Abstract
Background
Water pipe tobacco smoking is spreading globally and is increasingly becoming popular in the United States, particularly among young people. While many perceive water pipe smoking to be relatively safe, clinical experimental studies indicate significant exposures to tobacco smoke carcinogens following water pipe use. We investigated biomarkers of nicotine intake and carcinogen exposure from water pipe smoking in the naturalistic setting of hookah bars.
Methods
Fifty-five experienced water pipe users were studied before and after smoking water pipe in their customary way in a hookah bar. Urine samples were analyzed for nicotine, cotinine, the tobacco-specific nitrosamine 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1- butanol (NNAL), and mercapturic acid metabolites of volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
Results
We found an average 73-fold increase in nicotine, 4-fold increase in cotinine, 2-fold increase in NNAL, and 14-91% increase in VOC mercapturic acid metabolites immediately following water pipe smoking. We saw moderate to high correlations between changes in tobacco-specific biomarkers (nicotine, cotinine, and NNAL) and several mercapturic acid metabolites of VOC.
Conclusion
Water pipe smoking in a hookah bar is associated with significant nicotine intake and carcinogen exposure.
Impact
Given the significant intake of nicotine and carcinogens, chronic water pipe use could place users at increased risk of cancer and other chronic diseases.
Keywords: water pipe, hookah bars, nicotine, NNAL, alternative tobacco products, volatile organic compounds
INTRODUCTION
Tobacco has been smoked for centuries in devices known as hookah, shisha, sheesha, borry, goza, narghile, shui yun dai, hubble-dubble, or water pipe, depending on the country (“water pipe” is used in this report) (1). A water pipe typically consists of a head that is connected to a water jar and one or more hoses with a mouthpiece. A tobacco and moist fruit preparation is placed in the head of the water pipe, and burning charcoal is placed on top of the tobacco separated by a perforated aluminum foil. The smoker inhales through a mouthpiece, which draws air and hot combustion products from the burning charcoal through the tobacco preparation, creating an aerosol consisting of volatilized and pyrolized tobacco components. The smoke bubbles through the water in the jar, cooling the smoke, before being carried through the hose to the smoker.
In recent years water pipe use has increased significantly in the U.S., Europe, and in regions such as the eastern Mediterranean, especially among the youth (2). 1.5% of the U.S. adult population smoke water pipes compared to 19.5% who smoke cigarettes, but the prevalence of water pipe smoking is higher among young adults aged 18–24 (7.8%) (3) The popularity of water pipes is even higher among U.S. college students, with as many as 40% reporting ever smoking water pipes and up to 20% reporting current water pipe smoking (past 30-day) on some college campuses (4-5). Users of water pipes perceive it to be less harmful than cigarette smoking (6).
A typical water pipe smoking session lasts about 45–60 minutes (2, 7). During that time users are exposed to significant concentrations of carbon monoxide (CO), nicotine, tobacco specific nitrosamines (TSNA), carcinogenic polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), and volatile aldehydes in water pipe smoke (8-11). Biomarkers of exposure to these chemical constituents have been measured in water pipe users at considerable levels (9, 12-13). In a recent crossover study carried out in a clinical research ward, greater CO, benzene, and high molecular weight PAH exposure, lower nicotine intake, and less exposure to TSNA, 1,3-butadiene, acrolein, acrylonitrile, propylene oxide, ethylene oxide, and low molecular weight PAHs were measured while smoking water pipes compared to cigarettes (14).
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs), in addition to TSNAs and PAHs, are important classes of carcinogens, toxicants, and/or irritants present in tobacco smoke (15). The gas phase constituents in mainstream tobacco smoke contribute heavily towards tobacco smoke cancer risk indices (16-17). Benzene occurs in large quantities in tobacco smoke, is a known human carcinogen, and is associated with leukemia in smokers (18-19). Acrolein, also found in high amounts in tobacco smoke, is thought to be a major etiological agent for cigarette smoke-related lung cancer and cardiovascular disease (20-21). Systemic exposure to VOCs can be measured using highly specific mercapturic acid metabolites formed from glutathione (GSH) S-conjugates via the mercapturic acid pathway and excreted in the urine (22). VOC mercapturic acid metabolites have been measured in water pipe smokers in a clinical study (14).
The goal of the present study was to assess changes in biomarkers of nicotine, TSNAs, and VOCs after single evenings of water pipe smoking at commercial hookah bars or lounges. While salivary cotinine and expired CO have been reported in natural environment water pipe smokers (23), this is the first study, to our knowledge, to assess systemic exposure to TSNAs and VOCs from water pipe smoking in a naturalistic hookah bar setting.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Subjects
Fifty-five healthy and experienced water pipe smokers (43.6% female) participated in the study. We sought to recruit subjects who smoked water pipes exclusively or nearly exclusively if they agreed to refrain from smoking any other tobacco products for one week prior to going to the hookah bar. Eight subjects (2 females and 6 males) were later found to have pre-exposure urine cotinine levels that were greater than 30 ng/ml, a cut-point selected to discriminate between non-smokers and those who may be highly exposed to secondhand cigarette smoke or are light smokers (24). These subjects were kept in the study and are referred to as “suspected cigarette smokers”. Exclusion criteria included pregnancy or breast feeding; current alcohol or drug abuse; current use of smokeless tobacco, pipes, cigars, and nicotine medications; and, regular use of medications other than vitamins, oral contraceptives, hormone replacements, or aspirin. Study participants included 9 Asians, 4 African Americans, 32 non-Hispanic whites, and 10 of mixed ethnicity. The average age was 24.5 years (range, 18–48), and the average body mass index (BMI) was 23.3 (17.7–33.3). Twenty-four subjects (43.6%) reported some exposure to secondhand cigarette smoke over the past 7 days prior to the study day, and 22 subjects (40%) reported smoking marijuana within the past 30 days prior to the study day.
Participants were recruited through internet postings (Craigslist) and word of mouth. Subjects were financially compensated for their time. The study was approved by the Committee on Human Resource at the University of California, San Francisco.
Study protocol
This was a naturalistic study of water pipe smokers in hookah bars or lounges. Interested volunteers individually attended a recruitment session at a clinical research facility and were screened for study eligibility. Eligible subjects were admitted into the study after informed consent. Subjects were given three pre-labeled urine collection containers with storage bags, along with specimen and bar visit forms. On the study day, subjects collected a urine sample before going out to the hookah bar (referred to as “pre-exposure”), which was immediately refrigerated. Subjects then went out to a hookah bar of their choice in the San Francisco Bay area and smoked water pipe(s) as desired. Immediately after returning home from the hookah bar, subjects filled out the bar visit form with information on total time spent at the bar, total time spent smoking the water pipes, number of tobacco bowls smoked, number of shared users, and total time exposed to secondhand cigarette smoke during the visit, and collected a second urine sample (“post-exposure”). The first voided urine sample (referred to as “next day”) was collected after waking in the morning and stored with the other samples. All urine samples were kept refrigerated until they were brought to the clinical research facility where they were frozen at – 20°C until laboratory analyses.
Laboratory analysis
Nicotine, cotinine, and 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanol (NNAL), a metabolite of the lung-selective TSNA carcinogen 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone (NNK), were measured in pre-, post-exposure and next day urine samples. Because there is a lag between exposure, generation, and excretion of metabolites such as NNAL, we measured levels in next morning urine samples to ensure that peak concentrations were characterized. The following mercapturic acid metabolites of VOCs were measured in pre- and post-exposure urine samples (parent compounds listed in parentheses): 2-hydroxypropyl (propylene oxide), 3-hydroxypropyl (acrolein), 2-carbamoylethyl (acrylamide), cyanoethyl (acrylonitrile), 2-hydroxy-3-buten-1-yl or isomer(s) [abbrev. MHBMA] (1,3-butadiene), 2- hydroxyethyl (ethylene oxide), and phenyl (benzene). VOC metabolites were not measured in next day samples because of their relatively short half-lives (25). Analyses of urine samples were carried out using liquid chromatography – tandem mass spectrometry methods (14, 26-28).
Statistical analyses
Differences in demographic variables and pre-exposure (baseline) biomarker levels between males and females were analyzed using Fisher's exact test or the non-parametric Wilcoxon two-sample test. Smoking behavior and biomarkers of exposure differ between men and women who smoke cigarettes, hence the comparison of exposure to water pipe toxicants by sex (29). Since the biomarker data were not normally distributed, log transformation of the data was performed for the following analyses. Changes in biomarker levels over time (at pre-, post-exposure and next day) were assessed using repeated measures ANOVA, with or without covariates included. In the models with covariates, we included demographic variables (sex, age, and BMI) and exposure-related covariates, excluding highly collinear exposure-related variables. The exposure-related covariates included were: self-reported water pipe use (daily, weekly, monthly, and yearly, see Table 1 for description); secondhand cigarette smoke exposure in past 7 days prior to study (yes/no); marijuana use (yes/no); time spent smoking water pipe during study smoking session; number of bowls smoked per user (obtained as number of bowls smoked divided by number of shared users including study participant); and secondhand cigarette smoke exposure during hookah bar visit (yes/no). The repeated measures analyses were done for all subjects, and separately for “non-cigarette smokers” and “suspected cigarette smokers”. Test of differences in biomarker concentrations between time points were consistent with or without covariates included and the covariate-adjusted concentrations presented were very similar or equal to the unadjusted concentrations. Finally, Pearson correlation coefficients were computed between changes in biomarker concentrations, and between changes in biomarker concentrations and time in bar (min), smoking duration (min), number of bowls smoked, bowls smoked per user, and prior SHS (hr). All analyses were carried out using SAS v. 9.3 (SAS Institute, Inc., Cary, NC, USA) and statistical tests were considered significant at α = 0.05.
Table 1.
Demographics and baseline biomarkers by sex
| Characteristic | Females | Males | All subjects |
|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | 24 (43.6) | 31 (56.4) | 55 (100) |
| Age (mean, range) | 22.7 (19–33) | 25.9 (18–48)* | 24.5 (18–48) |
| BMI (mean, range) | 22.4 (17.7–33.3) | 24.0 (18.3–32.3)* | 23.3 (17.7–33.3) |
| Race (n, %) | |||
| Asian | 4 (7.3) | 5 (9.1)* | 9 (16.4) |
| Black | 2 (3.6) | 2 (3.6) | 4 (7.3) |
| White | 10 (18.2) | 22 (40.0) | 32 (58.2) |
| Mixed | 8 (14.6) | 2 (3.6) | 10 (18.2) |
| Suspected cigarette smoker | |||
| no (n,%) | 22 (40.0) | 25 (45.5) | 47 (85.5) |
| yes (n,%) | 2 (3.6) | 6 (10.9) | 8 (14.5) |
| Hookah use classification | |||
| daily (n, %) | 1 (1.8) | 2 (3.6) | 3 (5.5) |
| weekly (n, %) | 4 (7.3) | 6 (10.9) | 10 (18.2) |
| monthly (n, %) | 11 (20.0) | 11 (20) | 22 (40.0) |
| yearly (n, %) | 4 (7.3) | 3 (5.5) | 7 (12.7) |
| not reported (n, %) | 4 (7.3) | 9 (16.4) | 13 (23.6) |
| Marijuana use | |||
| no (n,%) | 15 (27.3) | 18 (32.7) | 33 (60.0) |
| yes (n,%) | 9 (16.4) | 13 (23.6) | 22 (40.0) |
| Time in bar (min)a | 108 (80–128) | 95 (60–120) | 101 (75–120) |
| Smoking duration (min)a | 71 (55–75) | 76 (45–80) | 74 (45–80) |
| Number of bowls useda | 1.3 (1.0–2.0) | 1.5 (1.0–2.0) | 1.5 (1.0–2.0) |
| Number of shared usersa | 2.9 (2.0–4.0) | 2.8 (2.0–4.0) | 2.9 (2.0–4.0) |
| Bowls per usera | 0.6 (0.3–0.8) | 0.6 (0.3–0.7) | 0.6 (0.3–0.7) |
| Prior SHS (hr)b | 3.0 (1.0–5.0) | 4.0 (2.0–5.0) | 3.0 (1.6–5.0) |
| no (n,%) | 13 (23.6) | 18 (32.7) | 31 (56.4) |
| yes (n,%) | 11 (20.0) | 13 (23.6) | 24 (43.6) |
| Bar SHS (min)b | 8.5 (5.0–21.0) | 8.5 (4.0–27.5) | 8.5 (5.0–27.5) |
| no (n,%) | 20 (36.4) | 23 (41.8) | 43 (78.2) |
| yes (n,%) | 4 (7.3) | 8 (14.6) | 12 (21.8) |
| Biomarkers c | |||
| Expired CO (ppm) | 2.5 (1.0–3.0) | 4.1 (2.0–6.0)* | 3.4 (2.0–4.0) |
| Cotinine (ng/mg creat) | 14.3 (9.30–22.0) | 13.1 (9.13–18.7) | 13.6 (10.4–17.7) |
| Nicotine (ng/mg creat) | 2.19 (0.99–4.88) | 2.45 (1.23–4.88) | 2.34 (1.41–3.87) |
| NNAL (pg/mg creat) | 1.03 (0.55–1.90) | 1.23 (0.73–2.07) | 1.14 (0.78–1.67) |
| VOC mercapturic acid metabolites (ng/mg creatinine) | |||
| 2-OH-propyl | 37.0 (26.3–52.2) | 40.6 (27.2–60.5) | 40.0 (30.0–50.7) |
| 3-OH-propyl | 315.1 (217.0–457.7) | 353.2 (255.1–489.2) | 336.1 (264.9–426.3) |
| 2-Carbamoylethyl | 96.8 (73.8–127.0) | 98.2 (75.7–127.5) | 97.6 (81.3–117.2) |
| Cyanoethyl | 4.56 (2.38–8.74) | 5.92 (3.04–11.5) | 5.28 (3.34–8.35) |
| MHBMA | 0.242 (0.166–0.354) | 0.198 (0.143–0.273) | 0.216 (0.170–0.274) |
| OH-ethyl | 3.30 (2.63–4.15) | 2.73 (2.19–3.41) | 2.97 (2.54–3.47) |
| Phenyl | 0.199 (0.137–0.290) | 0.188 (0.132–0.267) | 0.193 (0.150–0.247) |
NOTES: “Suspected cigarette smoker” if urine cotinine > 30 ng/ml; “smoking duration” = total time spent smoking hookah; “prior SHS” = total time exposed to secondhand cigarette smoke in past 7 days (hours); “bar SHS” = time exposed to secondhand cigarette smoke while in hookah bar (min); creat = creatinine;
presented as mean (interquartile range);
statistics for “yes” only;
geometric mean (95% CI);
daily = approximately daily use or 3 or more times per week; weekly = approximately weekly use (1-2 times per week); monthly = approximately monthly use (several times per month but not weekly); yearly = several times per year or less;
NNAL = 4–(methylnitrosamino)–1–(3–pyridyl)–1–butanol;
VOC mercapturic acid metabolites and parent compounds: 2-hydroxypropyl (propylene oxide), 3-hydroxypropyl (acrolein), 2-carbamoylethyl (acrylamide), cyanoethyl (acrylonitrile), 2-hydroxy-3-buten-1-yl or isomer(s) [abbrev. MHBMA] (1,3-butadiene), 2-hydroxyethyl (ethylene oxide), and phenyl (benzene)
significant difference between females and males (p < 0.05)
RESULTS
Demographic data and baseline (pre-exposure) biomarker levels by sex are presented in Table 1. Age (p=0.02), BMI (p=0.02), race (p=0.045), and expired CO (p=0.009) were significantly different by sex while the other variables were not significantly different. Of 55 subjects, 3 (5.5%) smoked water pipes at least daily, 10 (18.2%) at least weekly, 22 (40%) at least monthly, and 7 (12.7%) at least once a year [13 (23.6%) did not report smoking frequency; see Table 1 for description of water pipe use]. Subjects spent an average of 101 minutes at the hookah bars and smoked water pipes for an average of 74 minutes. On average, 1.5 bowls of tobacco preparation were smoked per session, 2.9 users including the study participants shared the water pipes, and study participants smoked an average of 0.6 bowls per user. Twelve subjects (21.8%) reported being exposed to secondhand cigarette smoke at the hookah bar for an average duration of 8.5 minutes.
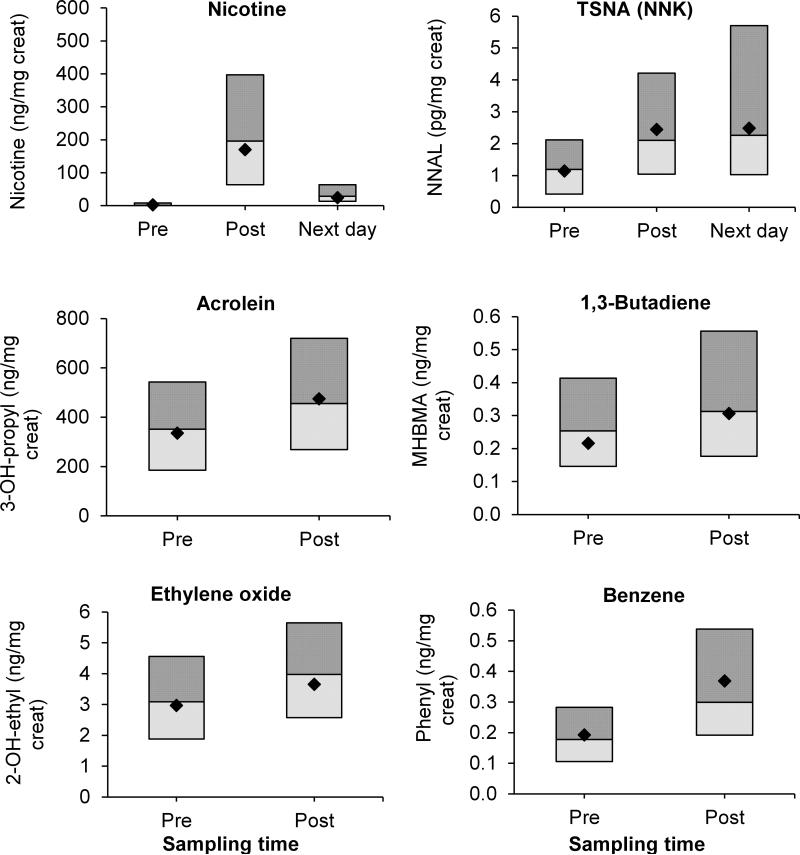
Geometric means and 95% CI for urine nicotine, cotinine, NNAL, and VOC mercapturic acid metabolite concentrations adjusted for covariates at pre-exposure, post-exposure, and next day where applicable, the ratio of post- to pre-exposure and next day to pre-exposure, and test of differences are presented in Table 2. Data are presented for all subjects, “non-cigarette smokers” and “suspected cigarette smokers”. Figure 1 shows the distribution of urine nicotine, NNAL, and mercapturic acid metabolites of acrolein, 1,3-butadiene, ethylene oxide, and benzene among all subjects.
Table 2.
Biomarker concentrations by sampling times, adjusted for covariates, for all subjects (n=55), “non-cigarette smokers” (n=47), and “suspected cigarette smokers” (n=8). Presented as GM and 95% CI.
| Biomarker | Sampling time |
Post to pre-exposure ratio | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-exposure | Post-exposure | |||
| Cotinine (ng/mg creatinine) | ||||
| all subjects | 14.4 (9.70–21.3) | 59.3 (40.0–87.7) | 4.13 (2.93–5.81) | <.001 |
| non-CS | 11.8 (7.21–19.2) | 55.3 (33.9–90.1) | 4.70 (3.23–6.83) | <.001 |
| suspected CS | 55.7 (27.8–111) | 107 (53.6–215) | 1.93 (1.04–3.56) | 0.04 |
| Nicotine (ng/mg creatinine) | ||||
| all subjects | 3.12 (1.74–5.60) | 227 (126–407) | 72.9 (37.8–140) | <.001 |
| non-CS | 2.59 (1.32–5.12) | 262 (132–516) | 101 (52.8–193) | <.001 |
| suspected CS | 14.8 (4.01–54.4) | 158 (42.9–581) | 10.7 (1.03–111) | 0.047 |
| NNAL (pg/mg creatinine) | ||||
| all subjects | 1.32 (0.83–2.11) | 2.84 (1.79–4.51) | 2.14 (1.44–3.20) | <.001 |
| non-CS | 1.24 (0.758–2.03) | 2.87 (1.76–4.69) | 2.32 (1.55–3.46) | <.001 |
| suspected CS | 3.23 (0.879–11.9) | 4.38 (1.19–16.1) | 1.36 (0.28–6.67) | 0.85 |
| 2-OH-propyl (ng/mg creatinine) | ||||
| all subjects | 38.5 (22.9–64.8) | 49.1 (29.2–82.5) | 1.27 (0.95–1.70) | 0.10 |
| non-CS | 52.0 (27.0–100) | 66.9 (34.8–128) | 1.29 (0.92–1.80) | 0.14 |
| suspected CS | 33.6 (19.0–59.0) | 40.2 (22.7–71.3) | 1.20 (0.76–1.87) | 0.38 |
| 3-OH–propyl (ng/mg creatinine) | ||||
| all subjects | 309 (203–471) | 437 (287–666) | 1.41 (1.21–1.65) | <.001 |
| non-CS | 281 (169.7–466) | 398 (240–661) | 1.42 (1.19–1.68) | <.001 |
| suspected CS | 390.0 (173–878) | 543 (241–1223) | 1.39 (0.89–2.18) | 0.12 |
| 2-Carbamoylethyl (ng/mg creatinine) | ||||
| all subjects | 89.3 (66.5–120) | 101 (75.6–136) | 1.14 (1.03–1.26) | 0.01 |
| non-CS | 93.5 (66.2–132) | 107 (76.3–152) | 1.15 (1.03–1.29) | 0.01 |
| suspected CS | 133 (67.9–261) | 140 (71.4–275) | 1.05 (0.85–1.30) | 0.59 |
| Cyanoethyl (ng/mg creatinine) | ||||
| all subjects | 5.68 (3.14–10.3) | 9.69 (5.36–17.5) | 1.71 (1.43–2.04) | <.001 |
| non-CS | 5.22 (2.55–10.7) | 9.30 (4.54–19.1) | 1.78 (1.46–2.18) | <.001 |
| suspected CS | 17.5 (3.01–102.1) | 23.1 (3.97–134) | 1.32 (0.84–2.08) | 0.19 |
| 2-Hydroxy-3-buten-1-yl (or MHBMA) (ng/mg creatinine) | ||||
| all subjects | 0.18 (0.11–0.28) | 0.25 (0.16–0.40) | 1.42 (1.08–1.85) | 0.01 |
| non-CS | 0.15 (0.10–0.24) | 0.21 (0.13–0.32) | 1.35 (1.03–1.77) | 0.03 |
| suspected CS | 0.17 (0.06–0.51) | 0.33 (0.11–0.96) | 1.89 (0.61–5.87) | 0.22 |
| OH–ethyl (ng/mg creatinine) | ||||
| all subjects | 2.98 (2.31–3.85) | 3.68 (2.85–4.75) | 1.23 (1.10–1.39) | <.001 |
| non-CS | 3.03 (2.22–4.15) | 3.75 (2.74–5.13) | 1.24 (1.09–1.41) | 0.002 |
| suspected CS | 3.65 (2.53-–5.26) | 4.45 (3.09–6.42) | 1.22 (0.88–1.69) | 0.192 |
| Phenyl (ng/mg creatinine) | ||||
| all subjects | 0.18 (0.12–0.27) | 0.34 (0.22–0.53) | 1.91 (1.48–2.47) | <.001 |
| non-CS | 0.19 (0.11–0.31) | 0.35 (0.21–0.58) | 1.87 (1.40–2.49) | <.001 |
| suspected CS | 0.25 (0.08–0.79) | 0.54 (0.17–1.74) | 2.21 (1.15–4.24) | 0.02 |
| Biomarker | Sampling time |
Next day to pre-exposure ratio | p–value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-exposure | Next day | |||
| Cotinine (ng/mg creatinine) | ||||
| all subjects | 14.4 (9.70 – 21.3) | 45.9 (31.0 – 67.9) | 3.20 (2.27 – 4.50) | <.001 |
| non-CS | 11.8 (7.21 – 19.2) | 45.2 (27.7 – 73.7) | 3.84 (2.64 – 5.59) | <.001 |
| suspected CS | 55.7 (27.8 – 111.7) | 60.2 (30.0 – 120.6) | 1.08 (0.58 – 2.00) | 0.76 |
| Nicotine (ng/mg creatinine) | ||||
| all subjects | 3.12 (1.74 – 5.60) | 32.3 (18.0 – 58.0) | 10.4 (5.37 – 20.0) | <.001 |
| non-CS | 2.59 (1.32 – 5.12) | 38.1 (19.3 – 75.1) | 14.7 (7.68 – 28.1) | <.001 |
| suspected CS | 14.8 (4.01 – 54.4) | 19.8 (5.37 – 72.7) | 1.34 (0.13 – 13.9) | 0.93 |
| NNAL (pg/mg creatinine) | ||||
| all subjects | 1.32 (0.83 – 2.11) | 2.88 (1.81 – 4.59) | 2.18 (1.46 – 3.25) | <.001 |
| non-CS | 1.24 (0.76 – 2.03) | 2.96 (1.81 – 4.84) | 2.39 (1.60 – 3.57) | <.001 |
| suspected CS | 3.23 (0.88 – 11.9) | 4.08 (1.11 – 15.0) | 1.26 (0.26 – 6.21) | 0.91 |
NOTES: Smoking status determined by urine cotinine cut–point of 30 ng/ml; non-CS = non-cigarette smoker; suspected CS = suspected cigarette smoker;
Adjusted for covariates: sex, age, BMI, hookah use category, prior SHS (yes/no), marijuana use (yes/no), time spent smoking hookah, average bowls, and bar SHS (yes/no);
NNAL = 4–(methylnitrosamino)–1–(3–pyridyl)–1–butanol;
VOC mercapturic acid metabolites and parent compounds: 2-hydroxypropyl (propylene oxide), 3-hydroxypropyl (acrolein), 2-carbamoylethyl (acrylamide), cyanoethyl (acrylonitrile), 2-hydroxy-3-buten-1-yl or isomer(s) [abbrev. MHBMA] (1,3-butadiene), 2-hydroxyethyl (ethylene oxide), and phenyl (benzene)
FIGURE 1.
Distribution of nicotine, the tobacco-specific nitrosamine (TSNA) NNAL, and mercapturic acid metabolites of volatile organic compounds, acrolein, 1,3-butadiene, ethylene oxide, and benzene, measured in urine of all subjects. Lines are 1st quartile, median, and 3rd quartile; marker (dot) is the geometric mean. Metabolite concentrations increased significantly after water pipe smoking (p<0.05).
Nicotine, cotinine, and NNAL levels increased significantly after smoking water pipes (p<.001). The average pre-exposure urine nicotine concentration was 3.1 ng/mg creatinine for all subjects, which increased within subjects an average 73-fold to 227.2 ng/mg creatinine post-exposure. Cotinine increased ~4-fold from average pre-exposure levels of 14.4 ng/mg creatinine to post-exposure levels of 59.3 ng/mg creatinine. NNAL approximately doubled (2.1-fold) from pre-exposure levels of 1.32 pg/mg creatinine to 2.84 pg/mg creatinine post-exposure. Concentrations of nicotine, cotinine, and NNAL remained significantly higher in next day samples compared to pre-exposure samples (p<.001), increasing 10.4-fold, 3.2-fold, and 2.2-fold, respectively. The differences between pre-, post-exposure, and next day levels were even more pronounced when we analyzed data for “non-cigarette smokers” only while they were less elevated or non-significant when we analyzed “suspected cigarette smokers” only (Table 2).
Following smoking of water pipes, all mercapturic acid metabolites of VOCs except for 2-hydroxypropylmercapturic acid, metabolite of propylene oxide, increased significantly when all subjects were included in the analysis, with boosts between 14% and 91%. 2-Carbamoylethylmercapturic acid, the metabolite of acrylamide, increased 14% from 89.3 ng/mg creatinine to 101.6 ng/mg creatinine. The benzene metabolite, phenylmercapturic acid, increased 91% from 0.179 ng/mg creatinine to 0.342 ng/mg creatinine. Similar changes were observed when “non-cigarette smokers” were analyzed. The changes for “suspected cigarette smokers” were non-significant except for phenyl mercapturic acid which increased an average 2.2-fold from 0.247 ng/mg creatinine to 0.544 ng/mg creatinine.
Pearson cross-correlations coefficients between changes in biomarkers are presented in Table 3. Changes in nicotine, cotinine, and NNAL from pre- to post-exposure and pre-exposure to next day were significantly correlated. Changes in nicotine, cotinine, and NNAL were not significantly correlated to MHBMA, poorly correlated to 2-hydroxypropyl, and had modest to high correlations with 2-carbamoylethyl, cyanoethyl, hydroxyethyl, and phenyl mercapturic acids. Time in bar, smoking duration, number of bowls smoked, bowls per user, and prior length of secondhand smoke exposure were generally not correlated with changes in biomarkers, particularly VOC mercapturic acids (Table 4). Among the significant correlations, smoking duration at the hookah bar was significantly correlated to pre-exposure to next day changes in urine nicotine (r = 0.41); and bowls per user was significant correlated to pre-exposure to post-exposure (r = 0.35) and pre-exposure to next day (r = 0.28) urine cotinine.
Table 3.
Cross correlations between changes in biomarkersa
| COTΔ1 | COTΔ2 | NICΔ1 | NICΔ2 | NNALΔ1 | NNALΔ2 | 2HPMAΔ1 | 3HPMAΔ1 | AAMAΔ1 | CNEMAΔ1 | MHBMAΔ1 | HEMAΔ1 | PMAΔ1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COTΔ1 | l | 0.90*** | 0.19 | 0.44*** | 0.73*** | 0.75*** | –0.04 | 0.29* | 0.74*** | 0.84*** | 0.10 | 0.65*** | 0.92*** |
| COTΔ2 | 1 | 0.09 | 0.51*** | 0.71*** | 0.78*** | –0.08 | 0.23 | 0.73*** | 0.86*** | 0.09 | 0.67*** | 0.92*** | |
| NICΔ1 | 1 | 0.52*** | 0.09 | 0.12 | –0.17 | 0.18 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 0.23 | 0.01 | ||
| NICΔ2 | 1 | 0.59*** | 0.66*** | –0.01 | 0.42** | 0.53*** | 0.43*** | 0.09 | 0.31* | 0.35** | |||
| NNALΔ1 | 1 | 0.94*** | 0.34** | 0.36** | 0.76*** | 0.70*** | 0.08 | 0.33* | 0.64*** | ||||
| NNALΔ2 | 1 | 0.09 | 0.42** | 0.86*** | 0.79*** | 0.10 | 0.44*** | 0.69*** | |||||
| 2HPMAΔ1 | 1 | –0.10 | –0.03 | –0.13 | –0.07 | –0.34* | –0.10 | ||||||
| 3HPMAΔ1 | 1 | 0.27* | 0.24 | 0.16 | 0.24 | 0.35** | |||||||
| AAMAΔ1 | 1 | 0.85*** | 0.09 | 0.45*** | 0.68*** | ||||||||
| CNEMAΔ1 | 1 | 0.12 | 0.64*** | 0.82*** | |||||||||
| MHBMAΔ1 | 1 | 0.30* | 0.14 | ||||||||||
| HEMAΔ1 | 1 | 0.70*** | |||||||||||
| PMAΔ1 | 1 |
All subjects included in the analysis; COT = cotinine; NIC = nicotine; NNAL = 4–(methylritrosamino)–1–(3–pyridyl)–1–butanol; VOC mercapturic acid metabolites (parent compound in parenthesis): 2HPMA=2-hydroxypropyl (propylene oxide), 3-HPMA=3-hydroxypropyl (acrolein), AAMA=2-carbamoylethyl (acrylamide), CNEMA=cyanoethyl (acrylonitrile), MHBMA=2-hydroxy-3-buten-1-yl or isomer(s) (1,3-butadiene), HEMA=2-hydroxyethyl (ethylene oxide), and PMA=phenyl (benzene);
Δ1 = post minus pre-exposure; Δ2 = nextday minus pre-exposure; VOC mercapturic acid metabolites were only measured in pre-exposure and post-exposure samples;
p < 0.05
p < 0.01
p < 0.001
Table 4.
Correlations between self-reported water pipe use and time of exposure and changes in biomarkersa
| COTΔ1 | COTΔ2 | NICΔ1 | NICΔ2 | NNALΔ1 | NNALΔ2 | 2HPMAΔ1 | 3HPMAΔ1 | AAMAΔ1 | CNEMAΔ1 | MHBMAΔ1 | HEMAΔ1 | PMAΔ1 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time in bar | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.05 | 0.21 | 0.11 | 0.04 | 0.27* | −0.28* | 0.13 | 0.05 | 0.18 | 0.03 | 0.07 |
| Smoking duration | 0.09 | 0.15 | 0.13 | 0.41** | 0.10 | 0.05 | 0.22 | −0.10 | −0.02 | −0.06 | 0.15 | −0.08 | 0.01 |
| Number of bowls | 0.27* | 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.08 | 0.05 | −0.18 | 0.21 | 0.19 | 0.13 | 0.10 | 0.19 |
| Bowls per user | 0.35** | 0.28* | 0.10 | 0.08 | 0.18 | 0.14 | 0.12 | −0.15 | 0.22 | 0.24 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.23 |
| Prior SHS | 0.21 | 0.25 | 0.02 | 0.22 | 0.21 | 0.26* | −0.06 | 0.04 | 0.20 | 0.16 | 0.07 | 0.20 | 0.22 |
All subjects included in the analysis; COT = cotinine; NIC = nicotine; NNAL = 4–(methylnitrosamino)–1–(3–pyridyl)–1–butanol; VOC mercapturic acid metabolites (parent compound in parenthesis): 2HPMA=2-hydroxypropyl (propylene oxide), 3-HPMA=3-hydroxypropyl (acrolein), AAMA=2-carbamoylethyl (acrylamide), CNEMA=cyanoethyl (acrylonitrile), MHBMA=2-hydroxy-3-buten-1-yl or isomer(s) (1,3-butadiene), HEMA=2-hydroxyethyl (ethylene oxide), and PMA=phenyl (benzene);
Δ1 = post minus pre-exposure; Δ2 = nextday minus pre-exposure; VOC mercapturic acid metabolites were only measured in pre-exposure and post-exposure samples;
p < 0.05
p < 0.01
*** p < 0.001
DISCUSSION
Our study found an average 73-fold increase in nicotine, 4-fold increase in cotinine, 2-fold increase in NNAL, and 14-91% increase in VOC mercapturic acid metabolites among all participants immediately after a single session of water pipe smoking in hookah bars. We also saw moderate to high correlations between changes in tobacco-specific biomarkers (nicotine, cotinine, and NNAL) and several VOC mercapturic acid metabolites, indicating simultaneous exposure to nicotine, NNK, and toxic VOCs while smoking water pipes. This is the first study, to our knowledge, which assessed systemic exposure to TSNAs and VOCs among water pipe smokers in hookah bars. Water pipe use has been shown to result in intake of toxicants and carcinogens such as NNK, PAHs, and VOCs (13-14). While informative, a limitation of these previous studies was that the participants individually smoked an entire water pipe in controlled clinical research settings. Given that water pipes are frequently smoked in social settings and shared with multiple users, the exposure from controlled clinical research studies may exceed what shared users are exposed to in a naturalistic setting. Therefore biomarker levels reported in the current study represent more realistic exposures to tobacco-smoke toxicants.
Nicotine intake
The 73-fold increase in urine nicotine confirms the results of previous studies that water pipe users take in nicotine, even after a single session with shared users. From a previous clinical study, the average plasma nicotine concentration over the first 24 h after smoking a full bowl of tobacco was 1.5 ng/mL (obtained using the published area under the plasma nicotine concentration-time curve (AUC0→24h) divided by 24 h) (13). This represents a systemic dose of 1.8–2.5 mg, which is equivalent to the dose from smoking 2 to 3 cigarettes (13). To compare nicotine intake from water pipe smoking in a hookah bar as assessed in the current study using urine nicotine and nicotine intake from smoking a full water pipe bowl in a clinical setting as assessed using plasma nicotine in the previous study, we used a urine to plasma nicotine ratio of 100:1 [derived from unpublished 24 h urine nicotine concentrations and plasma nicotine measured over 24 h in Jacob and colleagues’ study (14)]. We observed an average increase in urine nicotine of 103 ng/mg creatinine in the current study, [computed as (post-exposure minus pre-exposure + next day minus pre-exposure)/2], which reflects an estimated 24 h average plasma nicotine concentration of 1.03 ng/mL. This estimated 24 h average plasma nicotine concentration is 0.67 times the 24 h average plasma nicotine levels obtained from smoking a full water pipe bowl, and is realistic given that the average bowls smoked per participant in the current study was 0.6. Although the addictiveness of water pipe tobacco smoking is not established, nicotine levels reported here are likely to cause physiologic changes in nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the brain that would sustain nicotine addiction (30-31). This is particularly concerning for adolescents and young adults, given that early exposure to nicotine increases the severity of future nicotine dependence (32) and the prevalence of water pipe use among these age groups. Further, tobacco dependence has been observed among regular water pipe users in Egypt (33), and is a concern in occasional users.
Tobacco specific nitrosamines (TSNA)
We report a ~2-fold increase in urine NNAL concentrations following water pipe smoking (an average 1.6 pg/mg creatinine boost in “non-cigarette smokers”), which was sustained for several hours after the smoking sessions ended. In comparison, smoking of a full tobacco bowl in a clinical research setting resulted in an average urine NNAL boost of 5 pg/mg creatinine, a ~3-fold greater increase than was observed in the current study (13). NNAL exposure has been shown to be lower when smoking water pipes compared to cigarettes (14), similar to the findings of a cross-sectional study in which lower NNAL was measured in water pipe smokers compared to cigarette smokers in Egypt (34). NNAL, a metabolite of the potent lung carcinogen NNK, is used to characterize systemic exposure to TSNAs. TSNAs have been identified as causative agents in lung and pancreatic cancers and other cancers (35-36).
While there is uncertainty about the health effects associated with water pipe smoking, the health effects of secondhand cigarette smoke are well established (37). The presence of NNAL in the urine of nonsmokers provides a biochemical link between exposure to secondhand cigarette smoke and health outcomes. The boost in urine NNAL in this study are similar to increases in urine NNAL measured in nonsmokers exposed to secondhand cigarette smoke for 3 hours outside a bar with heavy outdoor cigarette smoking (38) and slightly less than what was recently measured in nonsmokers exposed to secondhand cigarette smoke in a partially enclosed car for 1 hour (39). Urine NNAL boosts ranged from 3.8 to 5.0 pg/mg creatinine after a few hours exposure to secondhand cigarette smoke inside hospitality venues (40-41). Further, urine NNAL ranged from 2.7 to 17.3 pg/mL in nonsmoking adults and children with persistent secondhand cigarette smoke exposure (42-44), with higher levels presumably resulting from the accumulation of NNAL due to its longer half-life of 10–18 days (45). Given the high carcinogenic potency of NNK and NNAL, the increase in NNAL excretion in urine signifies that water pipe smoking in a social, hookah bar setting could cause TSNA-associated lung and other cancers, with risk estimates similar to or above that of secondhand smoke, depending on the frequency and lifetime duration of water pipe smoking.
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs)
We report significant boosts in 3-hydroxypropyl, 2-carbamoylethyl, cyanoethyl, 2-hydroxy-3-buten-1-yl, hydroxyethyl, and phenyl mercapturic acids following single session water pipe smoking in a hookah bar. These mercapturic acid metabolites represent exposure to acrolein, acrylamide, acrylonitrile, 1,3-butadiene, ethylene oxide, and benzene, respectively. We did not see significant increases in 2-hydroxypropyl mercapturic acid, a biomarker of propylene oxide which is a class 2B carcinogen (46). While acrolein has not been shown be to carcinogenic in humans, it may be a major etiological agent for cigarette-smoke related lung cancer due to its ability to cause DNA damage and inhibition of DNA repair (20). Acrolein is also thought to be a major contributor to cardiovascular and respiratory diseases in smokers (21). Acrylonitrile and ethylene oxide are probable human carcinogens (class B1); and, 1,3-butadiene and benzene are carcinogenic in humans (class 1) (benzene is known to cause leukemia) (16, 19, 46). Significant increases in VOC metabolites in this study, particularly a 91% increase in the benzene metabolite (phenyl mercapturic acid), indicate systemic exposure to toxic VOCs from single sessions of water smoking in hookah bars. Comparisons between VOC exposure reported here and the only other study in which VOC mercapturic acid metabolites were measured in water pipe smokers are not appropriate since we report spot urine concentrations while 24 h concentrations were reported in the previous study (14).
The profile of VOC exposure from water pipes differs from cigarettes, with much higher benzene exposure associated with water pipe smoking (14). Charcoal combustion contributes greatly to benzene (47) as well as to CO and carcinogenic PAH yields (48). Greater systemic exposure to higher molecular weight PAHs, which tend to be more carcinogenic, were measured in water pipe smokers compared to cigarette smokers (14). Because of differences in smoke chemistry, the types and relative risks of diseases associated with water pipes may differ from cigarette-related diseases. Urine NNAL levels reported here, which are comparable to individuals with transient (a few hours) secondhand cigarette smoke exposure, indicate that the risks of TSNA-related diseases are likely similar among occasional water pipe smokers and nonsmokers with secondhand cigarette smoke exposure. On the other hand, previously reported higher benzene and carcinogenic PAHs from water pipe smoking suggest that the health risks associated with these toxicants are likely higher among water pipe smokers than nonsmokers with secondhand cigarette smoke exposure or even among light and intermittent cigarette smokers. In vitro studies show that water pipe smoke causes DNA damage, has cytotoxic and mutagenic effects, and causes endothelial dysfunction (49-51). Water pipe smoking compromised cardiac autonomic function in a clinical study (52). Meta-analyses of epidemiologic studies indicate that water pipe smoke is associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (53) and lung cancer (54). High quality epidemiologic studies that more accurately measure water pipe use, constituent exposures, disease outcomes, account for confounders, as well as distinguish between the myriad types of tobacco products and charcoal types are needed to assess the association between water pipe use and chronic diseases.
Finally, we saw moderate to high correlations between tobacco-specific biomarkers and mercapturic acid metabolites of VOCs. This suggests that water pipe smokers are simultaneously exposure to several classes of tobacco smoke constituents in water pipe smoke, including TSNA and VOCs. On the other hand, changes in the biomarkers were generally not significantly correlated to variables such as time in bar, smoking duration, number of bowls smoked and bowls per user. This indicates that the relationship between smoking behavior and smoke intake varies among some water pipe users, as have been shown among some cigarette smokers (55).
Limitations
The VOCs measured as mercapturic acid biomarkers are not specific to tobacco smoke. Among other sources, diet has been shown to contribute to acrolein and acrylamide exposure (56-57). While we are unable to give the source profile of the VOCs, the moderate to high correlations between tobacco-specific biomarkers and 3-hydroxypropyl and 2-carbamoylethyl mercapturic acids suggest that water pipe smoke was a source of acrolein and acrylamide. Furthermore, although we attempted to recruit water pipe smokers with no recent cigarette smoking, eight subjects had baseline urine cotinine levels consistent with individuals highly exposed to secondhand cigarette smoke or possibly light/occasional smokers. Although we did not exclude them from the study, their biomarker concentrations were generally higher than the other subjects. We addressed this by performing statistical analyses that included and excluded these subjects. Findings were generally similar with or without these subjects in the analysis. Also, we present data on biomarker exposure from a single evening of water pipe smoking. Some water pipe smokers, particularly in Middle Eastern countries, smoke multiple times every day. In those smokers levels of nicotine, carcinogen and VOC will be much higher.
CONCLUSION
We found an average ~73-fold increase in nicotine, ~4-fold increase in cotinine, ~2-fold increase in NNAL, and 14-91% increase in VOC mercapturic acid metabolites after single sessions of water pipe smoking in hookah bars. Given the significant intake of nicotine and carcinogens, chronic water pipe use may not be risk-free.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We acknowledge Dr. Faith Allen for data management, Lisa Yu, Christopher Havel, Lita Ramos, Lawrence Chan, and Kristina Bello for lab analyses, Sandra Tinetti for clinical assistance, and Scott Rostler for editorial assistance.
Authors’ research support: The study was supported by U.S. Public Health Service grants R25 CA113710 (S.A. Glantz); DA012393 (R.T. Jones) and RR026437 (P. Jacob, III) from the National Institutes of Health; and 15RT-0181 (P. Jacob, III, PI) from the California Tobacco-Related Disease Research Program.
Footnotes
Potential conflict(s) of interest: NL Benowitz: served on smoking cessation advisory boards for Pfizer and has been an occasional consultant to McNeil and GlaxoSmithKline, and has served as a paid expert witness in litigation against tobacco companies. The other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
REFERENCES
- 1.Martinasek MP, McDermott RJ, Martini L. Waterpipe (Hookah) Tobacco Smoking Among Youth. Current Problems in Pediatric and Adolescent Health Care. 2011;41:34–57. doi: 10.1016/j.cppeds.2010.10.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.WHO . Waterpipe tobacco smoking: health effects, research needs and recommended actions by regulators. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2005. [Google Scholar]
- 3.King BA, Dube SR, Tynan MA. Current tobacco use among adults in the United States: Findings from the national adult tobacco survey. Am J Public Health. 2012;102:e93–e100. doi: 10.2105/AJPH.2012.301002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Sutfin EL, McCoy TP, Reboussin BA, Wagoner KG, Spangler J, Wolfson M. Prevalence and correlates of waterpipe tobacco smoking by college students in North Carolina. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2011;115:131–6. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2011.01.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Eissenberg T, Ward KD, Smith-Simone S, Maziak W. Waterpipe Tobacco Smoking on a U.S. College Campus: Prevalence and Correlates. J Adolesc Health. 2008;42:526–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2007.10.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Aljarrah K, Ababneh ZQ, Al-Delaimy WK. Perceptions of hookah smoking harmfulness: predictors and characteristics among current hookah users. Tobacco Induced Diseases. 2009;5:16. doi: 10.1186/1617-9625-5-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Shihadeh A, Azar S, Antonios C, Haddad A. Towards a topographical model of narghile water-pipe café smoking: a pilot study in a high socioeconomic status neighborhood of Beirut, Lebanon. Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior. 2004;79:75–82. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2004.06.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Daher N, Saleh R, Jaroudi E, Sheheitli H, Badr Trs, Sepetdjian E, et al. Comparison of carcinogen, carbon monoxide, and ultrafine particle emissions from narghile waterpipe and cigarette smoking: Sidestream smoke measurements and assessment of second-hand smoke emission factors. Atmos Environ. 2010;44:8–14. doi: 10.1016/j.atmosenv.2009.10.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Schubert J, Hahn J, Dettbarn G, Seidel A, Luch A, Schulz TG. Mainstream smoke of the waterpipe: does this environmental matrix reveal as significant source of toxic compounds? Toxicol Lett. 2011;205:279–84. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2011.06.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Schubert J, Heinke V, Bewersdorff J, Luch A, Schulz TG. Waterpipe smoking: the role of humectants in the release of toxic carbonyls. Arch Toxicol. 2012;86:1309–16. doi: 10.1007/s00204-012-0884-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Shihadeh A, Saleh R. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, “tar”, and nicotine in the mainstream smoke aerosol of the narghile water pipe. Food Chem Toxicol. 2005;43:655–61. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2004.12.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Cobb CO, Shihadeh A, Weaver MF, Eissenberg T. Waterpipe tobacco smoking and cigarette smoking: a direct comparison of toxicant exposure and subjective effects. Nicotine Tob Res. 2011;13:78–87. doi: 10.1093/ntr/ntq212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Jacob P, Raddaha AHA, Dempsey D, Havel C, Peng M, Yu L, et al. Nicotine, carbon monoxide, and carcinogen exposure after a single use of a water pipe. Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers & Prevention. 2011;20:2345–53. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-11-0545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Jacob P, Raddaha AHA, Dempsey D, Havel C, Peng M, Yu L, et al. Comparison of Nicotine and Carcinogen Exposure with Water pipe and Cigarette Smoking. Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers & Prevention. 2013 doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-12-1422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Hecht SS. Tobacco carcinogens, their biomarkers and tobacco-induced cancer. Nature Reviews Cancer. 2003;3:733–44. doi: 10.1038/nrc1190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Fowles J, Dybing E. Application of toxicological risk assessment principles to the chemical constituents of cigarette smoke. Tob Control. 2003;12:424–30. doi: 10.1136/tc.12.4.424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Xie J, Marano KM, Wilson CL, Liu H, Gan H, Xie F, et al. A probabilistic risk assessment approach used to prioritize chemical constituents in mainstream smoke of cigarettes sold in China. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2012;62:355–62. doi: 10.1016/j.yrtph.2011.10.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.IARC . In: Some industrial chemicals and dyestuffs. IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Cancer IAfRo., editor. IARC; Lyon: 1982. pp. 93–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hoffmann D, Brunnemann KD, Hoffmann I. Advances in Modern Environmental Toxicology Benzene: Occupational and Environmental Hazards-Scientific Update Princeton. Princeton Scientific Publishing Co.; 1989. Significance of benzene in tobacco carcinogenesis. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Feng Z, Hu W, Hu Y, Tang M-s. Acrolein is a major cigarette-related lung cancer agent: Preferential binding at p53 mutational hotspots and inhibition of DNA repair. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2006;103:15404–9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0607031103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wang G-W, Guo Y, Vondriska TM, Zhang J, Zhang S, Tsai LL, et al. Acrolein consumption exacerbates myocardial ischemic injury and blocks nitric oxide-induced PKCε signaling and cardioprotection. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2008;44:1016–22. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2008.03.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ding YS, Blount BC, Valentin-Blasini L, Applewhite HS, Xia Y, Watson CH, et al. Simultaneous determination of six mercapturic acid metabolites of volatile organic compounds in human urine. Chem Res Toxicol. 2009;22:1018–25. doi: 10.1021/tx800468w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Bacha ZA, Salameh P, Waked M. Saliva cotinine and exhaled carbon monoxide levels in natural environment waterpipe smokers. Inhal Toxicol. 2007;19:771–7. doi: 10.1080/08958370701401699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Goniewicz ML, Eisner MD, Lazcano-Ponce E, Zielinska-Danch W, Koszowski B, Sobczak A, et al. Comparison of urine cotinine and the tobacco-specific nitrosamine metabolite 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanol (NNAL) and their ratio to discriminate active from passive smoking. Nicotine Tob Res. 2011;13:202–8. doi: 10.1093/ntr/ntq237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ashley DL, Bonin MA, Cardinali FL, McCraw JM, Wooten JV. Measurement of volatile organic compounds in human blood. Environ Health Perspect. 1996;104:871. doi: 10.1289/ehp.96104s5871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Jacob P, 3rd, Yu L, Wilson M, Benowitz NL. Selected ion monitoring method for determination of nicotine, cotinine and deuterium-labeled analogs: absence of an isotope effect in the clearance of (S)-nicotine-3',3'-d2 in humans. Biol Mass Spectrom. 1991;20:247–52. doi: 10.1002/bms.1200200503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Jacob P, 3rd, Havel C, Lee DH, Yu L, Eisner MD, Benowitz NL. Subpicogram per milliliter determination of the tobacco-specific carcinogen metabolite 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanol in human urine using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2008;80:8115–21. doi: 10.1021/ac8009005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Jacob P, 3rd, Wilson M, Benowitz NL. Determination of Phenolic Metabolites of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Human Urine as Their Pentafluorobenzyl Ether Derivatives Using Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2007;79:587–98. doi: 10.1021/ac060920l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Benowitz NL, Hatsukami D. Gender differences in the pharmacology of nicotine addiction. Addiction Biology. 1998;3:383–404. doi: 10.1080/13556219871930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Brody AL, Mandelkern MA, Costello MR, Abrams AL, Scheibal D, Farahi J, et al. Brain nicotinic acetylcholine receptor occupancy: effect of smoking a denicotinized cigarette. The International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology. 2009;12:305–16. doi: 10.1017/S146114570800922X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Benowitz NL. Nicotine addiction. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:2295–303. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra0809890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Dwyer JB, McQuown SC, Leslie FM. The dynamic effects of nicotine on the developing brain. Pharmacol Ther. 2009;122:125–39. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2009.02.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Auf R, Radwan G, Loffredo C, El Setouhy M, Israel E, Mohamed M. Assessment of tobacco dependence in waterpipe smokers in Egypt. The international journal of tuberculosis and lung disease: the official journal of the International Union against Tuberculosis and Lung Disease. 2012;16:132. doi: 10.5588/ijtld.11.0457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Radwan G, Hecht SS, Carmella SG, Loffredo CA. Tobacco-specific nitrosamine exposures in smokers and nonsmokers exposed to cigarette or waterpipe tobacco smoke. Nicotine Tob Res. 2013;15:130–8. doi: 10.1093/ntr/nts099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.USDHHS . A report of the Surgeon General: How tobacco smoke causes disease: The biology and behavioral basis for smoking-attributable disease. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Centers for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, Office on Smoking and Health; 2010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Hoffmann D, Djordjevic MV, Hoffmann I. The Changing Cigarette1. Prev Med. 1997;26:427–34. doi: 10.1006/pmed.1997.0183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.USDHHS . The health consequences of involuntary exposure to tobacco smoke: a report of the Surgeon General. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Centers for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, Office on Smoking and Health; 2006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.St.Helen G, Bernert JT, Hall DB, Sosnoff CS, Xia Y, Balmes JR, et al. Exposure to secondhand smoke outside of a bar and a restaurant leads to increases in tobacco exposure biomarkers in non-smokers. Environ Health Perspect. 2012;120:1010–6. doi: 10.1289/ehp.1104413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Jones IA, St.Helen G, Meyers MJ, Dempsey DA, Havel C, Jacob P, et al. Biomarkers of secondhand smoke exposure in automobiles. Tob Control. 2013 doi: 10.1136/tobaccocontrol-2012-050724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Tulunay OE, Hecht SS, Carmella SG, Zhang Y, Lemmonds C, Murphy S, et al. Urinary metabolites of a tobacco-specific lung carcinogen in nonsmoking hospitality workers. Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers & Prevention. 2005;14:1283–6. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-04-0570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Anderson KE, Kliris J, Murphy L, Carmella SG, Han S, Link C, et al. Metabolites of a tobacco-specific lung carcinogen in nonsmoking casino patrons. Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers & Prevention. 2003;12:1544–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Anderson KE, Carmella SG, Ye M, Bliss RL, Le C, Murphy L, et al. Metabolites of a tobacco-specific lung carcinogen in nonsmoking women exposed to environmental tobacco smoke. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2001;93:378–81. doi: 10.1093/jnci/93.5.378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Hecht SS, Carmella SG, Le K-A, Murphy SE, Boettcher AJ, Le C, et al. 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanol and its glucuronides in the urine of infants exposed to environmental tobacco smoke. Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers & Prevention. 2006;15:988–92. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-05-0596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Parsons WD, Carmella SG, Akerkar S, Bonilla LE, Hecht SS. A metabolite of the tobacco-specific lung carcinogen 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanone in the urine of hospital workers exposed to environmental tobacco smoke. Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers & Prevention. 1998;7:257–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Goniewicz ML, Havel CM, Peng MW, Jacob P, Dempsey D, Yu L, et al. Elimination kinetics of the tobacco-specific biomarker and lung carcinogen 4-(methylnitrosamino)-1-(3-pyridyl)-1-butanol. Cancer Epidemiology Biomarkers & Prevention. 2009;18:3421–5. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-09-0874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.IARC . IARC Monographs on evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans: Tobacco smoke and involuntary smoking. International Agency for Research on Cancer; Lyon (France): 2004. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Olsson M, Petersson G. Benzene emitted from glowing charcoal. Sci Total Environ. 2003;303:215–20. doi: 10.1016/S0048-9697(02)00403-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Monzer B, Sepetdjian E, Saliba N, Shihadeh A. Charcoal emissions as a source of CO and carcinogenic PAH in mainstream narghile waterpipe smoke. Food Chem Toxicol. 2008;46:2991–5. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2008.05.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Alsatari ES, Azab M, Khabour OF, Alzoubi KH, Sadiq MF. Assessment of DNA damage using chromosomal aberrations assay in lymphocytes of waterpipe smokers. International journal of occupational medicine and environmental health. 2012;25:218–24. doi: 10.2478/S13382-012-0027-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Rammah M, Dandachi F, Salman R, Shihadeh A, El-Sabban M. In vitro cytotoxicity and mutagenicity of mainstream waterpipe smoke and its functional consequences on alveolar type II derived cells. Toxicol Lett. 2012 doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2012.04.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Rammah M, Dandachi F, Salman R, Shihadeh A, El-Sabban M. In vitro effects of waterpipe smoke condensate on endothelial cell function: A potential risk factor for vascular disease. Toxicol Lett. 2013;219:133–42. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2013.02.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Cobb CO, Sahmarani K, Eissenberg T, Shihadeh A. Acute toxicant exposure and cardiac autonomic dysfunction from smoking a single narghile waterpipe with tobacco and with a “healthy” tobacco-free alternative. Toxicol Lett. 2012 doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2012.09.026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Raad D, Gaddam S, Schunemann HJ, Irani J, Jaoude PA, Honeine R, et al. Effects of Water-Pipe Smoking on Lung FunctionA Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. CHEST Journal. 2011;139:764–74. doi: 10.1378/chest.10-0991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Akl EA, Gaddam S, Gunukula SK, Honeine R, Jaoude PA, Irani J. Int J Epidemiol. 2010;he effects of waterpipe tobacco smoking on health outcomes: a systematic review.39:834–57. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyq002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Benowitz NL, Dains KM, Dempsey D, Wilson M, Jacob P. Racial differences in the relationship between number of cigarettes smoked and nicotine and carcinogen exposure. Nicotine Tob Res. 2011;13:772–83. doi: 10.1093/ntr/ntr072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Watzek N, Scherbl D, Feld J, Berger F, Doroshyenko O, Fuhr U, et al. Profiling of mercapturic acids of acrolein and acrylamide in human urine after consumption of potato crisps*. Molecular nutrition & food research. 2012;56:1825–37. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201200323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Boettcher MI, Bolt HM, Angerer J. Acrylamide exposure via the diet: influence of fasting on urinary mercapturic acid metabolite excretion in humans. Arch Toxicol. 2006;80:817–9. doi: 10.1007/s00204-006-0123-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]