Figure 3.
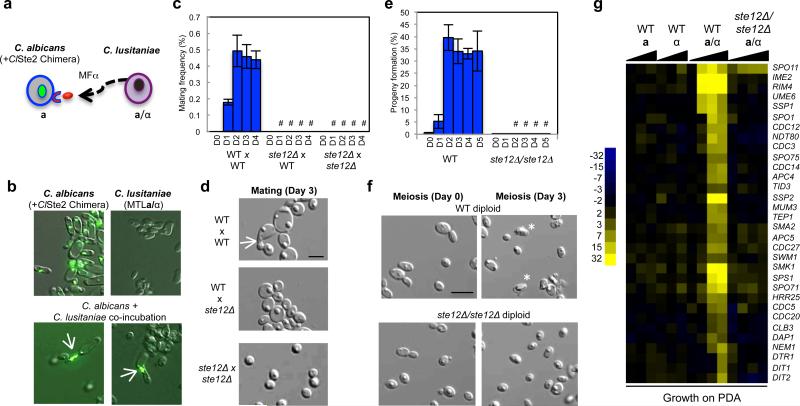
STE12 is essential for both mating and meiosis in C. lusitaniae. a, Schematic of assay to detect pheromone secretion from C. lusitaniae cells. C. lusitaniae a/α cells were co-incubated with GFP-labeled C. albicans a cells expressing the C. lusitaniae α pheromone receptor. b, C. albicans cells generate polarized mating projections (arrows) in response to C. lusitaniae pheromone, demonstrating that C. lusitaniae cells actively secrete pheromone during meiosis, n=2. c, Deletion of STE12 abolishes mating in C. lusitaniae (4 day time course, D1-D4). “#” represents P < 0.05, Kruskal Wallis, n=3. d, Mating occurs between wildtype C. lusitaniae cells (arrow) but not between ste12Δ mutant cells, n=3. e, Loss of STE12 inhibited the formation of meiotic haploid progeny (4 day time course, D1-D4). “#” represents P < 0.05, unequal variance t test, n=3. f, Absence of meiotic spores in C. lusitaniae cells lacking STE12, n=5. g, Gene expression changes when C. lusitaniae haploid, diploid, or ste12Δ/ste12Δ strains are incubated on PDA medium. Deletion of STE12 abolished most meiosis-specific gene expression changes. Where appropriate, scale bars, 5 μm; data represented as mean +/- s.em.