Abstract
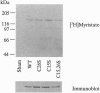
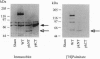
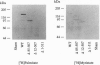
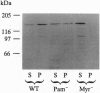
The endothelial nitric oxide synthase (ec-NOS) plays a key role in the transduction of signals from the bloodstream to the underlying smooth muscle. ecNOS undergoes a complex series of covalent modifications, including myristoylation and palmitoylation, which appear to play a role in ecNOS membrane association. Mutagenesis of the myristoylation site, which prevents both myristoylation and palmitoylation, blocks ecNOS targeting to cell membranes. Further, as described for some G-protein alpha subunits, both membrane association and palmitoylation of ecNOS are dynamically regulated: in response to agonists, the enzyme undergoes partial redistribution to the cell cytosol concomitant with depalmitoylation. To clarify the role of palmitoylation in determining ecNOS subcellular localization, we have constructed palmitoylation-deficient mutants of ecNOS. Serine was substituted for cysteine at two potential palmitoylation sites (Cys-15 and Cys-26) by site-directed mutagenesis. Immunoprecipitation of ecNOS mutants following cDNA transfection and biosynthetic labeling with [3H]palmitate revealed that mutagenesis of either cysteine residue attenuated palmitoylation, whereas replacement of both residues completely eliminated palmitoylation. Analysis of N-terminal deletion mutations of ecNOS demonstrated that the region containing these two cysteine residues is both necessary and sufficient for enzyme palmitoylation. The cysteines thus identified as the palmitoylation sites for ecNOS are separated by an unusual (Gly-Leu)5 sequence and appear to define a sequence motif for dual acylation. We analyzed the subcellular distribution of ecNOS mutants by differential ultracentrifugation and found that mutagenesis of the ecNOS palmitoylation sites markedly reduced membrane association of the enzyme. These results document that ecNOS palmitoylation is an important determinant for the subcellular distribution of ecNOS and identify a new motif for the reversible palmitoylation of signaling proteins.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alland L., Peseckis S. M., Atherton R. E., Berthiaume L., Resh M. D. Dual myristylation and palmitylation of Src family member p59fyn affects subcellular localization. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 17;269(24):16701–16705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Snyder S. H. Nitric oxide: a physiologic messenger molecule. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:175–195. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.63.070194.001135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busconi L., Michel T. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase. N-terminal myristoylation determines subcellular localization. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 25;268(12):8410–8413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camp L. A., Hofmann S. L. Purification and properties of a palmitoyl-protein thioesterase that cleaves palmitate from H-Ras. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 25;268(30):22566–22574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camp L. A., Verkruyse L. A., Afendis S. J., Slaughter C. A., Hofmann S. L. Molecular cloning and expression of palmitoyl-protein thioesterase. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 16;269(37):23212–23219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey P. J. Protein lipidation in cell signaling. Science. 1995 Apr 14;268(5208):221–225. doi: 10.1126/science.7716512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degtyarev M. Y., Spiegel A. M., Jones T. L. Palmitoylation of a G protein alpha i subunit requires membrane localization not myristoylation. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 9;269(49):30898–30903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J. Biosynthesis and metabolism of endothelium-derived nitric oxide. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1990;30:535–560. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.30.040190.002535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamas S., Marsden P. A., Li G. K., Tempst P., Michel T. Endothelial nitric oxide synthase: molecular cloning and characterization of a distinct constitutive enzyme isoform. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6348–6352. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marletta M. A. Nitric oxide synthase: aspects concerning structure and catalysis. Cell. 1994 Sep 23;78(6):927–930. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90268-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel T., Li G. K., Busconi L. Phosphorylation and subcellular translocation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6252–6256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan G., Parenti M., Magee A. I. The dynamic role of palmitoylation in signal transduction. Trends Biochem Sci. 1995 May;20(5):181–187. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)89004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Palmer R. M., Higgs E. A. Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 1991 Jun;43(2):109–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumby S. M., Kleuss C., Gilman A. G. Receptor regulation of G-protein palmitoylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 29;91(7):2800–2804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.7.2800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakaoka T., Kojima N., Ogita T., Tsuji S. Characterization of the phosphatidylserine-binding region of rat MARCKS (myristoylated, alanine-rich protein kinase C substrate). Its regulation through phosphorylation of serine 152. J Biol Chem. 1995 May 19;270(20):12147–12151. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.20.12147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C., Xie Q. W. Regulation of biosynthesis of nitric oxide. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 13;269(19):13725–13728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parenti M., Viganó M. A., Newman C. M., Milligan G., Magee A. I. A novel N-terminal motif for palmitoylation of G-protein alpha subunits. Biochem J. 1993 Apr 15;291(Pt 2):349–353. doi: 10.1042/bj2910349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peitzsch R. M., McLaughlin S. Binding of acylated peptides and fatty acids to phospholipid vesicles: pertinence to myristoylated proteins. Biochemistry. 1993 Oct 5;32(39):10436–10443. doi: 10.1021/bi00090a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollock J. S., Förstermann U., Mitchell J. A., Warner T. D., Schmidt H. H., Nakane M., Murad F. Purification and characterization of particulate endothelium-derived relaxing factor synthase from cultured and native bovine aortic endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10480–10484. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resh M. D. Myristylation and palmitylation of Src family members: the fats of the matter. Cell. 1994 Feb 11;76(3):411–413. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90104-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson L. J., Busconi L., Michel T. Agonist-modulated palmitoylation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jan 20;270(3):995–998. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.3.995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweizer A., Rohrer J., Kornfeld S. Determination of the structural requirements for palmitoylation of p63. J Biol Chem. 1995 Apr 21;270(16):9638–9644. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.16.9638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Buss J. E. The covalent modification of eukaryotic proteins with lipid. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;104(6):1449–1453. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.6.1449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sessa W. C., Barber C. M., Lynch K. R. Mutation of N-myristoylation site converts endothelial cell nitric oxide synthase from a membrane to a cytosolic protein. Circ Res. 1993 Apr;72(4):921–924. doi: 10.1161/01.res.72.4.921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenoy-Scaria A. M., Dietzen D. J., Kwong J., Link D. C., Lublin D. M. Cysteine3 of Src family protein tyrosine kinase determines palmitoylation and localization in caveolae. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;126(2):353–363. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.2.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venema R. C., Sayegh H. S., Arnal J. F., Harrison D. G. Role of the enzyme calmodulin-binding domain in membrane association and phospholipid inhibition of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jun 16;270(24):14705–14711. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.24.14705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedegaertner P. B., Wilson P. T., Bourne H. R. Lipid modifications of trimeric G proteins. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jan 13;270(2):503–506. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.2.503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]