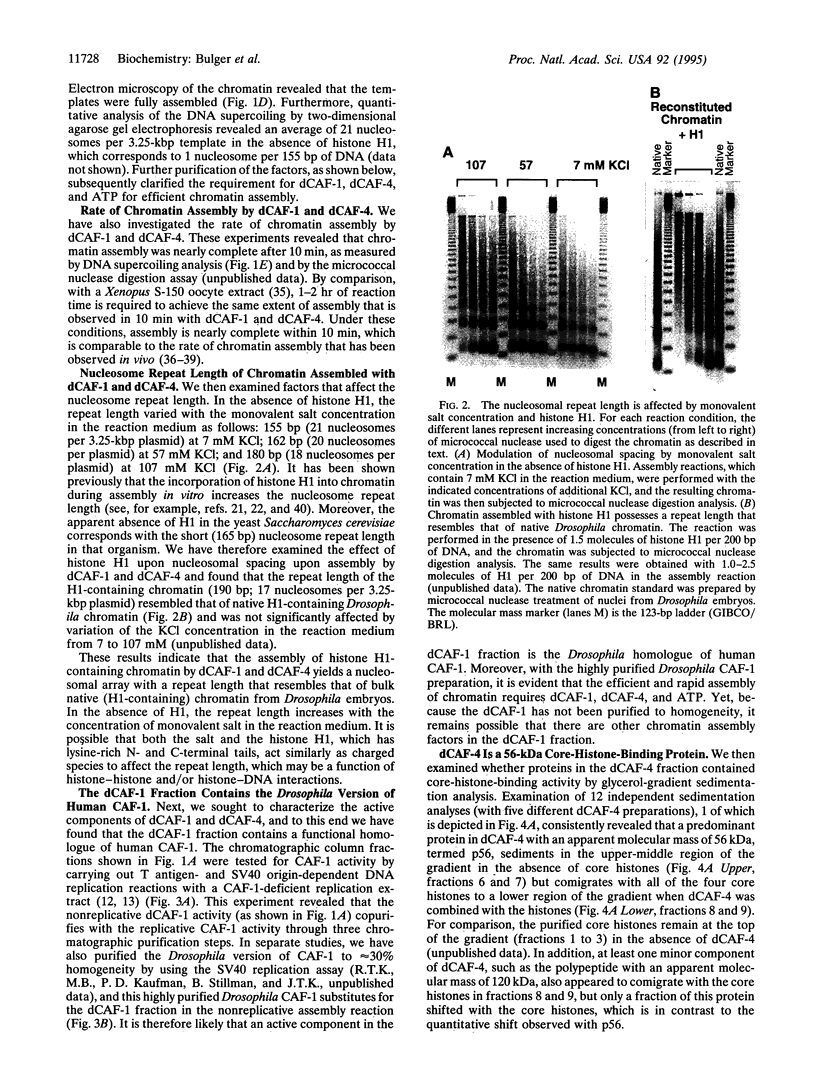
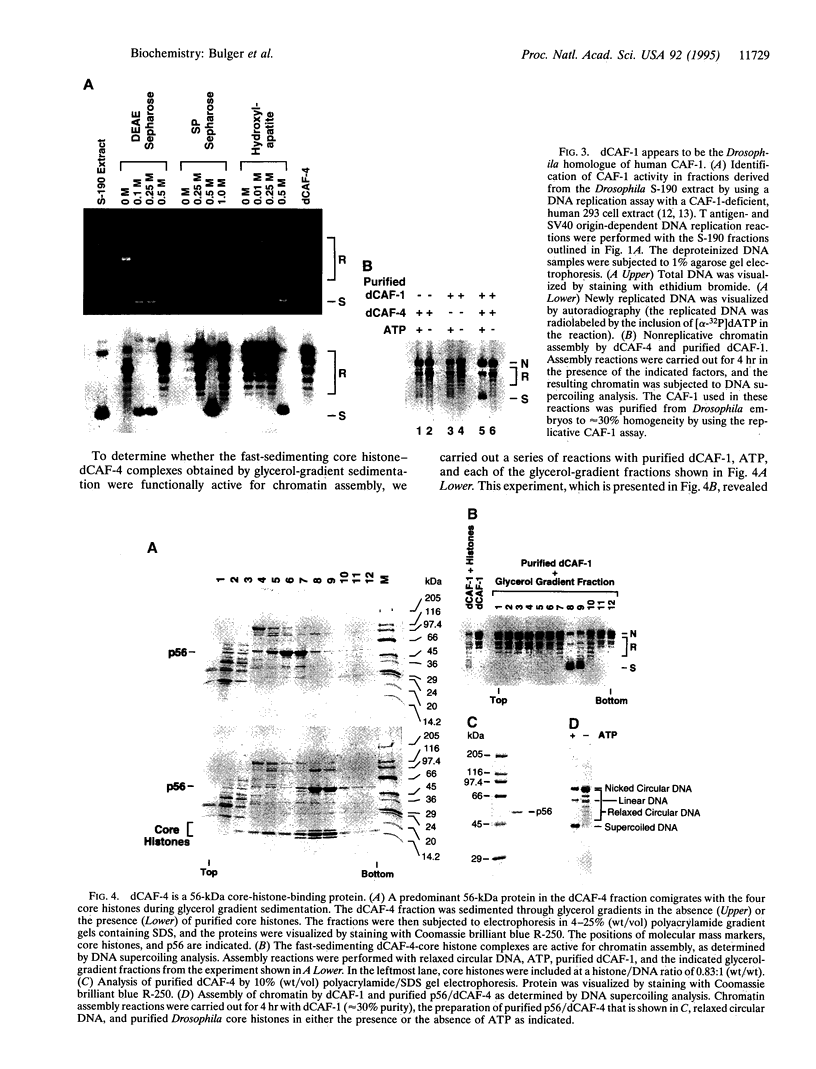
Abstract
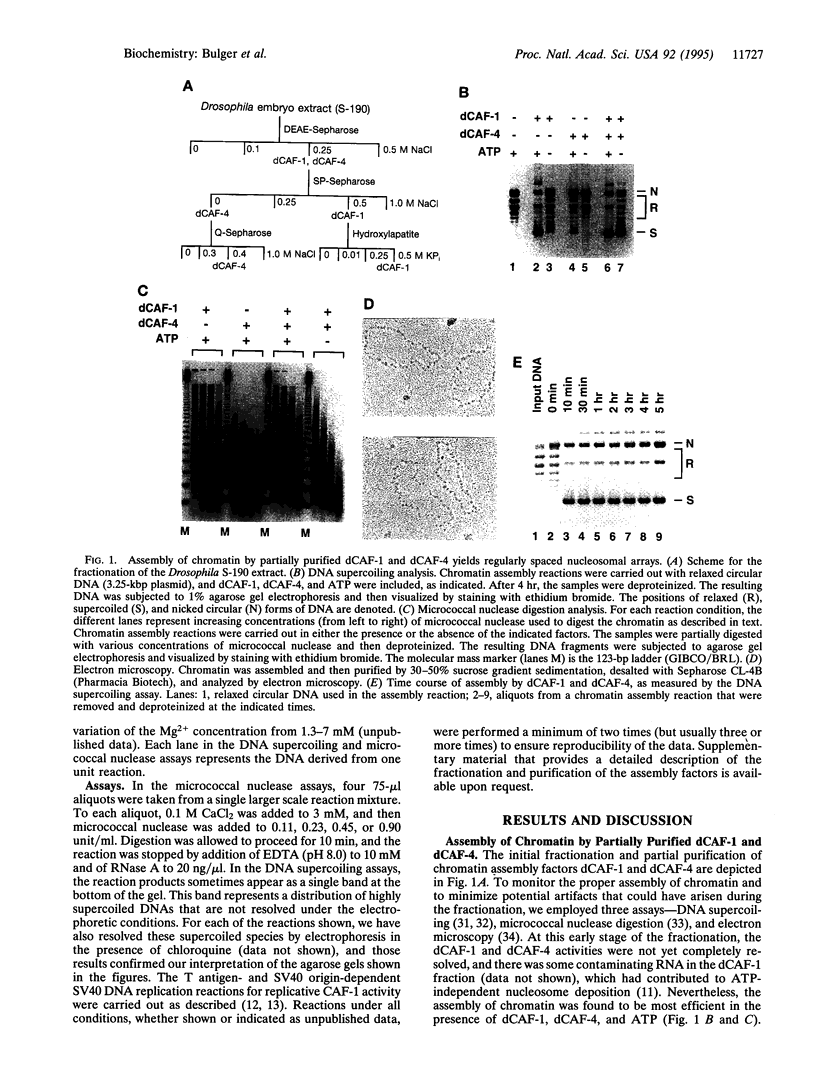
To ascertain the mechanism by which nucleosomes are assembled by factors derived from Drosophila embryos, two proteins termed Drosophila chromatin assembly factors (CAFs) 1 and 4 (dCAF-1 and dCAF-4) were fractionated and purified from a Drosophila embryo extract. The assembly of chromatin by dCAF-1, dCAF-4, purified histones, ATP, and DNA is a process that generates regularly spaced nucleosomal arrays with a repeat length that resembles that of bulk native Drosophila chromatin and is not obligatorily coupled to DNA replication. The assembly of chromatin by dCAF-1 and dCAF-4 is nearly complete within 10 min. The dCAF-1 activity copurified with the Drosophila version of chromatin assembly factor-1 (CAF-1), a factor that has been found to be required for the assembly of chromatin during large tumor (T) antigen-mediated, simian virus 40 (SV40) origin-dependent DNA replication. The dCAF-4 activity copurified with a 56-kDa core-histone-binding protein that was purified to > 90% homogeneity.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker P. B., Wu C. Cell-free system for assembly of transcriptionally repressed chromatin from Drosophila embryos. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):2241–2249. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.2241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cusick M. E., Lee K. S., DePamphilis M. L., Wassarman P. M. Structure of chromatin at deoxyribonucleic acid replication forks: nuclease hypersensitivity results from both prenucleosomal deoxyribonucleic acid and an immature chromatin structure. Biochemistry. 1983 Aug 2;22(16):3873–3884. doi: 10.1021/bi00285a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R. Reconstitution of short-spaced chromatin from the histone octamer and either HMG-14,17 or histone H1. J Mol Biol. 1993 Apr 5;230(3):824–836. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Germond J. E., Hirt B., Oudet P., Gross-Bellark M., Chambon P. Folding of the DNA double helix in chromatin-like structures from simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1843–1847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glikin G. C., Ruberti I., Worcel A. Chromatin assembly in Xenopus oocytes: in vitro studies. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):33–41. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90298-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruss C., Gutierrez C., Burhans W. C., DePamphilis M. L., Koller T., Sogo J. M. Nucleosome assembly in mammalian cell extracts before and after DNA replication. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2911–2922. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07482.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh T. S., Brown S. D., Huang P., Fostel J. Isolation and characterization of a gene encoding DNA topoisomerase I in Drosophila melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Dec 11;20(23):6177–6182. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.23.6177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishimi Y., Hirosumi J., Sato W., Sugasawa K., Yokota S., Hanaoka F., Yamada M. Purification and initial characterization of a protein which facilitates assembly of nucleosome-like structure from mammalian cells. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Aug 1;142(3):431–439. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08305.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishimi Y., Kikuchi A. Identification and molecular cloning of yeast homolog of nucleosome assembly protein I which facilitates nucleosome assembly in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 15;266(11):7025–7029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javaherian K., Tse Y. C., Vega J. Drosophila topoisomerase I: isolation, purification and characterization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6945–6955. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamakaka R. T., Bulger M., Kadonaga J. T. Potentiation of RNA polymerase II transcription by Gal4-VP16 during but not after DNA replication and chromatin assembly. Genes Dev. 1993 Sep;7(9):1779–1795. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.9.1779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamakaka R. T., Kaufman P. D., Stillman B., Mitsis P. G., Kadonaga J. T. Simian virus 40 origin- and T-antigen-dependent DNA replication with Drosophila factors in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;14(8):5114–5122. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.8.5114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman P. D., Kobayashi R., Kessler N., Stillman B. The p150 and p60 subunits of chromatin assembly factor I: a molecular link between newly synthesized histones and DNA replication. Cell. 1995 Jun 30;81(7):1105–1114. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80015-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinschmidt J. A., Seiter A., Zentgraf H. Nucleosome assembly in vitro: separate histone transfer and synergistic interaction of native histone complexes purified from nuclei of Xenopus laevis oocytes. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1309–1318. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08240.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Honda B. M., Mills A. D., Finch J. T. Nucleosomes are assembled by an acidic protein which binds histones and transfers them to DNA. Nature. 1978 Oct 5;275(5679):416–420. doi: 10.1038/275416a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lässle M., Richter A., Knippers R. Comparison of replicative and non-replicative chromatin assembly pathways in HeLa cell extracts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Aug 17;1132(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(92)90045-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson T., Wiegand R., Brutlag D. Ribonucleic acid and other polyanions facilitate chromatin assembly in vitro. Biochemistry. 1981 Apr 28;20(9):2594–2601. doi: 10.1021/bi00512a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll M., Kornberg R. D. Action of micrococcal nuclease on chromatin and the location of histone H1. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jan 25;109(3):393–404. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80019-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paranjape S. M., Kamakaka R. T., Kadonaga J. T. Role of chromatin structure in the regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:265–297. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.63.070194.001405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Campos A., Shimamura A., Worcel A. Assembly and properties of chromatin containing histone H1. J Mol Biol. 1989 Sep 5;209(1):135–150. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90177-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruberti I., Worcel A. Mechanism of chromatin assembly in Xenopus oocytes. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jun 5;189(3):457–476. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90317-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryoji M., Worcel A. Chromatin assembly in Xenopus oocytes: in vivo studies. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):21–32. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90297-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sapp M., Worcel A. Purification and mechanism of action of a nucleosome assembly factor from Xenopus oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):9357–9365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealy L., Cotten M., Chalkley R. Xenopus nucleoplasmin: egg vs. oocyte. Biochemistry. 1986 May 20;25(10):3064–3072. doi: 10.1021/bi00358a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. T., Thoma F., Brubaker J. M. Chromatin reconstituted from tandemly repeated cloned DNA fragments and core histones: a model system for study of higher order structure. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):799–808. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90276-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. A., Jackson V., Chalkley R. Two-stage maturation process for newly replicated chromatin. Biochemistry. 1984 Mar 27;23(7):1576–1581. doi: 10.1021/bi00302a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S., Stillman B. Immunological characterization of chromatin assembly factor I, a human cell factor required for chromatin assembly during DNA replication in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 25;266(18):12041–12047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S., Stillman B. Purification and characterization of CAF-I, a human cell factor required for chromatin assembly during DNA replication in vitro. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):15–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90398-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S., Stillman B. Stepwise assembly of chromatin during DNA replication in vitro. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):971–980. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08031.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman B. Chromatin assembly during SV40 DNA replication in vitro. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):555–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90287-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svaren J., Chalkley R. The structure and assembly of active chromatin. Trends Genet. 1990 Feb;6(2):52–56. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90074-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoma F., Koller T., Klug A. Involvement of histone H1 in the organization of the nucleosome and of the salt-dependent superstructures of chromatin. J Cell Biol. 1979 Nov;83(2 Pt 1):403–427. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.2.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tremethick D. J., Drew H. R. High mobility group proteins 14 and 17 can space nucleosomes in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):11389–11393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tremethick D. J., Frommer M. Partial purification, from Xenopus laevis oocytes, of an ATP-dependent activity required for nucleosome spacing in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):15041–15048. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worcel A., Han S., Wong M. L. Assembly of newly replicated chromatin. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):969–977. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90280-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker K., Worcel A. The histone H3/H4.N1 complex supplemented with histone H2A-H2B dimers and DNA topoisomerase I forms nucleosomes on circular DNA under physiological conditions. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14487–14496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]