Abstract
The mouse is the best model system for the study of mammalian genetics and physiology. Because of the feasibility and importance of studying genetic crosses, the mouse genetic map has received tremendous attention in recent years. It currently contains over 14,000 genetically mapped markers, including 700 mutant loci, 3500 genes, and 6500 simple sequence length polymorphisms (SSLPs). The mutant loci and genes allow insights and correlations concerning physiology and development. The SSLPs provide highly polymorphic anchor points that allow inheritance to be traced in any cross and provide a scaffold for assembling physical maps. Adequate physical mapping resources--notably large-insert yeast artificial chromosome (YAC) libraries--are available to support positional cloning projects based on the genetic map, but a comprehensive physical map is still a few years away. Large-scale sequencing efforts have not yet begun in mouse, but comparative sequence analysis between mouse and human is likely to provide tremendous information about gene structure and regulation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aitman T. J., Hearne C. M., McAleer M. A., Todd J. A. Mononucleotide repeats are an abundant source of length variants in mouse genomic DNA. Mamm Genome. 1991;1(4):206–210. doi: 10.1007/BF00352326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arratia R., Lander E. S., Tavaré S., Waterman M. S. Genomic mapping by anchoring random clones: a mathematical analysis. Genomics. 1991 Dec;11(4):806–827. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90004-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avner P., Amar L., Dandolo L., Guénet J. L. Genetic analysis of the mouse using interspecific crosses. Trends Genet. 1988 Jan;4(1):18–23. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90123-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beier D. R. Single-strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP) analysis as a tool for genetic mapping. Mamm Genome. 1993 Nov;4(11):627–631. doi: 10.1007/BF00360898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berrettini W. H., Ferraro T. N., Alexander R. C., Buchberg A. M., Vogel W. H. Quantitative trait loci mapping of three loci controlling morphine preference using inbred mouse strains. Nat Genet. 1994 May;7(1):54–58. doi: 10.1038/ng0594-54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonhomme F., Benmehdi F., Britton-Davidian J., Martin S. Analyse génétique de croisements interspécifiques Mus musculus L. x Mus spretus Lataste: liaison de Adh-1 avec Amy-1 sur le chromosome 3 et de Es-14 avec Mod-1 sur le chromosome 9. C R Seances Acad Sci D. 1979 Oct 1;289(6):545–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botstein D., White R. L., Skolnick M., Davis R. W. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet. 1980 May;32(3):314–331. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brannan C. I., Gilbert D. J., Ceci J. D., Matsuda Y., Chapman V. M., Mercer J. A., Eisen H., Johnston L. A., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. An interspecific linkage map of mouse chromosome 15 positioned with respect to the centromere. Genomics. 1992 Aug;13(4):1075–1081. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90021-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. D. Integrating maps of the mouse genome. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1994 Jun;4(3):389–394. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(94)90026-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchberg A. M., Brownell E., Nagata S., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G. A comprehensive genetic map of murine chromosome 11 reveals extensive linkage conservation between mouse and human. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):153–161. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callow M. J., Stoltzfus L. J., Lawn R. M., Rubin E. M. Expression of human apolipoprotein B and assembly of lipoprotein(a) in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 15;91(6):2130–2134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.6.2130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceci J. D., Justice M. J., Lock L. F., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G. An interspecific backcross linkage map of mouse chromosome 8. Genomics. 1990 Jan;6(1):72–79. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90449-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceci J. D., Kingsley D. M., Silan C. M., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. An interspecific backcross linkage map of the proximal half of mouse chromosome 14. Genomics. 1990 Apr;6(4):673–678. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90503-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceci J. D., Siracusa L. D., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G. A molecular genetic linkage map of mouse chromosome 4 including the localization of several proto-oncogenes. Genomics. 1989 Nov;5(4):699–709. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90111-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chartier F. L., Keer J. T., Sutcliffe M. J., Henriques D. A., Mileham P., Brown S. D. Construction of a mouse yeast artificial chromosome library in a recombination-deficient strain of yeast. Nat Genet. 1992 May;1(2):132–136. doi: 10.1038/ng0592-132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi T. K., Hollenbach P. W., Pearson B. E., Ueda R. M., Weddell G. N., Kurahara C. G., Woodhouse C. S., Kay R. M., Loring J. F. Transgenic mice containing a human heavy chain immunoglobulin gene fragment cloned in a yeast artificial chromosome. Nat Genet. 1993 Jun;4(2):117–123. doi: 10.1038/ng0693-117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. S. Positional cloning: let's not call it reverse anymore. Nat Genet. 1992 Apr;1(1):3–6. doi: 10.1038/ng0492-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. Development and applications of a molecular genetic linkage map of the mouse genome. Trends Genet. 1991 Apr;7(4):113–118. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90455-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A., Gilbert D. J., Eppig J. T., Maltais L. J., Miller J. C., Dietrich W. F., Weaver A., Lincoln S. E., Steen R. G. A genetic linkage map of the mouse: current applications and future prospects. Science. 1993 Oct 1;262(5130):57–66. doi: 10.1126/science.8211130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornall R. J., Aitman T. J., Hearne C. M., Todd J. A. The generation of a library of PCR-analyzed microsatellite variants for genetic mapping of the mouse genome. Genomics. 1991 Aug;10(4):874–881. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90175-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. D., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A., Lehrach H. Interspersed repetitive element polymerase chain reaction product mapping using a mouse interspecific backcross. Genomics. 1991 Jun;10(2):375–384. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90322-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich W. F., Lander E. S., Smith J. S., Moser A. R., Gould K. A., Luongo C., Borenstein N., Dove W. Genetic identification of Mom-1, a major modifier locus affecting Min-induced intestinal neoplasia in the mouse. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):631–639. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90484-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich W. F., Miller J. C., Steen R. G., Merchant M., Damron D., Nahf R., Gross A., Joyce D. C., Wessel M., Dredge R. D. A genetic map of the mouse with 4,006 simple sequence length polymorphisms. Nat Genet. 1994 Jun;7(2 Spec No):220–245. doi: 10.1038/ng0694supp-220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich W., Katz H., Lincoln S. E., Shin H. S., Friedman J., Dracopoli N. C., Lander E. S. A genetic map of the mouse suitable for typing intraspecific crosses. Genetics. 1992 Jun;131(2):423–447. doi: 10.1093/genetics/131.2.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eicher E. M. Foundation for the future: formal genetics of the mouse. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1981;45:1–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel W. N., Lee B. K., Stoye J. P., Coffin J. M., Eicher E. M. Characterization of the endogenous nonecotropic murine leukemia viruses of NZB/B1NJ and SM/J inbred strains. Mamm Genome. 1992;2(2):110–122. doi: 10.1007/BF00353859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel W. N., Stoye J. P., Taylor B. A., Coffin J. M. A linkage map of endogenous murine leukemia proviruses. Genetics. 1990 Feb;124(2):221–236. doi: 10.1093/genetics/124.2.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groot P. C., Moen C. J., Dietrich W., Stoye J. P., Lander E. S., Demant P. The recombinant congenic strains for analysis of multigenic traits: genetic composition. FASEB J. 1992 Jul;6(10):2826–2835. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.10.1634045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatada I., Hayashizaki Y., Hirotsune S., Komatsubara H., Mukai T. A genomic scanning method for higher organisms using restriction sites as landmarks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9523–9527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
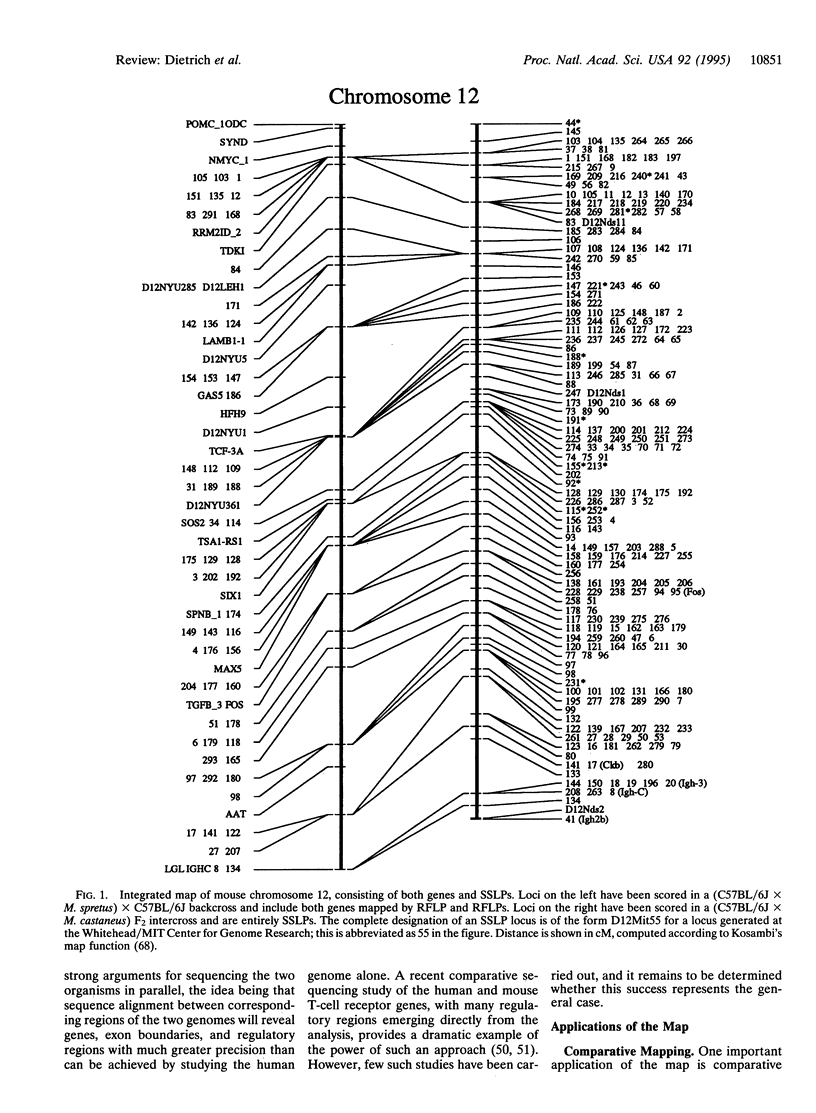
- Hood L., Koop B. F., Rowen L., Wang K. Human and mouse T-cell-receptor loci: the importance of comparative large-scale DNA sequence analyses. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1993;58:339–348. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1993.058.01.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob H. J., Brown D. M., Bunker R. K., Daly M. J., Dzau V. J., Goodman A., Koike G., Kren V., Kurtz T., Lernmark A. A genetic linkage map of the laboratory rat, Rattus norvegicus. Nat Genet. 1995 Jan;9(1):63–69. doi: 10.1038/ng0195-63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob H. J., Lindpaintner K., Lincoln S. E., Kusumi K., Bunker R. K., Mao Y. P., Ganten D., Dzau V. J., Lander E. S. Genetic mapping of a gene causing hypertension in the stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rat. Cell. 1991 Oct 4;67(1):213–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90584-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Taylor B. A., Lee B. K. Organization, distribution, and stability of endogenous ecotropic murine leukemia virus DNA sequences in chromosomes of Mus musculus. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):26–36. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.26-36.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julier C., de Gouyon B., Georges M., Guénet J. L., Nakamura Y., Avner P., Lathrop G. M. Minisatellite linkage maps in the mouse by cross-hybridization with human probes containing tandem repeats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4585–4589. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Justice M. J., Silan C. M., Ceci J. D., Buchberg A. M., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. A molecular genetic linkage map of mouse chromosome 13 anchored by the beige (bg) and satin (sa) loci. Genomics. 1990 Feb;6(2):341–351. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90575-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Justice M. J., Siracusa L. D., Gilbert D. J., Heisterkamp N., Groffen J., Chada K., Silan C. M., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. A genetic linkage map of mouse chromosome 10: localization of eighteen molecular markers using a single interspecific backcross. Genetics. 1990 Aug;125(4):855–866. doi: 10.1093/genetics/125.4.855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingsley D. M., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G. A molecular genetic linkage map of mouse chromosome 9 with regional localizations for the Gsta, T3g, Ets-1 and Ldlr loci. Genetics. 1989 Sep;123(1):165–172. doi: 10.1093/genetics/123.1.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koop B. F., Hood L. Striking sequence similarity over almost 100 kilobases of human and mouse T-cell receptor DNA. Nat Genet. 1994 May;7(1):48–53. doi: 10.1038/ng0594-48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruglyak L., Lander E. S. A nonparametric approach for mapping quantitative trait loci. Genetics. 1995 Mar;139(3):1421–1428. doi: 10.1093/genetics/139.3.1421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusumi K., Smith J. S., Segre J. A., Koos D. S., Lander E. S. Construction of a large-insert yeast artificial chromosome library of the mouse genome. Mamm Genome. 1993;4(7):391–392. doi: 10.1007/BF00360591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander E. S., Botstein D. Mapping mendelian factors underlying quantitative traits using RFLP linkage maps. Genetics. 1989 Jan;121(1):185–199. doi: 10.1093/genetics/121.1.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander E. S., Schork N. J. Genetic dissection of complex traits. Science. 1994 Sep 30;265(5181):2037–2048. doi: 10.1126/science.8091226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larin Z., Monaco A. P., Lehrach H. Yeast artificial chromosome libraries containing large inserts from mouse and human DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4123–4127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder A., Swan D., Ruddle F., D'Eustachio P., Leder P. Dispersion of alpha-like globin genes of the mouse to three different chromosomes. Nature. 1981 Sep 17;293(5829):196–200. doi: 10.1038/293196a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadeau J. H., Bedigian H. G., Bouchard G., Denial T., Kosowsky M., Norberg R., Pugh S., Sargeant E., Turner R., Paigen B. Multilocus markers for mouse genome analysis: PCR amplification based on single primers of arbitrary nucleotide sequence. Mamm Genome. 1992;3(2):55–64. doi: 10.1007/BF00431247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer S., Perry J., Ashworth A. A contravention of Ohno's law in mice. Nat Genet. 1995 Aug;10(4):472–476. doi: 10.1038/ng0895-472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed P. W., Davies J. L., Copeman J. B., Bennett S. T., Palmer S. M., Pritchard L. E., Gough S. C., Kawaguchi Y., Cordell H. J., Balfour K. M. Chromosome-specific microsatellite sets for fluorescence-based, semi-automated genome mapping. Nat Genet. 1994 Jul;7(3):390–395. doi: 10.1038/ng0794-390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rise M. L., Frankel W. N., Coffin J. M., Seyfried T. N. Genes for epilepsy mapped in the mouse. Science. 1991 Aug 9;253(5020):669–673. doi: 10.1126/science.1871601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandrin M. S., Vaughan H. A., Dabkowski P. L., McKenzie I. F. Anti-pig IgM antibodies in human serum react predominantly with Gal(alpha 1-3)Gal epitopes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):11391–11395. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schedl A., Montoliu L., Kelsey G., Schütz G. A yeast artificial chromosome covering the tyrosinase gene confers copy number-dependent expression in transgenic mice. Nature. 1993 Mar 18;362(6417):258–261. doi: 10.1038/362258a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siracusa L. D., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G. Identification and applications of repetitive probes for gene mapping in the mouse. Genetics. 1991 Jan;127(1):169–179. doi: 10.1093/genetics/127.1.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siracusa L. D., Silan C. M., Justice M. J., Mercer J. A., Bauskin A. R., Ben-Neriah Y., Duboule D., Hastie N. D., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A. A molecular genetic linkage map of mouse chromosome 2. Genomics. 1990 Mar;6(3):491–504. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90479-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss W. M., Dausman J., Beard C., Johnson C., Lawrence J. B., Jaenisch R. Germ line transmission of a yeast artificial chromosome spanning the murine alpha 1(I) collagen locus. Science. 1993 Mar 26;259(5103):1904–1907. doi: 10.1126/science.8096090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J. A., Aitman T. J., Cornall R. J., Ghosh S., Hall J. R., Hearne C. M., Knight A. M., Love J. M., McAleer M. A., Prins J. B. Genetic analysis of autoimmune type 1 diabetes mellitus in mice. Nature. 1991 Jun 13;351(6327):542–547. doi: 10.1038/351542a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. L., May P. E. Abundant class of human DNA polymorphisms which can be typed using the polymerase chain reaction. Am J Hum Genet. 1989 Mar;44(3):388–396. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh J., McClelland M. Fingerprinting genomes using PCR with arbitrary primers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7213–7218. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh J., Petersen C., McClelland M. Polymorphisms generated by arbitrarily primed PCR in the mouse: application to strain identification and genetic mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 25;19(2):303–306. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.2.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. G., Kubelik A. R., Livak K. J., Rafalski J. A., Tingey S. V. DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6531–6535. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward S. R., Sudweeks J., Teuscher C. Random sequence oligonucleotide primers detect polymorphic DNA products which segregate in inbred strains of mice. Mamm Genome. 1992;3(2):73–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00431249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Proenca R., Maffei M., Barone M., Leopold L., Friedman J. M. Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature. 1994 Dec 1;372(6505):425–432. doi: 10.1038/372425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



