Abstract
Coenzyme Q (CoQ) is an essential factor for aerobic growth and oxidative phosphorylation in the electron transport system. The biosynthetic pathway for CoQ has been proposed mainly from biochemical and genetic analyses of Escherichia coli and Saccharomyces cerevisiae; however, the biosynthetic pathway in higher eukaryotes has been explored in only a limited number of studies. We previously reported the roles of several genes involved in CoQ synthesis in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Here, we expand these findings by identifying ten genes (dps1, dlp1, ppt1, and coq3–9) that are required for CoQ synthesis. CoQ10-deficient S. pombe coq deletion strains were generated and characterized. All mutant fission yeast strains were sensitive to oxidative stress, produced a large amount of sulfide, required an antioxidant to grow on minimal medium, and did not survive at the stationary phase. To compare the biosynthetic pathway of CoQ in fission yeast with that in higher eukaryotes, the ability of CoQ biosynthetic genes from humans and plants (Arabidopsis thaliana) to functionally complement the S. pombe coq deletion strains was determined. With the exception of COQ9, expression of all other human and plant COQ genes recovered CoQ10 production by the fission yeast coq deletion strains, although the addition of a mitochondrial targeting sequence was required for human COQ3 and COQ7, as well as A. thaliana COQ6. In summary, this study describes the functional conservation of CoQ biosynthetic genes between yeasts, humans, and plants.
Introduction
Coenzyme Q (CoQ), also known as ubiquinone, is an isoprenoid quinone that is distributed widely in almost all living organisms [1]–[3]. CoQ is a component of the respiratory chain in the inner mitochondrial membrane of eukaryotes and functions primarily as an electron transporter during aerobic respiration and oxidative phosphorylation. CoQ serves as the electron transporter of the NADH dehydrogenase and succinate dehydrogenase complexes to form CoQ:cytochrome c reductase and thus is an essential component of the ATP synthesis pathway. CoQ also functions as a lipid-soluble antioxidant that scavenges reactive oxygen species in cellular biomembranes [4]. Additional roles of CoQ include disulfide bond formation [5], sulfide oxidation [6], and pyrimidine metabolism [7], [8].
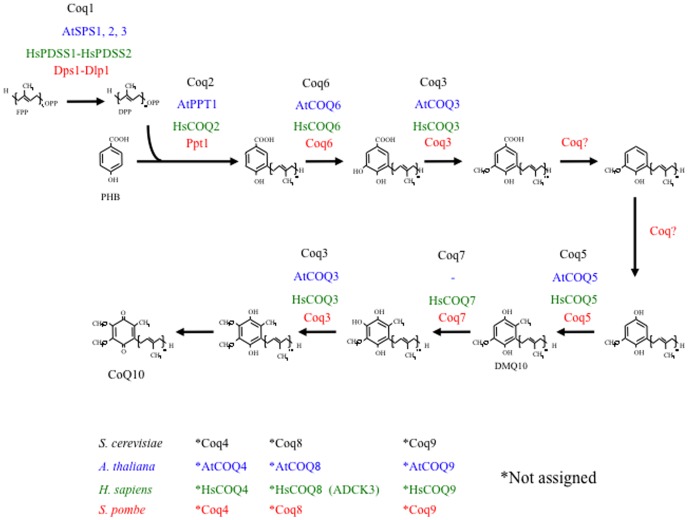
In living organisms, CoQ exists in a number of different forms with differing isoprenoid side chain lengths. For example, in humans and the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe, the CoQ side chain comprises ten isoprene units (CoQ10), whereas those in Arabidopsis thaliana and Saccharomyces cerevisiae are composed of nine (CoQ9) and six (CoQ6) units, respectively [1]. The length of the side chain is defined by trans-polyprenyl diphosphate synthases rather than by the p-hydroxybenzoate (PHB)-polyprenyl diphosphate transferases that catalyze the condensation of PHB and polyprenyl diphosphate [9]. Synthesis of CoQ occurs in two stages: the synthesis of isoprenoid and the synthesis of quinone (Figure 1). To synthesize the isoprenoid tail, a unit of prenyl diphosphate is synthesized by polyprenyl diphosphate synthase. In S. pombe and humans, this enzyme is a heterotetramer of decaprenyl diphosphate synthase (Dps1; also known as Pdss1) and D (aspartate)-less polyprenyl diphosphate synthase (Dlp1; also known as Pdss2) [10]–[12]. By contrast, in budding yeast and plants, polyprenyl diphosphate synthase is homomeric (presumably a homodimer) [13]–[16]. Although the synthesis of isoprenoid has been characterized, the mechanisms involved in quinone synthesis in eukaryotes are less well known. In S. cerevisiae, the biosynthetic pathway that converts PHB to CoQ comprises at least eight steps that require at least seven enzymes with assigned roles [1], [2], [17]; these steps include the condensation and transfer of the isoprenoid side chain to PHB, followed by methylations, decarboxylation and hydroxylations (Figure 1). Para-aminobenzoic acid (pABA) is also a precursor of CoQ biosynthesis in budding yeast [18]. PHB-polyprenyl diphosphate transferase, known as Coq2 in budding yeast [19] or Ppt1 in fission yeast [20], catalyzes the condensation of PHB (or pABA) with the isoprenoid chain. Coq3 (O-methyltransferase) catalyzes the two O-methylation steps in the CoQ biosynthetic pathway [21], [22]. Coq4 is absolutely required for CoQ biosynthesis but its enzymatic function remains unknown [23]. Coq5 (C-methyltransferase) catalyzes the only C-methylation step in the pathway [24]. Coq6 is a flavin-dependent monooxygenase responsible for adding the hydroxy group to polyprenyl-PHB at the C5 position [25], [26]. The mono-oxygenase Coq7 is involved in the penultimate step of CoQ biosynthesis [22]. Coq8 functions as a protein kinase that phosphorylates some Coq proteins and stabilizes the protein complex [27], [28]. Coq9 is required for CoQ biosynthesis but its enzymatic function is unknown [29]. Coq10 is a binding protein of CoQ [30], [31], and indirectly affects but is not required for CoQ synthesis [32].
Figure 1. The proposed CoQ biosynthesis pathway in S. cerevisiae, S. pombe, humans, and A. thaliana.
At least ten genes, three of which have unassigned roles, are responsible for CoQ biosynthesis in S. pombe. All of these S. pombe enzymes have human counterparts, but A. thaliana lacks Coq7 and a component of the prenyl diphosphate synthase in this plant species differs from that in S. pombe and humans. The functions of Coq4 and Coq9 are currently unknown. Coq8 is a protein kinase that regulates the stability of Coq proteins in S. cerevisiae. The involvement of pABA in the CoQ pathway in S. pombe, human and A. thaliana has not yet been established. For simplicity, ARH1 and YAH1, which are involved in CoQ synthesis through the regulation of Coq6 in S. cerevisiae, are not shown.
Although the CoQ biosynthetic pathway has been examined in bacteria and yeasts, little is known about the pathway in higher eukaryotes. Understanding the CoQ biosynthetic pathway in humans is important because CoQ is essential for energy production and is the only endogenously synthesized lipid-soluble antioxidant. Furthermore, CoQ deficiency can lead to the development of severe diseases such as Leigh syndrome [33].
Here, we identified ten genes (dps1, dlp1, ppt1, and coq3–9), including some that have been reported previously, that are related to CoQ biosynthesis in S. pombe. Deletion strains were constructed for all of these genes; all of the CoQ10-deficient mutants were sensitive to oxidative stress, produced a large quantity of sulfide, required an antioxidant to grow on minimal medium, and did not survive in the stationary phase. The biosynthetic pathway of CoQ in higher eukaryotes was also investigated by performing functional complementation analyses of the S. pombe coq deletion mutants using human and A. thaliana homologues.
Materials and Methods
Strains, media, and genetic manipulation
The S. pombe strains used in this study are listed in Table 1. Standard yeast culture media and genetic manipulations were used. The S. pombe strains were grown in complete YES medium (0.5% yeast extract, 3% glucose, 225 mg/l adenine, 225 mg/l leucine, 225 mg/l uracil, 225 mg/l histidine, and 225 mg/l lysine hydrochloride) or EMM medium (0.3% potassium hydrogen phthalate, 0.56% sodium phosphate, 0.5% ammonium chloride, 2% glucose, vitamins, minerals, and salts) [34]. The appropriate auxotrophic supplements were added as necessary (75 mg/l adenine, 75 mg/l leucine, 75 mg/l uracil, 75 mg/l histidine, 75 mg/l lysine, or 400 mg/l cysteine). Escherichia coli DH5α was used as the host strain for all plasmid manipulations and was grown in LB medium (1% bactotryptone, 0.5% yeast extract, and 1% NaCl; pH 7.0). Standard molecular biology techniques were followed [35]. The restriction enzymes (BamHI, BglII, XhoI, NdeI, NotI and SalI) were used according to the suppliers' recommendations (TOYOBO, Takara, NEB). Nucleotide sequences were determined by the dideoxynucleotide chain-termination method using an Applied Biosystems 3500 Genetic Analyzer.
Table 1. Strains used in this study.
| Strain | Genotype | Resource |
| L972 | h˜ | Lab stock |
| PR110 | h + leu1-32 ura4-D18 | Lab stock |
| LJ1030 | h + leu1-32 ura4-D18 dps1:: kanMX | [6] |
| RM19 | h + leu1-32 ura4-D18 dlp1:: kanMX6 | [22] |
| LA1 | h + leu1-32 ura4-D18 ade6.M210 dps1:: kanMX6 dlp1::ura4::ADE2 | [6] |
| KH2 | h + leu1-32 ura4-D18 ppt1(coq2)::kanMX6 | This study |
| KH3 (RM2) | h + leu1-32 ura4-D18 coq3:: kanMX6 | [22] |
| KH4 | h + leu1-32 ura4-D18 coq4:: kanMX6 | This study |
| KH5 | h + leu1-32 ura4-D18 coq5:: kanMX6 | This study |
| KH6 | h + leu1-32 ura4-D18 coq6:: kanMX6 | This study |
| KH7 (RM1) | h + leu1-32 ura4-D18 coq7:: kanMX6 | [22] |
| KH8 | h + leu1-32 ura4-D18 coq8:: kanMX6 | This study |
| KH9 | h + leu1-32 ura4-D18 coq9:: kanMX6 | This study |
Construction of the deletion strains
The S. pombe deletion strains were constructed by replacing the coq genes with a selectable marker; chromosomal genes were disrupted by homologous recombination using fragments generated by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) [36] (Figure S1). The 1.6 kb kanMX6 module was amplified with flanking sequences corresponding to the 5′ and 3′ ends of the target genes. Resistant colonies were selected on YES plates containing 100 mg/L G418 (Sigma) and disruption of the gene of interest was verified by colony PCR. DNA fragments of 400–500 bp corresponding to the 5' or 3' regions of the ppt1, coq4, coq5, coq6, coq8, or coq9 gene were amplified by PCR using the ppt1/coq4/5/6/8/9-w and ppt1/coq4/5/6/8/9-x or ppt1/coq4/5/6/8/9-y and ppt1/coq4/5/6/8/9-z primer pairs (Table S1). For each gene, the 5′ and 3′ amplified fragments were fused to the ends of the kanMX6 module by PCR. The wild type PR110 strain (Table 1) was transformed with the resulting ppt1::kanMX6, coq4::kanMX6, coq5::kanMX6, coq6::kanMX6, coq8::kanMX6, and coq9::kanMX6 fragments to form the deletion strains (Table 1). Transformants were selected using 100 mg/L G418. To confirm the chromosomal deletion of the ppt1, coq4, coq5, coq6, coq8, and coq9 genes, PCR was performed using the nb2 and ppt1/coq4/5/6/8/9-c primers (Table S1); the resulting deletion strains were designated KH2 (Δppt1), KH4 (Δcoq4), KH5 (Δcoq5), KH6 (Δcoq6), KH8 (Δcoq8), and KH9 (Δcoq9), respectively. The Δdps1 strain and the dps1-dlp1 double deletion strain were constructed as described previously (Zhang et al., 2008). The Δdlp1, Δcoq3 and Δcoq7 strains were also constructed as described previously (Miki et al., 2008).
Plasmid construction
The plasmids constructed in this study are shown in Figures S2, S3, Figure S4 and S5 and the primers used for plasmid construction are listed in Table S1. Each S. pombe coq gene was PCR amplified using primers containing restriction sites, digested using restriction endonucleases, and then inserted into the appropriate sites of the pREP1 or pREP2 vector by ligation. For example, pREP1-coq3 was constructed by inserting the PCR product amplified using the Coq3-N (SalI) and Coq3-C (SmaI) primers into the SalI and SmaI sites of pREP1 (Figure S2). The other plasmids were constructed similarly. To examine the cellular localization of Coq proteins, GFP-fusions were generated by inserting each coq gene into the pSLF272L-GFPS65A vector. For example, pSLF272L-GFPS65A-Coq3 was constructed by inserting the PCR product amplified using the Coq3-N-GFP (XhoI) and Coq3-C-GFP (NotI) primers into the XhoI and NotI sites of pSLF272L-GFPS65A. The other plasmids expressing GFP-fusion proteins were constructed similarly (Figure S3). The human (Hs) COQ genes (Table 2) were obtained from Funakoshi Corp. or from C. Clarke at UCLA. The DNA fragments were amplified by PCR using primers containing restriction sites (Table S1) and then cloned into the pREP1, pREP41, or pREP2 vectors [37]. For example, pREP1-HsCOQ3 was constructed by inserting the PCR product amplified using the HsCOQ3-N (NdeI) and HsCOQ3-C (BamHI) primers into the NdeI and BamHI sites of pREP1 (Figure S4). For expression of HsCOQ3 and HsCOQ7, the 5′ region and mitochondrial targeting sequence of coq3 and coq7 from S. pombe were fused with the human COQ3 and COQ7 sequences, respectively. The A. thaliana genes (Table 2) were obtained from the Arabidopsis Biological Resource Center (ABRC) or Riken BRC. The plasmids were constructed in the same manner as those expressing the human COQ3 genes. For expression of AtCOQ6, the mitochondrial targeting signal of coq6 from S. pombe was fused to the AtCOQ6 gene sequence (Figure S5). The genes amplified by PCR were verified by DNA sequencing.
Table 2. Genes involved in CoQ synthesis in S. cerevisiae, S. pombe, humans, and A. thaliana.
| S. cerevisiae | S. pombe | H. sapiens (accession #) | Arabidopsis (systematic name) | Enzyme (function) |
| COQ1 | dps1-dlp1 | HsPDSS1(AI590245)-HsPDSS2(BI551760) | AtSPS3 (At2g34630) | Polyprenyl diphosphate synthase |
| COQ2 | ppt1/coq2 | HsCOQ2 (BF026793) | AtPPT1 (At4g23660) | PHB-polyprenyldiphosphate transferase |
| COQ3 | coq3 | HsCOQ3 (AF193016) | AtCOQ3 (At2g30920) | O-Methyltransferase |
| COQ4 | coq4 | HsCOQ4 (BQ685658) | AtCOQ4 (At2g03690) | Unknown |
| COQ5 | coq5 | HsCOQ5 (BC004916) | AtCOQ5 (At5g57300) | C-Methyltransferase |
| COQ6 | coq6 | HsCOQ6 (BQ668512) | AtCOQ6 (At3g24200) | C5-Hydroxylation |
| COQ7 | coq7 | HsCOQ7 (AF032900) | - | Monooxygenase |
| COQ8/ABC1 | coq8 | HsCOQ8/ADCK3 (BC005171) | AtCOQ8 (At4g01660) | Protein kinase |
| COQ9 | coq9 | HsCOQ9 (BC064946) | AtCOQ9 (At1g19140) | Unknown |
Extraction and measurement of CoQ from S. pombe
CoQ was extracted from S. pombe as described previously [31]. Briefly, crude lipid extracts were analyzed by normal phase thin layer chromatography using authentic CoQ10 (as the standard) and benzene on a Kieselgel 60 F254 plate. Following UV visualization, the band containing CoQ10 was collected from the plate and extracted with chloroform/methanol (1∶1 v/v). The samples were dried and resolved in ethanol. Purified CoQ was analyzed further by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), with ethanol as the solvent.
Measurement of extracellular sulfide
Extracellular sulfide was quantified using the methylene blue method [6]. Briefly, S. pombe was grown to late log phase in YES or EMM medium (50 ml). The cultures (0.5 ml) were mixed with 0.1 ml of 0.1% dimethylphenylenediamine (in 5.5 N HCl) and 0.1 ml of 23 mM FeCl3 (in 1.2 N HCl) and then incubated at 37°C for 5 min. Following centrifugation at 12,000 g for 5 min, the supernatant was removed and absorbance was measured at 670 nm. The blank consisted of reagents alone.
Mitochondrial staining and fluorescence microscopy
Mitochondria were stained using MitoTracker Red FM dye (Invitrogen). The cells were suspended in 10 mM HEPES (pH 7.4) containing 5% glucose and MitoTracker Red FM was added to a final concentration of 50 nM. After incubation at room temperature for 15 min, the cells were visualized at 1000× magnification using a BX51 fluorescent microscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan). The fluorescence of GFPS65A was observed at an excitation wavelength of 485 nm. Fluorescent images were obtained using a digital camera (DP70, Olympus) connected to the microscope.
Results
Construction and phenotypes of the S. pombe coq deletion strains
The biosynthetic pathway of CoQ has been well characterized in S. cerevisiae [2]. Here, we examined the involvement of ten S. pombe coq genes (which are homologous to S. cerevisiae COQ genes) (Figure 1 and Table 2) in CoQ biosynthesis. We previously reported the construction and characterization of S. pombe Δdps1 [6], [38], Δdlp1 [11], Δdps1-Δdlp1 (Zhang et al., 2008), Δppt1/coq2 [20], Δcoq3 [22], Δcoq7 [22], and Δcoq8 [27] strains, which are unable to synthesize CoQ. Here, we constructed four new S. pombe deletion strains in which the coq4 (SPAC1687.12c), coq5 (SPCC4G3.04c), coq6 (SPBC146.12), or coq9 (SPAC19G12.11) gene was replaced with the kan r marker (Figure S1 and Table 1). S. pombe ppt1 or coq8 deletion strain containing the kan r marker was also generated to equalize a background of strains.
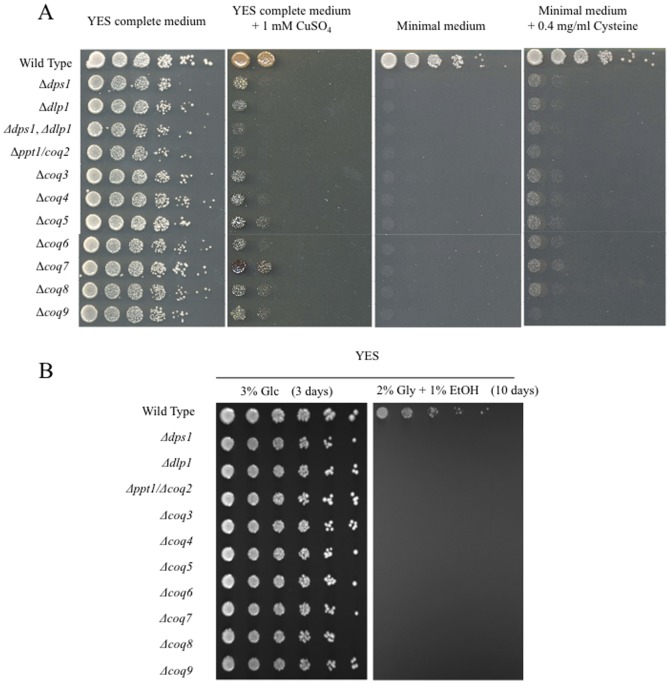
The phenotypes of eleven S. pombe deletion strains (Δdps1, Δdlp1, Δdps1-Δdlp1, Δppt1/coq2, Δcoq3, Δcoq4, Δcoq5, Δcoq6, Δcoq7, Δcoq8, and Δcoq9; Table 1) were determined. Unlike the wild type strain (PR110), all of the deletion strains required cysteine to grow on minimal medium and were sensitive to CuSO4 when grown on YES medium (Figure 2A). In addition, the ten single deletion strains (the Δdps1-Δdlp1 strain was not tested) were unable to grow on YES medium containing yeast extract supplemented with ethanol and glycerol (Figure 2B) and did not survive in the stationary phase (data not shown; [22]). The inability to grow on YES medium containing yeast extract supplemented with ethanol and glycerol and the sensitivity to CuSO4 are symptoms of respiration defective and oxidative stress-sensitive phenotypes, respectively. As reported previously for the S. pombe Δcoq7 strain [22], all ten single coq deletion strains were also sensitive to H2O2 (data not shown). Overall, these results suggest that the ten single coq deletion strains share common phenotypes.
Figure 2. Phenotypes of the S. pombe coq deletion mutants.
(A) Ten-fold serial dilutions of the indicated strains (1×106 cells) in sterilized water were spotted onto YES medium, YES medium supplemented with 1 mM CuSO4, EMM (minimal medium), and EMM supplemented with 0.4 mg/ml cysteine. The plates were incubated at 30°C for 4 days (B) The same dilutions of the strains were spotted onto YES medium containing 3 mM glucose (Glc) and YES medium lacking glucose but containing 2% glycerol (Gly) and 1% ethanol (EtOH). The plates were incubated at 30°C for 3 or 10 days.
Localization of the S. pombe Coq proteins
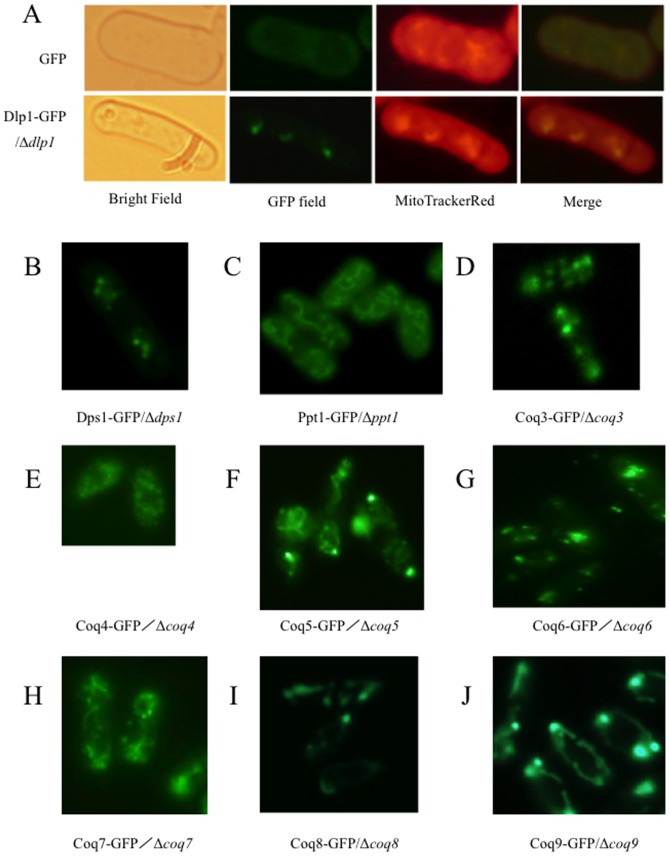
The cellular localizations of Ppt1/Coq2 and Coq7 from S. pombe have been reported previously [20]. GFP-fusions were constructed to examine the localization of these and other S. pombe Coq proteins (Figure S3). As shown in Figure 3A, the fluorescent signal generated by the Dlp1-GFP fusion protein expressed in the Δdlp1 strain overlapped with that of mitochondria stained using MitoTracker Red FM dye. The Dps1, Ppt1/Coq2, Coq3, Coq4, Coq5, Coq6, Coq7, Coq8, and Coq9 GFP fusion proteins also localized to the mitochondria (Figures 3B–J).
Figure 3. Mitochondrial localization of S. pombe Coq proteins.
The indicated Coq proteins were fused with GFP and their localization was observed under a fluorescence microscope. The plasmids used in this experiment are shown in Figure S2B. (A) A bright-field image and the GFP and MitoTracker Red signals in the Δdlp1 strain expressing the Dlp1-GFP fusion protein. The merged GFP and MitoTracker Red signals are also shown. (B–J) GFP signals of the Dps1-GFP fusion expressed in Δdps1 cells (B), the Ppt1(Coq2)-GFP fusion expressed in Δppt1 cells (C), the Coq3-GFP fusion expressed in Δcoq3 cells (D), the Coq4-GFP fusion expressed in Δcoq4 cells (E), the Coq5-GFP fusion expressed in Δcoq5 cells (F), the Coq6-GFP fusion expressed in Δcoq6 cells (G), the Coq7-GFP fusion expressed in Δcoq7 cells (H), the Coq8-GFP fusion expressed in Δcoq8 cells (I), and the Coq9-GFP fusion expressed in Δcoq9 cells (J). All cells were stained with MitoTracker Red to verify the localization of the Coq proteins to mitochondria (data not shown).
Complementation of the S. pombe coq deletion strains by human COQ genes
In an HPLC analysis, a lipid extract from the wild type S. pombe strain (PR110) yielded a major peak at 10 min, which was consistent with that of authentic CoQ10. To compare the biosynthetic pathways of CoQ in S. pombe and higher organisms, we determined whether defective CoQ10 production by S. pombe coq deletion strains could be functionally complemented by human genes encoding CoQ biosynthetic enzymes. Plasmids containing HsCOQ genes (which were identified on the basis of their sequence similarity to known S. pombe coq genes) (Figure 1 and Table 2) under the control of the nmt1 promoter were generated (Figure S4). For some human COQ genes, the use of a weaker promoter (nmt1*) was required to avoid growth inhibition caused by high levels of expression. The plasmids were expressed in the corresponding S. pombe deletion strains and lipid extracts were analyzed by HPLC.
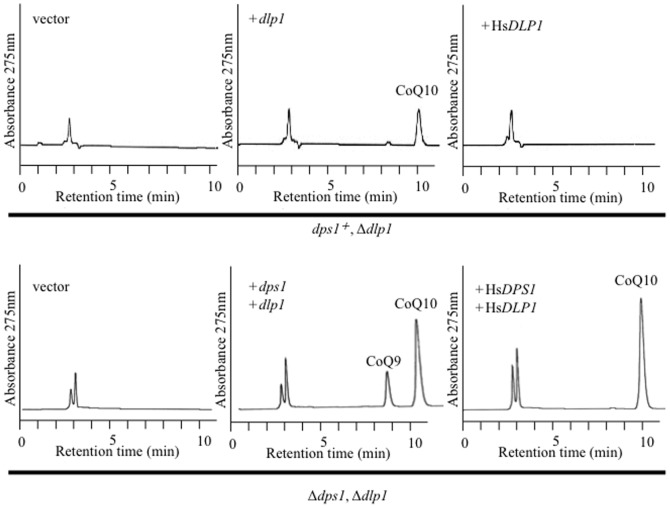
In a previous study, HsDPS1/PDSS1 was able to complement an S. pombe Δdps1 mutant, but HsDLP1/PDSS2 was not able to complement an S. pombe Δdlp1 mutant [12]. Here, the S. pombe Δdlp1 strain expressing HsDLP1 containing a mitochondrial targeting signal from dlp1 did not produce CoQ10 (Figure 4), indicating that the failure of complementation by this human gene is not due to mislocalization of the protein. By contrast, the S. pombe dps1-dlp1 double deletion strain expressing HsDPS1 and HsDLP1 was able to produce CoQ10 (Figure 4), indicating that HsDPS1 and HsDLP1 can form a functional complex in S. pombe. These results suggest that, in both human and S. pombe, Dps1 and Dlp1 are necessary to constitute a heterotetrameric decaprenyl diphosphate synthase.
Figure 4. Functional complementation of the S. pombe Δdps1 and Δdlp1 strains by HsDPS1 and HsDLP1.
HPLC analyses of lipid extracts from the RM19 (Δdlp1) strain expressing S. pombe dlp1 or HsDLP1 and the LA1 (Δdps1-Δdlp1) strain expressing S. pombe dps1 and dlp1 or HsDPS1 and HsDLP1.
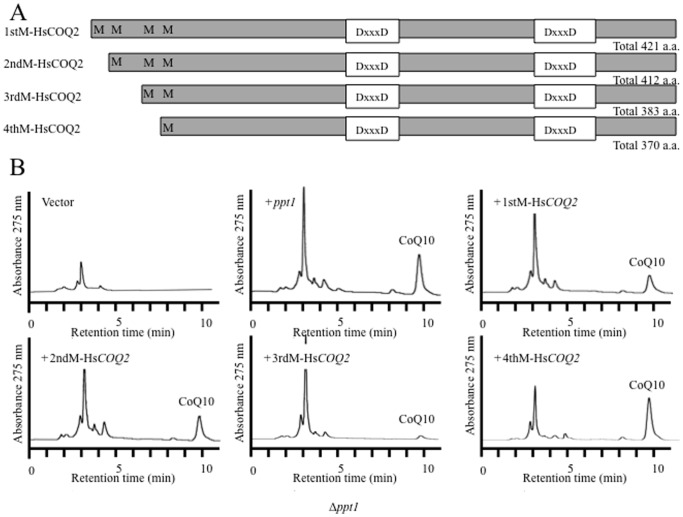
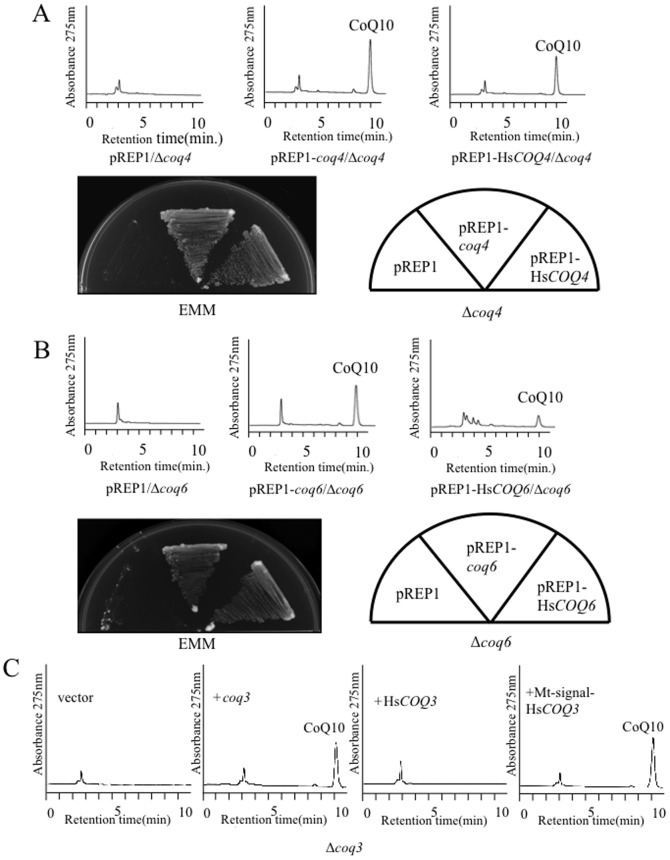
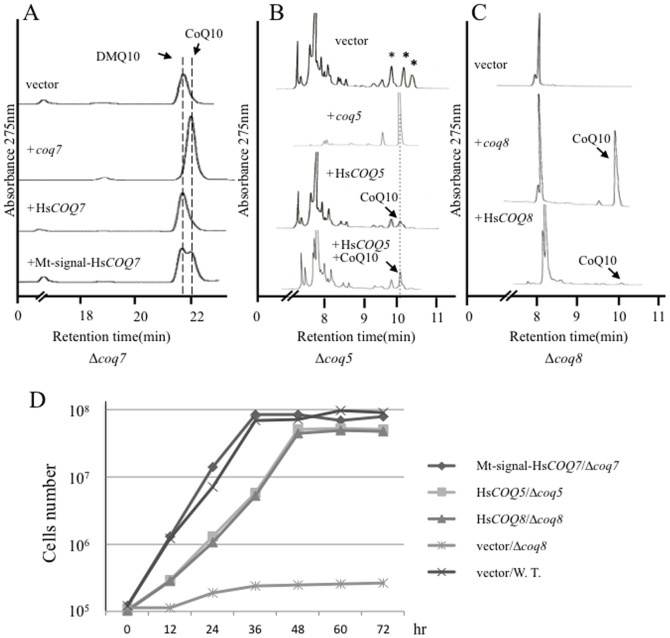
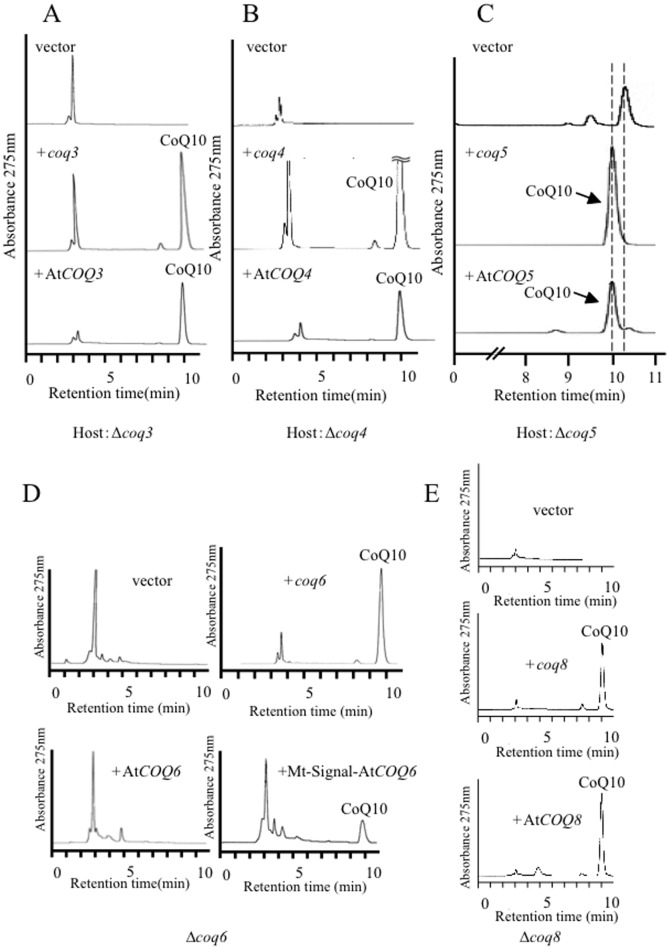
Four putative start codons were identified in the HsCOQ2 sequence; therefore, four plasmids that included a different putative start codon (1st–4th) of the gene were generated (Figure 5A). All of the HsCOQ2 constructs restored the growth of the S. pombe Δppt1 strain (data not shown) and recovered its defective production of CoQ10 (Figure 5B). Thus, the 4th methionine is sufficient for functional expression in the Δppt1 strain. Similar results were obtained when HsCOQ4 and HsCOQ6 were expressed in the Δcoq4 and Δcoq6 strains, respectively (Figures 6A and 6B). By contrast, HsCOQ3 (Figure 6C) and HsCOQ7 (Figure 7A) failed to complement their respective S. pombe deletion strains. Since all S. pombe Coq proteins localize to the mitochondria (Figure 3), the HsCOQ3 and HsCOQ7 constructs were modified to include a promoter region containing the mitochondrial targeting signal from the S. pombe coq3 and coq7 genes, respectively. Targeting of HsCOQ3 and HsCOQ7 to the mitochondria successfully recovered defective CoQ10 production by the S. pombe Δcoq3 (Figure 6C) and Δcoq7 (Figure 7A) strains. An HPLC peak that we previously identified as demethoxyubiquinone (DMQ10) [22] was detected in the Δcoq7 strain; this peak was fully converted to CoQ10 by expression of S. pombe coq7 and partly converted by expression of HsCOQ7 containing a mitochondrial targeting signal (Figure 7A).
Figure 5. Functional complementation of the S. pombe Δppt1 strain by HsCOQ2.
(A) Schematic illustration of the four HsCOQ2 plasmids that included different 5′ ends of the gene in pREP1. M, start codon; aa, amino acid. (B) HPLC analyses of lipid extracts from the KH2 (Δppt1) strain expressing S. pombe ppt1 or the four different HsCOQ2 constructs.
Figure 6. Complementation of the S. pombe Δcoq4, Δcoq6 and Δcoq3 strains by HsCOQ3, HsCOQ4 and HsCOQ6.
(A, B) HPLC analyses of lipid extracts from the KH4 (Δcoq4) strain expressing S. pombe coq4 or HsCOQ4 and the KH6 (Δcoq6) strain expressing S. pombe coq6 or HsCOQ6. Growth on minimal media (EMM) plates is also shown. (C) HPLC analyses of lipid extracts from the KH3 (Δcoq3) strain expressing S. pombe coq3, HsCOQ3, or HsCOQ3 fused with a mitochondrial targeting sequence (Mt-signal).
Figure 7. Complementation of the S. pombe Δcoq7, Δcoq5, and Δcoq8 strains by HsCOQ7, HsCOQ5 and HsCOQ8.
(A) HPLC analyses of lipid extracts from the KH7 (Δcoq7) strain expressing S. pombe coq7, HsCOQ7, or HsCOQ7 containing a mitochondrial targeting sequence (Mt-signal). The flow speed was doubled to separate the two peaks clearly. DMQ10, demethoxyubiquinone. (B) HPLC analyses of lipid extracts from the KH5 (Δcoq5) strain expressing S. pombe coq5 or HsCOQ5. CoQ10 was mixed with the lipid extracts from the KH5 (Δcoq5) strain expressing HsCOQ5. Asterisks indicate the intermediate like peaks found in a coq5 deletion strain. (C) HPLC analyses of lipid extracts from the KH8 (Δcoq8) strain expressing S. pombe coq8 or HsCOQ8. (D) Cell growth of the indicated strains over 72 h. W.T., wild type strain.
Unidentified peaks, which may represent intermediates, were identified in the S. pombe Δcoq5 strain (Figure 7B, asterisks); these peaks did not merge with the CoQ10 standard (data not shown). When the S. pombe coq5 gene was expressed in the Δcoq5 strain, the intermediate peaks disappeared and a CoQ10 peak was observed on the HPLC trace (Figure 7B). By contrast, expression of the HsCOQ5 gene in this strain failed to recover a clear CoQ10 production (Figure 7B); however, when the lipid extract from the HsCOQ5-complemented Δcoq5 strain was mixed with CoQ10, one of the peaks merged with that of CoQ10, indicating that a small amount of CoQ10 was in fact produced (Figure 7B). Similarly, CoQ10 production by the S. pombe Δcoq8 strain was fully recovered by expression of S. pombe coq8 but only moderately recovered by expression of HsCOQ8/ADCK3 (Figure 7C). Expression of HsCOQ7 containing a mitochondrial targeting signal from coq7 fully restored the growth of the Δcoq7 strain, and HsCOQ5 and HsCOQ8/ADCK3 partially restored growth of the Δcoq5 and Δcoq8 strains, respectively; the doubling times of these complemented strains were approximately 0.7 times that of the wild type strain (Figure 7D). Despite the inclusion of a mitochondrial targeting signal within its sequence, HsCOQ9 did not complement the S. pombe Δcoq9 mutant (data not shown). Overall, these data indicate that, like the S. pombe Δdps1, Δdlp1, Δppt1/coq2, Δcoq3, Δcoq7, and Δcoq8 strains described previously, the Δcoq4, Δcoq5, Δcoq6, and Δcoq9 strains are also unable to synthesize CoQ. Furthermore, with the exception of COQ9, human COQ biosynthetic genes can functionally complement their corresponding S. pombe coq mutants.
Sulfide and CoQ production
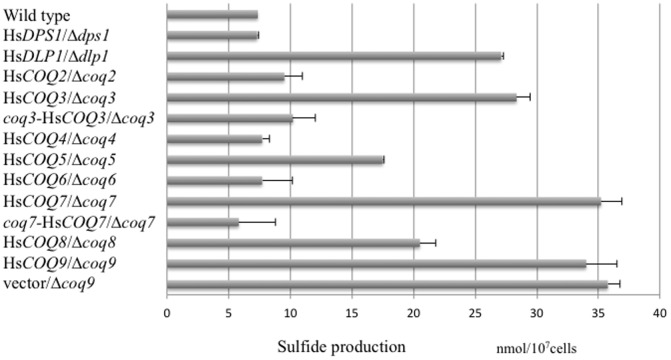
We next measured sulfide production to further determine the efficiency of complementation of the S. pombe coq deletion strains by human COQ genes. Sulfide production in the S. pombe coq deletion strains is known to be higher than that in the wild type strain [6]. Expression of HsDPS1, HsCOQ2, HsCOQ4, and HsCOQ6 in the corresponding deletion strains reversed this increase (Figure 8). Expression of HsCOQ5 and HsCOQ8 (ADCK3) also partially reversed the increased sulfide production (Figure 8). Expression of HsCOQ9 failed to reverse increased sulfide production by the Δcoq9 strain. Similarly, expression of HsCOQ3 and HsCOQ7 failed to reverse increased sulfide production by the Δcoq3 and Δcoq7 strains, respectively; however, the addition of a mitochondrial targeting signal to these human genes successfully recovered sulfide production to a level similar to that of the wild type strain (Figure 8). These results are consistent with the levels of CoQ10 production in the human gene-complemented coq deletion strains, indicating that the restoration of CoQ10 production and sulfide production was correlated.
Figure 8. Sulfide production by S. pombe coq deletion strains expressing human COQ genes.
Sulfide production was measured as described in the Materials and methods. Data are represented as the mean ± SD of n = 2 experiments. The coq3-HsCOQ3/Δcoq3 and coq7-HsCOQ7/Δcoq7 strains expressed the human genes containing a mitochondrial targeting sequence from S. pombe coq3 and coq7, respectively.
Complementation of S. pombe coq deletion strains by A. thaliana genes
Next, we examined the ability of A. thaliana (At) COQ genes (Table 2) to complement the S. pombe coq deletion mutants. Although AtSPS1 and AtSPS2, which encode two solanesyl diphosphate synthases in A. thaliana, complement the fission yeast Δdps1 mutant [13], recent studies show that At2g34630 (named here AtSPS3) is most likely responsible for CoQ synthesis in A. thaliana [39]. Here, the abilities of the AtCOQ3, AtCOQ4, AtCOQ5, AtCOQ6, and AtCOQ8 genes to complement the corresponding S. pombe mutants were determined. Expression of AtCOQ3, AtCOQ4 and AtCOQ5 recovered CoQ10 production by the S. pombe Δcoq3, Δcoq4 and Δcoq5 strains, respectively (Figures 9A–C). By contrast, expression of the AtCOQ6 gene did not complement the Δcoq6 strain; however, the addition of a mitochondrial targeting signal to AtCOQ6 did enable recovery of CoQ10 production when expressed in the Δcoq6 strain (Figure 9D). A. thaliana does not contain an ortholog of Coq7, and both Coq6 and Coq7 are involved in the hydroxylation step of CoQ biosynthesis; however, AtCOQ6 was unable to recover CoQ10 production by the S. pombe Δcoq7 strain (data not shown). It is still not clear what kind of enzyme is responsible for this hydroxylation step in A. thaliana. Unlike HsCOQ8/ADCK3, the AtCOQ8 gene was able to functionally complement the S. pombe Δcoq8 strain (Figure 9E); however, expression of AtCOQ9 did not recover CoQ10 production by the Δcoq9 strain (data not shown).
Figure 9. Complementation of the S. pombe coq deletion strains by A. thaliana COQ genes.
(A–E) HPLC analyses of lipid extracts from the KH3 (Δcoq3) strain expressing S. pombe coq3 or AtCOQ3 (A); the KH4 (Δcoq4) strain expressing S. pombe coq4 or AtCOQ4 (B); the KH5 (Δcoq5) strain expressing S. pombe coq5 or AtCOQ5 (C); the KH6 (Δcoq6) strain expressing S. pombe coq6, AtCOQ6, or AtCOQ6 fused with a mitochondrial targeting sequence (Mt-Signal) (D); and the KH8 (Δcoq8) strain expressing S. pombe coq8 or AtCOQ8 (E). DMQ10, demethoxyubiquinone.
Discussion
Ten coq deletion strains of the fission yeast S. pombe, including six that were reported previously (Uchida, et al., 2000, Saiki, et al., 2003, Miki, et al., 2008), were created. The ten deletion strains were phenotypically indistinguishable; they did not produce CoQ10 (were respiration defective), were sensitive to oxidative stress, produced a large amount of sulfide, required an antioxidant to grow on minimal medium, were sensitive to Cu2+, and did not survive long at the stationary phase. In recent large scale deletion library screening studies, a number of coq deletion strains were sensitive to Cd2+ and doxorubicin, an inhibitor of topoisomerase 2 [40], [41]. As a consequence of the various roles of CoQ, coq deletion strains show pleiotropic phenotypes. CoQ is an essential component of the electron transfer system; therefore, coq deletion strains grew slowly under non-fermentation conditions and failed to grow on medium containing glycerol and ethanol as carbon sources. Since CoQ functions as an antioxidant and couples sulfide oxidation and cysteine metabolism, the S. pombe coq deletion strains were sensitive to H2O2 and produced large amounts of sulfide. CoQ is also required for de novo UMP synthesis, resulting in poor growth of the coq deletion strains on minimal medium [7]. We did not see the growth recovery of CoQ deficient S. pombe cells by supplementation of CoQ10 (Figure S6), whereas supplementation of CoQ6 generally restored the growth of S. cerevisiae coq deletion mutants on non-fermentable carbon source [42]. The slow growth of a coq deficient mutant was partly recused by supplementation of CoQ10 encapsulated by γ–cyclodextrin, but its respiration was not restored [43]. It is not easy to test the effect of CoQ10 supplementation in S. pombe. In S. cerevisiae, the two essential genes, ARH1 and YAH1, are involved in CoQ synthesis through the regulation of Coq6 [26]. Although S. pombe contains orthologs of these genes, it will be difficult to determine their functions in CoQ biosynthesis via deletion analyses because they are essential for growth.
All S. pombe coq deletion strains failed to synthesize CoQ10, intermediate peaks were observed on HPLC traces of lipid extracts from the Δcoq5 and Δcoq7 strains. The peak identified in the Δcoq7 extract was previously determined to be DMQ10 [22], while those identified in the Δcoq5 extract are currently unknown. At least two peaks were detected in the Δcoq5 extract, which may indicate the existence of two pathways originating from the precursors PHB and pABA, as reported in S. cerevisiae [18]; however, additional studies are required to confirm this hypothesis.
The results presented here demonstrate that all of the S. pombe Coq proteins localize to mitochondria, indicating that CoQ biosynthesis occurs in these cellular compartments. These results are consistent with those of a previous study [44] that examined the localization of 4,431 S. pombe proteins, although Coq8 was not included. Coq proteins in S. cerevisiae also localize to mitochondria, where they form a complex [23]. A recent study showed that biosynthesis of CoQ in humans also occurs in the Golgi [45], where one of the CoQ biosynthetic steps, PHB-polyprenyl condensation, is mediated by the enzyme UBIAD1. Because this enzyme is absent in yeasts, it is likely that CoQ is synthesized predominantly in mitochondria in S. cerevisiae and S. pombe.
As mentioned above, HsDPS1/PDSS1 is able to complement an S. pombe Δdps1 mutant, but HsDLP1/PDSS2 is not able to complement an S. pombe Δdlp1 mutant [12]. This suggests that the S. pombe Dps1 protein cannot form a complex with the HsDLP1 protein, even though they share sequence similarity (28% identity; see Table 3). When HsDPS1 and HsDLP1 genes were expressed in a Δdps1 Δdlp1 strain, CoQ10 was predominantly produced, while S pombe naturally produce CoQ10 with a lesser amount of CoQ9 (Fig. 4). This result indicates decaprenyl diphosphate synthase from humans strictly produces 10 isoprene units of prenyl diphosphate, which is consistent with the observation that CoQ10 is predominantly found in human bodies.
Table 3. Amino acid sequence similarity of Coq proteins from S. pombe, S. cerevisiae, humans, and A. thaliana.
| Schizosaccharomyces pombe | SpDps1 (378 aa) | SpDlp1 (294 aa) | SpPpt1 (360 aa) | SpCoq3 (274 aa) | SpCoq4 (272 aa) | SpCoq5 (305 aa) | SpCoq6 (479 aa) | SpCoq7 (216 aa) | SpCoq8 (610 aa) | SpCoq9 (250 aa) | SpCoq10 (164 aa) |
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae | ScCoq1 (473 aa) | — | ScCoq2 (372 aa) | ScCoq3 (312 aa) | ScCoq4 (335 aa) | ScCoq5 (307 aa) | ScCoq6 (479 aa) | ScCoq7 (233 aa) | ScCoq8 (501 aa) | ScCoq9 (260 aa) | ScCoq10 (207 aa) |
| Identity | 37% | — | 48% | 35% | 43% | 53% | 36% | 51% | 50% | 29% | 30% |
| Positive | 53% | — | 65% | 51% | 62% | 69% | 58% | 66% | 69% | 53% | 49% |
| Homo sapiens | HsPDSS1 (415 aa) | HsPDSS2 (399 aa) | HsCOQ2 (371aa) | HsCOQ3 (369 aa) | HsCOQ4 (265 aa) | HsCOQ5 (327 aa) | HsCOQ6 (468 aa) | HsCOQ7 (217 aa) | HsCOQ8/ADCK3 (595 aa) | HsCOQ9 (318 aa) | HsCOQ10A (230 aa) |
| Identity | 45% | 28% | 48% | 38% | 44% | 47% | 34% | 45% | 46% | 32% | 31% |
| Positive | 62% | 49% | 63% | 54% | 64% | 63% | 49% | 64% | 62% | 53% | 47% |
| Arabidopsis thaliana | AtSPS3 (423 aa) | — | AtPPT1 (407 aa) | AtCOQ3 (322 aa) | AtCOQ4 (226 aa) | AtCOQ5 (288 aa) | AtCOQ6 (505 aa) | — | AtCOQ8 (623 aa) | AtCOQ9 (311 aa) | AtCOQ10 (256 aa) |
| Identity | 38% | — | 47% | 40% | 39% | 49% | 29% | — | 39% | 28% | 28% |
| Positive | 60% | — | 61% | 58% | 58% | 62% | 46% | — | 57% | 48% | 49% |
Homologues of all of the S. pombe coq genes exist in humans and homologues of all except coq7 exist in A. thaliana. In most cases, functional complementation of the S. pombe coq deletion strains by human or A. thaliana genes was successful (Figure 10); however, in some cases (HsCOQ3, HsCOQ7 and AtCOQ6), the addition of an N-terminal mitochondrial targeting sequence from the corresponding S. pombe coq gene was required for complementation. One of reasons may be a shortage of targeting sequences in cases of HsCOQ3 and HsCOQ7, as there are longer length transcriptional variants in these genes. The other reason may be incapability of working mitochondrial targeting sequence of humans or A. thaliana genes in S. pombe cells. The sequences of the N-terminal regions of the coq/COQ genes in S. pombe, humans, and A. thaliana are rather diverged, and we were unable to find any apparent rules that govern how the N-terminal sequences affect mitochondrial targeting.
Figure 10. Summary of complementation of S. pombe coq deletion strains by human and A. thaliana genes.
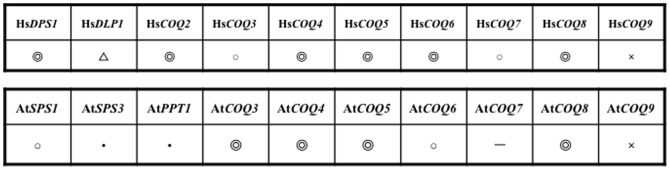
The double open circles indicate genes that complemented the S. pombe deletion mutants. The single open circles indicate genes that complemented the S. pombe deletion mutants after fusion of a mitochondrial targeting sequence. HsDLP1 is only functional in the presence of HsDPS1, so is denoted by a triangle. The “x” symbols indicate genes that failed to complement the S. pombe deletion mutants. A. thaliana does not contain a COQ7 ortholog. Closed circles indicate genes that complemented the corresponding S. cerevisiae mutants but were not tested in S. pombe.
Although some complementation analyses of S. cerevisiae coq deletion strains expressing human genes have been conducted, a comprehensive analysis has not yet been performed. Studies performed to date show that expression of HsCOQ2 [46], HsCOQ3 [21], HsCOQ4 [47], and HsCOQ6 [48] functionally complement their corresponding S. cerevisiae coq mutants. HsCOQ8 (ADCK3) also complements the S. cerevisiae Δcoq8 mutant weakly [49], which is consistent with the results presented here for S. pombe. To our knowledge, functional complementation of S. cerevisiae Δcoq5 and Δcoq7 mutants by human COQ5 or COQ7, respectively, has not yet been tested. AtSPS3, which encodes solanesyl diphosphate synthase, and AtPPT1, which encodes PHB-polyprenyl diphosphate transferase, complement the S. cerevisiae Δcoq1 and Δcoq2 mutants, respectively [9], [13].
HsCOQ9 and AtCOQ9 failed to complement the S. pombe Δcoq9 strain. Similarly, in a previous study, HsCOQ9 failed to complement the S. cerevisiae Δcoq9 mutant [50]. Although its exact function is still unknown, Coq9 is absolutely required for the biosynthesis of CoQ in S. cerevisiae and, as shown here, S. pombe. Genetic disorders of CoQ biosynthesis related to mutation of the HsCOQ9 gene [51] suggest that this enzyme is also involved in CoQ synthesis in humans. However, the function of COQ9 may not be conserved between humans, A. thaliana, and yeast because these Coq9 proteins share only 28–30% amino acid identity (Table 3).
Complementation analyses of plant genes encoding CoQ biosynthetic enzymes are scare. Based on an analysis of the AtPPT1 gene, CoQ appears to be essential for seed formation in A. thaliana [9]. AtSPS1 is functional when expressed in S. pombe [13] but the protein may not be involved in CoQ synthesis; on the other hand, AtSPS3 (At2g34630) is responsible for CoQ synthesis in this species [39]. Since A. thaliana does not contain a COQ7 gene, we tested the ability of the other COQ genes in this species (AtCOQ3, AtCOQ4, AtCOQ5, AtCOQ6, AtCOQ8, and AtCOQ9) to recover CoQ10 production in S. pombe coq deletion strains. With the exception of AtCOQ9, the functions of all other A. thaliana COQ proteins were conserved. In knockdown analyses of Caenorhabditis elegans, the coq7 deletion strain was able to survive for long periods, unlike other coq deletion strains. No apparent Coq9 ortholog was found in C. elegans, which might be relevant to the fact this organism produces rhodoquinone.
In conclusion, this study describes the functional conservation of CoQ biosynthetic genes in humans, plants, and the fission yeast S. pombe. It also demonstrates that the functions of the human COQ genes can be determined by expression in S. pombe deletion mutants. Determining the function of CoQ biosynthetic genes may be useful for understanding genetic disorders caused by human CoQ biosynthetic deficiencies.
Supporting Information
Construction of the S. pombe ppt1, coq4, coq5, coq6, coq8 , and coq9 deletion strains. One step homologous recombination was used to delete the S. pombe coq genes. The coq4 deletion strategy is shown as an example. The coq4-x and coq4-y primers were homologous to the flanking regions of the coq4 and kan resistance genes. The coq4-w and coq4-z primers were homologous to regions located approximately 500 bp downstream and upstream of the coq4 gene. The nb2 and coq4-c primers were used to verify the replacement of coq4 by kan. All other deletion strains were constructed similarly.
(TIFF)
Construction of the plasmids to express S. pombe coq genes. The S. pombe coq genes were inserted into the pREP1 or pREP2 vector under the control of the nmt1 promoter.
(TIFF)
Construction of the plasmids to express S. pombe coq-GFP . To determine the cellular localization of Coq proteins, GFP-fusions were generated by inserting the coq genes into the pSFL272L-GFPS65A vector (used in most cases).
(TIFF)
Construction of the plasmids to express human COQ genes. The human COQ genes were inserted into the pREP1, pREP41, or pREP2 vectors. The promoter region and mitochondrial targeting signal of dlp1, coq3 or coq7 from S. pombe were fused with the HsDLP1, HsCOQ3 or HsCOQ7 gene, respectively.
(TIFF)
Construction of the plasmids to express Arabidopsis COQ genes. The plasmids containing the A. thaliana COQ genes were constructed in the same manner as those expressing the human COQ3 gene. The S. pombe coq6 or coq9 mitochondrial targeting sequence was fused with the AtCOQ6 or AtCOQ9 gene, respectively.
(TIFF)
Growth profile of a dps1 deletion strain with supplementation of CoQ10. Cell growth of the Δdps1 strain (LJ1030) in YES or EMM suppemented with 10 µM CoQ10 (final concentration) dissolved in ethanol was monitored by the cell counter (Sysmex Corp.) over 72 h.
(TIFF)
Primers used in this study. Primers used for construction of various plasmids and deletion strains are listed.
(DOCX)
Acknowledgments
We thank C. Clarke for providing the human cDNAs. We also thank A. Yamamoto, T. Murao, Y. Hirakawa, A. Nagata, R. Miki, M. Yoshida, and M. Fujii for technical assistances.
Funding Statement
This work was supported by a grant-in-aid from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan (#24380056) and by Japanese Coenzyme Q association (http://www.coenzymeq-jp.com/index.html). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1. Kawamukai M (2009) Biosynthesis and bioproduction of coenzyme Q10 by yeasts and other organisms. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 53: 217–226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Tran UC, Clarke CF (2007) Endogenous synthesis of coenzyme Q in eukaryotes. Mitochondrion 7 Suppl 1: S62–S71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Turunen M, Olsson J, Dallner G (2004) Metabolism and function of coenzyme Q. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1660: 171–199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Bentinger M, Brismar K, Dallner G (2007) The antioxidant role of coenzyme Q. Mitochondrion. 7 Suppl: S41–50 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Inaba K (2009) Disulfide bond formation system in Escherichia coli . J Biochem (Tokyo) 146: 591–597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Zhang M, Wakitani S, Hayashi K, Miki R, Kawamukai M (2008) High production of sulfide in coenzyme Q deficient fission yeast. Biofactors 32: 91–98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Matsuo Y, Nishino K, Mizuno K, Akihiro T, Toda T, et al. (2013) Polypeptone induces dramatic cell lysis in ura4 deletion mutants of fission yeast. PLoS One 8: e59887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Lopez-Martin JM, Salviati L, Trevisson E, Montini G, Dimauro S, et al. (2007) Missense mutation of the COQ2 gene causes defects of bioenergetics and de novo pyrimidine synthesis. Hum Mol Genet 16: 1091–1097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Okada K, Ohara K, Yazaki K, Nozaki K, Uchida N, et al. (2004) The AtPPT1 gene encoding 4-hydroxybenzoate polyprenyl diphosphate transferase in ubiquinone biosynthesis is required for embryo development in Arabidopsis thaliana . Plant Mol Biol 55: 567–577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Suzuki K, Okada K, Kamiya Y, Zhu X, Tanaka K, et al. (1997) Analysis of the decaprenyl diphosphate synthase (dps) gene in fission yeast suggests a role of ubiquinone as an antioxidant. J Biochem (Tokyo) 121: 496–505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Saiki R, Nagata A, Uchida N, Kainou T, Matsuda H, et al. (2003) Fission yeast decaprenyl diphosphate synthase consists of Dps1 and the newly characterized Dlp1 protein in a novel heterotetrameric structure. Eur J Biochem 270: 4113–4121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Saiki R, Nagata A, Kainou T, Matsuda H, Kawamukai M (2005) Characterization of solanesyl and decaprenyl diphosphate synthases in mice and humans. FEBS J 272: 5606–5622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Jun L, Saiki R, Tatsumi K, Nakagawa T, Kawamukai M (2004) Identification and subcellular localization of two solanesyl diphosphate synthases from Arabidopsis thaliana . Plant Cell Physiol 45: 1882–1888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Zhang M, Luo J, Ogiyama Y, Saiki R, Kawamukai M (2008) Heteromer formation of a long-chain prenyl diphosphate synthase from fission yeast Dps1 and budding yeast Coq1. FEBS J 275: 3653–3668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Okada K, Kainou T, Matsuda H, Kawamukai M (1998) Biological significance of the side chain length of ubiquinone in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEBS Lett 431: 241–244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Kainou T, Okada K, Suzuki K, Nakagawa T, Matsuda H, et al. (2001) Dimer formation of octaprenyl-diphosphate synthase (IspB) is essential for chain length determination of ubiquinone. J Biol Chem 276: 7876–7883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Kawamukai M (2002) Biosynthesis, bioproduction and novel roles of ubiquinone. J Biosci Bioeng 94: 511–517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Pierrel F, Hamelin O, Douki T, Kieffer-Jaquinod S, Muhlenhoff U, et al. (2010) Involvement of mitochondrial ferredoxin and para-aminobenzoic acid in yeast coenzyme Q biosynthesis. Chem Biol 17: 449–459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Ashby MN, Kutsunai SY, Ackerman S, Tzagoloff A, Edwards PA (1992) COQ2 is a candidate for the structural gene encoding para-hydroxybenzoate:polyprenyltransferase. J Biol Chem 267: 4128–4136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Uchida N, Suzuki K, Saiki R, Kainou T, Tanaka K, et al. (2000) Phenotypes of fission yeast defective in ubiquinone production due to disruption of the gene for p-hydroxybenzoate polyprenyl diphosphate transferase. J Bacteriol 182: 6933–6939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Jonassen T, Clarke CF (2000) Isolation and functional expression of human COQ3, a gene encoding a methyltransferase required for ubiquinone biosynthesis. J Biol Chem 275: 12381–12387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Miki R, Saiki R, Ozoe Y, Kawamukai M (2008) Comparison of a coq7 deletion mutant with other respiration-defective mutants in fission yeast. FEBS J 275: 5309–5324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Marbois B, Gin P, Gulmezian M, Clarke CF (2009) The yeast Coq4 polypeptide organizes a mitochondrial protein complex essential for coenzyme Q biosynthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1791: 69–75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Barkovich RJ, Shtanko A, Shepherd JA, Lee PT, Myles DC, et al. (1997) Characterization of the COQ5 gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Evidence for a C-methlytransferase in ubiquinone biosynthesis. J Biol Chem 272: 9182–9188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Gin P, Hsu AY, Rothman SC, Jonassen T, Lee PT, et al. (2003) The Saccharomyces cerevisiae COQ6 gene encodes a mitochondrial flavin-dependent monooxygenase required for coenzyme Q biosynthesis. J Biol Chem 278: 25308–25316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Ozeir M, Muhlenhoff U, Webert H, Lill R, Fontecave M, et al. (2011) Coenzyme Q biosynthesis: Coq6 is required for the C5-hydroxylation reaction and substrate analogs rescue Coq6 deficiency. Chem Biol 18: 1134–1142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Saiki R, Ogiyama Y, Kainou T, Nishi T, Matsuda H, et al. (2003) Pleiotropic phenotypes of fission yeast defective in ubiquinone-10 production. A study from the abc1Sp (coq8Sp) mutant. Biofactors 18: 229–235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Marbois BN, Clarke CF (1996) The COQ7 gene encodes a protein in Saccharomyces cerevisiae necessary for ubiquinone biosynthesis. J Biol Chem 271: 2995–3004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Johnson A, Gin P, Marbois BN, Hsieh EJ, Wu M, et al. (2005) COQ9, a new gene required for the biosynthesis of coenzyme Q in Saccharomyces cerevisiae . J Biol Chem 280: 31397–31404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Barros MH, Johnson A, Gin P, Marbois BN, Clarke CF, et al. (2005) The Saccharomyces cerevisiae COQ10 gene encodes a START domain protein required for function of coenzyme Q in respiration. J Biol Chem 280: 42627–42635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Cui T-Z, Kawamukai M (2009) Coq10, a mitochondrial coenzyme Q binding protein, is required for proper respiration in Schizosaccharomyces pombe . FEBS J 276: 748–759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Allan CM, Hill S, Morvaridi S, Saiki R, Johnson JS, et al. (2013) A conserved START domain coenzyme Q-binding polypeptide is required for efficient Q biosynthesis, respiratory electron transport, and antioxidant function in Saccharomyces cerevisiae . Biochim Biophys Acta 1831: 776–791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Quinzii CM, Hirano M (2010) Coenzyme Q and mitochondrial disease. Dev Disabil Res Rev 16: 183–188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Moreno S, Klar A, Nurse P (1991) Molecular genetic analysis of fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe . Methods Enzymol 194: 795–823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a lablatory manual, 2nd ed. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY. [Google Scholar]
- 36. Bähler J, Wu JQ, Longtine MS, Shah NG, McKenzie A 3rd, et al. (1998) Heterologous modules for efficient and versatile PCR-based gene targeting in Schizosaccharomyces pombe . Yeast 14: 943–951. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Maundrell K (1990) nmt1 of fission yeast: a highly transcribed gene completely repressed by thiamine. J Biol Chem 265: 10857–10864. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Suzuki K, Okada K, Kamiya Y, Zhu XF, Nakagawa T, et al. (1997) Analysis of the decaprenyl diphosphate synthase (dps) gene in fission yeast suggests a role of ubiquinone as an antioxidant. J Biochem 121: 496–505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Ducluzeau AL, Wamboldt Y, Elowsky CG, Mackenzie SA, Schuurink RC, et al. (2012) Gene network reconstruction identifies the authentic trans-prenyl diphosphate synthase that makes the solanesyl moiety of ubiquinone-9 in Arabidopsis. Plant J 69: 366–375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Kennedy PJ, Vashisht AA, Hoe KL, Kim DU, Park HO, et al. (2008) A genome-wide screen of genes involved in cadmium tolerance in Schizosaccharomyces pombe . Toxicol Sci 106: 124–139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Tay Z, Eng RJ, Sajiki K, Lim KK, Tang MY, et al. (2013) Cellular robustness conferred by genetic crosstalk underlies resistance against chemotherapeutic drug doxorubicin in fission yeast. PLoS One 8: e55041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Do TQ, Hsu AY, Jonassen T, Lee PT, Clarke CF (2001) A defect in coenzyme Q biosynthesis is responsible for the respiratory deficiency in Saccharomyces cerevisiae abc1 mutants. J Biol Chem 276: 18161–18168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Nishida T, Kaino T, Ikarashi R, Nakata D, Terao K, et al. (2013) The effect of coenzyme Q10 included by gamma-cyclodextrin on the growth of fission yeast studied by microscope Raman spectroscopy. Journal of Molecular Structure 1048: 375–381. [Google Scholar]
- 44. Matsuyama A, Arai R, Yashiroda Y, Shirai A, Kamata A, et al. (2006) ORFeome cloning and global analysis of protein localization in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe . Nat Biotechnol 24: 841–847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Mugoni V, Postel R, Catanzaro V, De Luca E, Turco E, et al. (2013) Ubiad1 is an antioxidant enzyme that regulates eNOS activity by CoQ10 synthesis. Cell 152: 504–518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Forsgren M, Attersand A, Lake S, Grunler J, Swiezewska E, et al. (2004) Isolation and functional expression of human COQ2, a gene encoding a polyprenyl transferase involved in the synthesis of CoQ. Biochem J 382: 519–526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Casarin A, Jimenez-Ortega JC, Trevisson E, Pertegato V, Doimo M, et al. (2008) Functional characterization of human COQ4, a gene required for Coenzyme Q10 biosynthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 372: 35–39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Heeringa SF, Chernin G, Chaki M, Zhou W, Sloan AJ, et al. (2011) COQ6 mutations in human patients produce nephrotic syndrome with sensorineural deafness. J Clin Invest 121: 2013–2024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Xie LX, Hsieh EJ, Watanabe S, Allan CM, Chen JY, et al. (2011) Expression of the human atypical kinase ADCK3 rescues coenzyme Q biosynthesis and phosphorylation of Coq polypeptides in yeast coq8 mutants. Biochim Biophys Acta 1811: 348–360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Duncan AJ, Bitner-Glindzicz M, Meunier B, Costello H, Hargreaves IP, et al. (2009) A nonsense mutation in COQ9 causes autosomal-recessive neonatal-onset primary coenzyme Q10 deficiency: a potentially treatable form of mitochondrial disease. Am J Hum Genet 84: 558–566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Garcia-Corzo L, Luna-Sanchez M, Doerrier C, Garcia JA, Guaras A, et al. (2013) Dysfunctional Coq9 protein causes predominant encephalomyopathy associated with CoQ deficiency. Hum Mol Genet 22: 1233–1248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Construction of the S. pombe ppt1, coq4, coq5, coq6, coq8 , and coq9 deletion strains. One step homologous recombination was used to delete the S. pombe coq genes. The coq4 deletion strategy is shown as an example. The coq4-x and coq4-y primers were homologous to the flanking regions of the coq4 and kan resistance genes. The coq4-w and coq4-z primers were homologous to regions located approximately 500 bp downstream and upstream of the coq4 gene. The nb2 and coq4-c primers were used to verify the replacement of coq4 by kan. All other deletion strains were constructed similarly.
(TIFF)
Construction of the plasmids to express S. pombe coq genes. The S. pombe coq genes were inserted into the pREP1 or pREP2 vector under the control of the nmt1 promoter.
(TIFF)
Construction of the plasmids to express S. pombe coq-GFP . To determine the cellular localization of Coq proteins, GFP-fusions were generated by inserting the coq genes into the pSFL272L-GFPS65A vector (used in most cases).
(TIFF)
Construction of the plasmids to express human COQ genes. The human COQ genes were inserted into the pREP1, pREP41, or pREP2 vectors. The promoter region and mitochondrial targeting signal of dlp1, coq3 or coq7 from S. pombe were fused with the HsDLP1, HsCOQ3 or HsCOQ7 gene, respectively.
(TIFF)
Construction of the plasmids to express Arabidopsis COQ genes. The plasmids containing the A. thaliana COQ genes were constructed in the same manner as those expressing the human COQ3 gene. The S. pombe coq6 or coq9 mitochondrial targeting sequence was fused with the AtCOQ6 or AtCOQ9 gene, respectively.
(TIFF)
Growth profile of a dps1 deletion strain with supplementation of CoQ10. Cell growth of the Δdps1 strain (LJ1030) in YES or EMM suppemented with 10 µM CoQ10 (final concentration) dissolved in ethanol was monitored by the cell counter (Sysmex Corp.) over 72 h.
(TIFF)
Primers used in this study. Primers used for construction of various plasmids and deletion strains are listed.
(DOCX)