Abstract
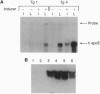
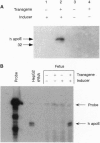
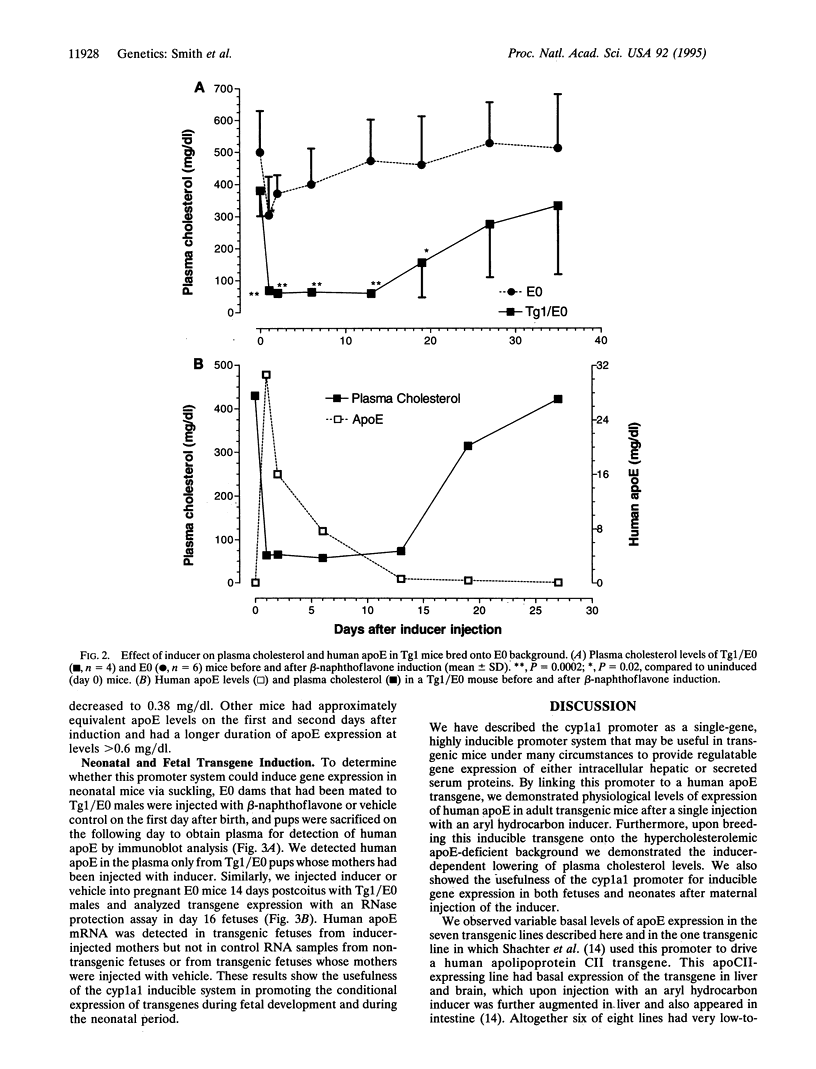
Transgenic and gene knockout techniques allow for in vivo study of the consequences of adding or subtracting specific genes. However, in some instances, such as the study of lethal mutations or of the physiological consequences of changing gene expression, turning on and off an introduced gene at will would be advantageous. We have used cytochrome p450 1A1 promoter to drive expression of the human apolipoprotein E (apoE) gene in transgenic mice. In six independent lines, robust expression of the transgene depended upon injection of the inducer beta-naphthoflavone, whereas the seventh line had high basal expression that was augmented further by the inducer. The low level of basal expression in an inducer-dependent line was confirmed upon breeding the transgene onto the hypercholesterolemic apoE-deficient background. In the basal state transgene expression was physiologically insignificant, as these mice were as hypercholesterolemic as their nontransgenic apoE-deficient littermates. When injected with the inducer, plasma cholesterol levels of the transgenic mice decreased dramatically as apoE expression was induced to yield greater than physiological levels in plasma. The inducer could pass transplacentally from an injected mother to her fetuses with concomitant induction of fetal transgene mRNA. Inducer could also pass via breast milk from an injected mother to her suckling neonatal pups, giving rise to the induction of human apoE in neonate plasma. These finding suggest a strategy to temporarily ameliorate genetic deficiencies that would otherwise lead to fetal or neonatal lethality.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackland-Berglund C. E., Leib D. A. Efficacy of tetracycline-controlled gene expression is influenced by cell type. Biotechniques. 1995 Feb;18(2):196–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das H. K., McPherson J., Bruns G. A., Karathanasis S. K., Breslow J. L. Isolation, characterization, and mapping to chromosome 19 of the human apolipoprotein E gene. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):6240–6247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emi M., Wu L. L., Robertson M. A., Myers R. L., Hegele R. A., Williams R. R., White R., Lalouel J. M. Genotyping and sequence analysis of apolipoprotein E isoforms. Genomics. 1988 Nov;3(4):373–379. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(88)90130-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein-Baak R., Lin Y., Bradshaw V., Cohn M. Inducible transformation of cells from transgenic mice expressing SV40 under lac operon control. Cell Growth Differ. 1992 Feb;3(2):127–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Salguero P., Pineau T., Hilbert D. M., McPhail T., Lee S. S., Kimura S., Nebert D. W., Rudikoff S., Ward J. M., Gonzalez F. J. Immune system impairment and hepatic fibrosis in mice lacking the dioxin-binding Ah receptor. Science. 1995 May 5;268(5211):722–726. doi: 10.1126/science.7732381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furth P. A., St Onge L., Böger H., Gruss P., Gossen M., Kistner A., Bujard H., Hennighausen L. Temporal control of gene expression in transgenic mice by a tetracycline-responsive promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Sep 27;91(20):9302–9306. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.20.9302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossen M., Bujard H. Tight control of gene expression in mammalian cells by tetracycline-responsive promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5547–5551. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossen M., Freundlieb S., Bender G., Müller G., Hillen W., Bujard H. Transcriptional activation by tetracyclines in mammalian cells. Science. 1995 Jun 23;268(5218):1766–1769. doi: 10.1126/science.7792603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hod Y. A simplified ribonuclease protection assay. Biotechniques. 1992 Dec;13(6):852–854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaiswal A. K., Gonzalez F. J., Nebert D. W. Human P1-450 gene sequence and correlation of mRNA with genetic differences in benzo[a]pyrene metabolism. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 25;13(12):4503–4520. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.12.4503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. N., Jones P. G., Ibarguen H., Caskey C. T., Craigen W. J. Induction of the Cyp1a-1 dioxin-responsive enhancer in transgenic mice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 11;19(23):6547–6551. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.23.6547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieger M., Herz J. Structures and functions of multiligand lipoprotein receptors: macrophage scavenger receptors and LDL receptor-related protein (LRP). Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:601–637. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.63.070194.003125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linton M. F., Atkinson J. B., Fazio S. Prevention of atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice by bone marrow transplantation. Science. 1995 Feb 17;267(5200):1034–1037. doi: 10.1126/science.7863332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W. Apolipoprotein E: cholesterol transport protein with expanding role in cell biology. Science. 1988 Apr 29;240(4852):622–630. doi: 10.1126/science.3283935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean A. E., Day P. A. The effect of diet on the toxicity of paracetamol and the safety of paracetamol-methionine mixtures. Biochem Pharmacol. 1975 Jan 1;24(1):37–42. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(75)90310-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima Y., Plump A. S., Raines E. W., Breslow J. L., Ross R. ApoE-deficient mice develop lesions of all phases of atherosclerosis throughout the arterial tree. Arterioscler Thromb. 1994 Jan;14(1):133–140. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.14.1.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W., Jones J. E. Regulation of the mammalian cytochrome P1-450 (CYP1A1) gene. Int J Biochem. 1989;21(3):243–252. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(89)90182-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebert D. W. The Ah locus: genetic differences in toxicity, cancer, mutation, and birth defects. Crit Rev Toxicol. 1989;20(3):153–174. doi: 10.3109/10408448909017908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omiecinski C. J., Redlich C. A., Costa P. Induction and developmental expression of cytochrome P450IA1 messenger RNA in rat and human tissues: detection by the polymerase chain reaction. Cancer Res. 1990 Jul 15;50(14):4315–4321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Norstedt G., Gelinas R. E., Hammer R. E., Brinster R. L. Metallothionein-human GH fusion genes stimulate growth of mice. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):809–814. doi: 10.1126/science.6356363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plump A. S., Smith J. D., Hayek T., Aalto-Setälä K., Walsh A., Verstuyft J. G., Rubin E. M., Breslow J. L. Severe hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice created by homologous recombination in ES cells. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):343–353. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90362-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shachter N. S., Hayek T., Leff T., Smith J. D., Rosenberg D. W., Walsh A., Ramakrishnan R., Goldberg I. J., Ginsberg H. N., Breslow J. L. Overexpression of apolipoprotein CII causes hypertriglyceridemia in transgenic mice. J Clin Invest. 1994 Apr;93(4):1683–1690. doi: 10.1172/JCI117151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shockett P., Difilippantonio M., Hellman N., Schatz D. G. A modified tetracycline-regulated system provides autoregulatory, inducible gene expression in cultured cells and transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jul 3;92(14):6522–6526. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.14.6522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit M., de Knijff P., Rosseneu M., Bury J., Klasen E., Frants R., Havekes L. Apolipoprotein E polymorphism in The Netherlands and its effect on plasma lipid and apolipoprotein levels. Hum Genet. 1988 Nov;80(3):287–292. doi: 10.1007/BF01790099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. D., Plump A. S., Hayek T., Walsh A., Breslow J. L. Accumulation of human apolipoprotein E in the plasma of transgenic mice. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):14709–14712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukamoto M., Ochiya T., Yoshida S., Sugimura T., Terada M. Gene transfer and expression in progeny after intravenous DNA injection into pregnant mice. Nat Genet. 1995 Mar;9(3):243–248. doi: 10.1038/ng0395-243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh A., Ito Y., Breslow J. L. High levels of human apolipoprotein A-I in transgenic mice result in increased plasma levels of small high density lipoprotein (HDL) particles comparable to human HDL3. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6488–6494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., O'Malley B. W., Jr, Tsai S. Y., O'Malley B. W. A regulatory system for use in gene transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 16;91(17):8180–8184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.17.8180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang S. H., Reddick R. L., Piedrahita J. A., Maeda N. Spontaneous hypercholesterolemia and arterial lesions in mice lacking apolipoprotein E. Science. 1992 Oct 16;258(5081):468–471. doi: 10.1126/science.1411543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Ree J. H., van den Broek W. J., Dahlmans V. E., Groot P. H., Vidgeon-Hart M., Frants R. R., Wieringa B., Havekes L. M., Hofker M. H. Diet-induced hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis in heterozygous apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Atherosclerosis. 1994 Nov;111(1):25–37. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(94)90188-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]