Abstract
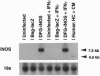
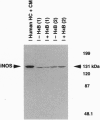
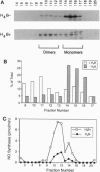
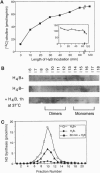
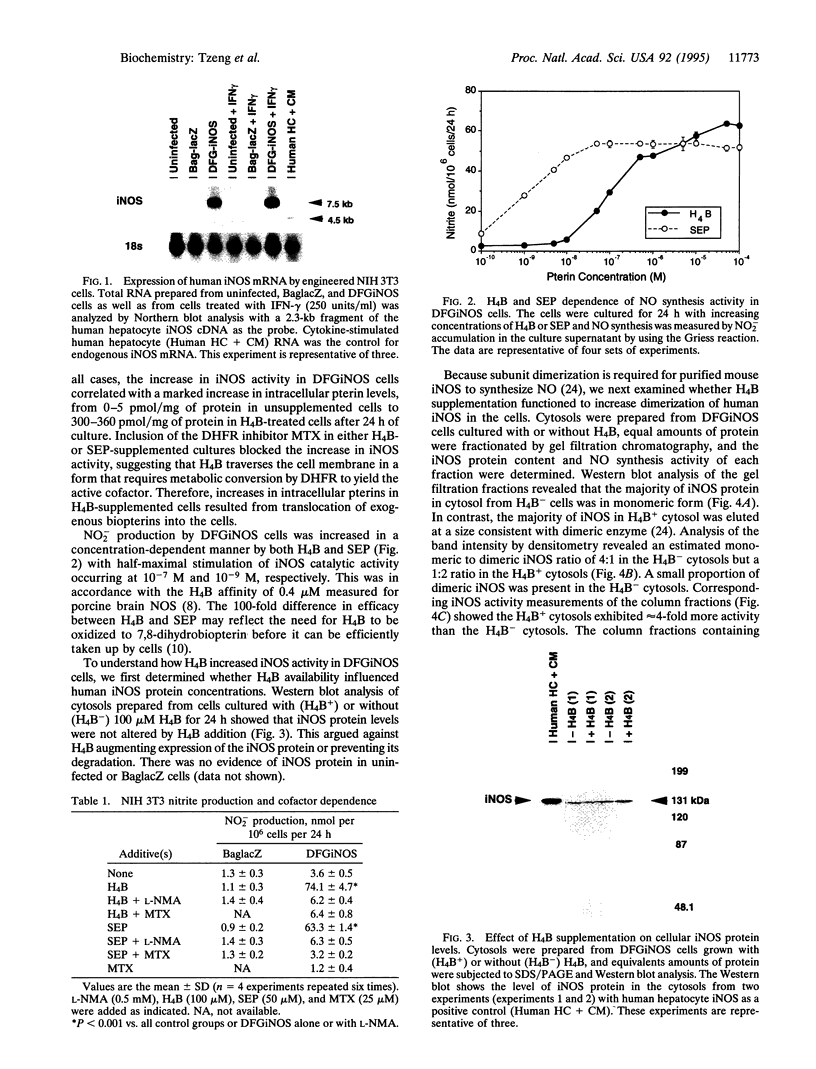
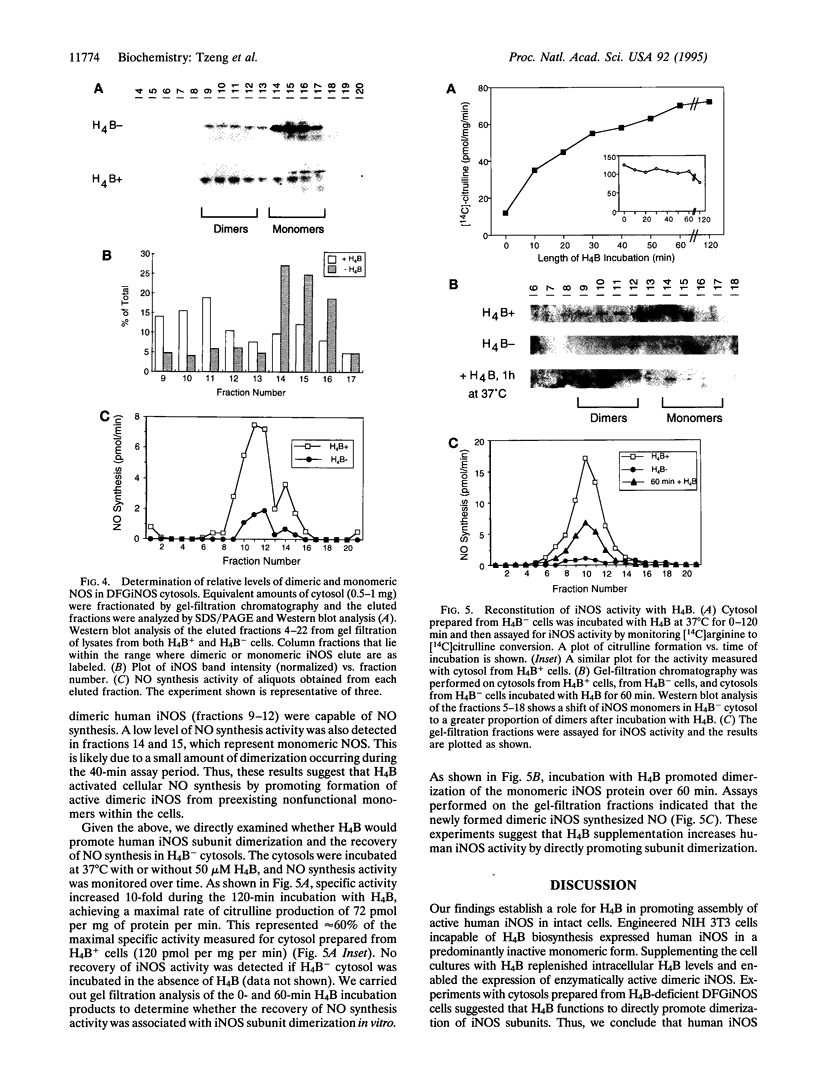
Murine inducible nitric oxide (NO) synthase (iNOS) is catalytically active only in dimeric form. Assembly of its purified subunits into a dimer requires H4B. To understand the structure-activity relationships of human iNOS, we constitutively expressed recombinant human iNOS in NIH 3T3 cells by using a retroviral vector. These cells are deficient in de novo H4B biosynthesis and the role of H4B in the expression and assembly of active iNOS in an intact cell system could be studied. In the absence of added H4B, NO synthesis by the cells was minimal, whereas cells grown with supplemental H4B or the H4B precursor sepiapterin generated NO (74.1 and 63.3 nmol of nitrite per 10(6) cells per 24 h, respectively). NO synthesis correlated with an increase in intracellular H4B but no increase in iNOS protein. Instead, an increased percentage of dimeric iNOS was observed, rising from 20% in cytosols from unsupplemented cells to 66% in H4B-supplemented cell cytosols. In all cases, only dimeric iNOS displayed catalytic activity. Cytosols prepared from H4B-deficient cells exhibited little iNOS activity but acquired activity during a 60- to 120-min incubation with H4B, reaching final activities of 60-72 pmol of citrulline per mg of protein per min. Reconstitution of cytosolic NO synthesis activity was associated with conversion of monomers into dimeric iNOS during the incubation. Thus, human iNOS subunits dimerize to form an active enzyme, and H4B plays a critical role in promoting dimerization in intact cells. This reveals a post-translational mechanism by which intracellular H4B can regulate iNOS expression.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abu-Soud H. M., Yoho L. L., Stuehr D. J. Calmodulin controls neuronal nitric-oxide synthase by a dual mechanism. Activation of intra- and interdomain electron transfer. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 23;269(51):32047–32050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baek K. J., Thiel B. A., Lucas S., Stuehr D. J. Macrophage nitric oxide synthase subunits. Purification, characterization, and role of prosthetic groups and substrate in regulating their association into a dimeric enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 5;268(28):21120–21129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Snyder S. H. Nitric oxide: a physiologic messenger molecule. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:175–195. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.63.070194.001135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chenais B., Yapo A., Lepoivre M., Tenu J. P. High-performance liquid chromatographic analysis of the unusual pathway of oxidation of L-arginine to citrulline and nitric oxide in mammalian cells. J Chromatogr. 1991 Feb 22;539(2):433–441. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)83952-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danos O., Mulligan R. C. Safe and efficient generation of recombinant retroviruses with amphotropic and ecotropic host ranges. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6460–6464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dranoff G., Jaffee E., Lazenby A., Golumbek P., Levitsky H., Brose K., Jackson V., Hamada H., Pardoll D., Mulligan R. C. Vaccination with irradiated tumor cells engineered to secrete murine granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor stimulates potent, specific, and long-lasting anti-tumor immunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3539–3543. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duch D. S., Bowers S. W., Woolf J. H., Nichol C. A. Biopterin cofactor biosynthesis: GTP cyclohydrolase, neopterin and biopterin in tissues and body fluids of mammalian species. Life Sci. 1984 Oct 29;35(18):1895–1901. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(84)90541-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman P. A., Kappelman A. H., Kaufman S. Partial purification and characterization of tryptophan hydroxylase from rabbit hindbrain. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jul 10;247(13):4165–4173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geller D. A., Lowenstein C. J., Shapiro R. A., Nussler A. K., Di Silvio M., Wang S. C., Nakayama D. K., Simmons R. L., Snyder S. H., Billiar T. R. Molecular cloning and expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase from human hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3491–3495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geller D. A., Nussler A. K., Di Silvio M., Lowenstein C. J., Shapiro R. A., Wang S. C., Simmons R. L., Billiar T. R. Cytokines, endotoxin, and glucocorticoids regulate the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase in hepatocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):522–526. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovanelli J., Campos K. L., Kaufman S. Tetrahydrobiopterin, a cofactor for rat cerebellar nitric oxide synthase, does not function as a reactant in the oxygenation of arginine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 15;88(16):7091–7095. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.16.7091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green L. C., Wagner D. A., Glogowski J., Skipper P. L., Wishnok J. S., Tannenbaum S. R. Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15N]nitrate in biological fluids. Anal Biochem. 1982 Oct;126(1):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith O. W., Stuehr D. J. Nitric oxide synthases: properties and catalytic mechanism. Annu Rev Physiol. 1995;57:707–736. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.57.030195.003423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross S. S., Levi R. Tetrahydrobiopterin synthesis. An absolute requirement for cytokine-induced nitric oxide generation by vascular smooth muscle. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):25722–25729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hevel J. M., Marletta M. A. Macrophage nitric oxide synthase: relationship between enzyme-bound tetrahydrobiopterin and synthase activity. Biochemistry. 1992 Aug 11;31(31):7160–7165. doi: 10.1021/bi00146a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAUFMAN S., LEVENBERG B. Further studies on the phenylalanine-hydroxylation cofactor. J Biol Chem. 1959 Oct;234:2683–2688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAUFMAN S. THE STRUCTURE OF THE PHENYLALANINE-HYDROXYLATION COFACTOR. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Dec;50:1085–1093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.6.1085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klatt P., Schmid M., Leopold E., Schmidt K., Werner E. R., Mayer B. The pteridine binding site of brain nitric oxide synthase. Tetrahydrobiopterin binding kinetics, specificity, and allosteric interaction with the substrate domain. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 13;269(19):13861–13866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon N. S., Nathan C. F., Stuehr D. J. Reduced biopterin as a cofactor in the generation of nitrogen oxides by murine macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20496–20501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luss H., DiSilvio M., Litton A. L., Molina y Vedia L., Nussler A. K., Billiar T. R. Inhibition of nitric oxide synthesis enhances the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase mRNA and protein in a model of chronic liver inflammation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Oct 28;204(2):635–640. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.2506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynn R., Rueter M. E., Guynn R. W. Mammalian brain dihydrofolate reductase. J Neurochem. 1977 Dec;29(6):1147–1149. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1977.tb06523.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B., John M., Böhme E. Purification of a Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent nitric oxide synthase from porcine cerebellum. Cofactor-role of tetrahydrobiopterin. FEBS Lett. 1990 Dec 17;277(1-2):215–219. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80848-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B., John M., Heinzel B., Werner E. R., Wachter H., Schultz G., Böhme E. Brain nitric oxide synthase is a biopterin- and flavin-containing multi-functional oxido-reductase. FEBS Lett. 1991 Aug 19;288(1-2):187–191. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81031-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCartney-Francis N., Allen J. B., Mizel D. E., Albina J. E., Xie Q. W., Nathan C. F., Wahl S. M. Suppression of arthritis by an inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase. J Exp Med. 1993 Aug 1;178(2):749–754. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.2.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichol C. A., Smith G. K., Duch D. S. Biosynthesis and metabolism of tetrahydrobiopterin and molybdopterin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:729–764. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.003501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price J., Turner D., Cepko C. Lineage analysis in the vertebrate nervous system by retrovirus-mediated gene transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):156–160. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rachmilewitz D., Stamler J. S., Karmeli F., Mullins M. E., Singel D. J., Loscalzo J., Xavier R. J., Podolsky D. K. Peroxynitrite-induced rat colitis--a new model of colonic inflammation. Gastroenterology. 1993 Dec;105(6):1681–1688. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)91063-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt H. H., Smith R. M., Nakane M., Murad F. Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent NO synthase type I: a biopteroflavoprotein with Ca2+/calmodulin-independent diaphorase and reductase activities. Biochemistry. 1992 Mar 31;31(12):3243–3249. doi: 10.1021/bi00127a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoedon G., Schneemann M., Hofer S., Guerrero L., Blau N., Schaffner A. Regulation of the L-arginine-dependent and tetrahydrobiopterin-dependent biosynthesis of nitric oxide in murine macrophages. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Apr 15;213(2):833–839. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17826.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiman R., Akino M., Kaufman S. Solubilization and partial purification of tyrosine hydroxylase from bovine adrenal medulla. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1330–1340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuehr D. J., Cho H. J., Kwon N. S., Weise M. F., Nathan C. F. Purification and characterization of the cytokine-induced macrophage nitric oxide synthase: an FAD- and FMN-containing flavoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7773–7777. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuehr D. J., Griffith O. W. Mammalian nitric oxide synthases. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1992;65:287–346. doi: 10.1002/9780470123119.ch8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuehr D. J., Kwon N. S., Nathan C. F., Griffith O. W., Feldman P. L., Wiseman J. N omega-hydroxy-L-arginine is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of nitric oxide from L-arginine. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6259–6263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tayeh M. A., Marletta M. A. Macrophage oxidation of L-arginine to nitric oxide, nitrite, and nitrate. Tetrahydrobiopterin is required as a cofactor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):19654–19658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J., Stuehr D. J., Rousseau D. L. Tetrahydrobiopterin-deficient nitric oxide synthase has a modified heme environment and forms a cytochrome P-420 analogue. Biochemistry. 1995 May 30;34(21):7080–7087. doi: 10.1021/bi00021a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner-Felmayer G., Werner E. R., Fuchs D., Hausen A., Reibnegger G., Wachter H. Tetrahydrobiopterin-dependent formation of nitrite and nitrate in murine fibroblasts. J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1599–1607. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner E. R., Werner-Felmayer G., Fuchs D., Hausen A., Reibnegger G., Yim J. J., Pfleiderer W., Wachter H. Tetrahydrobiopterin biosynthetic activities in human macrophages, fibroblasts, THP-1, and T 24 cells. GTP-cyclohydrolase I is stimulated by interferon-gamma, and 6-pyruvoyl tetrahydropterin synthase and sepiapterin reductase are constitutively present. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3189–3192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner E. R., Werner-Felmayer G., Wachter H. Tetrahydrobiopterin and cytokines. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1993 May;203(1):1–12. doi: 10.3181/00379727-203-43566a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]