Abstract
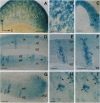
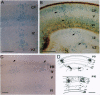
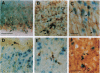
We have analyzed the developmental pattern of beta-galactosidase (beta-gal) expression in the cerebral cortex of the beta 2nZ3'1 transgenic mouse line, which was generated using regulatory elements of the beta 2-microglobulin gene and shows ectopic expression in nervous tissue. From embryonic day 10 onward, beta-gal was expressed in the medial and dorsal cortices, including the hippocampal region, whereas lateral cortical areas were devoid of labeling. During the period of cortical neurogenesis (embryonic days 11-17), beta-gal was expressed by selective precursors in the proliferative ventricular zone of the neocortex and hippocampus, as well as by a number of migrating and postmigratory neurons arranged into narrow radial stripes above the labeled progenitors. Thus, the transgene labels a subset of cortical progenitors and their progeny. Postnatally, radial clusters of beta-gal-positive neurons were discernible until postpartum day 10. At this age, the clusters were 250 to 500 microns wide, composed of neurons spanning all the cortical layers and exhibiting several neuronal phenotypes. These data suggest molecular heterogeneity of cortical progenitors and of the cohorts of postmitotic neurons originating from them, which implies intrinsic molecular mosaicism in both cortical progenitors and developing neurons. Furthermore, the data show that neurons committed to the expression of the transgene migrate along very narrow, radial stripes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altman J., Bayer S. A. Mosaic organization of the hippocampal neuroepithelium and the multiple germinal sources of dentate granule cells. J Comp Neurol. 1990 Nov 15;301(3):325–342. doi: 10.1002/cne.903010302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arimatsu Y., Miyamoto M., Nihonmatsu I., Hirata K., Uratani Y., Hatanaka Y., Takiguchi-Hayashi K. Early regional specification for a molecular neuronal phenotype in the rat neocortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):8879–8883. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.8879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arimatsu Y., Miyamoto M., Nihonmatsu I., Hirata K., Uratani Y., Hatanaka Y., Takiguchi-Hayashi K. Early regional specification for a molecular neuronal phenotype in the rat neocortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):8879–8883. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.8879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbe M. F., Levitt P. The early commitment of fetal neurons to the limbic cortex. J Neurosci. 1991 Feb;11(2):519–533. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-02-00519.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caviness V. S., Jr, Sidman R. L. Time of origin or corresponding cell classes in the cerebral cortex of normal and reeler mutant mice: an autoradiographic analysis. J Comp Neurol. 1973 Mar 15;148(2):141–151. doi: 10.1002/cne.901480202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen-Tannoudji M., Babinet C., Wassef M. Early determination of a mouse somatosensory cortex marker. Nature. 1994 Mar 31;368(6470):460–463. doi: 10.1038/368460a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen-Tannoudji M., Morello D., Babinet C. Unexpected position-dependent expression of H-2 and beta 2-microglobulin/lacZ transgenes. Mol Reprod Dev. 1992 Oct;33(2):149–159. doi: 10.1002/mrd.1080330206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis A. A., Temple S. A self-renewing multipotential stem cell in embryonic rat cerebral cortex. Nature. 1994 Nov 17;372(6503):263–266. doi: 10.1038/372263a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehay C., Giroud P., Berland M., Smart I., Kennedy H. Modulation of the cell cycle contributes to the parcellation of the primate visual cortex. Nature. 1993 Dec 2;366(6454):464–466. doi: 10.1038/366464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drezen J. M., Nouvel P., Babinet C., Morello D. Different regulation of class I gene expression in the adult mouse and during development. J Immunol. 1992 Jul 15;149(2):429–437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferri R. T., Levitt P. Cerebral cortical progenitors are fated to produce region-specific neuronal populations. Cereb Cortex. 1993 May-Jun;3(3):187–198. doi: 10.1093/cercor/3.3.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferri R. T., Levitt P. Regulation of regional differences in the differentiation of cerebral cortical neurons by EGF family-matrix interactions. Development. 1995 Apr;121(4):1151–1160. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.4.1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishell G., Mason C. A., Hatten M. E. Dispersion of neural progenitors within the germinal zones of the forebrain. Nature. 1993 Apr 15;362(6421):636–638. doi: 10.1038/362636a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grove E. A., Kirkwood T. B., Price J. Neuronal precursor cells in the rat hippocampal formation contribute to more than one cytoarchitectonic area. Neuron. 1992 Feb;8(2):217–229. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90289-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hockfield S., McKay R. D. Identification of major cell classes in the developing mammalian nervous system. J Neurosci. 1985 Dec;5(12):3310–3328. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-12-03310.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe L., Jeannotte L., Bikoff E. K., Robertson E. J. Analysis of beta 2-microglobulin gene expression in the developing mouse embryo and placenta. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 15;145(10):3474–3482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornack D. R., Rakic P. Radial and horizontal deployment of clonally related cells in the primate neocortex: relationship to distinct mitotic lineages. Neuron. 1995 Aug;15(2):311–321. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90036-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luskin M. B., Pearlman A. L., Sanes J. R. Cell lineage in the cerebral cortex of the mouse studied in vivo and in vitro with a recombinant retrovirus. Neuron. 1988 Oct;1(8):635–647. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90163-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConnell S. K. The control of neuronal identity in the developing cerebral cortex. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1992 Feb;2(1):23–27. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(92)90156-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mione M. C., Danevic C., Boardman P., Harris B., Parnavelas J. G. Lineage analysis reveals neurotransmitter (GABA or glutamate) but not calcium-binding protein homogeneity in clonally related cortical neurons. J Neurosci. 1994 Jan;14(1):107–123. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-01-00107.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misson J. P., Edwards M. A., Yamamoto M., Caviness V. S., Jr Identification of radial glial cells within the developing murine central nervous system: studies based upon a new immunohistochemical marker. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1988 Nov 1;44(1):95–108. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(88)90121-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowakowski R. S., Rakic P. The mode of migration of neurons to the hippocampus: a Golgi and electron microscopic analysis in foetal rhesus monkey. J Neurocytol. 1979 Dec;8(6):697–718. doi: 10.1007/BF01206671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Leary D. D. Do cortical areas emerge from a protocortex? Trends Neurosci. 1989 Oct;12(10):400–406. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(89)90080-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Rourke N. A., Dailey M. E., Smith S. J., McConnell S. K. Diverse migratory pathways in the developing cerebral cortex. Science. 1992 Oct 9;258(5080):299–302. doi: 10.1126/science.1411527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Rourke N. A., Sullivan D. P., Kaznowski C. E., Jacobs A. A., McConnell S. K. Tangential migration of neurons in the developing cerebral cortex. Development. 1995 Jul;121(7):2165–2176. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.7.2165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rakic P. Specification of cerebral cortical areas. Science. 1988 Jul 8;241(4862):170–176. doi: 10.1126/science.3291116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renfranz P. J., Cunningham M. G., McKay R. D. Region-specific differentiation of the hippocampal stem cell line HiB5 upon implantation into the developing mammalian brain. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):713–729. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90116-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. L., Rakic P., Goldman-Rakic P. S. Early phenotype expression of cortical neurons: evidence that a subclass of migrating neurons have callosal axons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1354–1358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soriano E., Del Rio J. A. Simultaneous immunocytochemical visualization of bromodeoxyuridine and neural tissue antigens. J Histochem Cytochem. 1991 Mar;39(3):255–263. doi: 10.1177/39.3.1671576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan S. S., Breen S. Radial mosaicism and tangential cell dispersion both contribute to mouse neocortical development. Nature. 1993 Apr 15;362(6421):638–640. doi: 10.1038/362638a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan S. S., Faulkner-Jones B., Breen S. J., Walsh M., Bertram J. F., Reese B. E. Cell dispersion patterns in different cortical regions studied with an X-inactivated transgenic marker. Development. 1995 Apr;121(4):1029–1039. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.4.1029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan S. S., Faulkner-Jones B., Breen S. J., Walsh M., Bertram J. F., Reese B. E. Cell dispersion patterns in different cortical regions studied with an X-inactivated transgenic marker. Development. 1995 Apr;121(4):1029–1039. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.4.1029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh C., Cepko C. L. Clonal dispersion in proliferative layers of developing cerebral cortex. Nature. 1993 Apr 15;362(6421):632–635. doi: 10.1038/362632a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh C., Cepko C. L. Clonal dispersion in proliferative layers of developing cerebral cortex. Nature. 1993 Apr 15;362(6421):632–635. doi: 10.1038/362632a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]