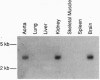
Abstract
Cyclic nucleotides modulate potassium (K) channel activity in many cells and are thought to act indirectly by inducing channel protein phosphorylation. Herein we report the isolation from rabbit of a gene encoding a K channel (Kcn1) that is specifically activated by cGMP and not by cAMP. Analysis of the deduced amino acid sequence (725 amino acids) indicates that, in addition to a core region that is highly homologous to Shaker K channels, Kcn1 also contains a cysteine-rich region similar to that of ligand-gated ion channels and a cyclic nucleotide-binding region. Northern blot analysis detects gene expression in kidney, aorta, and brain. Kcn1 represents a class of K channels that may be specifically regulated by cGMP and could play an important role in mediating the effects of substances, such as nitric oxide, that increase intracellular cGMP.
Full text
PDF
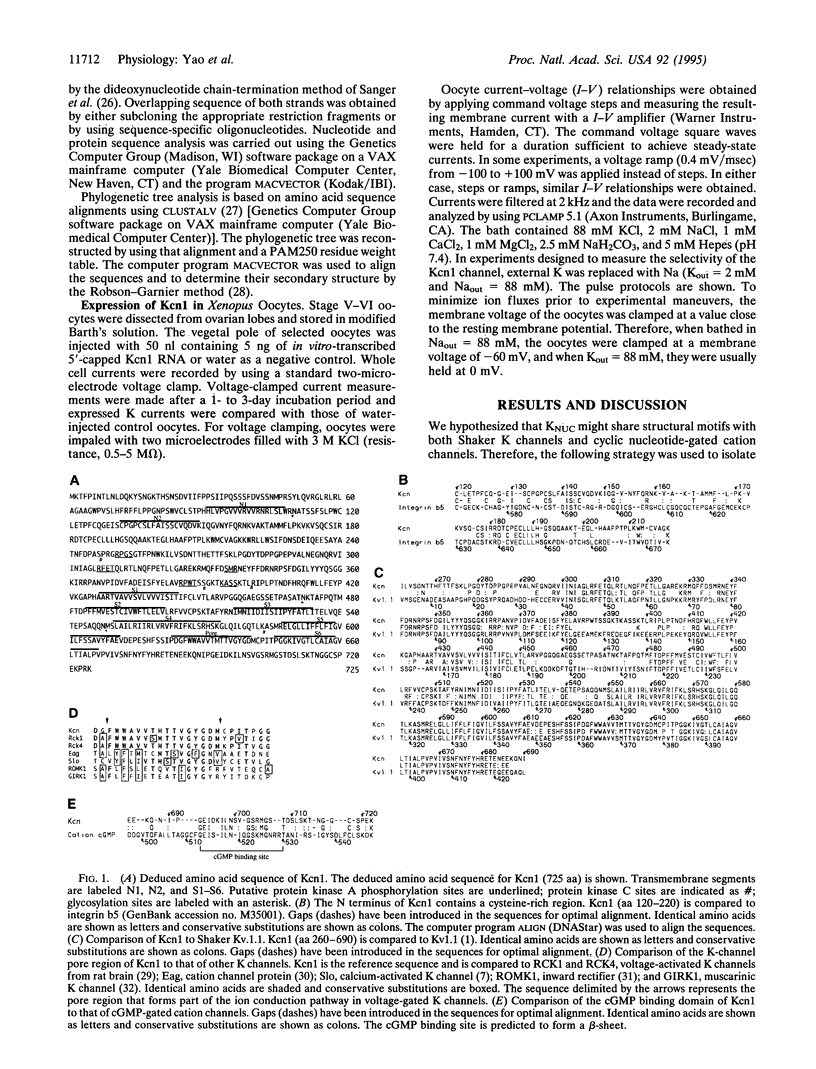
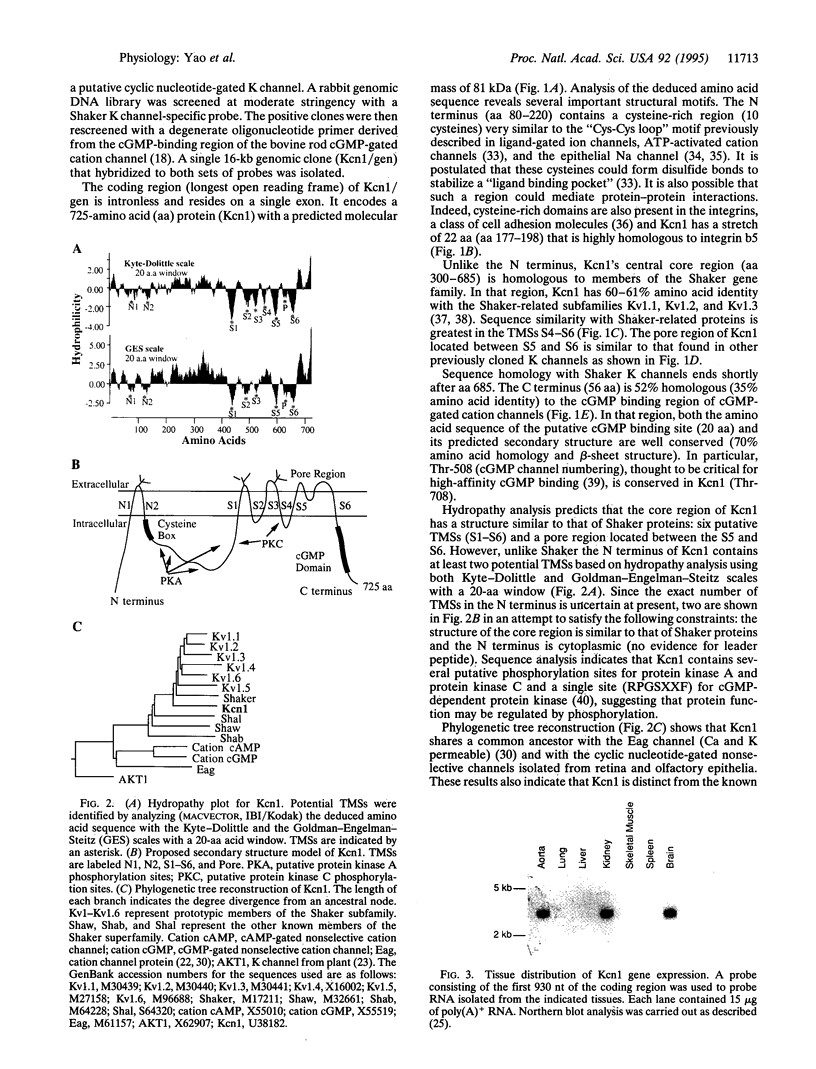
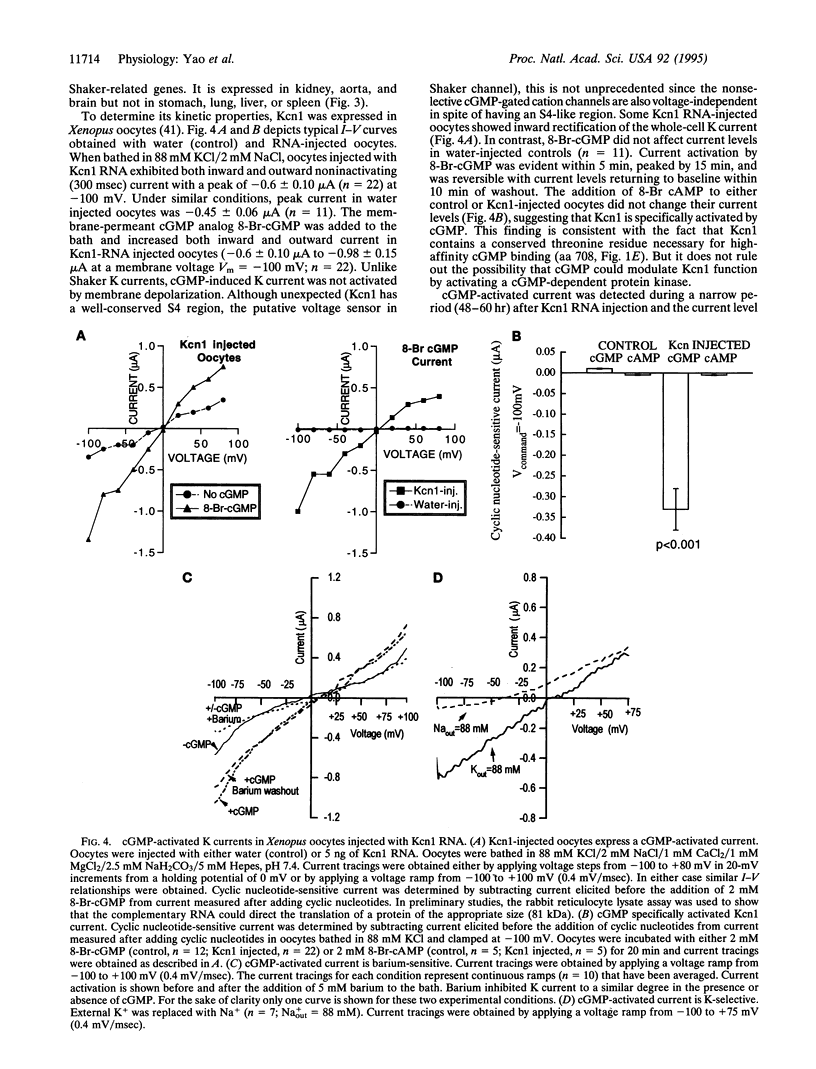

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelman J. P., Shen K. Z., Kavanaugh M. P., Warren R. A., Wu Y. N., Lagrutta A., Bond C. T., North R. A. Calcium-activated potassium channels expressed from cloned complementary DNAs. Neuron. 1992 Aug;9(2):209–216. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90160-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashford M. L., Bond C. T., Blair T. A., Adelman J. P. Cloning and functional expression of a rat heart KATP channel. Nature. 1994 Aug 11;370(6489):456–459. doi: 10.1038/370456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson N. S., Robertson G. A., Ganetzky B. A component of calcium-activated potassium channels encoded by the Drosophila slo locus. Science. 1991 Aug 2;253(5019):551–555. doi: 10.1126/science.1857984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brake A. J., Wagenbach M. J., Julius D. New structural motif for ligand-gated ion channels defined by an ionotropic ATP receptor. Nature. 1994 Oct 6;371(6497):519–523. doi: 10.1038/371519a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brüggemann A., Pardo L. A., Stühmer W., Pongs O. Ether-à-go-go encodes a voltage-gated channel permeable to K+ and Ca2+ and modulated by cAMP. Nature. 1993 Sep 30;365(6445):445–448. doi: 10.1038/365445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canessa C. M., Horisberger J. D., Rossier B. C. Epithelial sodium channel related to proteins involved in neurodegeneration. Nature. 1993 Feb 4;361(6411):467–470. doi: 10.1038/361467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canessa C. M., Schild L., Buell G., Thorens B., Gautschi I., Horisberger J. D., Rossier B. C. Amiloride-sensitive epithelial Na+ channel is made of three homologous subunits. Nature. 1994 Feb 3;367(6462):463–467. doi: 10.1038/367463a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandy K. G., Williams C. B., Spencer R. H., Aguilar B. A., Ghanshani S., Tempel B. L., Gutman G. A. A family of three mouse potassium channel genes with intronless coding regions. Science. 1990 Feb 23;247(4945):973–975. doi: 10.1126/science.2305265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen T. Y., Peng Y. W., Dhallan R. S., Ahamed B., Reed R. R., Yau K. W. A new subunit of the cyclic nucleotide-gated cation channel in retinal rods. Nature. 1993 Apr 22;362(6422):764–767. doi: 10.1038/362764a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colbran J. L., Francis S. H., Leach A. B., Thomas M. K., Jiang H., McAllister L. M., Corbin J. D. A phenylalanine in peptide substrates provides for selectivity between cGMP- and cAMP-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 15;267(14):9589–9594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delgado R., Hidalgo P., Diaz F., Latorre R., Labarca P. A cyclic AMP-activated K+ channel in Drosophila larval muscle is persistently activated in dunce. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):557–560. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desir G. V., Hamlin H. A., Puente E., Reilly R. F., Hildebrandt F., Igarashi P. Isolation of putative voltage-gated epithelial K-channel isoforms from rabbit kidney and LLC-PK1 cells. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jan;262(1 Pt 2):F151–F157. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1992.262.1.F151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desir G. V., Velázquez H. Identification of a novel K-channel gene (KC22) that is highly expressed in distal tubule of rabbit kidney. Am J Physiol. 1993 Jan;264(1 Pt 2):F128–F133. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1993.264.1.F128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhallan R. S., Macke J. P., Eddy R. L., Shows T. B., Reed R. R., Yau K. W., Nathans J. Human rod photoreceptor cGMP-gated channel: amino acid sequence, gene structure, and functional expression. J Neurosci. 1992 Aug;12(8):3248–3256. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-08-03248.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhallan R. S., Yau K. W., Schrader K. A., Reed R. R. Primary structure and functional expression of a cyclic nucleotide-activated channel from olfactory neurons. Nature. 1990 Sep 13;347(6289):184–187. doi: 10.1038/347184a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C. Anatomy of hypersensitive sites. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):213–214. doi: 10.1038/309213a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filatov G. N., Jainazarov A. B., Kolesnikov S. S., Lyubarsky A. L., Fesenko E. E. The effect of ATP, GTP and cAMP on the cGMP-dependent conductance of the fragments from frog rod plasma membrane. FEBS Lett. 1989 Mar 13;245(1-2):185–188. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80218-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frech G. C., VanDongen A. M., Schuster G., Brown A. M., Joho R. H. A novel potassium channel with delayed rectifier properties isolated from rat brain by expression cloning. Nature. 1989 Aug 24;340(6235):642–645. doi: 10.1038/340642a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frelin C. Mechanisms of vasoconstriction. Am Heart J. 1991 Mar;121(3 Pt 1):958–960. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(91)90226-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehlsen K. R., Dillner L., Engvall E., Ruoslahti E. The human laminin receptor is a member of the integrin family of cell adhesion receptors. Science. 1988 Sep 2;241(4870):1228–1229. doi: 10.1126/science.2970671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guy H. R., Durell S. R., Warmke J., Drysdale R., Ganetzky B. Similarities in amino acid sequences of Drosophila eag and cyclic nucleotide-gated channels. Science. 1991 Nov 1;254(5032):730–730. doi: 10.1126/science.1658932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heginbotham L., Abramson T., MacKinnon R. A functional connection between the pores of distantly related ion channels as revealed by mutant K+ channels. Science. 1992 Nov 13;258(5085):1152–1155. doi: 10.1126/science.1279807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henquin J. C. Adenosine triphosphate-sensitive K+ channels may not be the sole regulators of glucose-induced electrical activity in pancreatic B-cells. Endocrinology. 1992 Jul;131(1):127–131. doi: 10.1210/endo.131.1.1611991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. G., Bleasby A. J., Fuchs R. CLUSTAL V: improved software for multiple sequence alignment. Comput Appl Biosci. 1992 Apr;8(2):189–191. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/8.2.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho K., Nichols C. G., Lederer W. J., Lytton J., Vassilev P. M., Kanazirska M. V., Hebert S. C. Cloning and expression of an inwardly rectifying ATP-regulated potassium channel. Nature. 1993 Mar 4;362(6415):31–38. doi: 10.1038/362031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzmann S., Kukovetz W. R., Braida C., Pöch G. Pharmacological interaction experiments differentiate between glibenclamide-sensitive K+ channels and cyclic GMP as components of vasodilation by nicorandil. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Apr 29;215(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90600-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. Structural elements involved in specific K+ channel functions. Annu Rev Physiol. 1992;54:537–555. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.54.030192.002541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaupp U. B., Niidome T., Tanabe T., Terada S., Bönigk W., Stühmer W., Cook N. J., Kangawa K., Matsuo H., Hirose T. Primary structure and functional expression from complementary DNA of the rod photoreceptor cyclic GMP-gated channel. Nature. 1989 Dec 14;342(6251):762–766. doi: 10.1038/342762a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo Y., Reuveny E., Slesinger P. A., Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. Primary structure and functional expression of a rat G-protein-coupled muscarinic potassium channel. Nature. 1993 Aug 26;364(6440):802–806. doi: 10.1038/364802a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittler S. J., Lee A. K., Altherr M. R., Howard T. A., Seldin M. F., Hurwitz R. L., Wasmuth J. J., Baehr W. Primary structure and chromosomal localization of human and mouse rod photoreceptor cGMP-gated cation channel. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):6257–6262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rembold C. M. Regulation of contraction and relaxation in arterial smooth muscle. Hypertension. 1992 Aug;20(2):129–137. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.20.2.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rettig J., Wunder F., Stocker M., Lichtinghagen R., Mastiaux F., Beckh S., Kues W., Pedarzani P., Schröter K. H., Ruppersberg J. P. Characterization of a Shaw-related potassium channel family in rat brain. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2473–2486. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05312.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sentenac H., Bonneaud N., Minet M., Lacroute F., Salmon J. M., Gaymard F., Grignon C. Cloning and expression in yeast of a plant potassium ion transport system. Science. 1992 May 1;256(5057):663–665. doi: 10.1126/science.1585180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shabb J. B., Ng L., Corbin J. D. One amino acid change produces a high affinity cGMP-binding site in cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16031–16034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H. Nitric oxide: first in a new class of neurotransmitters. Science. 1992 Jul 24;257(5069):494–496. doi: 10.1126/science.1353273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stühmer W., Ruppersberg J. P., Schröter K. H., Sakmann B., Stocker M., Giese K. P., Perschke A., Baumann A., Pongs O. Molecular basis of functional diversity of voltage-gated potassium channels in mammalian brain. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3235–3244. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08483.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stühmer W., Stocker M., Sakmann B., Seeburg P., Baumann A., Grupe A., Pongs O. Potassium channels expressed from rat brain cDNA have delayed rectifier properties. FEBS Lett. 1988 Dec 19;242(1):199–206. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tare M., Parkington H. C., Coleman H. A., Neild T. O., Dusting G. J. Hyperpolarization and relaxation of arterial smooth muscle caused by nitric oxide derived from the endothelium. Nature. 1990 Jul 5;346(6279):69–71. doi: 10.1038/346069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W. H., McNicholas C. M., Segal A. S., Giebisch G. A novel approach allows identification of K channels in the lateral membrane of rat CCD. Am J Physiol. 1994 May;266(5 Pt 2):F813–F822. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1994.266.5.F813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]