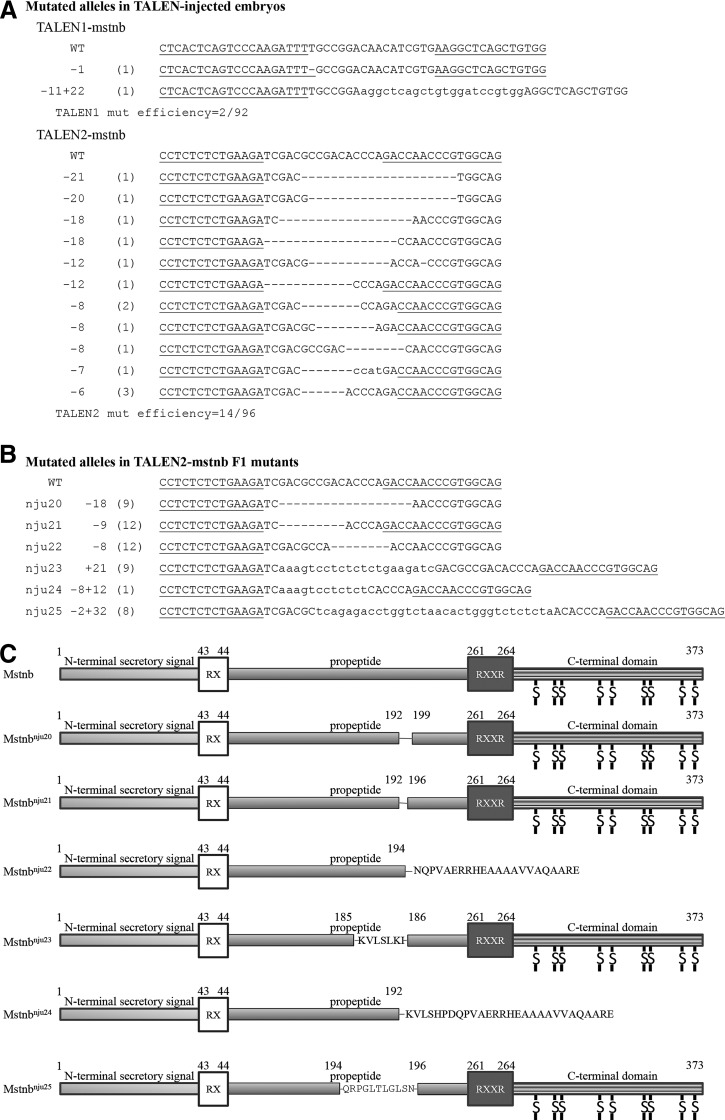
FIG. 6.
Generation of mstnb knockout yellow catfish (T. fulvidraco) using engineered TALENs. (A) TALEN1-mstnb and TALEN2-mstnb induced various mutations in injected embryos. Number in the leftmost of the panels shows the number of nucleotides deleted (−) or inserted (+) in the mutated mstnb gene. Number in the bracket shows the frequency of the mutated molecules. (B) Six mutated alleles were found in mutants of F1 yellow catfish, including mstnbnju20, mstnbnju21, mstnbnju22, mstnbnju23, mstnbnju24, and mstnbnju25. Partial sequence of each allele is shown. Numbers following the allele names show the number of nucleotides deleted (−) or inserted (+) in the mutated mstnb. Number in the bracket shows the number of mutants carrying the mutated alleles. (C) Schematic diagram shows that six mutated proteins would be produced from the six different strains of yellow catfish carrying different mutated mstnb alleles. mstnbnju22 and mstnbnju24 are frame shift mutations and encode truncated proteins lacking the bioactive C-terminal domain. Single lines in the propeptide domain show loss of amino acids. Amino acid sequences in the propeptide domain show inserted amino acid fragments. Amino acid sequences following incomplete propeptide domain are due to frame shift reading.