Abstract
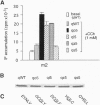
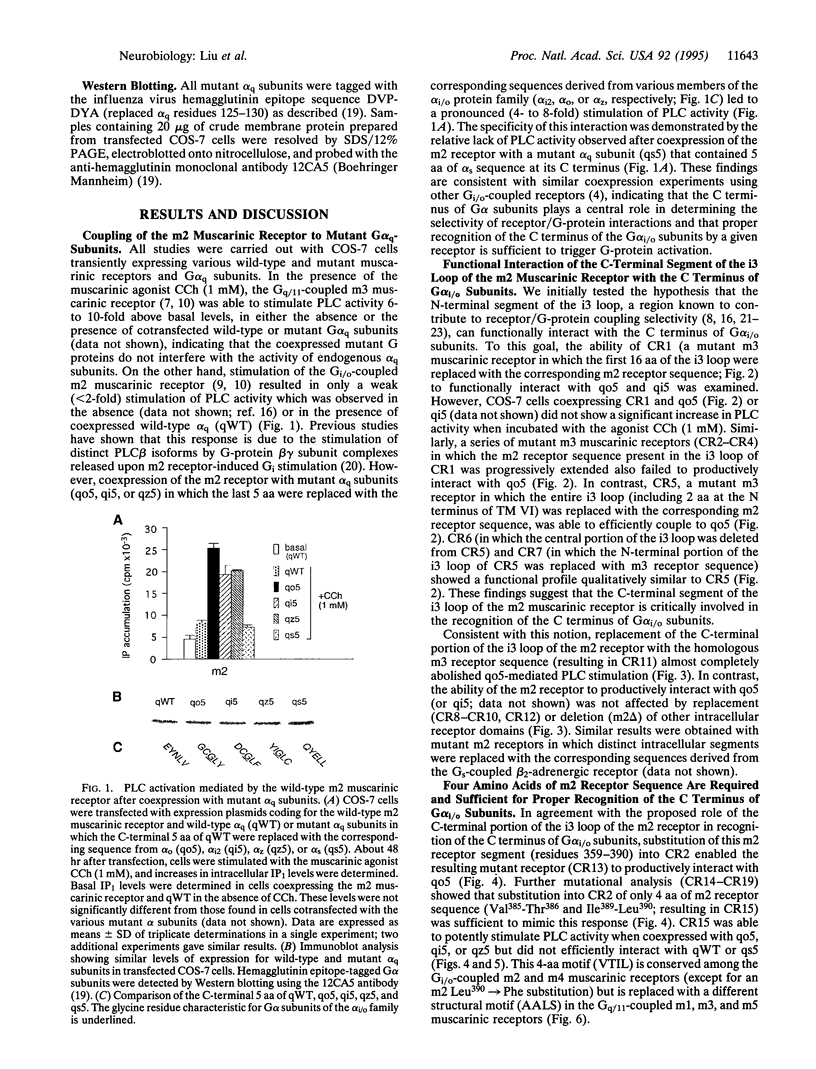
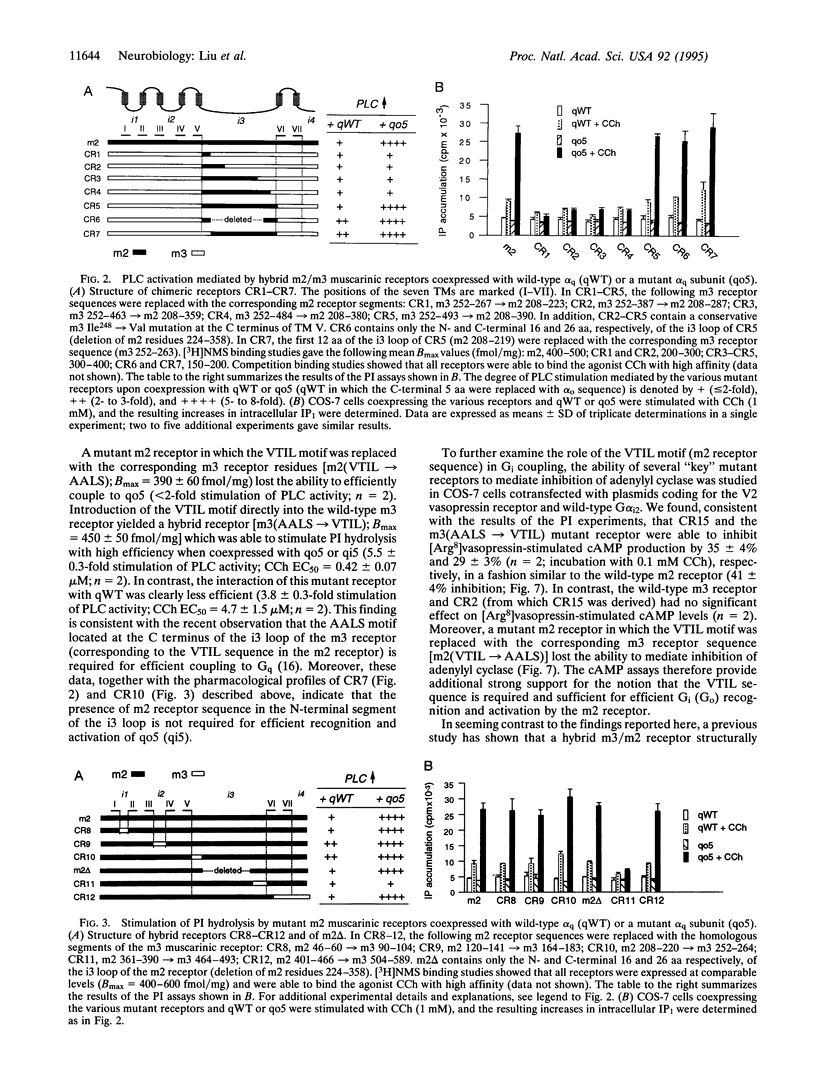
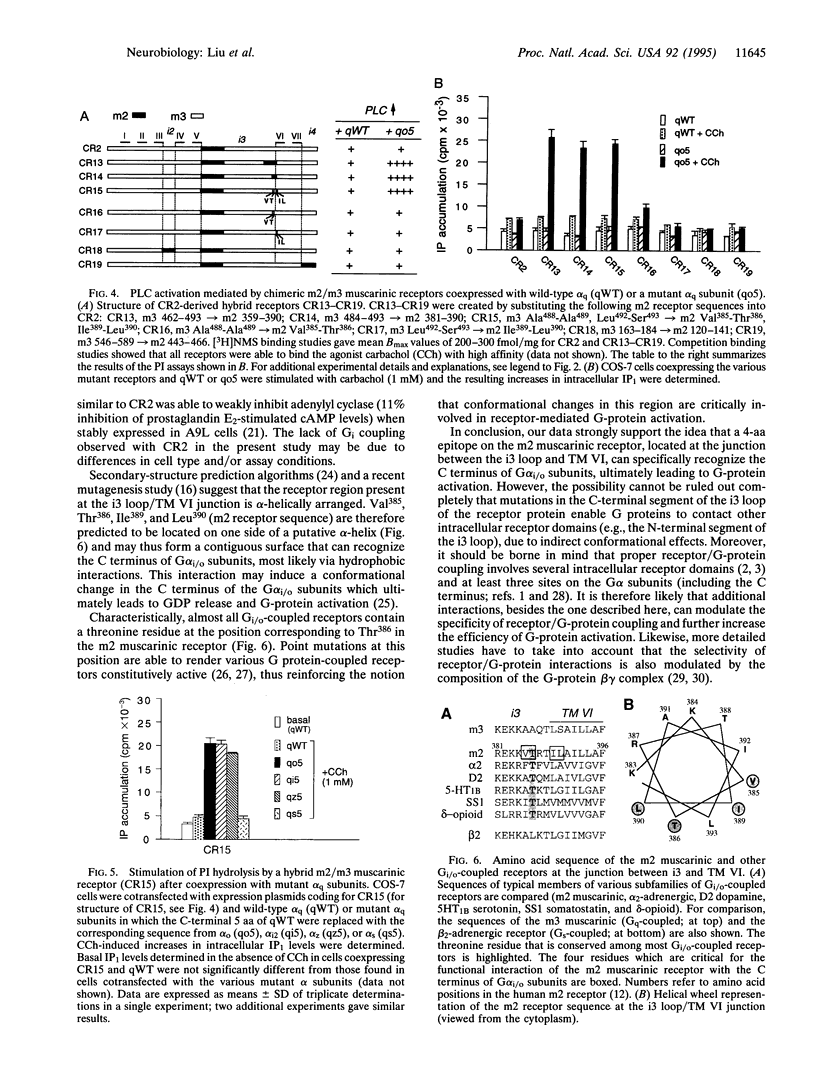
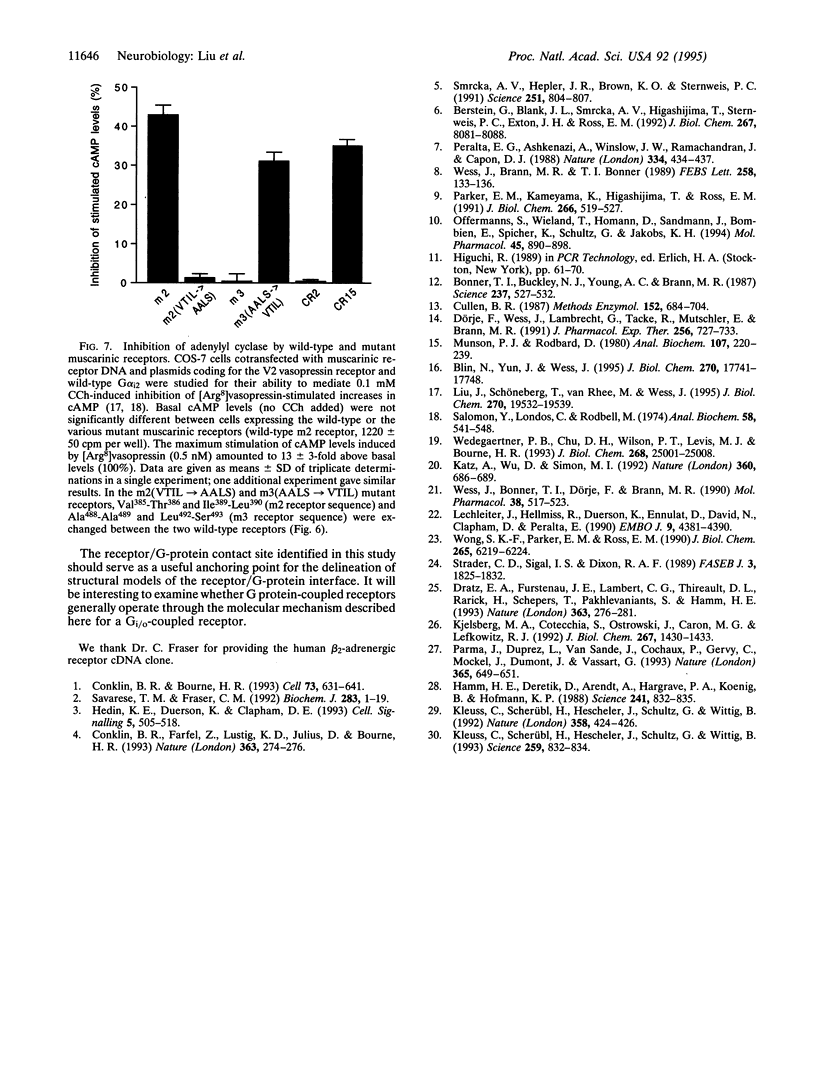
Each G protein-coupled receptor recognizes only a distinct subset of the many structurally closely related G proteins expressed within a cell. How this selectively is achieved at a molecular level is not well understood, particularly since no specific point-to-point contact sites between a receptor and its cognate G protein(s) have been identified. In this study, we demonstrate that a 4-aa epitope on the m2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor, a prototypical Gi/o-coupled receptor, can specifically recognize the C-terminal 5 aa of alpha subunits of the Gi/o protein family. The m2 receptor residues involved in this interaction are predicted to be located on one side of an alpha-helical receptor region present at the junction between the third intracellular loop and the sixth transmembrane domain. Coexpression studies with hybrid m2/m3 muscarinic receptors and mutant G-protein alpha q subunits showed that the receptor/G-protein contact site identified in this study is essential for coupling specificity and G-protein activation.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berstein G., Blank J. L., Smrcka A. V., Higashijima T., Sternweis P. C., Exton J. H., Ross E. M. Reconstitution of agonist-stimulated phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate hydrolysis using purified m1 muscarinic receptor, Gq/11, and phospholipase C-beta 1. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8081–8088. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blin N., Yun J., Wess J. Mapping of single amino acid residues required for selective activation of Gq/11 by the m3 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jul 28;270(30):17741–17748. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.30.17741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner T. I., Buckley N. J., Young A. C., Brann M. R. Identification of a family of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor genes. Science. 1987 Jul 31;237(4814):527–532. doi: 10.1126/science.3037705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conklin B. R., Bourne H. R. Structural elements of G alpha subunits that interact with G beta gamma, receptors, and effectors. Cell. 1993 May 21;73(4):631–641. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90245-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conklin B. R., Farfel Z., Lustig K. D., Julius D., Bourne H. R. Substitution of three amino acids switches receptor specificity of Gq alpha to that of Gi alpha. Nature. 1993 May 20;363(6426):274–276. doi: 10.1038/363274a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. Use of eukaryotic expression technology in the functional analysis of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:684–704. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52074-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dratz E. A., Furstenau J. E., Lambert C. G., Thireault D. L., Rarick H., Schepers T., Pakhlevaniants S., Hamm H. E. NMR structure of a receptor-bound G-protein peptide. Nature. 1993 May 20;363(6426):276–281. doi: 10.1038/363276a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dörje F., Wess J., Lambrecht G., Tacke R., Mutschler E., Brann M. R. Antagonist binding profiles of five cloned human muscarinic receptor subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Feb;256(2):727–733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamm H. E., Deretic D., Arendt A., Hargrave P. A., Koenig B., Hofmann K. P. Site of G protein binding to rhodopsin mapped with synthetic peptides from the alpha subunit. Science. 1988 Aug 12;241(4867):832–835. doi: 10.1126/science.3136547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedin K. E., Duerson K., Clapham D. E. Specificity of receptor-G protein interactions: searching for the structure behind the signal. Cell Signal. 1993 Sep;5(5):505–518. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(93)90046-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz A., Wu D., Simon M. I. Subunits beta gamma of heterotrimeric G protein activate beta 2 isoform of phospholipase C. Nature. 1992 Dec 17;360(6405):686–689. doi: 10.1038/360686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjelsberg M. A., Cotecchia S., Ostrowski J., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Constitutive activation of the alpha 1B-adrenergic receptor by all amino acid substitutions at a single site. Evidence for a region which constrains receptor activation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):1430–1433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleuss C., Scherübl H., Hescheler J., Schultz G., Wittig B. Different beta-subunits determine G-protein interaction with transmembrane receptors. Nature. 1992 Jul 30;358(6385):424–426. doi: 10.1038/358424a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleuss C., Scherübl H., Hescheler J., Schultz G., Wittig B. Selectivity in signal transduction determined by gamma subunits of heterotrimeric G proteins. Science. 1993 Feb 5;259(5096):832–834. doi: 10.1126/science.8094261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechleiter J., Hellmiss R., Duerson K., Ennulat D., David N., Clapham D., Peralta E. Distinct sequence elements control the specificity of G protein activation by muscarinic acetylcholine receptor subtypes. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4381–4390. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07888.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J., Schöneberg T., van Rhee M., Wess J. Mutational analysis of the relative orientation of transmembrane helices I and VII in G protein-coupled receptors. J Biol Chem. 1995 Aug 18;270(33):19532–19539. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.33.19532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offermanns S., Wieland T., Homann D., Sandmann J., Bombien E., Spicher K., Schultz G., Jakobs K. H. Transfected muscarinic acetylcholine receptors selectively couple to Gi-type G proteins and Gq/11. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 May;45(5):890–898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker E. M., Kameyama K., Higashijima T., Ross E. M. Reconstitutively active G protein-coupled receptors purified from baculovirus-infected insect cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):519–527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parma J., Duprez L., Van Sande J., Cochaux P., Gervy C., Mockel J., Dumont J., Vassart G. Somatic mutations in the thyrotropin receptor gene cause hyperfunctioning thyroid adenomas. Nature. 1993 Oct 14;365(6447):649–651. doi: 10.1038/365649a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peralta E. G., Ashkenazi A., Winslow J. W., Ramachandran J., Capon D. J. Differential regulation of PI hydrolysis and adenylyl cyclase by muscarinic receptor subtypes. Nature. 1988 Aug 4;334(6181):434–437. doi: 10.1038/334434a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y., Londos C., Rodbell M. A highly sensitive adenylate cyclase assay. Anal Biochem. 1974 Apr;58(2):541–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savarese T. M., Fraser C. M. In vitro mutagenesis and the search for structure-function relationships among G protein-coupled receptors. Biochem J. 1992 Apr 1;283(Pt 1):1–19. doi: 10.1042/bj2830001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smrcka A. V., Hepler J. R., Brown K. O., Sternweis P. C. Regulation of polyphosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C activity by purified Gq. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):804–807. doi: 10.1126/science.1846707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strader C. D., Sigal I. S., Dixon R. A. Structural basis of beta-adrenergic receptor function. FASEB J. 1989 May;3(7):1825–1832. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.7.2541037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedegaertner P. B., Chu D. H., Wilson P. T., Levis M. J., Bourne H. R. Palmitoylation is required for signaling functions and membrane attachment of Gq alpha and Gs alpha. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 25;268(33):25001–25008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wess J., Bonner T. I., Dörje F., Brann M. R. Delineation of muscarinic receptor domains conferring selectivity of coupling to guanine nucleotide-binding proteins and second messengers. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Oct;38(4):517–523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wess J., Brann M. R., Bonner T. I. Identification of a small intracellular region of the muscarinic m3 receptor as a determinant of selective coupling to PI turnover. FEBS Lett. 1989 Nov 20;258(1):133–136. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81633-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong S. K., Parker E. M., Ross E. M. Chimeric muscarinic cholinergic: beta-adrenergic receptors that activate Gs in response to muscarinic agonists. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 15;265(11):6219–6224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]