Erratum to: J Biol Phys
DOI 10.1007/s10867-013-9339-3
Due to an unfortunate technical problem in production, the original figure 6 showed incorrectly. Figure 6 has now been reproduced correctly and can be seen here.
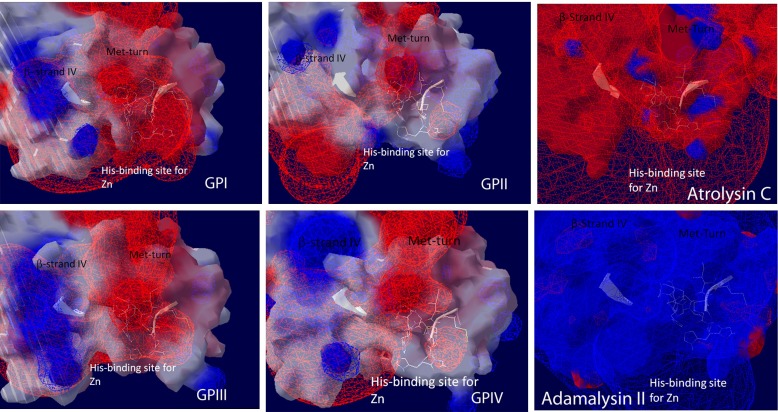
Fig. 1.
Rendering of field potential maps (Coulombic) for each molecular model of each C. s. scutulatus metalloproteinase group and for atrolysin C and adamalysin II crystal structures. Positive field potentials are shown as blue spheres whereas negative field potentials are shown as red spheres that conform the surface potential map and neutral regions are rendered white. For convenience to the viewer, the side chains of the amino acid residues of the zinc binding domain, Met turn, and β-strand IV (top of the catalytic groove) have been displayed (white) in order to locate the catalytic groove of each molecular model
Footnotes
The online version of the original article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10867-013-9339-3.
Contributor Information
Ruben K. Dagda, Email: rdagda@medicine.nevada.edu
Sardar E. Gasanov, Email: sgasanov@yahoo.com
Boris Zhang, Email: bzhang249483@gmail.com.
William Welch, Email: welch@unr.edu.
Eppie D. Rael, Email: eppierael@yahoo.com