Abstract
Ischemia-reperfusion injury is accompanied by endothelial hypoxia and reoxygenation that trigger oxidative stress with enhanced superoxide generation and diminished nitric oxide (NO) production leading to endothelial dysfunction. Oxidative depletion of the endothelial NO synthase (eNOS) cofactor tetrahydrobiopterin can trigger eNOS uncoupling, in which the enzyme generates superoxide rather than NO. Recently, it has also been shown that oxidative stress can induce eNOS S-glutathionylation at critical cysteine residues of the reductase site that serves as a redox switch to control eNOS coupling. While superoxide can deplete tetrahydrobiopterin and induce eNOS S-glutathionylation, the extent of and interaction between these processes in the pathogenesis of eNOS dysfunction in endothelial cells following hypoxia and reoxygenation remain unknown. Therefore, studies were performed on endothelial cells subjected to hypoxia and reoxygenation to determine the severity of eNOS uncoupling and the role of cofactor depletion and S-glutathionylation in this process. Hypoxia and reoxygenation of aortic endothelial cells triggered xanthine oxidase-mediated superoxide generation, causing both tetrahydrobiopterin depletion and S-glutathionylation with resultant eNOS uncoupling. Replenishing cells with tetrahydrobiopterin along with increasing intracellular levels of glutathione greatly preserved eNOS activity after hypoxia and reoxygenation, while targeting either mechanism alone only partially ameliorated the decrease in NO. Endothelial oxidative stress, secondary to hypoxia and reoxygenation, uncoupled eNOS with an altered ratio of oxidized to reduced glutathione inducing eNOS S-glutathionylation. These mechanisms triggered by oxidative stress combine to cause eNOS dysfunction with shift of the enzyme from NO to superoxide production. Thus, in endothelial reoxygenation injury, normalization of both tetrahydrobiopterin levels and the glutathione pool are needed for maximal restoration of eNOS function and NO generation.
Endothelial dysfunction (ED) is an early indicator of numerous vascular diseases as well as a key contributor to the pathophysiology of ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury. ED is commonly associated with increased cellular oxidative stress and with decreased nitric oxide (NO) bioavailability,1−3 resulting in dysregulation of vascular tone and ultimately compromised cardiovascular function. The oxidative stress seen in ED is generated by a variety of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (ROS and RNS, respectively), predominantly superoxide (O2•–), which is responsible for the oxidation of a variety of redox-sensitive molecules.4−6 Several enzymes are thought to contribute to oxidative stress in the heart and vascular tissue during I/R, including NADPH oxidase, the mitochondrial electron transport chain, aldehyde oxidase (AO), and xanthine oxidase (XO).7−13 In endothelial cells, xanthine dehydrogenase (XDH), which catalyzes the conversion of hypoxanthine/xanthine to uric acid using NAD+ as an electron acceptor, is widely reported to be a major contributor to oxidative stress after I/R injury.7,14−20 This mechanism involves a reversible conversion of XDH to XO during ischemia with a concomitant enhancement of ATP catabolism resulting in accumulation of the XO substrates hypoxanthine (HX) and xanthine (X).17 The steric modification to XDH impacts the ability of NAD+ to access the FAD site of the protein, leaving O2 to act as the electron acceptor, generating O2•– and H2O2 during conversion of hypoxanthine to uric acid.21
NO synthases (NOSs) make up a family of homodimeric proteins that convert l-arginine and O2 to l-citrulline and NO using NADPH as a reducing substrate.22−25 They also require a critical redox-sensitive cofactor, tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4). While there are three known NOS isoforms, endothelial NOS (eNOS or NOS3) is the major NOS isoform expressed in endothelial cells, and eNOS-derived NO mediates endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation.26−28 No significant expression of inducible or neuronal NOS has been observed in endothelial cells under normal physiological conditions.29,30 While hypoxic stress has been reported to induce iNOS expression in smooth muscle, there is a lack of iNOS induction in endothelial cells with only eNOS expression detected.30−32
The increased O2•– production during ED impairs the catalytic activity of eNOS, severely compromising cellular NO generation. Diminished NO production in endothelial cells in various pathological conditions does not correlate with a decrease in the level of eNOS protein.33−35 The enzyme level remains the same or even increases in ED, in preatherosclerotic states, heart failure, and hypertension. Under such circumstances, with increased oxidative stress, the oxidation of the essential eNOS cofactor, BH4, to dihydrobiopterin (BH2) is thought to cause eNOS uncoupling,36,37 an enzymatic state in which O2•– rather than NO is generated. Competition between the oxidized and reduced forms of the pteridine cofactor for the eNOS binding site is ultimately involved in eNOS uncoupling.38,39 While the impact of O2•– on BH4 has been shown both in vitro and in vivo,40 the extent to which a lack of this cofactor influences eNOS activity in endothelial cells under intrinsic oxidative stress is not well-understood. Neither is it known if other mechanisms, triggered by O2•–, play a crucial role in eNOS uncoupling and ED.
We have recently discovered that eNOS can be uncoupled, regardless of the presence or absence of BH4, by S-glutathionylation of critical Cys residues, in particular Cys 689 and Cys 908 of the reductase domain. Oxidized glutathione (GSSG) can induce dose-dependent eNOS S-glutathionylation (eNOS-SG) through disulfide exchange.41 This process is regulated by the ratio of the oxidized to reduced glutathione (GSSG/GSH) present in the intracellular pool. Because GSH is present in the range of millimoles per liter in a large variety of cell types, including endothelial cells, the GSSG/GSH ratio is a critical determinant of the redox state.4,42 Interconversion between reduced and oxidized forms is critical for cell redox homeostasis, and oxidative stress may shift the ratio toward GSSG, thereby defining eNOS-SG as another possible pathway of eNOS uncoupling in ED induced by the processes of hypoxia and reoxygenation or related I/R injury.
In this study, the extent and mechanisms of eNOS uncoupling in endothelial cells subjected to hypoxia and reoxygenation (H/R) were investigated. eNOS S-glutathionylation was demonstrated for the first time as a consequence of intrinsic oxidative stress in endothelial cells, as well as BH4-dependent eNOS uncoupling. Using aortic endothelial cells in an adherent cell model of H/R, we observed that these two mechanisms act together to cause eNOS uncoupling.
Materials and Methods
Materials
Potassium phosphate monobasic (KH2PO4), dl-dithiothreitol (DTT), citric acid, diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid (DTPA), oxypurinol, menadione (vitamin K3), and N-acetyl-l-cysteine (NAC) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO). Acetonitrile (ACN), ammonium acetate, methanol, an iodine solution, and potassium iodide were purchased from Thermo-Fisher. Octyl sulfate sodium salt (OSA) was purchased from Acros Organics (Waltham, MA). 7,8-Dihydro-l-biopterin (BH2), dihydroxanthopterin (XH2), pterin (P), isoxanthopterin (IX), xanthopterin (XP), and l-biopterin (B) were purchased from Schircks Laboratories (Jone, Switzerland). (6R)-l-Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4), l-NG-nitroarginine methyl ester (l-NAME), and Mn(III)TBAP were purchased from Cayman Chemical (Ann Arbor, MI). Dihydroethidium (DHE) and 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride (DAPI) were purchased from Invitrogen (Carlsbad, CA). Anti-NOS3 antibodies were purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Santa Cruz, CA). The anti-glutathione antibody was purchased from Virogen (Boston, MA). The superoxide probe tetrathiatriarylmethyl (TAM) radical with a single aromatic hydrogen (CT02-H) was synthesized in house as reported previously.43,44
Hypoxia and Reoxygenation (H/R) Model
BAECs were washed with PBS and kept with serum-free DMEM in a hypoxic environment created by placing the flasks containing cells at confluence into a Billups-Rothenberg modular incubator chamber flushed with a 95% N2/5% CO2 gas mixture. The oxygen level was monitored with an oxygen electrode placed inside the incubator chamber interfaced with an Apollo 4000 control unit. Cells were kept inside the chamber at 37 °C for 24 h with an O2 concentration in the medium of ∼4 Torr followed by reoxygenation for 1 h by replacing the hypoxic medium with normoxic PBS with calcium, magnesium, 1 g/L d-glucose, and 36 mg/L sodium pyruvate. Cell viability was checked by trypan blue exclusion. Cells were stained with 0.02% trypan blue in PBS, and cell counts were performed with a Zeiss Laboratory light microscope.45
Detection of Superoxide by Confocal Microscopy
Detection of O2•– generated by BAECs was performed using 10 μM DHE on cells grown on cover glass and treated in six-well plates and then fixed prior to detection. DHE fluoresces when it is oxidized. Blue fluorescent DAPI was used to stain cell nuclei. The images were acquired using a 60× magnification lens on an Olympus FV1000 confocal microscope.
Measurement of Superoxide Using CT02-H Probe by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
Tetrathiatriarylmethyl (TAM) radical with a single aromatic hydrogen (CT02-H) was synthesized and purified as previously described.44 Upon reaction with O2•–, the green CT02-H is dehydrogenated to produce a purple diamagnetic quinone methide detected on an ESA HPLC system via electrochemical oxidation by applying an 800 mV potential to the ESA 6210 coulometric four-channel cell and/or by following the UV absorbance at 540 nm (ε = 15900 M–1 cm–1). The HPLC conditions consisted of a mobile phase (40/30/30 20 mM ammonium acetate/methanol/acetonitrile) at pH 7.0, while the stationary phase was a C18 Tosoh Bioscience ODS-80Tm column (250 mm × 4.6 mm, 5 μm). CT02-H was added to a final concentration of 50 μM to ∼3 × 106 cells cultured in a T25 flask with PBS containing calcium and magnesium, 1 g/L d-glucose, and 36 mg/L sodium pyruvate. The supernatant was collected after reoxygenation for 1 h and injected into the HPLC system, following isocratic elution at a flow rate of 1.2 mL/min.
HPLC Analysis of Pteridines
The HPLC analysis of pteridines was conducted using an HPLC system from ESA equipped with a Waters Atlantis T3 reversed phase column (5 μm, 4.6 mm × 150 mm). The isocratic elution was performed at a flow rate of 1.2 mL/min using a buffer consisting of 100 mM KH2PO4, 6 mM citric acid, 2.5 mM OSA, 0.1 mM DTPA, 1 mM DTT, and 2% methanol (pH 2.5). The detection of the pteridines was performed using the following detector parameters: UV absorption at 254 nm, fluorescence with excitation set at 348 nm and emission set at 444 nm, and electrochemical detection (ESA coulometric four-channel array cell model 6210) with a potential of 100 mV. The indirect detection of pteridines was conducted following previously reported methodology.46 This method was chosen for both robustness and sensitivity in determining the levels of BH4 and BH2. In parallel, direct electrochemical detection of pteridines was used to confirm the indirect measurements of BH4 and to assess the presence of other pteridines that are poorly detected or not detected with fluorescence, such as XP and XH2. For BAEC pteridine analysis, approximately 20 × 106 cells were harvested and lysed using an extraction buffer consisting of 0.1 N HCl and sonication. The supernatant was then split into two aliquots: one for the indirect measurement of BH4 and BH2 and one for the direct measurement of pteridines. For the latter, final concentrations of 1 mM DTT, 1 mM ascorbate, and 100 μM DTPA were added to preserve the redox status of the pteridines throughout sample handling.47
Nitric Oxide Measurement by EPR
Spin trapping measurements of NO from BAECs were performed with a Bruker EMX EPR spectrometer with Fe2+-(N-methyl-d-glucamine dithiocarbamate)2 [Fe2+-(MGD)2] as a NO spin trap.48 The experiments were performed on 3 × 106 cells grown in T-25 flasks. Cells were washed with PBS; then 1.8 mL of PBS containing glucose (1 g/L), pyruvate (36 mg/L), CaCl2, MgCl2, the NO spin trap Fe2+-(MGD)2 (0.25 mM Fe2+ and 2.5 mM MGD), and calcium ionophore A23187 (1 μM) were added to each flask, and the cells were incubated for 20 min at 37 °C in a humidified environment containing 5% CO2. After the incubation, the supernatant from each flask was collected and concentrated by being dried under vacuum using a SpeedVac, and finally, the trapped NO in the supernatants was quantified by EPR. For NOS inhibition, l-NAME was used at a concentration of 2 mM to ensure complete inhibition. Spectra recorded from these cellular preparations were obtained with the following parameters: microwave power of 20 mW, modulation amplitude of 4.0 G, and modulation frequency of 100 kHz.
Immunoprecipitation, Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate–Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS–PAGE), and Immunoblotting
Approximately 20 × 106 cells were harvested and suspended in RIPA buffer containing 10 mM NEM and protease inhibitors and then lysed via sonication. The cell lysate was then incubated with the bead-conjugated eNOS antibody overnight at 4 °C under constant rotation. eNOS was then eluted from the bead–antibody–eNOS complex using the loading buffer, and the supernatant containing the eNOS was collected for SDS–PAGE. Standard procedures previously described were followed.49 Briefly, protein extracts were separated by a 4 to 20% polyacrylamide gel, and protein bands were then transferred electrophoretically to a nitrocellulose membrane. Membranes were blocked with 5% milk in TBS containing 0.05% Tween 20 (TTBS) and then incubated overnight with the anti-glutathione monoclonal antibody (1000/1). Membranes were then washed and incubated with the HRP-labeled anti-mouse antibody. Subsequently, the signal was detected with ECL Western blotting detection reagents (Bio-Rad), and the signal intensity was digitized and quantified with ImageJ (National Institutes of Health). Membranes were then reprobed for eNOS as a loading control.
Statistical Analysis
Data are expressed as means ± the standard error of the mean (SEM). All experiments were repeated at least three times. Microsoft Excel and Sigma Plot (SPSS, Inc.) were used for data analysis. A Student’s t test was used for statistical analysis, with P < 0.05 being considered significant.
Results
Xanthine Oxidase Is a Major Source of Superoxide in BAECs under H/R
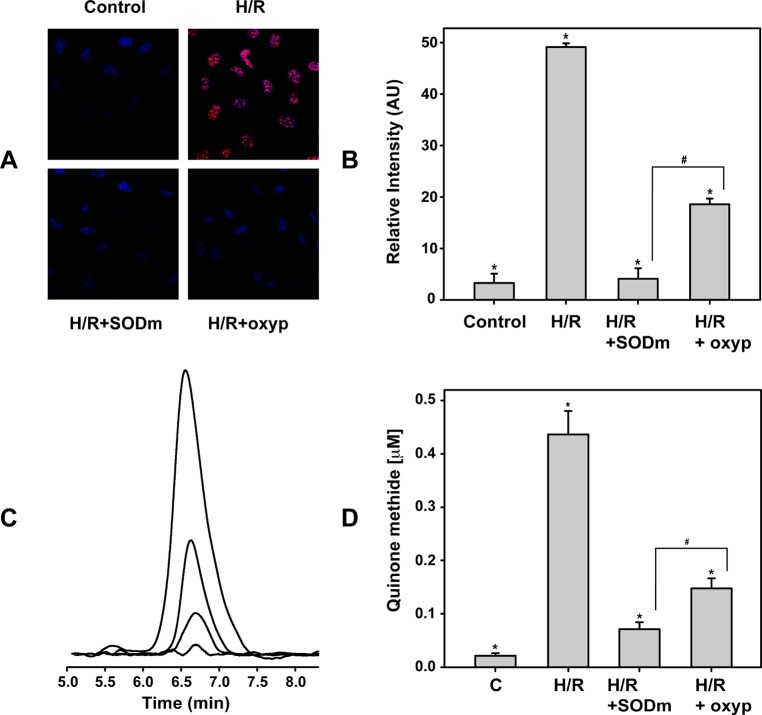
We verified that the adherent BAEC H/R model generates O2•– by two independent assays. First, confocal microscopy was used to detect the fluorescence emitted by oxidized DHE.41 As previously reported,45 cells undergoing H/R produce O2•–. As illustrated in panels A and B of Figure 1, the DHE-derived fluorescence signal from the cells undergoing H/R was more than 15 times higher than the control (no H/R). This fluorescence was quenched by incubating the cells during H/R with 50 μM Mn(III)TBAP, a cell permeable SOD mimetic (SODm) with an O2•– dismutation rate of 107 M–1 s–1, confirming that it was derived from O2•–. The fluorescence signal was nearly totally abolished by the SODm. To determine the role of XO in this process of O2•– generation, the cells were treated with the XO inhibitor oxypurinol (2 mM) preceding H/R and the detected level of O2•– was 62% decreased compared to that from H/R.
Figure 1.
Generation of superoxide from BAECs. (A and B) Cells undergoing H/R show strong DHE-derived fluorescence on confocal microscopy in contrast to that in control cells (red fluorescence against staining of nuclei with blue DAPI). Both SODm and oxypurinol decreased this fluorescence when they were added to the cells prior to H/R. The relative levels of O2•– (as DHE-derived fluorescence intensity) are reported at the right. *H/R vs control, H/R+SODm, and H/R+oxypurinol: p < 2 × 10–5. #H/R+SODm vs H/R+oxyp: p < 0.002. (C and D) Amounts of superoxide released by the cells as detected by HPLC using the CT02-H probe. The highest intensity is reported from cells undergoing H/R, followed by the signal coming from cells undergoing H/R and treated with oxypurinol and SODm prior to H/R. The control is near the baseline. Panel D shows the level of the quinone methide (proportional to O2•–). *H/R vs control, H/R+SODm, and H/R+oxypurinol: p < 0.002. #H/R+SODm vs H/R+oxyp: p < 0.017.
To further confirm these results, O2•– production was assayed by HPLC using the O2•– probe CT02-H. This compound, unlike other spin traps or fluorescence-based O2•- assays, is well-suited for an adherent cell study, and its impermeability to cell membranes allows quantification of O2•– that reaches the extracellular space. The amount of quinone methide generated after the O2•– dehydrogenation of CT02-H was determined. Panels C and D of Figure 1 show the quinone methide production in cells undergoing H/R that closely resembled the pattern seen with DHE confocal microscopy. In particular, the concentration of quinone methide is increased from 22 ± 6 nM in the control to 437 ± 44 nM after H/R, which was then reduced >6-fold with SODm addition prior to H/R, while inhibiting XO with oxypurinol prior to H/R resulted in a 3-fold decrease. For comparison, as a positive control, administration of 50 μM menadione (vitamin K3), which is reported to stimulate large amounts of O2•– production,50 resulted in a higher concentration of quinone methide, reaching 2.04 ± 0.09 μM, ∼4.6 times higher than in endothelial cells after H/R (data not shown).
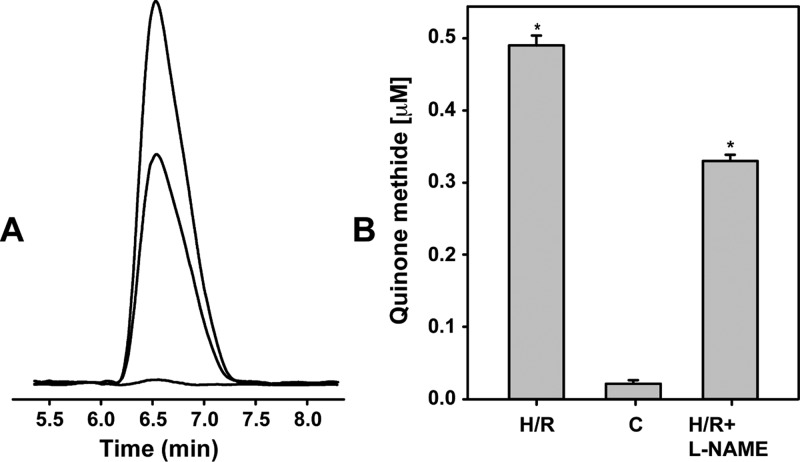
The amount of O2•– generated by uncoupled eNOS was also assessed. As shown in panels A and B of Figure 2, the amount of quinone methide detected in BAECs after H/R was ∼33% lower when cells were treated with the NOS inhibitor l-NAME (2 mM) prior to H/R compared to identical experiments with untreated cells. Thus, uncoupling of eNOS gives rise to prominent O2•– generation in BAECs subjected to H/R.
Figure 2.
Generation of superoxide from uncoupled eNOS in BAECs undergoing H/R. (A and B) Amounts of superoxide released by the cells as detected by HPLC using the CT02-H probe. A 33% decrease in the concentration of detected quinone methide from BAECs pretreated with eNOS inhibitor l-NAME (2 mM) prior to H/R is seen compared to levels from untreated cells undergoing H/R, and this corresponds to uncoupled eNOS-mediated O2•– generation. *H/R vs H/R+l-NAME: p < 0.001.
The BH4/BH2 Ratio Is Decreased after H/R and Preserved by Scavenging O2•– or Inhibiting XO
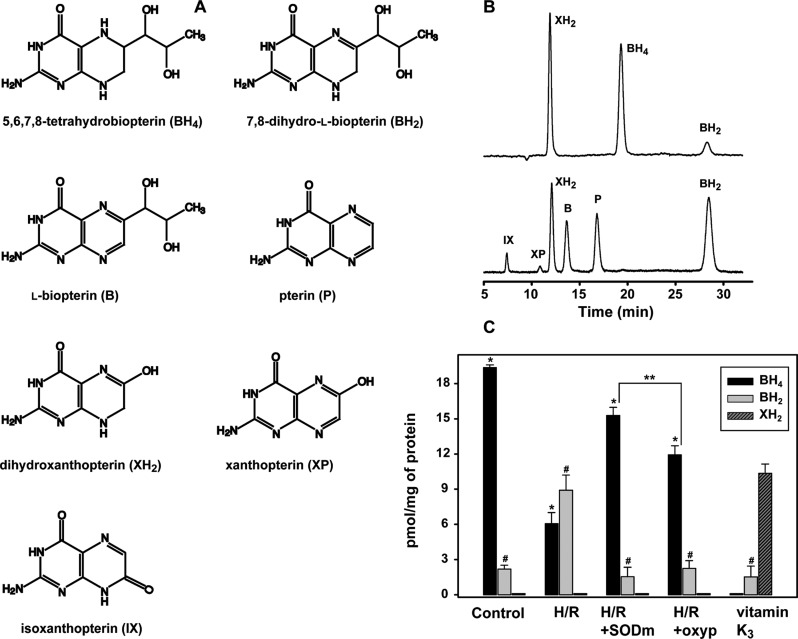
Panels A and B of Figure 3 show the molecular structures and chromatographic elution profiles of BH4 and the corresponding products of BH4 oxidation. As a consequence of O2•– oxidation, analysis of the pteridines from cells undergoing H/R showed that the decrease in the level of BH4 paralleled the increase in the level of BH2, exhibiting a pattern similar to that reported in vitro.40 As shown in Figure 3C, the level of BH4 decreased from 19.3 ± 0.2 pmol/mg of protein in the control (no H/R) to 6.1 ± 0.9 pmol/mg of protein after H/R (∼70% less) while the level of BH2 increased from 2.2 ± 0.3 to 8.9 ± 1.3 pmol/mg of protein (∼4 times higher than in the control). Therefore, the intracellular BH4/BH2 ratio dramatically decreased from ∼9.2 in the control to ∼0.7 after H/R treatment. Moreover, with no other detectable pteridines, the total pteridine content was reduced from 21.5 ± 0.8 pmol/mg of protein in the control to 15.0 ± 1.4 pmol/mg of protein after H/R (∼30% decrease). When 50 μM SODm was added to the cells before H/R, the level of BH4 after the reoxygenation was significantly higher, 15.3 ± 0.7 pmol/mg of protein, ∼2.5 times higher than in H/R and ∼80% of the level detected in the control, while the level of BH2 was 1.5 ± 0.8 pmol/mg, approximately the same level as in the control cells. The total pteridine pool in SODm-treated cells after H/R of 16.8 ± 0.5 pmol/mg of protein was not significantly different compared to that of cells subjected to H/R, indicating that the change observed in the BH4/BH2 ratio could only be attributed to the scavenging properties of SODm and not to increased biosynthetic activity. We also verified that the inhibition of XO, using 2 mM oxypurinol, substantially reduced the level of BH4 oxidation; indeed, its level after H/R was 11.9 ± 0.8 pmol/mg of protein, a value that was ∼2 times higher than in H/R and 62% of the control. In parallel, the BH2 level was reduced (as in the SODm treatment) to the control level (2.2 ± 0.6 pmol/mg of protein). No relevant differences in the total pteridine pool were detected after this treatment either (14.2 ± 0.7 pmol/mg of protein). To further determine the extent to which O2•– was able to oxidize BH4, cells were treated with 50 μM vitamin K3. In this case, the amount of radical produced was able to completely oxidize BH4 and almost completely oxidize BH2, as well (1.5 ± 0.9 pmol/mg of protein), leaving XH2 as a final product of oxidation (10.3 ± 0.8 pmol/mg of protein) that could be detected only under this extreme condition of oxidative stress. No other detectable pteridines were seen at significant levels.
Figure 3.
Pteridines in BAECs undergoing H/R. (A) Molecular structure of BH4 and its main products of oxidation or rearrangement. (B) Chromatographic elution profile of the pteridines in a given mix of standards: (top) electrochemical oxidation of pteridines at 100 mV and (bottom) signal from fluorescence detection for the same pteridines. (C) Pteridines detected by HPLC from the BAEC lysate. Cells under H/R have 69% less BH4 (*p < 8 × 10–5) than the control, while the level of BH2 is 4 times higher (#p < 0.004). SODm- and oxypurinol-treated cells were able to preserve their BH4 pool at levels comparable to the control and significantly different from the H/R level (∼2.5- and ∼2-fold, respectively): *p < 0.005; ** H/R+SODm vs H/R+oxyp, p < 0.016. The BH2 level, on the other hand, was near the control level in all treatments and significantly different from that of H/R: #p < 0.005. In stark contrast to the H/R model, cells treated with vitamin K3 show no BH4 and a minimal level of BH2. The main detected pteridine in this case was XH2.
eNOS-Mediated NO Production Decreases as a Consequence of BH4 Oxidation after H/R
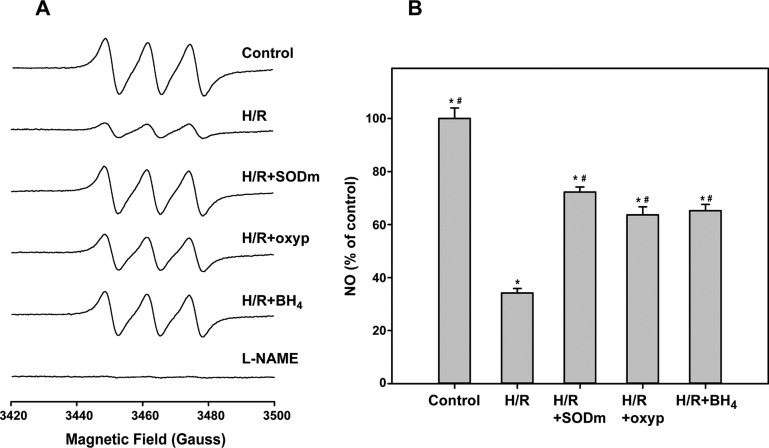
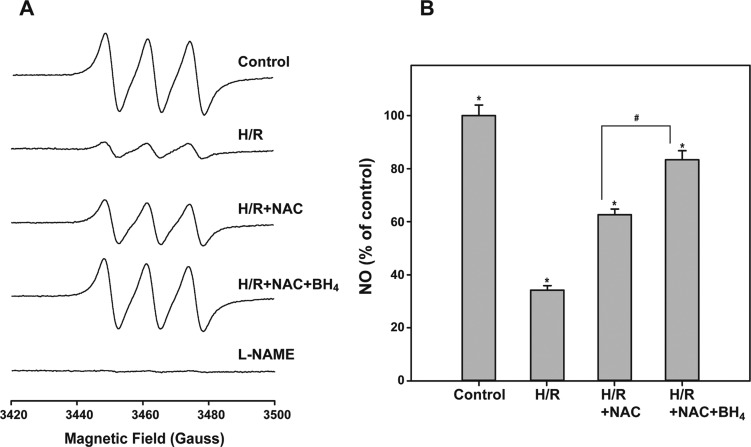
The relative change in NO production from cells undergoing H/R compared to control cells (no H/R) was analyzed by EPR spectroscopy using Fe2+-(MGD)2. A decrease in the NO production of cells following H/R was observed. Panels A and B of Figure 4 show that NO production was reduced to 34.2 ± 1.7% of the control (100%) after cells were subjected to H/R, consistent with O2•– production and BH4 oxidation. Conversely, when the cells were treated with 50 μM SODm prior to H/R, significant preservation of NO levels was seen (72.3 ± 1.9%), and to a lesser extent, the inhibition of XO by oxypurinol also partially preserved NO levels after H/R (63.7 ± 3.0% of the control). To further test the relevance of an O2•–-driven decrease in the BH4/BH2 ratio to eNOS uncoupling and the consequent reduction of the NO level, BAECs were incubated with 100 μM BH4 2 h after the onset of the hypoxic conditioning to avoid depletion of the cofactor. The level of pteridines was then checked at the end of the reoxygenation step by washing, harvesting, and lysing the cells. The cells effectively internalized BH4 with its intracellular concentration reaching 455 ± 34 pmol/mg of protein, ∼24-fold higher than that in the control sample. While the intracellular concentration of BH2 also increased, reaching 15.0 ± 1.2 pmol/mg of protein, the treatment provided the highest BH4/BH2 ratio of ∼30 (more then 3-fold higher than in the control). This translated to an increase in NO production compared to that of untreated H/R cells, with levels reaching 65.2 ± 2.4% of the untreated control. Thus, when compared with that of cells under H/R, administration of BH4 significantly preserved the NO level throughout the course of H/R. Interestingly, while the decrease in the BH4/BH2 ratio was reversed, restoration of NO production remained incomplete, suggesting the presence of other mechanisms of eNOS dysfunction driven by the oxidative stress occurring during H/R, but independent of BH4 levels or the BH4/BH2 ratio.
Figure 4.
Production of NO in BAECs undergoing H/R. NO levels from cells undergoing H/R, as detected through EPR spin trapping (A), decreased to 34.2% of the control: *p < 6 × 10–5. (B) Cell treatments, with 50 μM SODm or 2 mM oxypurinol, significantly preserved NO levels as compared to H/R: *p < 0.002. Addition of 100 μM BH4 preserved NO at a level similar to that observed in the other two treatments when compared to H/R: *p < 0.002; #control vs H/R+SODm, H/R+oxyp, and H/R+BH4, p < 0.001.
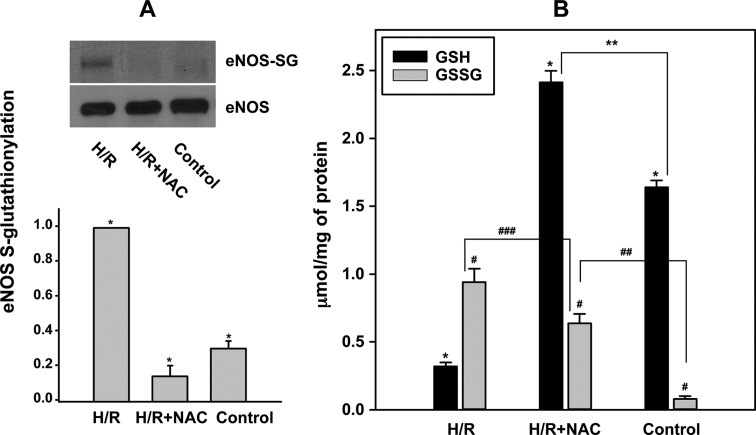
eNOS Is S-Glutathionylated in BAECs after H/R
We have recently demonstrated that eNOS S-glutathionylation (eNOS-SG) can also function as an important mechanism of eNOS uncoupling following oxidative stress.41,51 eNOS-SG and a decrease in the BH4/BH2 ratio may have additive detrimental effects on NO biosynthesis.41,47 Therefore, measurements of eNOS-SG were performed in endothelial cells undergoing H/R. Following H/R, prominent levels of eNOS-SG were seen, more than 3 times higher than in the control cells (no H/R) as shown in Figure 5A. A concomitant reduction in GSH and an increase in GSSG were observed in the intracellular pool when measured via HPLC. As illustrated in Figure 5B, after H/R, the level of GSH was 0.32 ± 0.03 μmol/mg of protein compared to 1.64 ± 0.03 μmol/mg of protein in the control. Conversely, GSSG increased from 0.08 ± 0.02 μmol/mg of protein in the control to 0.94 ± 0.1 μmol/mg of protein after H/R, an increase in the GSSG/GSH ratio from ∼0.05 in the control to ∼2.9 in H/R. Notably, it was then verified that eNOS-SG in cells undergoing H/R might be completely prevented by increasing the intracellular GSH concentration. To increase the cellular concentration of GSH, 2 mM N-acetyl-l-cysteine (NAC) was given to the cells overnight. NAC, which is required for the biosynthesis of GSH, increased the level of GSH in control cells up to ∼2.6-fold compared to the control (data not shown), while after H/R, the GSH reached 2.4 ± 0.1 μmol/mg of protein, considerably higher than the control and ∼7.5 times higher than in untreated cells after H/R. Despite an increase in GSSG to 0.6 ± 0.1 μmol/mg of protein, the GSSG/GSH ratio was dramatically reduced to ∼0.3. The level of eNOS-SG under these circumstances was approximately half that of the control and ∼7 times lower than in untreated cells after H/R.
Figure 5.
eNOS-SG in BAECs undergoing H/R. (A) eNOS-SG as determined by immunoprecipitation followed by immunoblotting. The sample from H/R has a 3-fold higher level of eNOS-SG than the control. The sample from the 2 mM NAC pretreatment has the lowest detectable level of eNOS-SG, approximately 15% of that of the untreated H/R sample. *H/R vs H/R+NAC, control, p < 3 × 10–5. (B) GSH and GSSG cellular content as observed by HPLC. The oxidized/reduced ratio notably increased from 0.05 to 2.9 going from the control (untreated cells) to H/R cells, respectively. Addition of 2 mM NAC kept the ratio at 0.3. For GSH: *H/R vs H/R+NAC, control, p < 2 × 10–5; **control vs H/R+NAC, p < 0.001. For GSSG: #H/R vs H/R+NAC, control, p < 0.04; ##control vs H/R+NAC, p < 0.001; ###H/R vs H/R+NAC, p < 0.04.
eNOS Activity in BAECs Undergoing H/R Is Reduced Because of the Concomitant Effects of eNOS S-Glutathionylation and the Reduced BH4/BH2 Ratio
The effect of eNOS-SG alone and eNOS-SG together with BH4 oxidation on uncoupling eNOS was also investigated. As reported in panels A and B of Figure 6, the level of NO in cells undergoing H/R was significantly preserved in cells incubated with 2 mM NAC, reaching 62.6 ± 2.2% of the control (no H/R), a level very close to that seen in cells treated with 100 μM BH4 prior to H/R. A substantial increase in the level of NO was observed when cells were incubated with 2 mM NAC along with 100 μM BH4. Under these conditions, the detected level of NO after H/R increased to 83.4 ± 3.4% of the control and was ∼2.4-fold higher than that seen after H/R in untreated cells, demonstrating a positive additive effect that far exceeds the preservation of eNOS activity observed with individual treatments alone.
Figure 6.
Production of NO from BAECs treated with NAC, BH4, or both after H/R. (A and B) Relative production of NO from eNOS. Treating cells with 100 μM BH4 together with 2 mM NAC resulted in >85% NO preservation as compared to the control. NAC treatment alone also significantly preserved NO but to a lesser extent. *H/R vs control, H/R+NAC, H/R+NAC+BH4: p < 0.002. #H/R+NAC vs H/R+NAC+BH4: p < 0.003.
Discussion
Endothelial dysfunction (ED), as a consequence of I/R injury, is associated with an overall decrease in NO production due to eNOS uncoupling, a process by which the enzyme switches from NO to O2•– production.52−54 In prior studies, this phenomenon was primarily linked to depletion of the eNOS cofactor, BH4. It was shown that oxidative stress47 was a primary cause of BH4 depletion and that the oxidized form, BH2, was able to compete for the same binding site on the oxygenase domain of eNOS.38 Despite these advances in understanding the fundamental process of eNOS uncoupling, the discordance between the function of BH4 in maintaining eNOS coupling in vitro and the marginal results obtained by supplementation of BH4 in ex vivo and in vivo experiments as well as in clinical trials47,55,56 prompted further investigation to consider if other processes may be involved in triggering eNOS uncoupling and ED.
Building on previous reports by our group and others,45,57,58 we found that XO plays a major role in O2•– production in adherent endothelial cells under H/R. Furthermore, we observed that XO-generated O2•– triggers intracellular oxidative stress leading to a critical shift from reduced to oxidized pteridines. We quantified the decrease in the level of NO attributed to the decrease in the BH4/BH2 ratio in endothelial cells undergoing H/R, and consistent with previous observations, eNOS was significantly, but not solely, affected by the decrease in this ratio. Moreover, we observed only a partial recovery by saturating the enzyme with BH4 through administration of the cofactor to endothelial cells prior to and during H/R. Therefore, BH4 depletion and the parallel increase in BH2 account for only a portion of the eNOS uncoupling, and this possibly explains the lack of efficacy in addressing eNOS-dependent ED with BH4 supplementation alone.
Recently, S-glutathionylation of critical cysteines of the eNOS reductase domain was identified as yet another fundamental mechanism of eNOS uncoupling, in this case triggered by increased levels of GSSG.41,51 To elicit this post-translational modification, endothelial cells were treated with BCNU or modified by molecular genetic manipulation to inhibit glutathione reductase (GR), leading to an increase in the intracellular GSSG concentration.41,51,59 However, the post-translational modification of this thiol redox switch on eNOS function in the process of ED following the pathophysiological stress of H/R remained unexplored.
Oxidative stress significantly increases the GSSG/GSH ratio in the heart, and preventing this increase by scavenging the generated ROS is associated with a decrease in GSSG concentration and higher recovery of heart function.4,42,60 Therefore, we first investigated whether an increased GSSG/GSH ratio occurred and was proportional to a decrease in NO production and an increase in O2•– formation, and secondarily if a consequent S-glutathionylation of eNOS represented an additional mechanism of eNOS uncoupling. Consistent with this hypothesis, the S-glutathionylation of eNOS was proportional to the increase in the intracellular GSSG/GSH ratio detected in endothelial cells after H/R. It was further shown that increasing the GSH pool through administration of its precursor, N-acetyl-l-cysteine (NAC), increased the eNOS activity after H/R with a decrease in the level of eNOS S-glutathionylation.
While the interplay between these two mechanisms of eNOS uncoupling requires further investigation, we observed that the effects on eNOS are additive and reversible by saturating the enzyme with BH4 together with enhancing the intracellular GSH pool, thus preventing or reversing the S-glutathionylation. With supplementation of both BH4 and NAC, the highest recovery of NO production was observed.
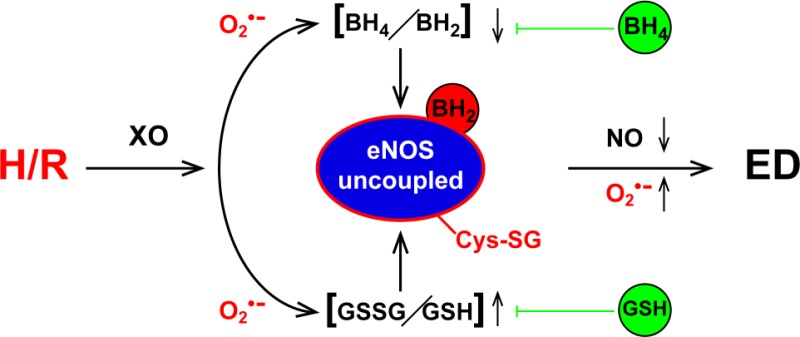
The overall scenario that occurs in endothelial cells under the oxidative stress associated with H/R was found to be predominantly XO-driven, triggering BH4 oxidation, with a concomitant increase in the level of BH2. Thus, the pteridine ratio dramatically shifts toward the oxidized pteridine. In parallel, the O2•– and secondary ROS generated oxidize the GSH pool and thus activate the process of S-glutathionylation because of an increase in the intracellular GSSG concentration, resulting in further uncoupling and enhanced production of O2•– from eNOS (Figure 7).
Figure 7.
Modulation of eNOS by H/R. BAECs under H/R show increased production of O2•– mainly generated by XO. As a consequence, the intracellular redox state is shifted toward oxidation with an increase in GSSG over GSH in parallel with an increase in the oxidized form of the eNOS cofactor, BH2 over BH4. The oxidative shift of these two ratios ultimately uncouples eNOS via two mechanisms. An increased GSSG/GSH ratio generates S-glutathionylation of critical cysteines in the reductase domains of eNOS, resulting in O2•– production from the flavins, while a decrease in the BH4/BH2 ratio uncouples the oxidase domains either by BH2 outcompeting BH4 or by loss of a cofactor leading to the production of O2•– from the heme centers. Overall, uncoupled eNOS contributes to O2•– production, exacerbating the cellular oxidative state. Depletion of BH4 and NAC effectively recouples eNOS by replenishing cofactor and by deglutathionylation, respectively. The eNOS schematic structure is based on the work of Garcin et al.63
Although other mechanisms besides ROS formation are reported to influence eNOS uncoupling, including l-arginine depletion and methylarginine competition for the catalytic site of eNOS,61,62 the significant recovery of NO production shown here in cells undergoing H/R with co-administration of BH4 and NAC to address the cofactor oxidation and to reverse S-glutathionylation, respectively, emphasizes not only a primary role for these two phenomena over the others but also the effectiveness of this cotreatment in recovering nearly complete eNOS function. In addition, the impact of a larger intracellular GSH pool may reduce the negative consequences of O2•– production, acting directly as a physiological ROS scavenger.60
Taken together, the two mechanisms of eNOS uncoupling are thus having an additive detrimental effect on NO synthesis. Nonetheless, it is worth noting that BH4 depletion will affect the increased level of O2•– production from the eNOS oxygenase domain, thereby exacerbating oxidative stress, possibly leading to irreversible protein modification, while S-glutathionylation of eNOS may not be as detrimental to cellular homeostasis because of its reversibility. The reversible S-glutathionylation of eNOS allows recoupling of the enzyme once the endothelial cells re-establish a physiological redox state. In this sense, eNOS-SG works as a switch regulated by the cellular oxidative state expressed by the GSSG/GSH ratio. In this scenario, glutathione reductase (GR), which regulates this ratio, would also play a critical role in actively controlling the process of eNOS-SG, as can be inferred from prior reports.41,59
In conclusion, this work provides important insights into the consequences of redox stress on eNOS function and NO production in endothelial cells. While most O2•– generation in this adherent endothelial cell model undergoing H/R is shown to be initially driven by xanthine oxidase, this in turn leads to eNOS uncoupling through two distinct mechanisms. Both BH4 depletion and GSSG/GSH-dependent S-glutathionylation serve as important mechanisms by which eNOS is uncoupled in BAECs undergoing H/R. These findings suggest that the combination of O2•–-mediated BH4 depletion and redox-regulated eNOS S-glutathionylation trigger eNOS dysfunction and uncoupling in the endothelium under conditions of hypoxia and reoxygenation that occurs in I/R injury in tissues. As such, these results suggest that for optimal therapy to reduce the extent of endothelial dysfunction a combined approach to replenish BH4 and restore intracellular thiol redox balance will be required.
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Yangping Liu who synthesized the superoxide probe CT-02H used in these studies. We also thank Tina Nicole Burger for preparation of the illustration presented in Figure 7.
Glossary
Abbreviations
- H/R
hypoxia and reoxygenation
- BH4
tetrahydrobiopterin
- BH2
dihydrobiopterin
- GSSG
glutathione disulfide
- eNOS or NOS3
endothelial nitric oxide synthase
- eNOS-SG
eNOS S-glutathionylation
- NAC
N-acetyl-l-cysteine
- ED
endothelial dysfunction
- I/R
ischemia-reperfusion
- ROS
reactive oxygen species
- RNS
reactive nitrogen species
- O2•–
superoxide
- XO
xanthine oxidase
- XDH
xanthine dehydrogenase
- AO
aldehyde oxidase
- HX
hypoxanthine
- X
xanthine
- SODm
Mn(III)TBAP.
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health Grants HL038324, EB004900, and EB016096 (J.L.Z.) and HL103846 (C.-A.C.).
Funding Statement
National Institutes of Health, United States
References
- Halcox J. P.; Schenke W. H.; Zalos G.; Mincemoyer R.; Prasad A.; Waclawiw M. A.; Nour K. R.; Quyyumi A. A. (2002) Prognostic value of coronary vascular endothelial dysfunction. Circulation 106, 653–658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schachinger V.; Britten M. B.; Zeiher A. M. (2000) Prognostic impact of coronary vasodilator dysfunction on adverse long-term outcome of coronary heart disease. Circulation 101, 1899–1906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suwaidi J. A.; Hamasaki S.; Higano S. T.; Nishimura R. A.; Holmes D. R. Jr.; Lerman A. (2000) Long-term follow-up of patients with mild coronary artery disease and endothelial dysfunction. Circulation 101, 948–954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceconi C.; Bernocchi P.; Boraso A.; Cargnoni A.; Pepi P.; Curello S.; Ferrari R. (2000) New insights on myocardial pyridine nucleotides and thiol redox state in ischemia and reperfusion damage. Cardiovasc. Res. 47, 586–594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar V.; Kleffmann T.; Hampton M. B.; Cannell M. B.; Winterbourn C. C. (2013) Redox proteomics of thiol proteins in mouse heart during ischemia/reperfusion using ICAT reagents and mass spectrometry. Free Radical Biol. Med. 58, 109–117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao L.; Jiao X.; Gao E.; Lau W. B.; Yuan Y.; Lopez B.; Christopher T.; RamachandraRao S. P.; Williams W.; Southan G.; Sharma K.; Koch W.; Ma X. L. (2006) Nitrative inactivation of thioredoxin-1 and its role in postischemic myocardial apoptosis. Circulation 114, 1395–1402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry C. E.; Hare J. M. (2004) Xanthine oxidoreductase and cardiovascular disease: Molecular mechanisms and pathophysiological implications. J. Physiol. 555, 589–606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griendling K. K.; Sorescu D.; Ushio-Fukai M. (2000) NAD(P)H oxidase: Role in cardiovascular biology and disease. Circ. Res. 86, 494–501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kundu T. K.; Hille R.; Velayutham M.; Zweier J. L. (2007) Characterization of superoxide production from aldehyde oxidase: An important source of oxidants in biological tissues. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 460, 113–121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H.; Cui H.; Kundu T. K.; Alzawahra W.; Zweier J. L. (2008) Nitric oxide production from nitrite occurs primarily in tissues not in the blood: Critical role of xanthine oxidase and aldehyde oxidase. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 17855–17863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano P. J.; Ito Y.; Tornheim K.; Gallop P. M.; Tauber A. I.; Cohen R. A. (1995) An NADPH oxidase superoxide-generating system in the rabbit aorta. Am. J. Physiol. 268, H2274–H2280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa T.; Edelstein D.; Du X. L.; Yamagishi S.; Matsumura T.; Kaneda Y.; Yorek M. A.; Beebe D.; Oates P. J.; Hammes H. P.; Giardino I.; Brownlee M. (2000) Normalizing mitochondrial superoxide production blocks three pathways of hyperglycaemic damage. Nature 404, 787–790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page M. M.; Robb E. L.; Salway K. D.; Stuart J. A. (2010) Mitochondrial redox metabolism: Aging, longevity and dietary effects. Mech. Ageing Dev. 131, 242–252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori M.; Gotoh K.; Kitakaze M.; Iwai K.; Iwakura K.; Sato H.; Koretsune Y.; Inoue M.; Kitabatake A.; Kamada T. (1991) Role of oxygen-derived free radicals in myocardial edema and ischemia in coronary microvascular embolization. Circulation 84, 828–840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCord J. M. (1985) Oxygen-derived free radicals in postischemic tissue injury. N. Engl. J. Med. 312, 159–163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks D. A.; Granger D. N. (1983) Ischemia-induced vascular changes: Role of xanthine oxidase and hydroxyl radicals. Am. J. Physiol. 245, G285–G289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xia Y.; Khatchikian G.; Zweier J. L. (1996) Adenosine deaminase inhibition prevents free radical-mediated injury in the postischemic heart. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 10096–10102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson-Gorman S. L.; Zweier J. L. (1990) Evaluation of the role of xanthine oxidase in myocardial reperfusion injury. J. Biol. Chem. 265, 6656–6663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweier J. L.; Kuppusamy P.; Thompson-Gorman S.; Klunk D.; Lutty G. A. (1994) Measurement and characterization of free radical generation in reoxygenated human endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. 266, C700–C708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xia Y.; Zweier J. L. (1995) Substrate control of free radical generation from xanthine oxidase in the postischemic heart. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 18797–18803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishino T.; Okamoto K.; Kawaguchi Y.; Hori H.; Matsumura T.; Eger B. T.; Pai E. F. (2005) Mechanism of the conversion of xanthine dehydrogenase to xanthine oxidase: Identification of the two cysteine disulfide bonds and crystal structure of a non-convertible rat liver xanthine dehydrogenase mutant. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 24888–24894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuehr D. J.; Kwon N. S.; Nathan C. F.; Griffith O. W.; Feldman P. L.; Wiseman J. (1991) Nω-Hydroxy-l-arginine is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of nitric oxide from l-arginine. J. Biol. Chem. 266, 6259–6263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marletta M. A. (1994) Nitric oxide synthase: Aspects concerning structure and catalysis. Cell 78, 927–930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurshman A. R.; Krebs C.; Edmondson D. E.; Huynh B. H.; Marletta M. A. (1999) Formation of a pterin radical in the reaction of the heme domain of inducible nitric oxide synthase with oxygen. Biochemistry 38, 15689–15696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuehr D. J. (2004) Enzymes of the l-arginine to nitric oxide pathway. J. Nutr. 134, 2748S–2751S, discussion 2765S–2767S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alderton W. K.; Cooper C. E.; Knowles R. G. (2001) Nitric oxide synthases: Structure, function and inhibition. Biochem. J. 357, 593–615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papapetropoulos A.; Rudic R. D.; Sessa W. C. (1999) Molecular control of nitric oxide synthases in the cardiovascular system. Cardiovasc. Res. 43, 509–520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith O. W.; Stuehr D. J. (1995) Nitric oxide synthases: Properties and catalytic mechanism. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 57, 707–736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox J. N.; Subramanian R. R.; Sundell C. L.; Tracey W. R.; Pollock J. S.; Harrison D. G.; Marsden P. A. (1997) Expression of multiple isoforms of nitric oxide synthase in normal and atherosclerotic vessels. Arterioscler., Thromb., Vasc. Biol. 17, 2479–2488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz P. A.; Garvin J. L. (2003) Cardiovascular and renal control in NOS-deficient mouse models. Am. J. Physiol. 284, R628–R638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zulueta J. J.; Sawhney R.; Kayyali U.; Fogel M.; Donaldson C.; Huang H.; Lanzillo J. J.; Hassoun P. M. (2002) Modulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase by hypoxia in pulmonary artery endothelial cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 26, 22–30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann A.; Gloe T.; Pohl U. (2001) Hypoxia-induced upregulation of eNOS gene expression is redox-sensitive: A comparison between hypoxia and inhibitors of cell metabolism. J. Cell. Physiol. 188, 33–44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauersachs J.; Bouloumie A.; Fraccarollo D.; Hu K.; Busse R.; Ertl G. (1999) Endothelial dysfunction in chronic myocardial infarction despite increased vascular endothelial nitric oxide synthase and soluble guanylate cyclase expression: Role of enhanced vascular superoxide production. Circulation 100, 292–298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosentino F.; Hishikawa K.; Katusic Z. S.; Luscher T. F. (1997) High glucose increases nitric oxide synthase expression and superoxide anion generation in human aortic endothelial cells. Circulation 96, 25–28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hink U.; Li H.; Mollnau H.; Oelze M.; Matheis E.; Hartmann M.; Skatchkov M.; Thaiss F.; Stahl R. A.; Warnholtz A.; Meinertz T.; Griendling K.; Harrison D. G.; Forstermann U.; Munzel T. (2001) Mechanisms underlying endothelial dysfunction in diabetes mellitus. Circ. Res. 88, E14–E22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouloumie A.; Bauersachs J.; Linz W.; Scholkens B. A.; Wiemer G.; Fleming I.; Busse R. (1997) Endothelial dysfunction coincides with an enhanced nitric oxide synthase expression and superoxide anion production. Hypertension 30, 934–941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xia Y.; Zweier J. L. (1997) Superoxide and peroxynitrite generation from inducible nitric oxide synthase in macrophages. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 94, 6954–6958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasquez-Vivar J.; Martasek P.; Whitsett J.; Joseph J.; Kalyanaraman B. (2002) The ratio between tetrahydrobiopterin and oxidized tetrahydrobiopterin analogues controls superoxide release from endothelial nitric oxide synthase: An EPR spin trapping study. Biochem. J. 362, 733–739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabtree M. J.; Hale A. B.; Channon K. M. (2011) Dihydrofolate reductase protects endothelial nitric oxide synthase from uncoupling in tetrahydrobiopterin deficiency. Free Radical Biol. Med. 50, 1639–1646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biondi R.; Ambrosio G.; De Pascali F.; Tritto I.; Capodicasa E.; Druhan L. J.; Hemann C.; Zweier J. L. (2012) HPLC analysis of tetrahydrobiopterin and its pteridine derivatives using sequential electrochemical and fluorimetric detection: Application to tetrahydrobiopterin autoxidation and chemical oxidation. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 520, 7–16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. A.; Wang T. Y.; Varadharaj S.; Reyes L. A.; Hemann C.; Talukder M. A.; Chen Y. R.; Druhan L. J.; Zweier J. L. (2010) S-glutathionylation uncouples eNOS and regulates its cellular and vascular function. Nature 468, 1115–1118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhalla N. S.; Elmoselhi A. B.; Hata T.; Makino N. (2000) Status of myocardial antioxidants in ischemia-reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc. Res. 47, 446–456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decroos C.; Li Y.; Bertho G.; Frapart Y.; Mansuy D.; Boucher J. L. (2009) Oxidation of tris-(p-carboxyltetrathiaaryl)methyl radical EPR probes: Evidence for their oxidative decarboxylation and molecular origin of their specific ability to react with O2. Chem. Commun. 1416–1418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y.; Song Y.; De Pascali F.; Liu X.; Villamena F. A.; Zweier J. L. (2012) Tetrathiatriarylmethyl radical with single aromatic hydrogen as a highly sensitive and specific superoxide probe. Free Radical Biol. Med. 53, 2081–2091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweier J. L.; Kuppusamy P.; Lutty G. A. (1988) Measurement of endothelial cell free radical generation: Evidence for a central mechanism of free radical injury in postischemic tissues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 85, 4046–4050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima T.; Nixon J. C. (1980) Analysis of reduced forms of biopterin in biological tissues and fluids. Anal. Biochem. 102, 176–188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumitrescu C.; Biondi R.; Xia Y.; Cardounel A. J.; Druhan L. J.; Ambrosio G.; Zweier J. L. (2007) Myocardial ischemia results in tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) oxidation with impaired endothelial function ameliorated by BH4. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 104, 15081–15086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xia Y.; Cardounel A. J.; Vanin A. F.; Zweier J. L. (2000) Electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy with N-methyl-d-glucamine dithiocarbamate iron complexes distinguishes nitric oxide and nitroxyl anion in a redox-dependent manner: Applications in identifying nitrogen monoxide products from nitric oxide synthase. Free Radical Biol. Med. 29, 793–797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. A.; Druhan L. J.; Varadharaj S.; Chen Y. R.; Zweier J. L. (2008) Phosphorylation of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase regulates superoxide generation from the enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 27038–27047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen G. M.; Freeman B. A. (1984) Detection of superoxide generated by endothelial cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 81, 7269–7273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. A.; Lin C. H.; Druhan L. J.; Wang T. Y.; Chen Y. R.; Zweier J. L. (2011) Superoxide induces endothelial nitric-oxide synthase protein thiyl radical formation, a novel mechanism regulating eNOS function and coupling. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 29098–29107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- List B. M.; Klosch B.; Volker C.; Gorren A. C.; Sessa W. C.; Werner E. R.; Kukovetz W. R.; Schmidt K.; Mayer B. (1997) Characterization of bovine endothelial nitric oxide synthase as a homodimer with down-regulated uncoupled NADPH oxidase activity: Tetrahydrobiopterin binding kinetics and role of haem in dimerization. Biochem. J. 323(Part 1), 159–165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasquez-Vivar J.; Kalyanaraman B.; Martasek P.; Hogg N.; Masters B. S.; Karoui H.; Tordo P.; Pritchard K. A. Jr. (1998) Superoxide generation by endothelial nitric oxide synthase: The influence of cofactors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 95, 9220–9225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xia Y.; Dawson V. L.; Dawson T. M.; Snyder S. H.; Zweier J. L. (1996) Nitric oxide synthase generates superoxide and nitric oxide in arginine-depleted cells leading to peroxynitrite-mediated cellular injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 93, 6770–6774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunnington C.; Van Assche T.; Shirodaria C.; Kylintireas I.; Lindsay A. C.; Lee J. M.; Antoniades C.; Margaritis M.; Lee R.; Cerrato R.; Crabtree M. J.; Francis J. M.; Sayeed R.; Ratnatunga C.; Pillai R.; Choudhury R. P.; Neubauer S.; Channon K. M. (2012) Systemic and vascular oxidation limits the efficacy of oral tetrahydrobiopterin treatment in patients with coronary artery disease. Circulation 125, 1356–1366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroes E.; Kastelein J.; Cosentino F.; Erkelens W.; Wever R.; Koomans H.; Luscher T.; Rabelink T. (1997) Tetrahydrobiopterin restores endothelial function in hypercholesterolemia. J. Clin. Invest. 99, 41–46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malik U. Z.; Hundley N. J.; Romero G.; Radi R.; Freeman B. A.; Tarpey M. M.; Kelley E. E. (2011) Febuxostat inhibition of endothelial-bound XO: Implications for targeting vascular ROS production. Free Radical Biol. Med. 51, 179–184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweier J. L. (1988) Measurement of superoxide-derived free radicals in the reperfused heart. Evidence for a free radical mechanism of reperfusion injury. J. Biol. Chem. 263, 1353–1357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabtree M. J.; Brixey R.; Batchelor H.; Hale A. B.; Channon K. M. (2013) Integrated redox sensor and effector functions for tetrahydrobiopterin- and glutathionylation-dependent endothelial nitric-oxide synthase uncoupling. J. Biol. Chem. 288, 561–569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tritto I.; Duilio C.; Santoro G.; Elia P. P.; Cirillo P.; De Simone C.; Chiariello M.; Ambrosio G. (1998) A short burst of oxygen radicals at reflow induces sustained release of oxidized glutathione from postischemic hearts. Free Radical Biol. Med. 24, 290–297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardounel A. J.; Xia Y.; Zweier J. L. (2005) Endogenous methylarginines modulate superoxide as well as nitric oxide generation from neuronal nitric-oxide synthase: Differences in the effects of monomethyl- and dimethylarginines in the presence and absence of tetrahydrobiopterin. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 7540–7549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Druhan L. J.; Forbes S. P.; Pope A. J.; Chen C. A.; Zweier J. L.; Cardounel A. J. (2008) Regulation of eNOS-Derived Superoxide by Endogenous Methylarginines. Biochemistry. 47, 7256–7263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcin E. D.; Bruns C. M.; Lloyd S. J.; Hosfield D. J.; Tiso M.; Gachhui R.; Stuehr D. J.; Tainer J. A.; Getzoff E. D. (2004) Structural basis for isozyme-specific regulation of electron transfer in nitric-oxide synthase. Biochemistry 279, 37918–37927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]