Abstract
Kidney tubule plays a critical role in recovering or secreting solutes, but the detailed morphogenesis remains unclear. Our previous studies have found that grouper tshβ (gtshβ) is also expressed in kidney, however, the distribution significance is still unknown. To understand the gtshβ role and kidney tubule morphogenesis, here, we have generated a transgenic zebrafish line Tg(gtshβ:GFP) with green fluorescent protein driven by the gtshβ promoter. Similar to the endogenous tshβ in zebrafish or in grouper, the gtshβ promoter-driven GFP is expressed in pituitary and kidney, and the developing details of proximal kidney tubule are marked in the transgenic zebrafish line. The gfp initially transcribes at 16 hours post fertilization (hpf) above the dorsal mesentery, and partially co-localizes with pronephric tubular markers slc20a1a and cdh17. Significantly, the GFP specifically localizes in proximal pronephric segments during embryogenesis and resides at kidney duct epithelium in adult fish. To test whether the gtshβ promoter-driven GFP may serve as a readout signal of the tubular development, we have treated the embryos with retinoic acid signaing (RA) reagents, in which exogenous RA addition results in a distal extension of the proximal segments, while RA inhibition induces a weakness and shortness of the proximal segments. Therefore, this transgenic line provides a useful tool for genetic or chemical analysis of kidney tubule.
Introduction
Kidney is an organ that removes metabolic waste from the blood, and regulates the homeostasis of electrolytes and metabolite concentrations in a physiological range for supporting the functions of all other organs [1], [2]. In higher vertebrates, kidney is a complicated and highly branched system containing thousands of nephrons, the basic structural and functional unit of kidney, while in zebrafish, the simper kidney only has a bilaterally pair of nephrons [3]. Although there are some differences among various vertebrate kidneys, their cellular composition and molecular regulation are similar [4].
In zebrafish, pronephric tubule is also segmented into many regions similar to the segments in mammals. They include neck, proximal convoluted tubule (PCT), proximal straight tubule (PST), distal early (DE), corpuscle of Stannius (CS), and distal late (DL) [5]. Moreover, some factors influencing kidney segmentation have been identified in zebrafish [6]. For example, retinoic acid (RA) signaling has been revealed to play a principal role in proximal-distal segment determination of the pronephric tubule [5], [7], [8], [9], in which RA inhibits the distal segments and enables development of the proximal segments in a concentration-dependent manner [5]. In addition, canonical Wnt signaling and zinc finger transcription factor osr1 have been found to be required for the formation of proximal pronephric tubule [10], [11], [12], [13], and noncanonical Wnt pathway has been demonstrated to regulate morphogenesis of the proximal and intermediate pronephros [14]. Recently, transcription factor Hnf1b is also confirmed to play a key role in nephron proximo-distal segmentation [15]. However, how these specific tubule segments are regionalized has remained unclear in zebrafish pronephros [3], [16].
Cell fate tracing and tissue-specific transgene technique provide powerful tools to study tissue development and organ formation [17], [18], [19]. In zebrafish, several transgenic lines with green fluorescent protein (GFP) have been constructed to visualize morphogenesis of the kidney organ. For example, the podocyte-specific transgenic zebrafish lines have been generated, in which GFP expression is driven by wt1b gene promoter [20] or podocin gene promoter [21]. In transgenic line Tg(dβh:EGFP), the dopamine-β-hydroxylase (dβh) promoter-driven EGFP is expressed in interrenal gland [22]. In Na, K-ATPase alpha1A4:GFP transgenic line, GFP is highly expressed in pronephric epithelia that power the ion-transport activities [23]. In ret1:GFP zebrafish line, the ret loci-driven GFP expression appears in the most distal pronephric duct [24]. Furthermore, the ET33-D10 zebrafish line with GFP expression marks the proximal movement of the pronephric tubule, but it displays relative high background and a wide GFP distribution [25]. So far, the specific transgenic line that clearly marks proximal pronephric tubule remains absent.
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) is a glycoprotein secreted by anterior pituitary [26]. Until recently, it has been thought solely to mediate thyroid development and production of thyroid hormones that are important for metabolism, growth and development [27], [28]. TSH consists of two subunits, the alpha and the beta subunit. The alpha subunit is nearly identical to all glycoprotein hormones, while the beta subunit is specific to each one. However, TSH receptors are expressed more ubiquitously, suggested by radio-ligand binding and mRNA analysis [29], [30]. Significantly, our previous studies in sex reversal groupers [31] have found that grouper tshβ (gtshβ) is also expressed in kidney in addition to its expression in pituitary [32]. These findings imply that some potential physiological functions of the hormone remain unknown. To explore these functions and thereby to understand kidney tubule morphogenesis, we have cloned the promoter of gtshβ and preliminarily analyzed its activity [33], but the marking values and potentials have been not investigated. In this study, we have generated a stable transgenic zebrafish line Tg(gtshβ:GFP) driven by the gtshβ promoter, revealed its marking ability to understand kidney tubule morphogenesis, and exploited its potentials for signaling regulation or chemical analysis of kidney tubule development.
Materials and Methods
Fish Maintenance
Zebrafish were maintained in the aquarium of Freshwater Ecology and Biotechnology Laboratory. Spawning, fertilization and embryo development were raised at 28.5°C as described previously [34]. The animal treatments for this research were approved by the Institute of Hydrobiology Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (Approval ID: keshuizhuan 0829).
Genome Walking
Genomic DNA was extracted from fin clips of groupers by a standard phenol-chloroform method, and the genomic walking PCR programs were referred to the manual proposal as described previously [35], [36]. The conserved synteny analysis was performed as described [37].
Whole-mount in situ Hybridization and Immunofluorescence Staining
In situ hybridization and immunofluorescence staining were carried out as previously described [18], [38]. Riboprobes were made by using DIG RNA labeling kit (Roche) for the following genes, including gfp, slc20a1a, wt1a, cdh17, vasa, mhc, pax2a, hnf1ba and hnf1bb [20], [39], [40], [41], [42]. The WISH embryos were embedded using OCT (Sakura), and were sectioned for direct observation. Vasa antibody was used at 1∶200 as described [43].
Confocal Microscopy and Fluorophotometry
For analyzing GFP expression, embryos were treated in PTU (sigma) from 16 hpf. At the indicated time, embryos were anesthetized with 30 mg/ml MS-222 (Sigma) for imaging using Leica sp2 confocal microscope or Leica MZ16FA stereomicroscope as described [44].
30 embryos were dechorionated and lysed using passive lysis buffer (promega). The supernatants were then collected for fluorophotometric scan (TECAN).
Morpholino Oligonucleotides, Constructs and mRNA Injections
Morpholino oligonucleotides of dead-end (dnd) [45], pax2a [46] and hnf1ba [47] were obtained from Gene Tools. The RFP-CVLS chimera mRNA [48] was synthesized by cloning the PCR amplified fragment into the pCS2+ vector and by using Message Machine-Kit (Ambion). The microinjections were performed as described previously [49], [50].
RA Treatments
Embryos at 10 hpf were incubated in 0.5 um ATRA (Sigma), 16 um DEAB (sigma) or DMSO (control) in E3 embryo media overnight, and fixed for in situ hybridization.
Results
Evolutionary Conservation of tshβ and the Neighbor Genes
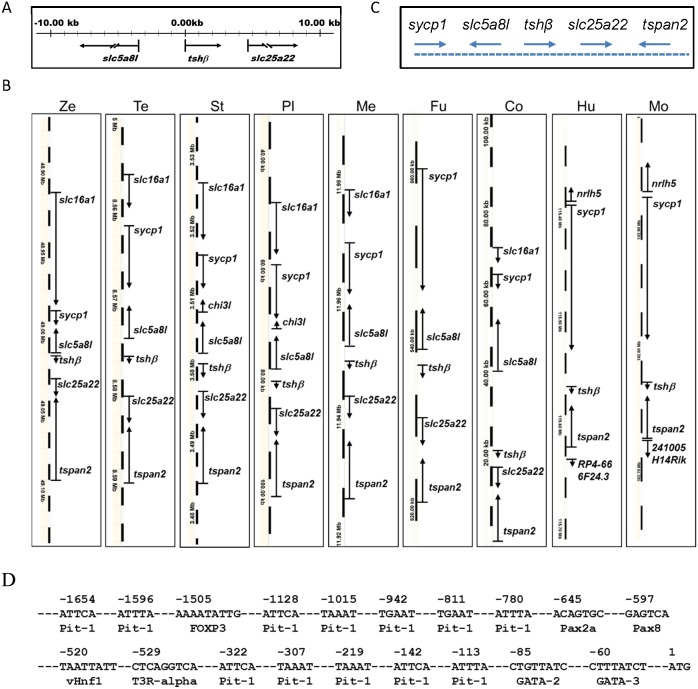
Two neighborhood genes of grouper tshβ were firstly screened by genome walking. As shown in Figure 1A, the grouper tshβ localizes between slc5a8l (solute carrier family 5 (iodide transporter), member 8-like) and slc25a22 (mitochondrial glutamate carrier 1), and both of them belong to the family of solute carrier. Subsequently, we compared the detailed genome regions around tshβ in vertebrates including zebrafish (Danio rerio), tetraodon (Tetraodon nigroviridis), stickleback (Gasterosteus aculeatus), platyfish (Xiphophorus maculatus), medaka (Oryzias latipes), fugu (Takifugu rubripes), cod (Gadus morhua), human (Homo sapiens) and mouse (Mus musculus). Interestingly, the tshβ localization in genomes and the neighbor genes are almost identical in fish (Figure 1B), and a highly conserved synteny of sycp1-slc5a8l-tshβ-slc25a22-tspan2 gene cluster (Figure 1C) exists in all of these fish. In mammals including human and mouse, tshβ also localizes in a sycp1-tshβ-tspan2 cluster that is similar to that in fish on a large scale (Figure 1B).
Figure 1. Genomic synteny conservation of tshβ and the neighbor genes.
(A) The neighbor genes of tshβ in grouper. (B) Schematic diagram of genomic regions around tshβ in vertebrates. Ze: zebrafish, Te: tetraodon, St: stickleback, Pl: platyfish, Me: medaka Fu: fugu, Co: cod, Hu: human and Mo: mouse. (C) A representative diagram of the conserved genomic structure around tshβ in fish. (D) Putative pituitary and kidney-specific regulatory elements identified in the 1828 bp of proximal 5′ flanking regulation region in the grouper tshβ promoter.
Characterization of gtshβ Promoter
Moreover, we analyzed potential regulatory DNA sequences in the upstream sequence of gtshβ start codon using PROMO program as described [51]. Some putative transcription factor binding elements important for mammalian pituitary development were found in this sequence. They include twelve consensus motifs for Pit-1 (at −1654, −1596, −1128, −1015, −942, −811, −780, −322, −307, −219, −142, and −113) [52], one for FOXP3 (at −1505) [53], one for T3R-alpha (at −529) [54], and one for GATA-2 (at −85) [55] respectively (Figure 1D). Interestingly, there are also many putative response elements critical for kidney morphogenesis in this region (Figure 1D). They include Pax2a responsive site (−645) [56], Pax8 responsive site (−587) [57], vHnf1 (also named as Hnf1b) responsive site (−520) [58], and GATA-3 responsive site (−60) [59], [60]. Therefore, the upstream region of gtshβ contains some significant information for directing its expression in vivo.
Generation of Transgenic Zebrafish Line Tg(gtshβ:GFP)
A series of gtshβ 5′-flanking fragments with different length were cloned into the Tol2 vector [33]. These constructs were respectively injected into one-cell zebrafish embryos, and their activities were analyzed as described previously [17], [61]. Thereby, a proximal 1.8-kb DNA fragment was used to generate transgenic line. A total of 33 larvae (11%) with specific GFP signal were screened and raised to adulthood from the injected 300 embryos. By mating to wild type zebrafish, only 1 female F1 founder (3%) through germline transmission was identified from the 33 adults, and 25 F2 offspring with positive GFP signal were obtained from the 310 fertilized eggs between the female founder and wild type male due to the mosaicism of transgene in germline cells. As the positive F2 females were mated with the positive F2 males, about 25% embryos appeared strongly green fluorescence, and thereby, a stable and homozygous gtshβ promoter-driven transgenic zebrafish line was established in F3. When the homozygous transgenic zebrafish line was out-crossed to wild type, about 50% of the offspring showed specific GFP expression, suggesting that only one single integration site might exist in the transgenic line. We nominated the homozygous gtshβ promoter-driven transgenic zebrafish line as Tg(gtshβ:GFP) for all subsequent works.
Dynamic GFP Expression Pattern during Embryogenesis in Tg(gtshβ:GFP)
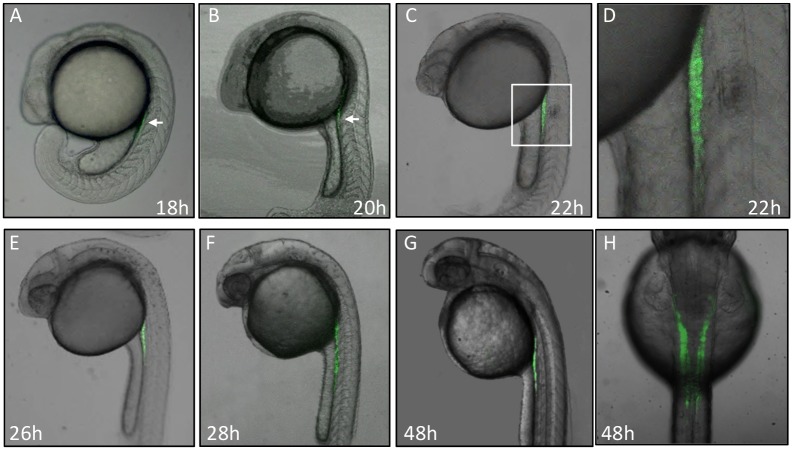
As judged by confocal microscopy, the GFP fluorescence signal is initially detectable from 18 hpf above the dorsal mesentery and persists throughout the subsequent embryogenesis in Tg(gtshβ:GFP) (Figure 2). The initial GFP signal localizes above the anterior region of the yolk extension, and extends from the adjacent fifth somite to the eighth somite (Figure 2A and 2B), where is the occurrence region of pronephros and gonad, although it is difficult to distinguish them at the early stages. As embryos develop, the GFP fluorescence becomes stronger and extends above the yolk sac, manifesting a bilateral tube-like structure (Figure 2C–2H). At 48 hpf, it displays a slight curve, which is likely the pronephric neck and tubule (Figure 2H). Therefore, the specific GFP expression driven by gtshβ promoter would be an excellent marker for pronephric tubule morphogenesis. In this paper, we only focused on the GFP expression in this region, although it can be detected in pituitary (data not shown).
Figure 2. Dynamic GFP expression pattern during embryogenesis in Tg(gtshβ::GFP) line.
(A, B, C, E, F and G) show the lateral view of Tg(gtshβ:GFP) embryos at the indicated stages. A dorsal view of 48 hpf embryo is shown in H. The arrows show the expressed GFP in A and B. The boxed area in C was shown with a higher magnification in D.
The gtshβ Promoter-driven GFP is Expressed in Pronephric Tubules
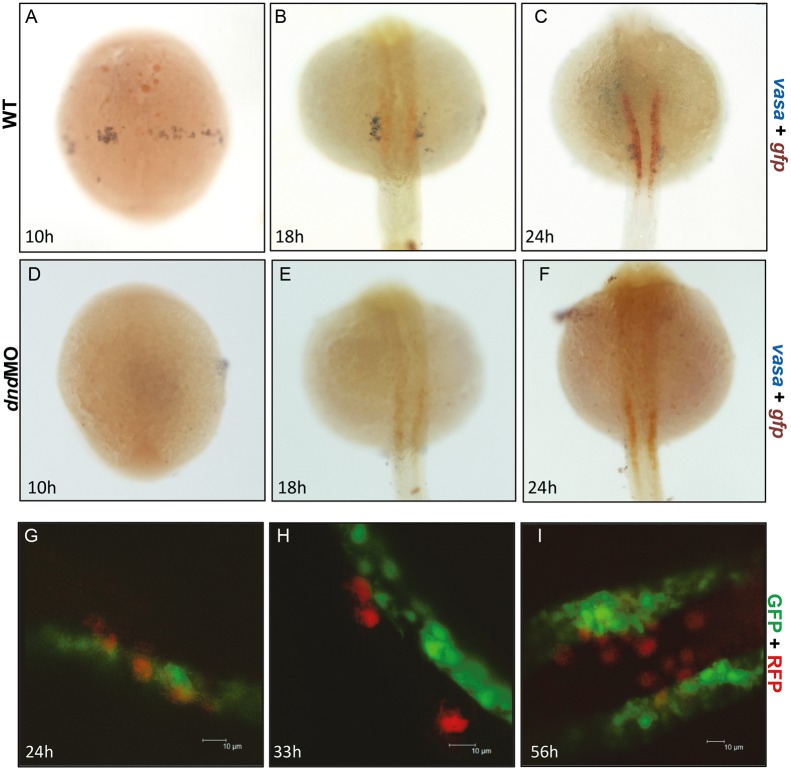
To reveal the exact localization of GFP driven by gtshβ promoter, we used double whole mount in situ hybridization (dWISH) to compare the transcript distribution between vasa (purple), a specific PGC marker, and gfp (red) in Tg(gtshβ:GFP) embryos. Similarly to the description reported previously [62], two clusters of the vasa-labeled PGCs were observed at the trunk border from somitogenesis beginning at 10 hpf (Figure 3A). At 18 hpf and 24 hpf, PGCs migrated and concentrated to the dorsal mesentery at the level of the yolk ball and yolk tube boundary (Figure 3B and 3C). At the corresponding stages, the red gfp transcript signal was found to localize on the bilateral strips in adjacent to and separated from the purple vasa signal (Figure 3A–3C). To confirm the above finding, the PGC-deleted embryos were produced via knocking down the dnd gene [45]. If gfp is transcribed in PGC, it would be hindered by PGC deletion. As shown in Figure 3D–3F, the red gfp transcript signal is still localized on the bilateral strips while the vasa expression is missing, indicating that the PGC deletion does not influence the expression of gfp message. We also applied RFP-nos 3′UTR to visualize PGCs by injecting the synthesized mRNA at one-cell stage as described [20], [63]. Similar to the results in dWISH assays (Figure 3A–3C), GFP was not co-localized with RFP in protein level and they were neighboring (Figure 3G–3I). Therefore, these data indicate that gtshβ promoter-driven GFP is not expressed in PGCs.
Figure 3. The gtshβ promoter-driven GFP was not localized with PGC.
(A–C) dWISH of gfp (red) and vasa (purple) in Tg(gtshβ::GFP) embryos injecting control (A–C) and dnd-morpholino (dnd-MO) (D–F). (G–I) Tg(gtshβ::GFP) embryos injected with RFP-nos 3′UTR mRNA (red) were observed using confocal microscopy at the indicated stages. Bar = 10 um.
To determine whether the GFP strips adjoining to PGCs belong to pronephros, we used pronephric markers to pursue the co-localization with gfp by dWISH. Wilms tumor gene wt1a is a transcription factor essential for the formation of glomerular structures [20]. Zebrafish cdh17 is exclusively expressed in all pronephric tubules and ducts [40]. Therefore, the two markers combination could show the whole pronephros in zebrafish embryos (Figure 4A–4D) [64]. As shown in Figure 4, the wt1a and cdh17 transcripts are partially covered by the gfp transcript at 19 hpf and 24 hpf (Figure 4C and 4D). Therefore, the overlapping region is likely the PCT segment that follows the Bowman’s capsule and neck segment. To test the deduction, a PCT segment marker slc20a1a was further applied to dWISH assay. Indeed, slc20a1a is co-localized with gfp in PCT segment from 18 hpf to 24 hpf (Figure 4E–4H). Interestingly, they are not totally overlapped, and the slc20a1a transcript resides in the anterior and middle parts of the gfp domain. Since Nuance multispectral imaging system could characterize all the spectral components in a sample [65], we further used it to clearly show the partial co-localization relationship between slc20a1a and gfp in pronephric tubule (Figure 4I). All together, these data indicate that the gtshβ promoter-driven GFP is mainly expressed in proximal pronephric tubules, and its distribution is more extended than PCT segment.
Figure 4. The gtshβ promoter-driven GFP is expressed in pronephric tubules.
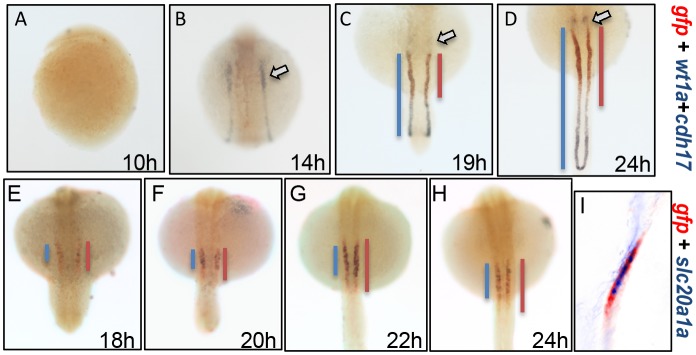
(A–D) dWISH analyses of gfp (red), wt1a1 (purple) and cdh17 (purple) in Tg(gtshβ::GFP) embryos at the somitogenic stages from 10 hpf to 24 hpf. (E–H) dWISH analyses of gfp (red) and slc20a1a (purple) in Tg(gtshβ::GFP) embryos at the somitogenic stages from 18 hpf to 24 hpf. (I) Nuance multispectral imaging of gfp-slc20a1a-double-stained Tg(gtshβ::GFP) embryos at 24 hpf. The podocytes stained with wt1a1 are indicated by arrows. The blue or red lines are drawn according to the expression patterns of the kidney tubule markers.
Pax2a and Hnf1b Involve the gtshβ Promoter-driven Expression
Some putative binding elements for Pax2a and Hnf1b, the known transcription factors for kidney development, were also identified in the gtshβ promoter region (Figure 1D). To test whether Pax2a and Hnf1b are required for the GFP expression in pronephric tubules, we firstly examined and compared their expression patterns with the gtshβ promoter-driven GFP in the Tg(gtshβ:GFP) embryos. As shown in Figure 5, the pax2a transcript expresses in the entire pronephros at 19 hpf, and co-localizes with gfp in the proximal tubules (Figure 5A). At 26 hpf, however, the pax2a transcript disappears in most of the gfp territory except a small part of posterior region (Figure 5B). In zebrafish, there are two paralogues of hnf1b (hnf1ba and hnf1bb), and both of them co-localize with gfp at 19 hpf and 26 hpf (Figure 5C–5F). The hnf1ba transcript is distributed in entire pronephric tubules (Figure 5C and 5D), whereas the hnf1bb distribution is shorter at the caudal area than that of hnf1ba (Figure 5E and 5F). Moreover, we analyzed the GFP expression in the Pax2a and Hnf1b knockdown Tg(gtshβ:GFP) embryos by using confocal imaging and fluorophotometry. As shown in Figure 5G–5J, the GFP expression level is significantly impaired by the Pax2a knockdown or Hnf1b knockdown. These results indicate that Pax2a and Hnf1b, the known transcription factors for kidney development, mediate the gtshβ promoter-driven expression.
Figure 5. The gtshβ promoter-driven GFP is regulated by Pax2a and Hnf1b.
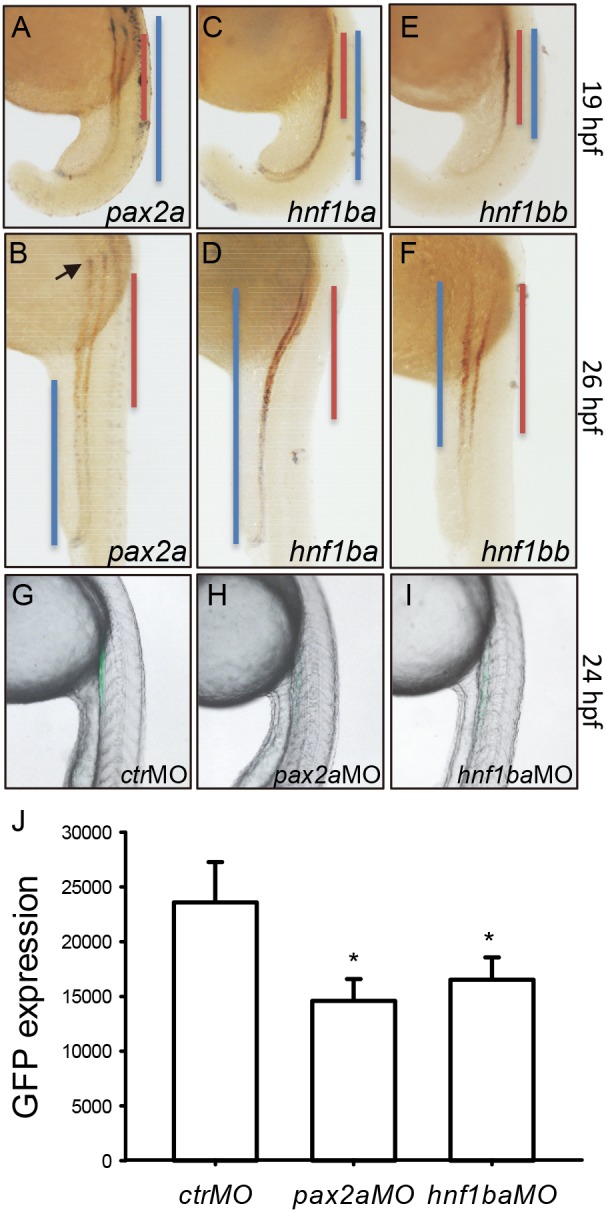
(A–F) dWISH analyses of gfp (red) and kidney transcription factors (purple) as indicated in Tg(gtshβ::GFP) embryos at 19 hpf and 26 hpf. (G–I) show the lateral view of Tg(gtshβ:GFP) embryos injected with morpholinos as indicated at 24 hpf. (J) Fluorophotometric measurement of GFP in the embryos in G–I. The podocyte is indicated by arrow. The blue or red lines are drawn according to the expression patterns of the transcription factors and gfp, respectively. Error bars represent mean ± s.d., *P<0.001 one way AVOVA with Holm-Sidak method.
Onset Expression of gtshβ Promoter-driven gfp Transcript Occurs as the Formation of Pronephric Tubules
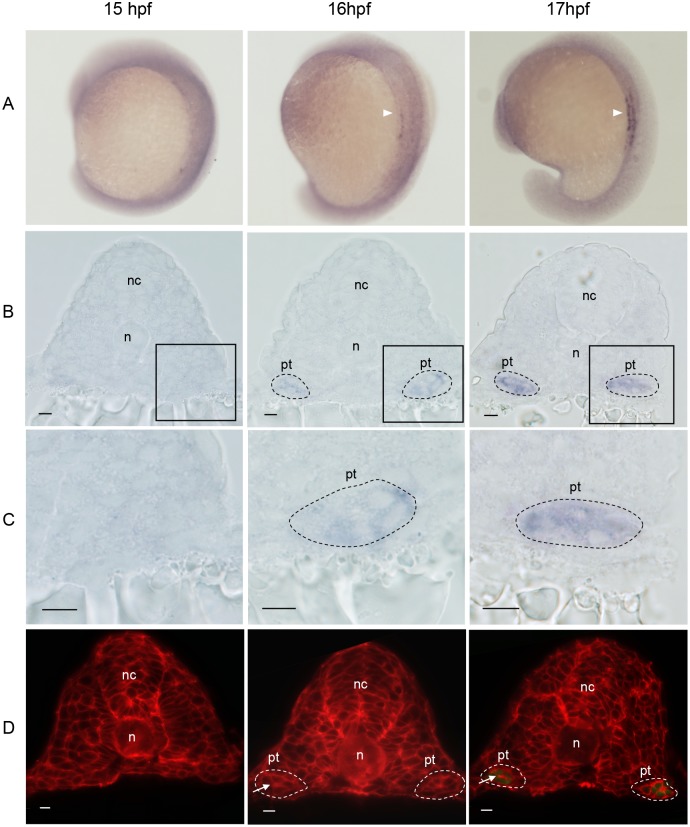
To clarify the onset expression of gfp driven by gtshβ promoter, we examined gfp transcription in Tg(gtshβ:GFP) embryos at the early somitogenesis by using alkaline phosphatase-NBT/BCIP color system. The gfp mRNA is initially detected at 16 hpf when the embryos develop to 14-somite stage (Figure 6A). It is clear that the gfp transcription is earlier than the GFP protein translation at 18 hpf observed by using confocal microscopy (Figure 2). Furthermore, the gfp expressed cells form a clustered clump structure lateral to the both sides of somites (Figure 6B and 6C, black dash lines), and locate on the position where intermediate mesoderm (IM) develops to pronephros [66]. At 17 hpf (about 17-somite stage), the gfp signal becomes stronger (Figure 6A), and the cell clusters are more tightly organized than that at 16 hpf (Figure 6B and 6C, black dash lines). The data suggest that they might be undergoing reorganization events to form cylinder-type tubules structure during the stages.
Figure 6. Onset expression of gfp mRNA during somitogenesis in Tg(gtshβ:GFP).
(A) WISH analysis of gfp (arrowheads) in 15, 16 and 17 hpf embryos, dorsal-lateral view. (B) Transverse sections of the embryos in A. (C) Higher magnification of boxed regions of B. (D) Cell boundary staining by the RFP-CVLS chimera protein on transverse sections of Tg(gtshβ:GFP) embryos. The gfp-positive cells are outlined by black dash lines. The tubular structures are outlined by white dash lines. Arrows indicate the lumen. nc: neural cord; n: notochord; pt: pronephric tubule. Bar = 10 µm.
To confirm the suggestion, we injected the RFP-CVLS chimera mRNA into 1-cell Tg(gtshβ:GFP) embryos to express a RFP that targets to the plasma membrane and thereby to visualize the tubular formation. As shown in Figure 6D, the limits of tubular structures begin to form at 16 hpf, and the cell boundaries indicated by the RFP-CVLS chimera protein obviously outline a characteristic circular shape at the 16-somite stage of 17 hpf. This implies that the cells in IM undergo structure organization to form a tubular tissue, and a small lumen can be observed in its middle (Figure 6D, arrows). Therefore, the onset expression of tshβ promoter-driven gfp occurs as the formation of pronephric tubules.
The gtshβ Promoter-driven GFP Marks Pronephric Tubule Morphogenesis
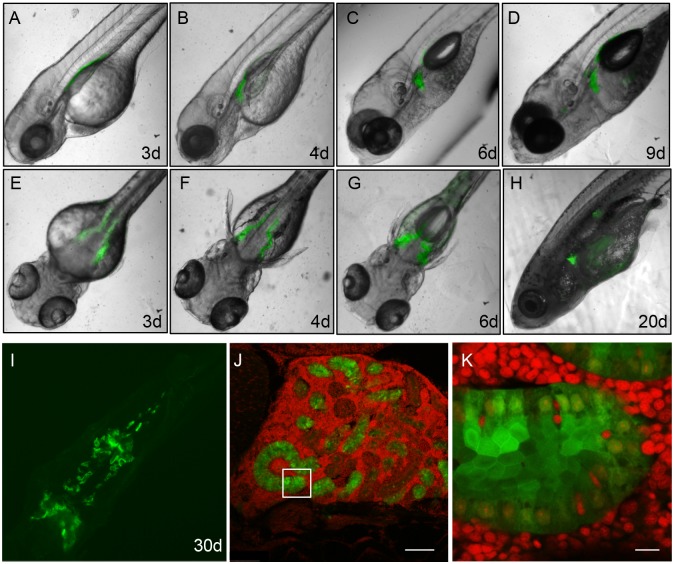
Subsequently, we examined pronephric tubule morphogenesis by pursuing the GFP expression pattern in the transgenic line from larvae to adults. As shown in Figure 7, GFP expressed in the hatched larvae appears in bilateral tubes of pronephros and persists into adults. The GFP expression domain moves forward and twists as the kidney develops (Figure 7A–7I). At 30 days after hatching, the cells expressing GFP clearly reside in a tubular structure (Figure 7J). They are squamous with cuboidal or columnar cell morphology and arrange very well (Figure 7K). Likely, these cells tightly contact to each other and form the epithelium tissue, which constitutes the nephric tubules [67], [68]. Therefore, the dynamic progression of nephron tubule morphogenesis throughout kidney development is marked by gtshβ promoter-driven GFP.
Figure 7. GFP expression pattern in Tg(gtshβ::GFP) larvae and adults.
(A–I) show the lateral view (A, B, C, D and H) and the dorsal view (E–G, I) of Tg(gtshβ::GFP) larvae and adults from 3 dfp to 30 dfp. (J) The Tg(gtshβ::GFP) adult kidney section stained with DAPI (red). Bar = 100 µm (K) The higher magnification in the boxed area of J. Bar = 10 µm.
The gtshβ Promoter-driven GFP Expression is Regulated by Retinoic Acid
Retinoic acid (RA) signaling had been demonstrated to play a key function in controlling proximo-distal segmentation of the zebrafish pronephros [5]. Therefore, we used all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA), the ligand of RA signaling, and 4-diethylaminobenzaldehyde (DEAB), an effective inhibitor for the de novo RA synthesis to treat the Tg(gtshβ::GFP) embryos at bud stage, and thereby explored whether gfp expression is influenced by RA signaling. Moreover, to better define the changes of segment pattern, we mapped the expression domain of gfp relative to the somites with myosin heavy chain (mhc) [5]. As shown in Figure 8, the exogenous RA treatment results in distal expansion of the proximal segment, in which the gfp-positive strips are extended and fused at the prospective sites of cloaca (Figure 8A and 8B). In contrast, DEAB treatment attenuates and shortens the gfp expression pattern (Figure 8A and 8B). Interestingly, the front-end edge of gfp signal in DEAB-treated embryos moves posteriorly to the site of somite 5, compared with the somite 4 in DMSO controls (arrows in Figure 8). In the ATRA-treatment embryos, inversely, the leading edge of gfp expression shifts anteriorly to the somite 3 (arrows in Figure 8). These are similar to the previous report about the effects of RA on proximal tubule segmentation [5]. Therefore, the gtshβ promoter-driven GFP expression pattern in pronephros is regulated by retinoic acid, and RA signaling is required for the pronephric tubule residence and segment.
Figure 8. RA signaling regulates pronephric tubule segmentation.
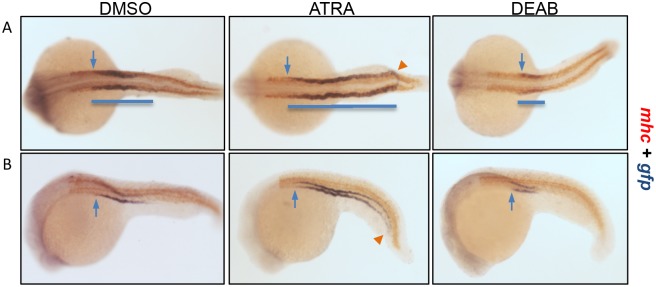
The Tg(gtshβ::GFP) embryos at bud stage were treated with DMSO (as control), ATRA or DEAB, and fixed at 22 hpf to perform double whole-mount in situ hybridization with gfp (purple) and mhc (red) probes. (A) Dorsal view. (B) Lateral view. Cloacas are indicated by arrowheads. The most anterior positions of gfp expression are indicated by arrows. The blue lines are drawn to mark the gfp expression patterns.
Discussion
TSH is a glycoprotein hormone expressed and secreted from pituitary in mammals. It stimulates the production of thyroxine and then thiiodothyronine from thyroid to regulate the metabolism of almost every tissue. Besides a generally robust expression in pituitary, TSHβ mRNA was also found in gonads and kidney both in grouper [32] and zebrafish (data not shown). Genomic synteny analysis indicates that tshβ is localized with conserved genomic neighborhoods in many fish species (Figure 1A), suggesting the regulating elements may be similar in promoter region. Furthermore, our transgenic fish demonstrates that the promoter of grouper tshβ can direct the pituitary and kidney-specific expression of GFP in zebrafish, similar to the endogenous (Figure 1D). Therefore, the tissue distribution pattern of tshβ might be conserved in teleost fish. Although the significance of these expressions is unknown, the ubiquitous distribution of TSHR may suggest a divergent endocrine or paracrine TSH system in non-pituitary tissues [69], [70], [71].
Kidney tubule morphogenesis and segmentation are important for kidney function [72], but most of the process is unknown. In proximal tubule, phosphate, glucose, amino acid and bicarbonate are reabsorbed and transported. Only one transgenic fish line that marks the proximal tubule development was reported in zebrafish [25]. However, this transgenic fish line ET33-D10 displayed relative high background and a wide GFP distribution in various tissues, such as forebrain, hindbrain, spinal cord and ionocytes (http://plover.imcb.a-star.edu.sg/webpages/ET33-D10.html). In this case, the transgenic zebrafish line Tg(gtshβ::GFP) specifically expresses GFP in pronephric proximal tubule, besides in pituitary as previous report [73]. GFP is partially co-localized with proximal PCT segment marker slc20a1a, and the distribution pattern of GFP in pronephric tubule is a little extended than slc20a1a at the distal portion (Figure 4), which belongs to PST segment. When treated with RA, GFP signal elongates distally and almost connects at cloaca (Figure 8A), similar with the expression of the PST segment marker trpm7 in response to RA [5]. Therefore, gtshβ promoter-driven GFP is specifically expressed in the proximal pronephric tubule, and is a valuable marker for PCT and PST segments.
Pax2a is one of the earliest acting transcription factors throughout the IM, and has been identified to control the mesenchyme-to-epithelial transition (MET) of nephron progenitors [74], [75]. Furthermore, Pax2a and the closely related Pax8 act upstream of hnf1b genes, which initiate the gene expression programs specific to pronephric segmentation [15], [76], [77], [78]. However, the epithelialization of IM is still unaffected in Hnf1b-deficient embryos, indicating that pronephric epithelialization and segmentation are separate and the early epithelialization is Hnf1b-independent [15]. The results suggest that both Pax2a and Hnf1b regulate the transcription of gfp through acing on gtshβ promoter (Figure 1D and 5). Consistently, gfp message is initially detected at 16 hpf, just as the formation of pronephric tubular lumen (Figure 6). It is the time that the EMT is undergoing and the segmentation is initialing. Therefore, GPF driven by the gtshβ promoter gives us a good marker to visualize the initial processes of pronephric development.
Through tracing the GFP signal, the gtshβ promoter-driven Tg(gtshβ::GFP) can be easily utilized to observe the convolution of the proximal tubules and the dynamic progression of nephron morphogenesis during the whole lifetime (Figure 2 and 7). Additionally, the expressed GFP can be used as a readout signal of the tubular development to detect the RA signaling alteration in response RA reagent treatment. Therefore, the transgenic line Tg(gtshβ::GFP) provides a potential tool for understanding morphogenesis and segmentation of pronephric tubules and for genetic or chemical analysis of kidney pathology [79].
Funding Statement
This work was supported by grants from the National Major Basic Research Program (2010CB126301), the National 863 High Technology Research Program (Grants No 2012AA092201-3), the Ministry of Agriculture of China within the special Fund for Agro-scientific Research in the Public Interest (200903045), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No.30971414). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1.Vize PD, Woolf AS, Bard JBL (2002) The Kidney: From Normal Development to Congenital Diseases. Amsterdam and Boston: Academic Press.
- 2. Tryggvason K, Wartiovaara J (2005) How Does the Kidney Filter Plasma? Physiology 20: 96–101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Drummond IA, Davidson AJ (2010) Zebrafish Kidney Development. Methods in Cell Biology. 233–260. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 4. Dooley K, Zon LI (2000) Zebrafish: a model system for the study of human disease. Current Opinion in Genetics & Development 10: 252–256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Wingert RA, Selleck R, Yu J, Song H, Chen Z, et al. (2007) The cdx Genes and Retinoic Acid Control the Positioning and Segmentation of the Zebrafish Pronephros. PLoS Genet 3: e189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Wingert RA, Davidson AJ (2008) The zebrafish pronephros: A model to study nephron segmentation. Kidney International 73: 1120–1127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Wingert RA, Davidson AJ (2011) Zebrafish nephrogenesis involves dynamic spatiotemporal expression changes in renal progenitors and essential signals from retinoic acid and irx3b. Developmental Dynamics 240: 2011–2027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. de Groh ED, Swanhart LM, Cosentino CC, Jackson RL, Dai W, et al. (2010) Inhibition of Histone Deacetylase Expands the Renal Progenitor Cell Population. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 21: 794–802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Burrow CR (2000) Retinoids and renal development. Exp Nephrol 8: 219–225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Tena JJ, Neto A, de la Calle-Mustienes E, Bras-Pereira C, Casares F, et al. (2007) Odd-skipped genes encode repressors that control kidney development. Developmental Biology 301: 518–531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Mudumana SP, Hentschel D, Liu Y, Vasilyev A, Drummond IA (2008) odd skipped related1 reveals a novel role for endoderm in regulating kidney versus vascular cell fate. Development 135: 3355–3367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Lyons JP, Miller RK, Zhou X, Weidinger G, Deroo T, et al. (2009) Requirement of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in pronephric kidney development. Mechanisms of Development 126: 142–159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. He W, Dai C, Li Y, Zeng G, Monga SP, et al. (2009) Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Promotes Renal Interstitial Fibrosis. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 20: 765–776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Lienkamp S, Ganner A, Boehlke C, Schmidt T, Arnold SJ, et al. (2010) Inversin relays Frizzled-8 signals to promote proximal pronephros development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107: 20388–20393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Naylor RW, Przepiorski A, Ren Q, Yu J, Davidson AJ (2013) HNF1β Is Essential for Nephron Segmentation during Nephrogenesis. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 24: 77–87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Gerlach GF, Wingert RA (2013) Kidney organogenesis in the zebrafish: insights into vertebrate nephrogenesis and regeneration. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Developmental Biology 2: 559–585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Wang R, Li Z, Wang Y, Gui J (2011) An Apo-14 Promoter-Driven Transgenic Zebrafish That Marks Liver Organogenesis. PLoS ONE 6: e22555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Wang Y, Zhou L, Li Z, Li W, Gui J (2013) Apolipoprotein C1 regulates epiboly during gastrulation in zebrafish. SCIENCE CHINA Life Sciences 56: 975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Zorn AM, Wells JM (2009) Vertebrate Endoderm Development and Organ Formation. Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology 25: 221–251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Perner B, Englert C, Bollig F (2007) The Wilms tumor genes wt1a and wt1b control different steps during formation of the zebrafish pronephros. Dev Biol 309: 87–96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. He B, Ebarasi L, Hultenby K, Tryggvason K, Betsholtz C (2011) Podocin-Green Fluorescence Protein Allows Visualization and Functional Analysis of Podocytes. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 22: 1019–1023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Zhu S, Lee J, Guo F, Shin J, Perez-Atayde AR, et al. (2012) Activated ALK Collaborates with MYCN in Neuroblastoma Pathogenesis. Cancer Cell 21: 362–373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Liu Y, Pathak N, Kramer-Zucker A, Drummond IA (2007) Notch signaling controls the differentiation of transporting epithelia and multiciliated cells in the zebrafish pronephros. Development 134: 1111–1122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Fisher S, Grice EA, Vinton RM, Bessling SL, McCallion AS (2006) Conservation of RET Regulatory Function from Human to Zebrafish Without Sequence Similarity. Science 312: 276–279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Vasilyev A, Liu Y, Mudumana S, Mangos S, Lam P, et al. (2009) Collective Cell Migration Drives Morphogenesis of the Kidney Nephron. PLoS Biol 7: e1000009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Grossmann M, Weintraub BD, Szkudlinski MW (1997) Novel Insights into the Molecular Mechanisms of Human Thyrotropin Action: Structural, Physiological, and Therapeutic Implications for the Glycoprotein Hormone Family. Endocrine Reviews 18: 476–501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Roelfsema F, Veldhuis JD (2013) Thyrotropin Secretion Patterns in Health and Disease. Endocrine Reviews. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 28. Davies T, Marians R, Latif R (2002) The TSH receptor reveals itself. The Journal of Clinical Investigation 110: 161–164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Wang HC, Dragoo J, Zhou Q, Klein JR (2003) An intrinsic thyrotropin-mediated pathway of TNF-alpha production by bone marrow cells. Blood 101: 119–123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Inoue M, Tawata M, Yokomori N, Endo T, Onaya T (1998) Expression of thyrotropin receptor on clonal osteoblast-like rat osteosarcoma cells. Thyroid 8: 1059–1064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Zhou L, Gui J (2010) Molecular mechanisms underlying sex change in hermaphroditic groupers. Fish Physiology and Biochemistry 36: 181–193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Wang Y, Zhou L, Yao B, Li C, Gui J (2004) Differential expression of thyroid-stimulating hormone β subunit in gonads during sex reversal of orange-spotted and red-spotted groupers. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology 220: 77–88. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Li C, Wang Y, Zhou L, Gui J (2010) Cloning of red-spotted grouper TSHb promoter and its localization expression in primitive gonad and pituitary of zebrafish embryos. Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica 34: 822–827. [Google Scholar]
- 34. Mei J, Zhang Q, Li Z, Lin S, Gui J (2008) C1q-like inhibits p53-mediated apoptosis and controls normal hematopoiesis during zebrafish embryogenesis. Developmental Biology 319: 273–284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Xia W, Zhou L, Yao B, Li CJ, Gui JF (2007) Differential and spermatogenic cell-specific expression of DMRT1 during sex reversal in protogynous hermaphroditic groupers. Mol Cell Endocrinol 263: 156–172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Dan C, Mei J, Wang D, Gui J (2013) Genetic Differentiation and Efficient Sex-specific Marker Development of a Pair of Y- and X-linked Markers in Yellow Catfish. Int J Biol Sci 9(10): 1043–1049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Peng JX, Xie JL, Zhou L, Hong YH, Gui JF (2009) Evolutionary conservation of Dazl genomic organization and its continuous and dynamic distribution throughout germline development in gynogenetic gibel carp. J Exp Zool B Mol Dev Evol 312: 855–871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Hurtado R, Mikawa T (2006) Enhanced sensitivity and stability in two-color in situ hybridization by means of a novel chromagenic substrate combination. Developmental Dynamics 235: 2811–2816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Bryson-Richardson RJ, Daggett DF, Cortes F, Neyt C, Keenan DG, et al. (2005) Myosin heavy chain expression in zebrafish and slow muscle composition. Developmental Dynamics 233: 1018–1022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Horsfield J, Ramachandran A, Reuter K, LaVallie E, Collins-Racie L, et al. (2002) Cadherin-17 is required to maintain pronephric duct integrity during zebrafish development. Mechanisms of Development 115: 15–26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Nichane M, Van Campenhout C, Pendeville H, Voz ML, Bellefroid EJ (2006) The Na+/PO4 cotransporter SLC20A1 gene labels distinct restricted subdomains of the developing pronephros in Xenopus and zebrafish embryos. Gene Expression Patterns 6: 667–672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Yoon C, Kawakami K, Hopkins N (1997) Zebrafish vasa homologue RNA is localized to the cleavage planes of 2- and 4-cell-stage embryos and is expressed in the primordial germ cells. Development 124: 3157–3165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Xu H, Gui J, Hong Y (2005) Differential expression of vasa RNA and protein during spermatogenesis and oogenesis in the gibel carp (Carassius auratus gibelio), a bisexually and gynogenetically reproducing vertebrate. Developmental Dynamics 233: 872–882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Yue H, Li Z, Wu N, Liu Z, Wang Y, et al.. (2013) Oocyte-Specific H2A Variant H2af1o Is Required for Cell Synchrony Before Mid-Blastula Transition in Early Zebrafish Embryos. Biology of Reproduction. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 45. Weidinger G, Stebler J, Slanchev K, Dumstrei K, Wise C, et al. (2003) dead end, a Novel Vertebrate Germ Plasm Component, Is Required for Zebrafish Primordial Germ Cell Migration and Survival. Current Biology 13: 1429–1434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Bricaud O, Collazo A (2006) The Transcription Factor six1 Inhibits Neuronal and Promotes Hair Cell Fate in the Developing Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Inner Ear. The Journal of Neuroscience 26: 10438–10451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Lancman JJ, Zvenigorodsky N, Gates KP, Zhang D, Solomon K, et al. (2013) Specification of hepatopancreas progenitors in zebrafish by hnf1ba and wnt2bb. Development 140: 2669–2679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Goodwin JS, Drake KR, Rogers C, Wright L, Lippincott-Schwartz J, et al. (2005) Depalmitoylated Ras traffics to and from the Golgi complex via a nonvesicular pathway. The Journal of Cell Biology 170: 261–272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Liu S, Li Z, Gui J (2009) Fish-Specific Duplicated dmrt2b Contributes to a Divergent Function through Hedgehog Pathway and Maintains Left-Right Asymmetry Establishment Function. PLoS ONE 4: e7261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Zhong J, Zhou L, Li Z, Wang Y, Gui J (2014) Zebrafish Noxa promotes mitosis in early embryonic development and regulates apoptosis in subsequent embryogenesis. Cell Death and Differentiation. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Retracted]
- 51. Huang W, Zhou L, Li Z, Gui JF (2009) Expression pattern, cellular localization and promoter activity analysis of ovarian aromatase (Cyp19a1a) in protogynous hermaphrodite red-spotted grouper. Mol Cell Endocrinol 307: 224–236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Ingraham HA, Chen R, Mangalam HJ, Elsholtz HP, Flynn SE, et al. (1988) A tissue-specific transcription factor containing a homeodomain specifies a pituitary phenotype. Cell 55: 519–529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Jung DO, Jasurda JS, Egashira N, Ellsworth BS (2012) The Forkhead Transcription Factor, FOXP3, Is Required for Normal Pituitary Gonadotropin Expression in Mice. Biology of Reproduction 86: 144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Bauer-Hofmann R, Alonso A (1995) Thyroid hormone receptors bind to the promoter of the mouse histone H10 gene and modulate its transcription. Nucleic Acids Res 23: 5034–5040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Alexander LM, Gordon DF, Wood WM, Kao MY, Ridgway EC, et al. (1989) Identification of thyrotroph-specific factors and cis-acting sequences of the murine thyrotropin beta subunit gene. Mol Endocrinol 3: 1037–1045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Majumdar A, Lun K, Brand M, Drummond IA (2000) Zebrafish no isthmus reveals a role for pax2.1 in tubule differentiation and patterning events in the pronephric primordia. Development 127: 2089–2098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Carroll TJ, Vize PD (1999) Synergism between Pax-8 and lim-1 in embryonic kidney development. Dev Biol 214: 46–59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Sun Z, Hopkins N (2001) vhnf1, the MODY5 and familial GCKD-associated gene, regulates regional specification of the zebrafish gut, pronephros, and hindbrain. Genes & Development 15: 3217–3229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Grote D, Boualia SK, Souabni A, Merkel C, Chi X, et al. (2008) Gata3 Acts Downstream of β-Catenin Signaling to Prevent Ectopic Metanephric Kidney Induction. PLoS Genet 4: e1000316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Grote D, Souabni A, Busslinger M, Bouchard M (2006) Pax 2/8-regulated Gata 3 expression is necessary for morphogenesis and guidance of the nephric duct in the developing kidney. Development 133: 53–61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Jin JY, Zhou L, Wang Y, Li Z, Zhao JG, et al. (2010) Antibacterial and antiviral roles of a fish beta-defensin expressed both in pituitary and testis. PLoS One 5: e12883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Braat AK, van de Water S, Goos H, Bogerd J, Zivkovic D (2000) Vasa protein expression and localization in the zebrafish. Mechanisms of Development 95: 271–274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Köprunner M, Thisse C, Thisse B, Raz E (2001) A zebrafish nanos-related gene is essential for the development of primordial germ cells. Genes & Development 15: 2877–2885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. O’Brien LL, Grimaldi M, Kostun Z, Wingert RA, Selleck R, et al. (2011) Wt1a, Foxc1a, and the Notch mediator Rbpj physically interact and regulate the formation of podocytes in zebrafish. Developmental Biology 358: 318–330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. Levenson RM, Mansfield JR (2006) Multispectral imaging in biology and medicine: Slices of life. Cytometry Part A 69A: 748–758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66. Dressler GR (2006) The Cellular Basis of Kidney Development. Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology 22: 509–529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67. Emerman J, Pitelka D (1977) Maintenance and induction of morphological differentiation in dissociated mammary epithelium on floating collagen membranes. In Vitro 13: 316–328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68. Drummond I (2003) Making a zebrafish kidney: a tale of two tubes. Trends in Cell Biology 13: 357–365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69. Sellitti DF, Hill R, Doi SQ, Akamizu T, Czaja J, et al. (1997) Differential expression of thyrotropin receptor mRNA in the porcine heart. Thyroid 7: 641–646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70. Kumar RS, Trant JM (2001) Piscine glycoprotein hormone (gonadotropin and thyrotropin) receptors: a review of recent developments. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B: Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 129: 347–355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71. MacKenzie DS, Jones RA, Miller TC (2009) Thyrotropin in teleost fish. General and Comparative Endocrinology 161: 83–89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72. Walsh SB, Unwin RJ (2012) Renal tubular disorders. Clin Med 12: 476–479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73. Ji C, Jin X, He J, Yin Z (2012) Use of TSHbeta: EGFP transgenic zebrafish as a rapid in vivo model for assessing thyroid-disrupting chemicals. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 262: 149–155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74. Bouchard M, Souabni A, Mandler M, Neubüser A, Busslinger M (2002) Nephric lineage specification by Pax2 and Pax8. Genes & Development 16: 2958–2970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75. Rothenpieler UW, Dressler GR (1993) Pax-2 is required for mesenchyme-to-epithelium conversion during kidney development. Development 119: 711–720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Naylor RW, Davidson AJ (2013) Hnf1beta and nephron segmentation. Pediatr Nephrol. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 77. Heliot C, Desgrange A, Buisson I, Prunskaite-Hyyryläinen R, Shan J, et al. (2013) HNF1B controls proximal-intermediate nephron segment identity in vertebrates by regulating Notch signalling components and Irx1/2. Development 140: 873–885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78. Massa F, Garbay S, Bouvier R, Sugitani Y, Noda T, et al. (2013) Hepatocyte nuclear factor 1β controls nephron tubular development. Development 140: 886–896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79. Gui J, Zhu Z (2012) Molecular basis and genetic improvement of economically important traits in aquaculture animals. Chinese Science Bulletin 57: 1751–1760. [Google Scholar]