Abstract
Patients with primary myelofibrosis have increased risk for bleeding and thrombosis. It is debated whether propensity to thrombosis is due to increased numbers of platelet microparticles and/or to pathological platelet-neutrophil interactions. Platelet neutrophil interactions are mediated by P-selectin and even though the megakaryocytes of myelofibrosis patients express normal levels of P-selectin, it remains abnormally localized to the demarcation membrane system rather than being assembled into the α-granules in platelets. Mice carrying the hypomorphic Gata1low mutation express the same megakaryocyte abnormalities presented by primary myelofibrosis patients, including abnormal P-selectin localization to the DMS and develop with age myelofibrosis, a disease that closely resembles human primary myelofibrosis. Whether these mice would also develop thrombosis has not been investigated as yet. The aim of this study was to determine whether Gata1low mice would develop thrombosis with age and, in this case, the role played by P-selectin in the development of the trait. To this aim, Gata1low mice were crossed with P-selnull mice according to standard genetic protocols and Gata1lowP-selwt, Gata1lowP-selnull and Gata1WTP-selnull or Gata1wtP-selwt (as controls) littermates obtained. It was shown that platelet counts, but not hematocrit, are reduced in Gata1low mice. Moreover, platelet microparticles are reduced in Gata1low mice and P-selectin positive platelet microparticles were not found. To determine the phenotypic implications of the different mutations, bleeding time was estimated by a tail cut procedure. Mutant mice were sacrificed and presence of thrombosis was determined by immunohistological staining of organs. Gata1low mice with or without the P-selectin null trait had a prolonged bleeding time compared to wild type mice. However, in Gata1low mice significantly higher frequency of thrombotic events was seen in adult and old Gata1low mice compared to Gata1lowP-selnull mice. Thus, presence of the P-selectin null trait rescued Gata1low mice from the thrombotic phenotype, but did not change the level of platelet microparticles. Taken together these data indicate that abnormal localization of P-selectin, induced by the Gata1low mutation, and thus, increased pathological interactions with leucocytes, is responsible for the increased presence of thrombosis seen in these mice.
Keywords: Microparticles, myelofibrosis, P-selectin, platelet, thrombosis
Introduction
Primary myelofibrosis (PMF) is a myeloproliferative disorder characterized by bone marrow (BM) fibrosis and extensive extramedullary hematopoiesis [1]. According to current understanding, it is caused by sequential somatic mutations affecting the mpl-TPO pathway in an early stem cell with capacity to differentiate into myeloid, erythroid and megakaryocytic linages [2].
A main characteristic of patients with myeloproliferative disorders, that also include polycythemia vera (PV) and essential thrombocytosis (ET), is an increased incidence of thrombosis, responsible for the major morbidity in the two latter diseases [3]. However, contrary to ET and PV, where a normal life expectancy can be anticipated, PMF is characterized by a progressive clinical course and a shortened life expectancy, with median survival after diagnosis of less than 5 years [1]. Main causes of morbidity and mortality are the result of leukemic transformation, infection, portal hypertension and vascular complications, i.e. both bleeding and thrombosis. The incidence of thrombosis in patients with PMF is increased compared with the general population [4] and comparable with the incidence of patients with ET. JAK2 V617F mutational status has an independent prognostic role and interacts with leukocytosis [5].
In PV and ET increased cell mass (red cell mass and platelet count, respectively) is an important factor that contribute to the pathogenesis of thrombosis [6]. It has been suggested that in PV and ET, the interplay between prothrombotic changes of the malignant clone (i.e. increased release of platelet microparticles (PMPs) and leukocyte-derived proteases) and the inflammatory response by host endothelial cells (i.e. secretion of pro-coagulant molecules, cytokines and expression of adhesion molecules) ultimately provokes the pro coagulant phenotype [7]. In myelofibrosis, anemia is a hallmark of the disease and thrombocytopenia is often seen at late stages, leaving increased cell mass an unlikely cause of thrombosis in these patients. Instead, one might hypothesize that pro-fibrotic and pro-angiogenic growth factors released by immature megakaryocytes (MKs) in the bone marrow might induce a pro coagulant state by a direct action on endothelial cells. However, patients with PV and fibrosis were recently shown to be less prone to develop thrombosis than PV patients without [8]. Moreover, bone marrow fibrosis has recently been demonstrated in X-linked thrombocytopenia with thalassemia (XLTT) [9], a rare inherited disorder characterized by presence of immature MKs in the bone marrow, thrombocytopenia, red cell hemolysis, splenomegaly and a β-thalassemia trait due to the mutation 216R>Q in exon 4 of the GATA-1 gene on the X-chromosome. In contrast to patients with patients with PMF, the reticulin fibrosis seems non progressive and patients have a bleeding diathesis and do not develop thrombosis [10, 11]. Taken together, these findings make a direct link between fibrosis and a pro thrombotic phenotype unlikely. In PMF one study has shown that some, but not all pro thrombotic changes of cells derived from the malignant clone present in PV and ET are seen (increased leukocyte count, pathological platelet activation and increased numbers of PMPs, but no increase in neutrophil-neutrophil aggregates) [12]. The interpretation of these results is made difficult both by the small number of patients investigated and by the fact that most of them were on either cytoreductive or platelet inhibitory treatment.
To study the underlying mechanisms of thrombosis in PMF in the untreated state, we have used an animal model represented by mice harboring a mutation resulting in reduced levels of Gata1 expression [13]. These mutants develop with age a PMF-like syndrome characterized by the presence of anemia, teardrop poikilocytes, bone marrow (BM) fibrosis and hematopoietic foci in the spleen and liver [14]. The hemizygous Gata1low mice that survive fetal anemia will in adult life still have less platelets in the peripheral blood, 15% compared to normal, and display an abnormal circular shape [13]. While patients with PMF have increased expression of P-selectin (P-sel) on platelets [12], levels of platelet P-sel expression in Gata1low mice has not yet been studied, but are normal in MKs. However, localization of P-sel in MKs is abnormal, P-sel fail to localize to α-granules and is found mainly in vacuoles and on the DMS [15]. Whether Gata1low mice also develop thrombosis is not known.
The aim of this study was to determine whether Gata1low mice develop thrombosis with age and, in this case, the role played by P-sel. To this aim, Gata1low mice were crossed with P-selnull mice according to standard genetic protocols and Gata1lowP-selwt, Gata1lowP-selnull and Gata1wtP-selnull or Gata1wtP-selwt (as controls) littermates obtained. We show here that Gata1low mice, similar to patients with PMF, have and increased incidence of thrombosis. Moreover, P-sel deficient Gata1low mice are rescued from thrombosis, implicating a major role of P-sel for the pro thrombotic phenotype of Gata1low mice and possibly, patients with PMF.
Materials and methods
Mice
The Gata1low mutation was experimentally induced in mice by deleting the first enhancer (DNA hypersensitive site I) and the distal promoter of the gene [16, 17]. A colony harboring the mutation in the CD1 background is bred at the animal facilities of the Istituto Superiore di Sanità, Rome, Italy. Littermates were genotyped at birth by PCR [18, 19], and those found not to carry the mutation were used as normal controls. Gata1low mice were then crossed with P-selnull mice (kindly provided by Dr Frenette) [20, 21] according to standard genetic protocols and Gata1lowP-selwt Gata1lowP-selnull and Gata1wtP-selnull or Gata1wtP-selwt (as controls) littermates were obtained. Blood sampling was performed by puncture of the retro-orbital plexus. All the experiments were performed with sex- and age-matched mice under protocols approved by the institutional animal care committee.
Hematological parameters
Freshly drawn blood was collected into sodium citrate containing tubes, yielding a final concentration of 0.1 M, (0.5 ml/sampling). Hematocrit (Hct), platelet (plt), counts were determined manually.
Determinations of platelet size and frequency of platelet microparticles
Platelet size was estimated by comparing their relative forward side scatter (FSC) signals with that of reference microspheres provided by the Flow Cytometry Size Calibration Kit (Invitrogen Moleclular Probe, Eugene, OR). Flow cytometry determinations were performed with the ARIA cell sorter (Becton Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, NJ). PMPs were determined essentially as described by Forlow et al. [22]. In short, platelet poor plasma (PPP) was obtained by serial centrifugation steps. PMPs were stained with biotin coupled anti CD62 with subsequent addition of phycoerythrin cyanine dye 7 (Pe-Cy7)-streptavidin, as well as Fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) conjugated anti CD61 both at 1 μl/106 cells. After washing, cells were resuspended in 300 μl 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid (HEPES) buffer pH 7.4. To estimate MP concentration, 50 μl of Count bright™ Absolute Counting Beads (Molecular Probes) was added to 300 μl of PPP and immediately analyzed by flow cytometry (Forlow SB, McEver RP et al. 2000). All antibodies were from PharMingen (San Diego, CA). Non-specific signals and dead cells were excluded, respectively, by fluorochrome-conjugated isotype controls and propidium iodide staining (5μg/mL; Sigma-Aldrich). Cell fluorescence was analyzed with the FACS Aria (Becton Dickinson, San Jose, CA, USA) and FlowJo (Ashland, OR, USA) software. Calculation of MP concentration was performed using the following formula:
where
A=number of cell events,
B=number of bead events,
C=assigned bead count of the lot (beads/50 μl),
D=volume of sample
Bleeding time
Bleeding time was determined as previously described [23]. Briefly, a 5mm segment was cut off the distal portion of the tail with a scalpel. The exposed vein was immediately submerged into a beaker containing 0.9% physiological saline. Bleeding from tail was observed and timed until bleeding cessation, which was defined as no bleeding or re bleeding for at least 60 seconds. Of ethical reasons the experiment was stopped after 600 seconds.
Splenectomy
Mice were anaesthetized with xylazine (10 mg/kg, Bayer, Milan, Italy) and ketamine (200 mg/kg, Gellini Farmaceutics, Latina, Italy) and the spleen was removed after double ligation of the splenic artery and vein, as described [24] The muscle, peritoneum and skin were closed in separate layers using sterile 5–0 absorbable suture.
Quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction determinations
Mice bone marrow cells were incubated for 30 min on ice with a Fcγ blocker (CD16/CD32) and then with phyco-erythrin (PE)-conjugated anti-CD61, and fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-conjugated anti-CD41 (all from BD-Pharmingen, San Diego, CA). Dead cells and non-specific signals were excluded by propidium iodide staining (5 mg/ml, Sigma-Aldrich) and appropriate isotype controls (BD-Pharmingen). Cells in the megakaryocytic gate (CD41+/CD61+) were isolated by sorting with the Aria cell sorter as described [25]. Total RNA was prepared by lysing the isolated cell population into Trizol (Gibco BRL). RNA was reverse transcribed with 2.5 μM random hexamers using the superscript kit (Invitrogen) and gene expression levels were quantified by real-time reverse-transcription PCR, as described [26]. GAPDH cDNA was amplified as an internal standard. Reactions were performed in an ABI PRISM 7700 Sequence Detection System (Applied Biosystems). Cycle threshold (Ct) was calculated with the SDS software Version 1.3.1 (Applied Biosystems) and mRNA levels were expressed as 2 − ΔCt (ΔCt=target gene Ct−GAPDH Ct).
Immuno electron microscopy
Spleen samples were fixed for 3 hours at 4 °C in a mixture of 2% paraformaldehyde and 0.1% glutaraldehyde in 0.1M cacodylate buffer, pH 7.6. They were dehydrated in alcohol at progressively higher concentrations and embedded in Bioacryl resin (British Biocell, Cardiff, United Kingdom), followed by UV polymerization, according to standard procedures [27]. Ultrathin sections were cut and mounted on 300 mesh nickel grids. To block non-specific binding sites, these grids were treated with a blocking buffer made of phosphate buffer saline supplemented with 0.1% Tween-20, 0.1% bovine serum albumin and 4% normal rabbit serum. Grids were incubated overnight in the presence of goat anti-P-selectin (catalogue no. sc-8068, Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA, USA.). The antibody recognizes the antigen expressed by human, mouse and rat cells. Thereafter, the grids were incubated for 1 hour with rabbit anti-goat IgG conjugated with 15 nm colloidal gold particles (British Biocell, Cardiff, United Kingdom). After washings, grids were again incubated with goat anti-von Willebrand factor (catalogue no. sc-6941) followed by incubation with rabbit-anti-goat IgG conjugated with 20 nm colloidal gold particles. Sections were then counterstained in uranyl acetate to evidentiate the cell morphology, and observed with EM 109 Zeiss. Cells treated as above, but not exposed to the primary antibody represented negative controls.
Immunohistochemistry
Mice were divided into three different age groups: young (2 months), adult (5–9 months) and old (10–16 months). After killing the mice, the spleens, livers, hearts, and kidneys were removed and fixed overnight in methanol: formaldehyde 9:1. Immunohistochemistry was performed essentially as described in [28]. In short: Fixed tissues were dehydrated, embedded in paraffin, and sectioned. Tissue sections were then deparaffinized in xylene, transferred to 99.7% ethanol and rehydrated by serial incubation in diminishing concentrations of ethanol. Sections were blocked using 0.3% hydrogen peroxide–methanol and 5% normal goat serum- phosphate buffer saline (PBS) pH 7.4. A rabbit anti-human fibrin–fibrinogen antibody (DAKO, Glostrup, Denmark) was added, and after washing, anti-rabbit IgG antibody conjugated with biotin and avidin-biotin complex conjugated with horseradish peroxidase (Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA). Staining was visualized with diaminobenzidine tetra hydrochloride–Ni3+, Co2+ (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech, Piscataway, NJ) yielding a brown color. Sections were analyzed under light microscope and the presence of thrombosis was determined using standard histological criteria.
Statistical analyses
Results are presented as mean (±SD) of at least three separate measurements per experimental point, unless otherwise stated. Statistical analyses were performed by analysis of variance (Anova test), Kruskal–Wallis two-sided test, Wilcoxon rank test using Origin 3.5 software for Windows (Microcal Software Inc., Northampton, MA, USA). Data on numbers of thrombosis are presented as means with ranges. Analyses comparing numbers of thrombosis were performed using the Kruskal–Wallis test and analyses comparing the frequency of thrombosis were performed using Pearson Chi square test.
Results
Platelet counts, but not hematocrit, are reduced in Gata1low mice
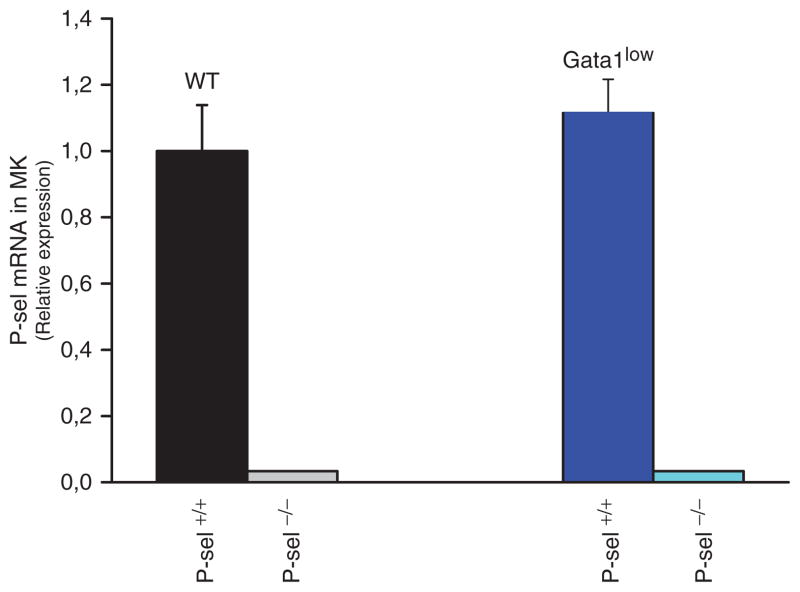
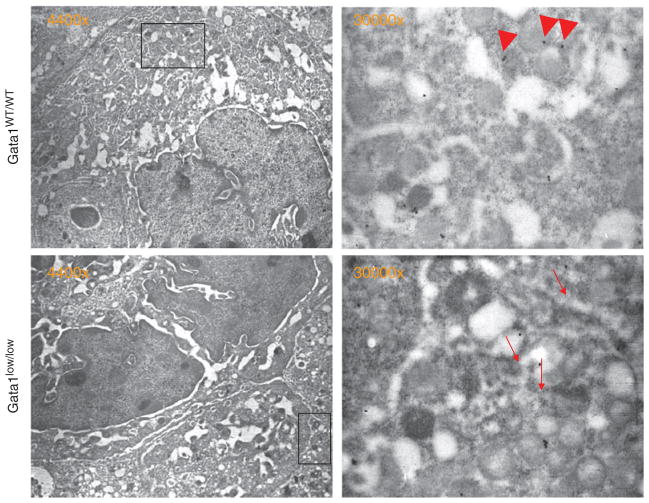
MKs from Gata1low mice express levels of P-sel mRNA comparable to that expressed by MKs from wild type mice at the Gata1 locus (Figure 1). As expected, P-Sel mRNA was not detected in MKs purified from Gata1lowP-selnull or Gata1wtP-sel null mice. In spite the normal levels of P-sel expression in Gata1low MK, the P-sel protein is abnormally localized on the membrane demarcation region and is not assembled in the granules, which are present in the platelet territories (Figure 2).
Figure 1.
P-selectin expression in megakaryocytes from the bone marrow of mice either wild type at the Gata1 locus or carrying the Gata1 low mutation and containing (P-selWT/WT) or not (P-sel−/−) the P-sel gene. Mice megakaryocyte was isolated and total RNA was prepared and gene expression levels were quantified by real-time reverse-transcription PCR. Results are expressed as relative expression with respect to values observed in wild type mice and presented as mean (±SD) of results obtained in three separate purification experiments. As expected P-sel mRNA was not detected in mice carrying the P-sel null trait, but was present in wild type and mice only carrying the Gata1 low hypomorphic mutation. The difference in P-sel expression between the MKs from wild type and Gata1low mice is not statistically significant.
Figure 2.
P-sel distribution in megakaryocytes of wild type and Gata1low mice. Semi thin sections of spleen from WT (a) and Gata1low (b) mice, immune stained for P-sel and analyzed by immuno-electron microscopy. Representative MKs are presented on the left panels and the region of their cytoplasm included in the rectangle are shown at greater magnification in the panels on the right, P-sel staining appears as dots. P-sel was found in the α-granule membrane (arrow heads) as well as in the cytoplasm of MKs from wild type mice. However, in the immature MKs from Gata1low mice, P-sel staining was found primarily in the cytoplasm, lining the DMS (arrow-heads).
Platelet counts and Hct were determined on Gata1lowP-selwt, Gata1lowP-selnull and Gata1wtP-selnull and Gata1WTP-selwt (Table I). There were no significant differences among the four groups of mice with respect of Hct (Kruskal–Wallis nonparametric analysis of variance, two-sided p=0.89) although there were differences among these groups with respect to platelet levels (Kruskal–Wallis two-sided, p=0.002). In particular, Gata1wt mice had significantly greater platelet levels than Gata1low mice regardless of P-sel (Wilcoxon rank test, p≤0.0001, no adjustment for multiple comparisons).
Table I.
Hct, ptl and PMP in the blood of mice carrying the Gata1low and/or P-selnull mutation.
| Number of Mice | Gata1WTP-selWT
|
Gata1lowP-selWT
|
Gata1WTP-selneg
|
Gata1lowP-selneg
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 4 | 14 | 5 | |
| Hct (%) Mean (s.d); Median (range) | 47.4 (2.6); 46.9 (44–52) | 44.9(4.7); 47.2 (37.9–47.5) | 47.7 (3.2); 46.9 (43.6–53.3) | 47.4 (2.7); 48.5 (42.8–49.2) |
| Ptl (×106) Mean (s.d); Median (range) | 1.0 (0.15); 0.93 (0.90–1.1) | 0.67 (0.075); 0.68 (0.57–0.74) | 1.06 (0.18); 1.05 (0.87–1.5) | 0 48 (0.06); 0.49 (0.41–0.55) |
| Number of mice | 2 | 4 | 2 | 2 |
| PMP* Range | 25.2–42.7 | 2.6–8.9 | 1.2–2.1 | 2.5–2.7 |
| P-selpostPMP (%) Range | 22.7–34.3 | 1.1–6.8 | 0.8–1.2 | 1.3–1.6 |
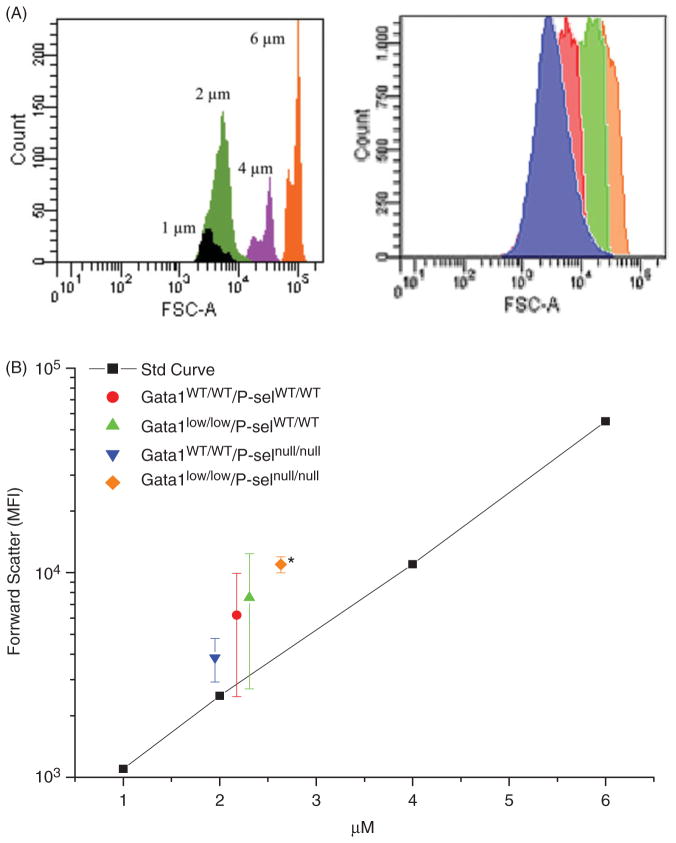
Morphological observations had indicated that the size of platelets from Gata1low mice is larger than normal [17, 19]. To take into account that the fact that platelets may vary considerably in shape makes it difficult to precisely assess platelet size by morphology, we have reassessed the size of the platelets from wild type and Gata1low mice by flow cytometry by comparing the forward size scatter of the platelets with that of microbeads with defined diameter (Figure 3). These analyses included platelets from Gata1lowP-selwt, Gata1lowP-selnull and Gata1wtP-selnull and Gata1wtP-selwt mice. The average diameter of platelets from Gata1wtP-selnull and Gata1wtP-selwt were 2.18±0.36 and 1.95±0.09 μm, respectively, while those from Gata1lowP-selwt and Gata1lowP-selnull were 2.31±0.46 and 2.63±0.05, respectively. Although slightly larger than normal (2.3 μm in diameter), the size of the platelets from Gata1low mice was not statistically different from that of wild type mice, but that of platelets from Gata1low mice lacking the P-sel gene was significantly larger from that of platelets from mice wild type at the Gata1 locus with (p<0.05) or without (p<0.01) the P-sel gene.
Figure 3.
Determination of platelet size in wild type, single and double mutant mice by flow cytometry. Platelets were recognized on the basis of CD61 staining and their size evaluated by comparing the relative forward side scatter (FSC) signal with that of reference microspheres. A. Representative histograms of the FSC expressed by the reference microspheres (on the left) and by platelets from Gata1wt/wt P-selwt/wt (red), Gata1low/lowP-selwt/wt (green), Gata1wt/wt P-selnull/null (blue) and Gata1low/low P-selnull/null. B. FSC vs. reference microsphere regression curve and mean (±SD) of FSC of platelets determined in three separate experiments each one with three mice per group. Platelets from Gata1low mice lacking the P-sel gene (orange diamond) were significantly larger than platelets from wild type mice at the Gata1 locus (blue inverted triangle) with the P-sel null trait (p<0.01).
PMPs are reduced in Gata1low mice and do not express P-selectin
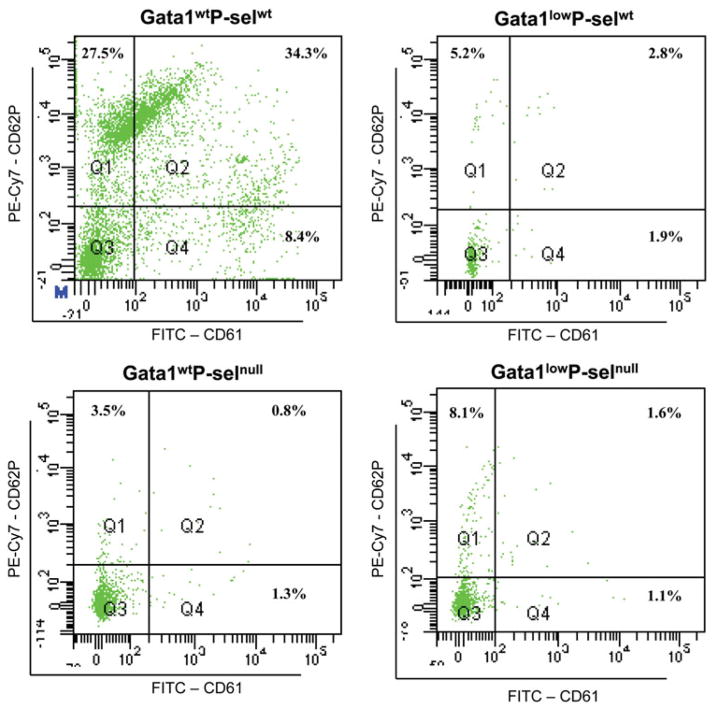
PMPs were found to be reduced in Gata1low mice compared to Gata1wt littermates (Table I, Figure 4). Gata1wtP-selnull and Gata1lowP-selnull littermates had also reduced numbers of PMPs. P-sel was only expressed by PMPs from Gata1wtP-selwt. The lack of expression of P-sel in the platelets of Gata1low mice was expected since the protein is retained in the DMS of the MKs as shown in Figure 2.
Figure 4.
Platelet microparticles are reduced in mice carrying the Gata1 low mutation and containing the P-sel gene. PMPs were quantified in platelet poor plasma from Gata1lowP-selwt, Gata1lowP-selnull and Gata1WTP-selnull and Gata1wtP-selwt mice obtained by serial centrifugation steps. PMPs were stained by anti CD62 and CD61 and quantified as anti-CD61pos events against the events of constant numbers of microbeads as calibrators. Representative plots show that P-sel positive PMPs (events double positive for CD61 and CD62) in significant numbers was only seen in plasma from Gata1wtP-selwt mice, being greatly reduced in plasma from Gata1lowP-selwt, Gata1lowP-selnull and Gata1wtP-selnull mice.
Gata1low mice with or without the P-sel null trait have a prolonged bleeding time but only those with P-sel survive poorly during small surgeries
To determine the biological effects of removing P-sel in the Gata1low background, bleeding times were assessed by amputation of the distal portion of the tail in single, double as well as non mutated mice. It was seen that adult and old Gata1lowP-selwt mice, but also Gata1wtP-selnull and Gata1lowP-selnull littermates had bleeding times longer (>600 sec) than those observed with Gata1wtP-selwt mice (181±69 seconds). Ethical limitations in bleeding time estimates prevented assessment of eventual differences between the bleeding times of mice carrying the different mutations.
The physiological relevance of the increased bleeding times observed in mutants harboring the Gata1low gene and/or lacking the P-sel gene was assessed by measuring survival post-surgery to remove the spleen. Gata1wtP-selwt (5 mice) bled modestly during the surgery and all survived surgery. By contrast, Gata1wtP-selnull and Gata1lowPselnull mice (five mice per experimental group) and Gata1lowP-selwt mice (15 mice) bled consistently during the procedure. The long bleeding time did not affect the survival of Gata1wtP-selnull and Gata1lowP-Selnull mice but 8 of the 15 Gata1low P-selwt mice (53%) died during the surgery. This functional data indicate that in spite the bleeding time of Gata1low mice lacking the P-sel gene remains long, removal of the P-sel gene compensate for the coagulative defects of Gata1low mice.
Thrombosis is seen in adult and old Gata1low mice, but the Gata1low/P-selnull mice are rescued
The presence of thrombosis in spleen, liver, heart and kidney of mice carrying the different mutations was determined according to standard histological criteria. In these experiments, mice were divided into age groups of young (2 months), adult (5–9 months) and old (10–16 months) mice. Thrombi were only found in kidneys and hearts, therefore only results from these organs were included the statistical analyses.
No thrombosis was found in young Gata1wtP-selwt or Gata1lowP-selwt mice; therefore this age group was not investigated in Gata1lowP-selwt and Gata1lowP-selnull mice. However thrombosis were present in adult and old Gata1lowP-selwt and Gata1lowP-selnull mice and in adult mice the percentage of mice having thrombosis in heart and/or kidney was significantly higher in the Gata1lowP-selwt compared to wild type, single or double mutant mice (100 vs. 0 vs. 0 vs. 33% respectively, Pearson Chi-square test p=0.037) (Figures 5 and 6A). In old mice, no significant difference in the frequency of thrombosis was seen. However, old Gata1lowP-selwt mice had significantly higher number of thrombosis per section in heart or kidney compared to Gata1wtP-selwt (Figures 4 and 6B).
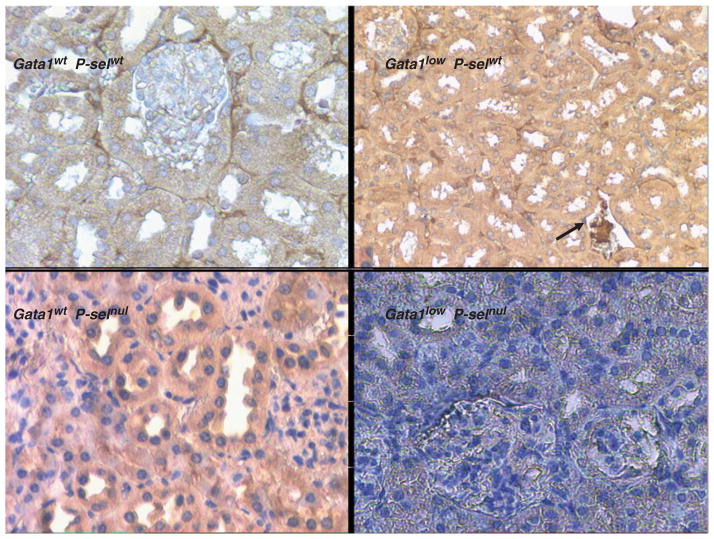
Figure 5.
Deletion of the P-sel gene reduces the frequency of thrombotic events detected in kidney sections from Gata1low mice. Mice without or with Gata1low (upper right and left, respectively) as well as mice carrying the P-sel-null trait without or with the Gata1low mutation (lower left and right respectively), all at 9 months of age, were killed and kidneys removed. Tissues were paraffin embedded, sectioned immunohistochemically stained for fibrinogen. This antibody crosses reacts with fibrin, visualizing a thrombus in a kidney vein (arrow) from a mouse carrying the Gata1low hypomorphic mutation (upper right). Significantly fewer numbers of thrombosis was found in mice carrying the P-sel null trait, even in combination with the Gata1low mutation as well as in wild type mice. Wild-type mice were also free from thrombosis. Similar results were observed in sections from the heart of the mutant mice (data not shown).
Figure 6.
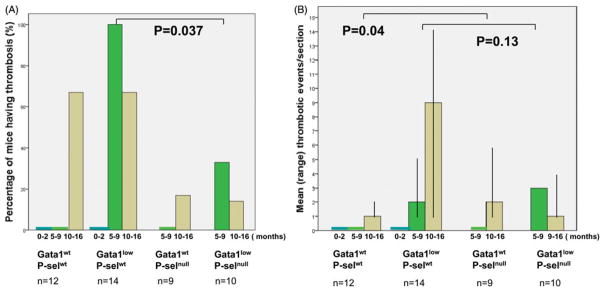
Frequency of mice presenting histological evidence of thrombosis in sections from kidney and/or heart (A) and mean number of thrombotic events per positive section of each mouse (B). Wild-type and mutant mice at different ages (0–2, 5–9 and 10–16, as indicated) and thrombotic events in heart and kidney sections evaluated as indicated in the legend of Figure 5. The mice genotype is specified the below the x axes. The number of mice analyzed in each group is indicated with n.
Discussion
P-sel is a member of the selectin family of adhesive molecules that also includes L-and E-selectin and has key functions in both coagulation and in the inflammatory response [29]. It is stored in the Weibel Palade bodies of endothelial cells and in the α-granules and dense bodies of platelets, being translocated to the surface upon activation of these cells. The binding of endothelial cell P-sel to its receptor P-Selectin Glycoprotein Ligand-1 (PSGL-1) on leukocytes initiates leukocyte rolling on the endothelial cell surface [30]. Platelet P-sel has multiple actions in coagulation. When expressed on the platelet surface it induces the release of pro coagulant MPs that carry tissue factor (TF), the initial trigger for thrombogenesis, and other pro coagulant factors. Platelet P-sel also up-regulates TF on monocytes, modulating the initial thrombus amplification [31]. It is a key receptor in the forming of platelet-leukocyte aggregates that has proven to exert pro coagulative properties. Platelet P-sel mediates the initial binding between leukocytes and platelets thereby activating leukocytes. Downstream signaling leads to expression of the leukocyte β2-integrin Mac-1 binding to platelet GpIb resulting in firm adhesion between the cells. The signaling cascade initiated by platelet P-sel up regulates TF on the leukocyte surface and increases leukocyte fibrin deposition [32].
The presence of increased circulating platelet-leukocyte aggregates has been observed in stable and unstable angina, myocardial infarction and in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary interventions and heart valve replacement [29]. Aggregates are also elevated in inflammatory disease such as inflammatory lung disease, cystic fibrosis and inflammatory bowel disease [33].
After binding to its ligand, P-sel is proteolytically cleaved from the surface and can be detected in plasma in its soluble form. Blood levels represent a measure of platelet and/or endothelial cell activation and elevated soluble P-sel levels have been shown to be a risk factor atherosclerosis [34, 35]. Plasma from mice engineered to express permanently elevated levels of soluble P-sel has been shown to clot one minute faster than plasma from wild-type mice and contains higher concentration of pro-coagulant MPs [36]. MPs are 0.1–1 μm membrane vesicles formed on cell activation or apoptosis from membrane blebs that are released from the cell surface. MPs are pro coagulant because they provide a membrane surface containing anionic phospholipids, particularly phosphatidyl serine (PS) for the assembly of components of the coagulation protease cascade. Their plasma membrane contains most of the membrane-associated proteins of the cells they stem from, many of which have pro-coagulant, fibrinolytic and proteolytic properties [37]. The majority of pro-coagulant MPs is derived from activated leukocytes and platelets. When recruited to the area of thrombosis, MPs amplify thrombogenesis via TF and the extrinsic coagulation and the recruitment of MPs is largely dependent on the interaction of MP PSGL-1 with platelet P-sel [38]. MPs contribute to the pathogenesis of ischemic stroke, metastasis and tumor development [39, 40], and repeated studies have shown an association between tumor-derived TF+MPs and venous thrombosis in cancer patients [41].
Increased PMPs, and also the presence of leukocyte-platelet aggregates and increased levels of P-sel have been demonstrated in PV and ET, but information is limited in PMF [42-44]. However, as in PV and ET, leukocytosis has been demonstrated to be a risk factor for thrombosis also in PMF [5, 45–47] suggesting that leukocyte interactions are important for the pathogenesis of thrombosis in these diseases. This is supported by the findings by Alvarez-Larrán et al. who showed significantly higher levels of soluble and platelet P-sel expression, and also higher percentages of platelet–monocyte complexes in patients with PMF [48].
We show here that in addition to the previously described hallmarks of human myelofibrosis, the MK maturation defect caused by the Gata1low mutation in mice also induces a pro-thrombotic state detectable from 5 to 9 months of age. The presence of the P-sel null mutation rescues the thrombotic phenotype but not the platelet count, PMPs or bleeding time deficiency induced by the Gata1 low mutation. P-sel positive PMPs were virtually absent from Gata1low mice platelets, indicating that abnormal P-sel localization also disrupts the formation of PMPs. Thus, abnormal P-sel localization to the DMS and subsequent abnormal interactions with leukocytes, rather than elevated PMP numbers, appears to be responsible for the thrombogenicity induced by the Gata1 low mutation. These results suggest P-sel as the possible target for therapeutic prevention of thrombosis in PMF.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Antonio Di Virgilio and Agostino Eusebi for performing animal manipulations, Professor Jan Palmblad, Department of Medicine Karolinska Institute and Stockholm, Sweden, for outstanding intellectual feedback during the preparation of the manuscript and Inger Vedin, PhD, Department of Medicine Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, for excellent help with immunohistochemical staining.
Footnotes
Declaration of interest
The authors report no declarations of interest. This study was supported by a grant from the National Cancer Institute (P01-CA108671), and by Associazione Italiana Ricerca sul Cancro (AIRC).
References
- 1.Tefferi A. Myelofibrosis with myeloid metaplasia. N Eng J Med. 2000;342(17):1255–1265. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200004273421706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Villeval JL, James C, Pisani DF, Casadevall N, Vainchenker W. New insights into the pathogenesis of JAK2 V617F-positive myeloproliferative disorders and consequences for the management of patients. Semin Thrombosis Hemostasis. 2006;32(4 Pt 2):341–351. doi: 10.1055/s-2006-942755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Schafer AI. Bleeding and thrombosis in the myeloproliferative disorders. Blood. 1984;64(1):1–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Cervantes F, Alvarez-Larran A, Arellano-Rodrigo E, Granell M, Domingo A, Montserrat E. Frequency and risk factors for thrombosis in idiopathic myelofibrosis: Analysis in a series of 155 patients from a single institution. Leukemia. 2006;20(1):55–60. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2404048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Barbui T, Carobbio A, Cervantes F, Vannucchi AM, Guglielmelli P, Antonioli E, Alvarez-Larrán A, Rambaldi A, Finazzi G, Barosi G. Thrombosis in primary myelofibrosis: Incidence and risk factors. Blood. 2010;115(4):778–782. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-08-238956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Barbui T, Finazzi MC, Finazzi G. Front-line therapy in polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia. Blood Rev. 2012;26(5):205–211. doi: 10.1016/j.blre.2012.06.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Falanga A, Marchetti M. Thrombotic disease in the myeloproliferative neoplasms. Hematology. 2012;2012:571–581. doi: 10.1182/asheducation-2012.1.571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Barbui T, Thiele J, Passamonti F, Rumi E, Boveri E, Randi ML, Bertozzi I, Marino F, Vannucchi AM, Pieri L, et al. Initial bone marrow reticulin fibrosis in polycythemia vera exerts an impact on clinical outcome. Blood. 2012;119(10):2239–2241. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-11-393819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Danielsson S, Merup M, Olsson L, Palmblad J, Astrom M. X-linked thrombocytopenia with thalassemia in two families in Sweden. Consider hereditary causes of thrombocytopenia and bone marrow fibrosis. Lakartidningen. 2012;109(34–35):1474–1477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ciovacco WA, Raskind WH, Kacena MA. Human phenotypes associated with GATA-1 mutations. Gene. 2008;427(1–2):1–6. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2008.09.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Balduini CL, Pecci A, Loffredo G, Izzo P, Noris P, Grosso M, Bergamaschi G, Rosti V, Magrini U, Ceresa IF, et al. Effects of the R216Q mutation of GATA-1 on erythropoiesis and megakaryocytopoiesis. Thrombosis Haemostasis. 2004;91(1):129–140. doi: 10.1160/TH03-05-0290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Villmow T, Kemkes-Matthes B, Matzdorff AC. Markers of platelet activation and platelet-leukocyte interaction in patients with myeloproliferative syndromes. Thrombosis Res. 2002;108(2–3):139–145. doi: 10.1016/s0049-3848(02)00354-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.McDevitt MA, Shivdasani RA, Fujiwara Y, Yang H, Orkin SH. A ‘‘knockdown’’ mutation created by cis-element gene targeting reveals the dependence of erythroid cell maturation on the level of transcription factor GATA-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94(13):6781–6785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.13.6781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Vannucchi AM, Bianchi L, Cellai C, Paoletti F, Rana RA, Lorenzini R, Migliaccio G, Migliaccio AR. Development of myelofibrosis in mice genetically impaired for GATA-1 expression (GATA-1(low) mice) Blood. 2002;100(4):1123–1132. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-06-1913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Zingariello M, Fabucci ME, Bosco D, Migliaccio AR, Martelli F, Rana RA, Lorenzini R, Migliaccio G, Migliaccio AR. Differential localization of P-selectin and von Willebrand factor during megakaryocyte maturation. Biotechnic Histochem. 2010;85(3):157–170. doi: 10.3109/10520290903149612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.McDevitt MA, Fujiwara Y, Shivdasani RA, Orkin SH. An upstream, DNase I hypersensitive region of the hematopoietic-expressed transcription factor GATA-1 gene confers developmental specificity in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:7976–7981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.15.7976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Vyas P, Ault K, Jackson CW, Orkin SH, Shivdasani RA. Consequences of GATA-1 deficiency in megakaryocytes and platelets. Blood. 1999;93:2867–2875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Migliaccio AR, Rana RA, Sanchez M, Lorenzini R, Centurione L, Bianchi L, et al. GATA-1 as a regulator of mast cell differentiation revealed by the phenotype of the GATA-1low mouse mutant. J Exp Med. 2003;197(3):281–296. doi: 10.1084/jem.20021149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Vannucchi AM, Bianchi L, Cellai C, Paoletti F, Carrai V, Calzolari A, Vannucchi AM, Migliaccio G, Orkin SH. Accentuated response to phenylhydrazine and erythropoietin in mice genetically impaired for their GATA-1 expression (GATA-1(low) mice) Blood. 2001;97(10):3040–3050. doi: 10.1182/blood.v97.10.3040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Robinson SD, Frenette PS, Rayburn H, Cummiskey M, Ullman-Cullere M, Wagner DD, Hynes RO. Multiple, targeted deficiencies in selectins reveal a predominant role for P-selectin in leukocyte recruitment. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999;96(20):11452–11457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.20.11452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hartwell DW, Butterfield CE, Frenette PS, Kenyon BM, Hynes RO, Folkman J, Wagner DD. Angiogenesis in P- and E-selectin-deficient mice. Microcirculation. 1998;5(2–3):173–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Forlow SB, McEver RP, Nollert MU. Leukocyte-leukocyte interactions mediated by platelet microparticles under flow. Blood. 2000;95(4):1317–1323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Murad JP, Espinosa EV, Ting HJ, Khasawneh FT. Characterization of the in vivo antiplatelet activity of the antihypertensive agent losartan. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Therap. 2012;17(3):308–314. doi: 10.1177/1074248411425491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Migliaccio AR, Martelli F, Verrucci M, Sanchez M, Valeri M, Migliaccio G, Vannucchi AM, Zingariello M, Di Baldassarre A, Ghinassi B, et al. Gata1 expression driven by the alternative HS2 enhancer in the spleen rescues the hematopoietic failure induced by the hypomorphic Gata1low mutation. Blood. 2009;114(10):2107–2120. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-03-211680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Migliaccio AR, Martelli F, Verrucci M, Migliaccio G, Vannucchi AM, Ni H, Xu M, Jiang Y, Nakamoto B, Papayannopoulou T, et al. Altered SDF-1/CXCR4 axis in patients with primary myelofibrosis and in the Gata1 low mouse model of the disease. Exp Hematol. 2008;36(2):158–171. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2007.10.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ghinassi B, Sanchez M, Martelli F, Amabile G, Vannucchi AM, Migliaccio G, Xu M, Jiang Y, Nakamoto B, Papayannopoulou T, et al. The hypomorphic Gata1low mutation alters the proliferation/ differentiation potential of the common megakaryocytic-erythroid progenitor. Blood. 2007;109(4):1460–1471. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-07-030726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Falcieri E, Bassini A, Pierpaoli S, Luchetti F, Zamai L, Vitale M, Guidotti L, Zauli G. Ultrastructural characterization of maturation, platelet release, and senescence of human cultured megakaryocytes. Anat Rec. 2000;258(1):90–99. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0185(20000101)258:1<90::AID-AR10>3.0.CO;2-G. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Yanada M, Kojima T, Ishiguro K, Nakayama Y, Yamamoto K, Matsushita T, Kadomatsu K, Nishimura M, Muramatsu T, Saito H. Impact of antithrombin deficiency in thrombogenesis: Lipopolysaccharide and stress-induced thrombus formation in heterozygous antithrombin-deficient mice. Blood. 2002;99(7):2455–2458. doi: 10.1182/blood.v99.7.2455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Cerletti C, de Gaetano G, Lorenzet R. Platelet – leukocyte interactions: Multiple links between inflammation, blood coagulation and vascular risk. Mediterranean J Hematol Infect Dis. 2010;2(3):e2010023. doi: 10.4084/MJHID.2010.023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Huo Y, Xia L. P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 plays a crucial role in the selective recruitment of leukocytes into the atherosclerotic arterial wall. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2009;19(4):140–145. doi: 10.1016/j.tcm.2009.07.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.del Conde I, Nabi F, Tonda R, Thiagarajan P, Lopez JA, Kleiman NS. Effect of P-selectin on phosphatidylserine exposure and surfacedependent thrombin generation on monocytes. Arteriosclerosis, thrombosis, and vascular biology. 2005;25(5):1065–1070. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000159094.17235.9b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Cerletti C, Tamburrelli C, Izzi B, Gianfagna F, de Gaetano G. Platelet-leukocyte interactions in thrombosis. Thrombosis Res. 2012;129(3):263–266. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2011.10.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Totani L, Evangelista V. Platelet-leukocyte interactions in cardiovascular disease and beyond. Arteriosclerosis Thrombosis Vascular Biol. 2010;30(12):2357–2361. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.110.207480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Ridker PM, Buring JE, Rifai N. Soluble P-selectin and the risk of future cardiovascular events. Circulation. 2001;103(4):491–495. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.103.4.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Linden MD, Furman MI, Frelinger AL, 3rd, Fox ML, Barnard MR, Li Y, Przyklenk K, Michelson AD. Indices of platelet activation and the stability of coronary artery disease. J Thrombosis Haemostasis. 2007;5(4):761–765. doi: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2007.02462.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Andre P, Hartwell D, Hrachovinova I, Saffaripour S, Wagner DD. Pro-coagulant state resulting from high levels of soluble P-selectin in blood. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000;97(25):13835–13840. doi: 10.1073/pnas.250475997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ramacciotti E, Hawley AE, Farris DM, Ballard NE, Wrobleski SK, Myers DD, Jr, Henke PK, Wakefield TW. Leukocyte- and platelet-derived microparticles correlate with thrombus weight and tissue factor activity in an experimental mouse model of venous thrombosis. Thrombosis Haemostasis. 2009;101(4):748–754. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Falati S, Liu Q, Gross P, Merrill-Skoloff G, Chou J, Vandendries E, Celi A, Croce K, Furie BC, Furie B. Accumulation of tissue factor into developing thrombi in vivo is dependent upon microparticle P-selectin glycoprotein ligand 1 and platelet P-selectin. J Exp Med. 2003;197(11):1585–1598. doi: 10.1084/jem.20021868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Dean WL, Lee MJ, Cummins TD, Schultz DJ, Powell DW. Proteomic and functional characterisation of platelet micro-particle size classes. Thrombosis Haemostasis. 2009;102(4):711–718. doi: 10.1160/TH09-04-243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Dashevsky O, Varon D, Brill A. Platelet-derived microparticles promote invasiveness of prostate cancer cells via upregulation of MMP-2 production. Int J Cancer. 2009;124(8):1773–1777. doi: 10.1002/ijc.24016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Owens AP, 3rd, Mackman N. Microparticles in hemostasis and thrombosis. Circulation Res. 2011;108(10):1284–1297. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.233056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Karakantza M, Giannakoulas NC, Zikos P, Sakellaropoulos G, Kouraklis A, Aktypi A, Metallinos IC, Theodori E, Zoumbos NC, Maniatis A. Markers of endothelial and in vivo platelet activation in patients with essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera. Int J Hematol. 2004;79(3):253–259. doi: 10.1532/ijh97.e0316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Falanga A, Marchetti M, Vignoli A, Balducci D, Barbui T. Leukocyte-platelet interaction in patients with essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera. Exp Hematol. 2005;33(5):523–530. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2005.01.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Tefferi A, Elliott M. Thrombosis in myeloproliferative disorders: Prevalence, prognostic factors, and the role of leukocytes and JAK2V617F. Semin Thrombosis Hemostasis. 2007;33(4):313–320. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-976165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Carobbio A, Finazzi G, Guerini V, Spinelli O, Delaini F, Marchioli R, Borrelli G, Rambaldi A, Barbui T. Leukocytosis is a risk factor for thrombosis in essential thrombocythemia: Interaction with treatment, standard risk factors, and Jak2 mutation status. Blood. 2007;109(6):2310–2313. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-09-046342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Carobbio A, Antonioli E, Guglielmelli P, Vannucchi AM, Delaini F, Guerini V, et al. Leukocytosis and risk stratification assessment in essential thrombocythemia. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(16):2732–2736. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.15.3569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Finazzi G, Carobbio A, Thiele J, Passamonti F, Rumi E, Ruggeri M, Rodeghiero F, Randi ML, Bertozzi I, Vannucchi AM, et al. Incidence and risk factors for bleeding in 1104 patients with essential thrombocythemia or prefibrotic myelofibrosis diagnosed according to the 2008 WHO criteria. Leukemia. 2012;26(4):716–719. doi: 10.1038/leu.2011.258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Alvarez-Larran A, Arellano-Rodrigo E, Reverter JC, Domingo A, Villamor N, Colomer D, Cervantes F. Increased platelet, leukocyte, and coagulation activation in primary myelofibrosis. Ann Hematol. 2008;87(4):269–276. doi: 10.1007/s00277-007-0386-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]