Abstract
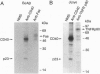
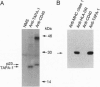
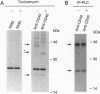
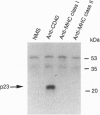
CD40 is a 45-kDa glycoprotein member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR) family expressed on B cells, thymic epithelial cells, dendritic cells, and some carcinoma cells. The unique capacity of CD40 to trigger immunoglobulin isotype switching is dependent on the activation of protein-tyrosine kinases, yet CD40 possesses no kinase domain and no known consensus sequences for binding to protein-tyrosine kinases. Recently, an intracellular protein (CD40bp/LAP-1/CRAF-1) which belongs to the family of TNFR-associated proteins was reported to associate with CD40. We describe a 23-kDa cell surface protein (p23) which is specifically associated with CD40 on B cells and on urinary bladder transitional carcinoma cells. Protein microsequencing revealed that p23 shows no homology to any known protein. A rabbit antibody raised against a peptide derived from p23 recognized a 23-kDa protein in CD40 immunoprecipitates. In contrast to CD40bp/LAP-1/CRAF-1, p23 was not associated with TNFR p80 (CD120b). These findings suggest that p23 is a novel member of the CD40 receptor complex.
Full text
PDF

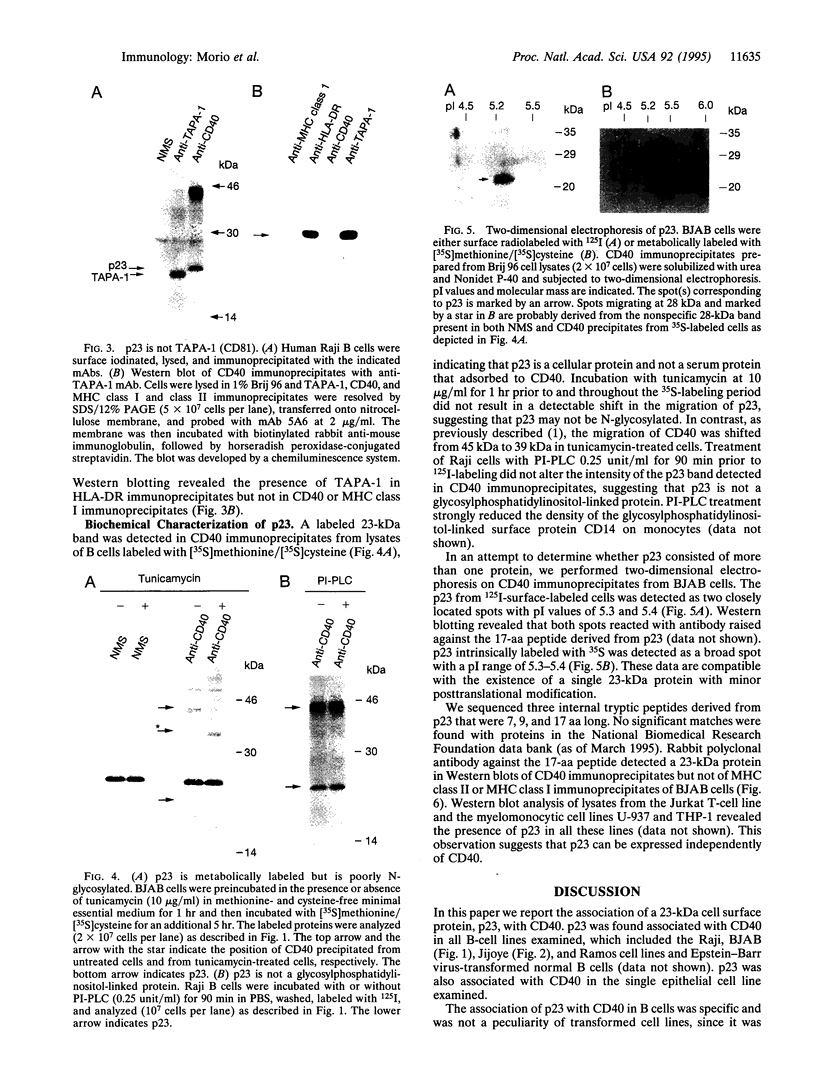

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banchereau J., Bazan F., Blanchard D., Brière F., Galizzi J. P., van Kooten C., Liu Y. J., Rousset F., Saeland S. The CD40 antigen and its ligand. Annu Rev Immunol. 1994;12:881–922. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.12.040194.004313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury L. E., Goldmacher V. S., Tedder T. F. The CD19 signal transduction complex of B lymphocytes. Deletion of the CD19 cytoplasmic domain alters signal transduction but not complex formation with TAPA-1 and Leu 13. J Immunol. 1993 Sep 15;151(6):2915–2927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castigli E., Alt F. W., Davidson L., Bottaro A., Mizoguchi E., Bhan A. K., Geha R. S. CD40-deficient mice generated by recombination-activating gene-2-deficient blastocyst complementation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 6;91(25):12135–12139. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.25.12135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng G., Cleary A. M., Ye Z. S., Hong D. I., Lederman S., Baltimore D. Involvement of CRAF1, a relative of TRAF, in CD40 signaling. Science. 1995 Mar 10;267(5203):1494–1498. doi: 10.1126/science.7533327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faris M., Gaskin F., Parsons J. T., Fu S. M. CD40 signaling pathway: anti-CD40 monoclonal antibody induces rapid dephosphorylation and phosphorylation of tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins including protein tyrosine kinase Lyn, Fyn, and Syk and the appearance of a 28-kD tyrosine phosphorylated protein. J Exp Med. 1994 Jun 1;179(6):1923–1931. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.6.1923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foy T. M., Laman J. D., Ledbetter J. A., Aruffo A., Claassen E., Noelle R. J. gp39-CD40 interactions are essential for germinal center formation and the development of B cell memory. J Exp Med. 1994 Jul 1;180(1):157–163. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.1.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu H. M., O'Rourke K., Boguski M. S., Dixit V. M. A novel RING finger protein interacts with the cytoplasmic domain of CD40. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 2;269(48):30069–30072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabara H. H., Fu S. M., Geha R. S., Vercelli D. CD40 and IgE: synergism between anti-CD40 monoclonal antibody and interleukin 4 in the induction of IgE synthesis by highly purified human B cells. J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1861–1864. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawabe T., Naka T., Yoshida K., Tanaka T., Fujiwara H., Suematsu S., Yoshida N., Kishimoto T., Kikutani H. The immune responses in CD40-deficient mice: impaired immunoglobulin class switching and germinal center formation. Immunity. 1994 Jun;1(3):167–178. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(94)90095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koho H., Paulie S., Ben-Aissa H., Jónsdóttir I., Hansson Y., Lundblad M. L., Perlmann P. Monoclonal antibodies to antigens associated with transitional cell carcinoma of the human urinary bladder. I. Determination of the selectivity of six antibodies by cell ELISA and immunofluorescence. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1984;17(3):165–172. doi: 10.1007/BF00205481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh R. K., Jabara H. H., Ren C. L., Fu S. M., Geha R. S. Role of protein tyrosine kinases in CD40/interleukin-4-mediated isotype switching to IgE. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1994 Oct;94(4):784–792. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(94)90187-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh R. K., Jabara H. H., Ren C. L., Fu S. M., Vercelli D., Geha R. S. Role of protein tyrosine kinases and phosphatases in isotype switching: crosslinking CD45 to CD40 inhibits IgE isotype switching in human B cells. Immunol Lett. 1995 Feb;45(1-2):99–106. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(94)00233-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallett S., Barclay A. N. A new superfamily of cell surface proteins related to the nerve growth factor receptor. Immunol Today. 1991 Jul;12(7):220–223. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90033-P. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morio T., Geha R. S., Chatila T. A. Engagement of MHC class II molecules by staphylococcal superantigens activates src-type protein tyrosine kinases. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Mar;24(3):651–658. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830240325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosialos G., Birkenbach M., Yalamanchili R., VanArsdale T., Ware C., Kieff E. The Epstein-Barr virus transforming protein LMP1 engages signaling proteins for the tumor necrosis factor receptor family. Cell. 1995 Feb 10;80(3):389–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90489-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren C. L., Morio T., Fu S. M., Geha R. S. Signal transduction via CD40 involves activation of lyn kinase and phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase, and phosphorylation of phospholipase C gamma 2. J Exp Med. 1994 Feb 1;179(2):673–680. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.2.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schick M. R., Levy S. The TAPA-1 molecule is associated on the surface of B cells with HLA-DR molecules. J Immunol. 1993 Oct 15;151(8):4090–4097. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholl P. R., Geha R. S. Physical association between the high-affinity IgG receptor (Fc gamma RI) and the gamma subunit of the high-affinity IgE receptor (Fc epsilon RI gamma). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 1;90(19):8847–8850. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.19.8847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spertini F., Chatila T., Geha R. S. Signals delivered via MHC class II molecules synergize with signals delivered via TCR/CD3 to cause proliferation and cytokine gene expression in T cells. J Immunol. 1992 Jul 1;149(1):65–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. V., Scholl P. R., Geha R. S. Physical and functional association of the high affinity immunoglobulin G receptor (Fc gamma RI) with the kinases Hck and Lyn. J Exp Med. 1994 Sep 1;180(3):1165–1170. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.3.1165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yellin M. J., Sinning J., Covey L. R., Sherman W., Lee J. J., Glickman-Nir E., Sippel K. C., Rogers J., Cleary A. M., Parker M. T lymphocyte T cell-B cell-activating molecule/CD40-L molecules induce normal B cells or chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells to express CD80 (B7/BB-1) and enhance their costimulatory activity. J Immunol. 1994 Jul 15;153(2):666–674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]