Abstract
Biologists require genetic as well as molecular tools to decipher genomic information and ultimately to understand gene function. The Berkeley Drosophila Genome Project is addressing these needs with a massive gene disruption project that uses individual, genetically engineered P transposable elements to target open reading frames throughout the Drosophila genome. DNA flanking the insertions is sequenced, thereby placing an extensive series of genetic markers on the physical genomic map and associating insertions with specific open reading frames and genes. Insertions from the collection now lie within or near most Drosophila genes, greatly reducing the time required to identify new mutations and analyze gene functions. Information revealed from these studies about P element site specificity is being used to target the remaining open reading frames.
Full text
PDF

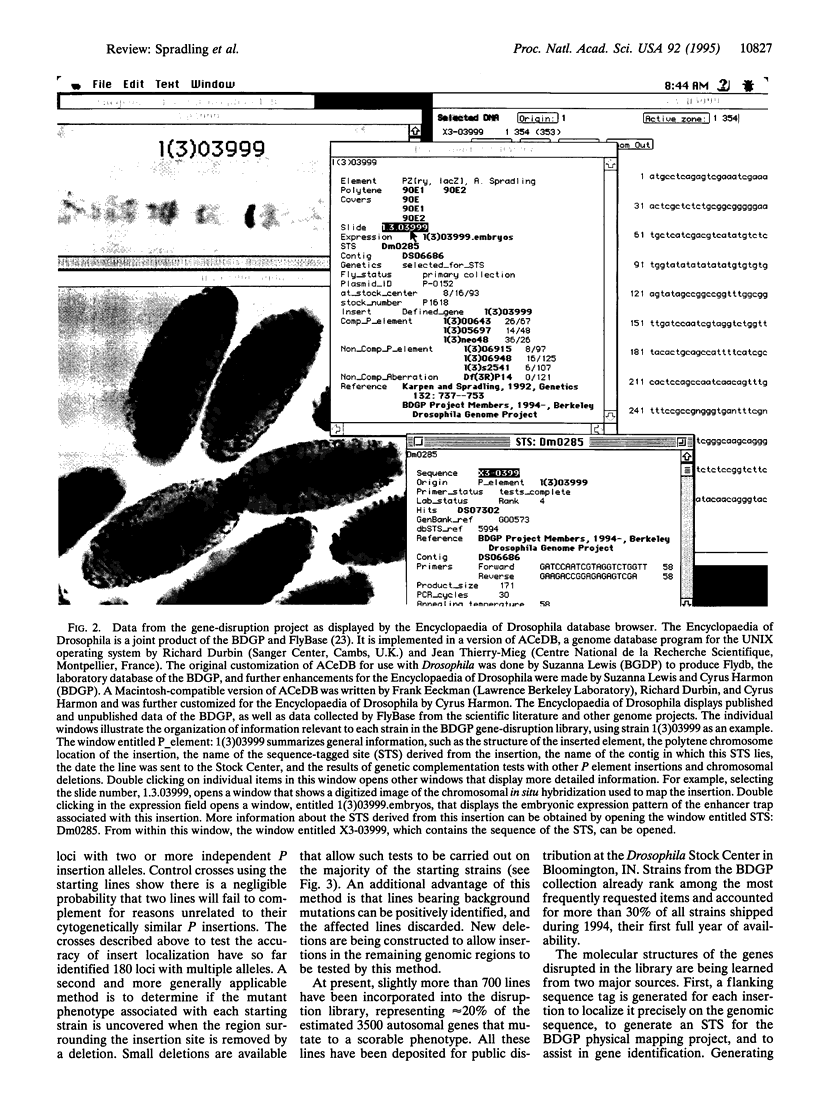



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashburner M., Thompson P., Roote J., Lasko P. F., Grau Y., el Messal M., Roth S., Simpson P. The genetics of a small autosomal region of Drosophila melanogaster containing the structural gene for alcohol dehydrogenase. VII. Characterization of the region around the snail and cactus loci. Genetics. 1990 Nov;126(3):679–694. doi: 10.1093/genetics/126.3.679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bier E., Vaessin H., Shepherd S., Lee K., McCall K., Barbel S., Ackerman L., Carretto R., Uemura T., Grell E. Searching for pattern and mutation in the Drosophila genome with a P-lacZ vector. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1273–1287. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bingham P. M., Levis R., Rubin G. M. Cloning of DNA sequences from the white locus of D. melanogaster by a novel and general method. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):693–704. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90176-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossy B., Hall L. M., Spierer P. Genetic activity along 315 kb of the Drosophila chromosome. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2537–2541. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02169.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand A. H., Perrimon N. Targeted gene expression as a means of altering cell fates and generating dominant phenotypes. Development. 1993 Jun;118(2):401–415. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.2.401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Z., Price B. D., Bockheim S., Boedigheimer M. J., Smith R., Laughon A. Molecular and genetic characterization of the Drosophila tartan gene. Dev Biol. 1993 Dec;160(2):315–332. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1993.1310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooley L., Kelley R., Spradling A. Insertional mutagenesis of the Drosophila genome with single P elements. Science. 1988 Mar 4;239(4844):1121–1128. doi: 10.1126/science.2830671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutforth T., Rubin G. M. Mutations in Hsp83 and cdc37 impair signaling by the sevenless receptor tyrosine kinase in Drosophila. Cell. 1994 Jul 1;77(7):1027–1036. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90442-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dujon B., Alexandraki D., André B., Ansorge W., Baladron V., Ballesta J. P., Banrevi A., Bolle P. A., Bolotin-Fukuhara M., Bossier P. Complete DNA sequence of yeast chromosome XI. Nature. 1994 Jun 2;369(6479):371–378. doi: 10.1038/369371a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engels W. R. A trans-acting product needed for P factor transposition in Drosophila. Science. 1984 Dec 7;226(4679):1194–1196. doi: 10.1126/science.6095450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franz G., Loukeris T. G., Dialektaki G., Thompson C. R., Savakis C. Mobile Minos elements from Drosophila hydei encode a two-exon transposase with similarity to the paired DNA-binding domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 24;91(11):4746–4750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.11.4746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaul U., Mardon G., Rubin G. M. A putative Ras GTPase activating protein acts as a negative regulator of signaling by the Sevenless receptor tyrosine kinase. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1007–1019. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90073-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golic K. G., Lindquist S. The FLP recombinase of yeast catalyzes site-specific recombination in the Drosophila genome. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):499–509. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90033-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandel E., Abel T. Neuropeptides, adenylyl cyclase, and memory storage. Science. 1995 May 12;268(5212):825–826. doi: 10.1126/science.7754367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpen G. H., Spradling A. C. Analysis of subtelomeric heterochromatin in the Drosophila minichromosome Dp1187 by single P element insertional mutagenesis. Genetics. 1992 Nov;132(3):737–753. doi: 10.1093/genetics/132.3.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley M. R., Kidd S., Berg R. L., Young M. W. Restriction of P-element insertions at the Notch locus of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1545–1548. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchner J., Connolly C. M., Sandmeyer S. B. Requirement of RNA polymerase III transcription factors for in vitro position-specific integration of a retroviruslike element. Science. 1995 Mar 10;267(5203):1488–1491. doi: 10.1126/science.7878467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N., Roth J., Botstein D. Genetic engineering in vivo using translocatable drug-resistance elements. New methods in bacterial genetics. J Mol Biol. 1977 Oct 15;116(1):125–159. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90123-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konopka R. J., Benzer S. Clock mutants of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2112–2116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozlova T. u., Semeshin V. F., Tretyakova I. V., Kokoza E. B., Pirrotta V., Grafodatskaya V. E., Belyaeva E. S., Zhimulev I. F. Molecular and cytogenetical characterization of the 10A1-2 band and adjoining region in the Drosophila melanogaster polytene X chromosome. Genetics. 1994 Mar;136(3):1063–1073. doi: 10.1093/genetics/136.3.1063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krumlauf R. Evolution of the vertebrate Hox homeobox genes. Bioessays. 1992 Apr;14(4):245–252. doi: 10.1002/bies.950140408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebman S. W., Newnam G. A ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme, RAD6, affects the distribution of Ty1 retrotransposon integration positions. Genetics. 1993 Mar;133(3):499–508. doi: 10.1093/genetics/133.3.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin C. H., Mayeda C. A., Davis C. A., Ericsson C. L., Knafels J. D., Mathog D. R., Celniker S. E., Lewis E. B., Palazzolo M. J. Complete sequence of the bithorax complex of Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Aug 29;92(18):8398–8402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.18.8398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Kane C. J., Gehring W. J. Detection in situ of genomic regulatory elements in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9123–9127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T., Bernstein A. Receptor tyrosine kinases: genetic evidence for their role in Drosophila and mouse development. Trends Genet. 1990 Nov;6(11):350–356. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90276-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M., Spradling A. C. Genetic transformation of Drosophila with transposable element vectors. Science. 1982 Oct 22;218(4570):348–353. doi: 10.1126/science.6289436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandmeyer S. B., Hansen L. J., Chalker D. L. Integration specificity of retrotransposons and retroviruses. Annu Rev Genet. 1990;24:491–518. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.24.120190.002423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D., Wohlgemuth J., Calvi B. R., Franklin I., Gelbart W. M. hobo enhancer trapping mutagenesis in Drosophila reveals an insertion specificity different from P elements. Genetics. 1993 Dec;135(4):1063–1076. doi: 10.1093/genetics/135.4.1063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spradling A. C., Rubin G. M. Transposition of cloned P elements into Drosophila germ line chromosomes. Science. 1982 Oct 22;218(4570):341–347. doi: 10.1126/science.6289435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steller H., Pirrotta V. A transposable P vector that confers selectable G418 resistance to Drosophila larvae. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):167–171. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02332.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sulston J., Du Z., Thomas K., Wilson R., Hillier L., Staden R., Halloran N., Green P., Thierry-Mieg J., Qiu L. The C. elegans genome sequencing project: a beginning. Nature. 1992 Mar 5;356(6364):37–41. doi: 10.1038/356037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tower J., Karpen G. H., Craig N., Spradling A. C. Preferential transposition of Drosophila P elements to nearby chromosomal sites. Genetics. 1993 Feb;133(2):347–359. doi: 10.1093/genetics/133.2.347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsubota S., Ashburner M., Schedl P. P-element-induced control mutations at the r gene of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2567–2574. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Török T., Tick G., Alvarado M., Kiss I. P-lacW insertional mutagenesis on the second chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster: isolation of lethals with different overgrowth phenotypes. Genetics. 1993 Sep;135(1):71–80. doi: 10.1093/genetics/135.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson K. L., Justice R. W., Bryant P. J. Drosophila in cancer research: the first fifty tumor suppressor genes. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1994;18:19–33. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1994.supplement_18.4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]