment of thalassemias in utero. The heterozygous animals will be useful for studying the pathophysiology of thalassemias and have the potential of generating a model of sickle cell anemia when mated with appropriate transgenic animals.
Full text
PDF

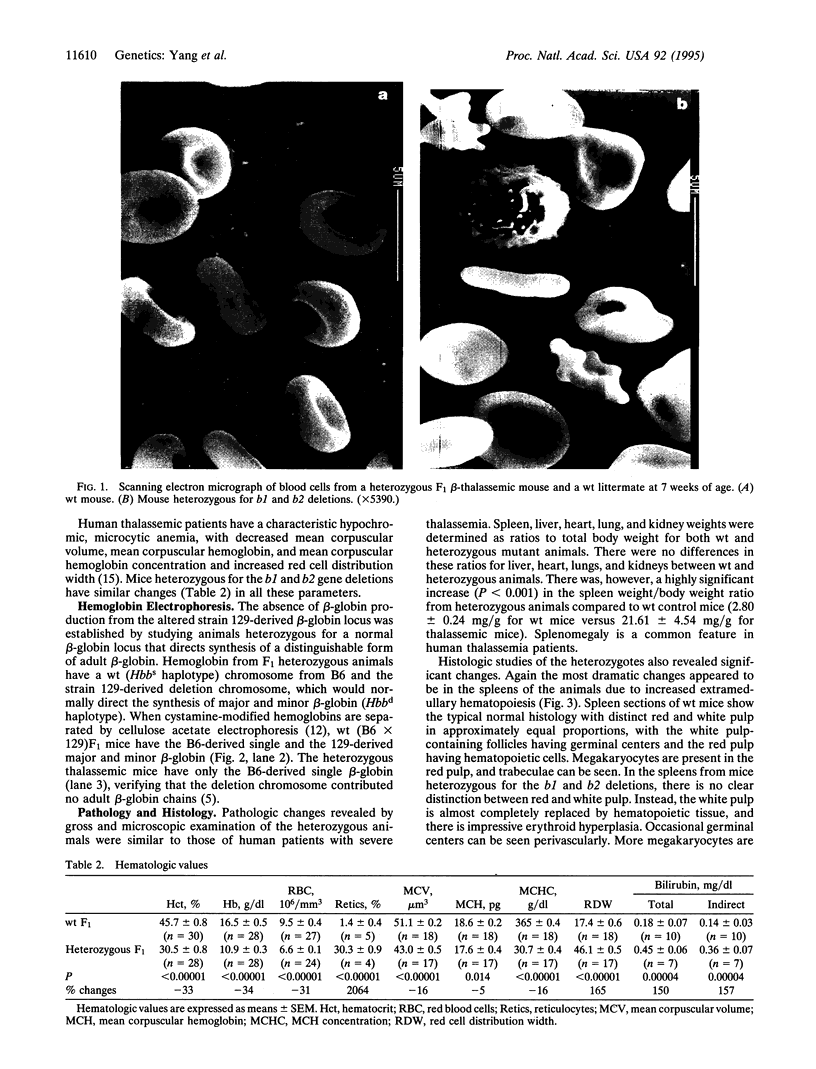
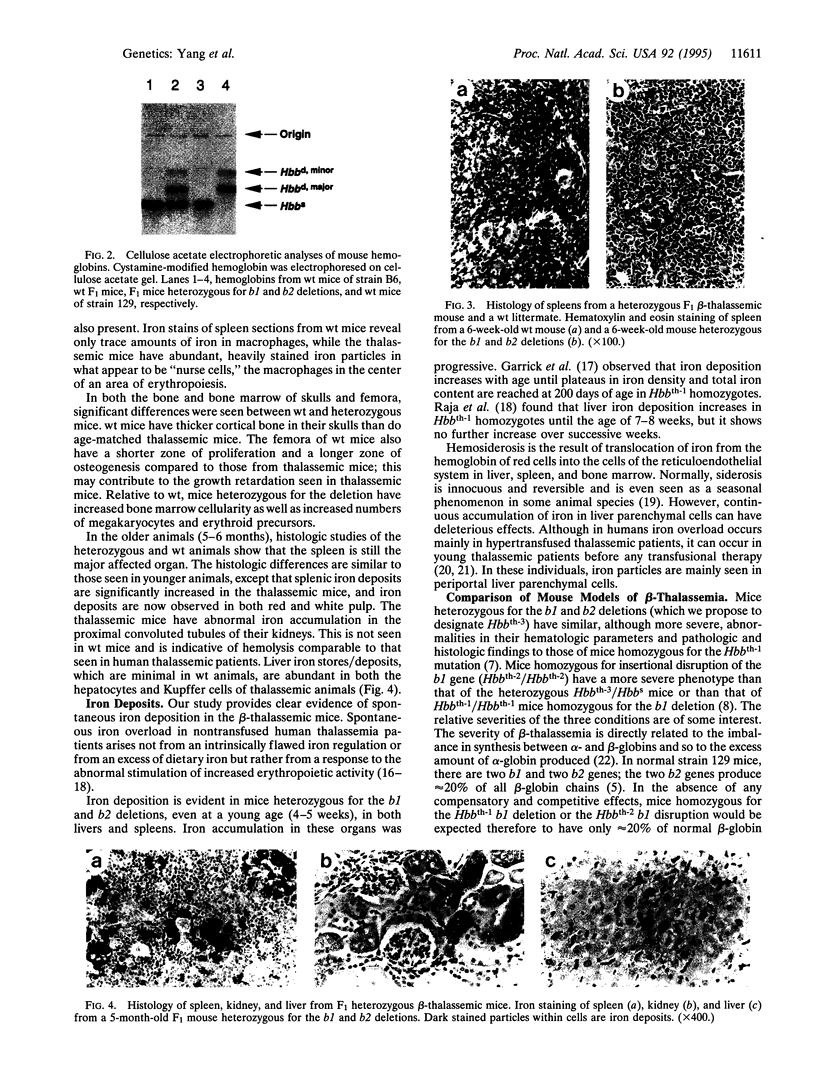

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Advani R., Rubin E., Mohandas N., Schrier S. L. Oxidative red blood cell membrane injury in the pathophysiology of severe mouse beta-thalassemia. Blood. 1992 Feb 15;79(4):1064–1067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borch-Iohnsen B., Nilssen K. J. Seasonal iron overload in Svalbard reindeer liver. J Nutr. 1987 Dec;117(12):2072–2078. doi: 10.1093/jn/117.12.2072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciavatta D. J., Ryan T. M., Farmer S. C., Townes T. M. Mouse model of human beta zero thalassemia: targeted deletion of the mouse beta maj- and beta min-globin genes in embryonic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Sep 26;92(20):9259–9263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.20.9259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Codrington J. F., Li H. W., Kutlar F., Gu L. H., Ramachandran M., Huisman T. H. Observations on the levels of Hb A2 in patients with different beta-thalassemia mutations and a delta chain variant. Blood. 1990 Sep 15;76(6):1246–1249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curcio M. J., Kantoff P., Schafer M. P., Anderson W. F., Safer B. Compensatory increase in levels of beta minor globin in murine beta-thalassemia is under translational control. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 5;261(34):16126–16132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detloff P. J., Lewis J., John S. W., Shehee W. R., Langenbach R., Maeda N., Smithies O. Deletion and replacement of the mouse adult beta-globin genes by a "plug and socket" repeated targeting strategy. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;14(10):6936–6943. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.10.6936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrick L. M., Strano-Paul L. A., Hoke J. E., Kirdani-Ryan L. A., Alberico R. A., Everett M. M., Bannerman R. M., Garrick M. D. Tissue iron deposition in untransfused beta-thalassemic mice. Exp Hematol. 1989 Jun;17(5):423–428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iancu T. C., Landing B. H., Neustein H. B. Pathogenetic mechanisms in hepatic cirrhosis of thalassemia major: light and electron microscopic studies. Pathol Annu. 1977;12(Pt 1):171–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iancu T. C., Shiloh H. Morphologic observations in iron overload: an update. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1994;356:255–265. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-2554-7_27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn C. L., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Phillips S. J., Weaver S., Haigwood N. L., Voliva C. F., Edgell M. H. DNA sequence organization of the beta-globin complex in the BALB/c mouse. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):159–168. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90123-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller B. H., Kim H. S., Latour A. M., Brigman K., Boucher R. C., Jr, Scambler P., Wainwright B., Smithies O. Toward an animal model of cystic fibrosis: targeted interruption of exon 10 of the cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator gene in embryonic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10730–10734. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popp R. A., Popp D. M., Johnson F. M., Skow L. C., Lewis S. E. Hematology of a murine beta-thalassemia: a longitudinal study. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;445:432–444. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb17213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raja K. B., Simpson R. J., Peters T. J. Intestinal iron absorption studies in mouse models of iron-overload. Br J Haematol. 1994 Jan;86(1):156–162. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1994.tb03267.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell E. S. Hereditary anemias of the mouse: a review for geneticists. Adv Genet. 1979;20:357–459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shehee W. R., Oliver P., Smithies O. Lethal thalassemia after insertional disruption of the mouse major adult beta-globin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3177–3181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skow L. C., Burkhart B. A., Johnson F. M., Popp R. A., Popp D. M., Goldberg S. Z., Anderson W. F., Barnett L. B., Lewis S. E. A mouse model for beta-thalassemia. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):1043–1052. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90562-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VANABLE J. W., Jr GRANULAR GLAND DEVELOPMENT DURING XENOPUS LAEVIS METAMORPHOSIS. Dev Biol. 1964 Dec;10:331–357. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(64)90049-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Wyck D. B., Tancer M. E., Popp R. A. Iron homeostasis in beta-thalassemic mice. Blood. 1987 Nov;70(5):1462–1465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitelaw E., Tsai S. F., Hogben P., Orkin S. H. Regulated expression of globin chains and the erythroid transcription factor GATA-1 during erythropoiesis in the developing mouse. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6596–6606. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitney J. B., 3rd Simplified typing of mouse hemoglobin (Hbb) phenotypes using cystamine. Biochem Genet. 1978 Aug;16(7-8):667–672. doi: 10.1007/BF00484723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]