Abstract
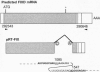
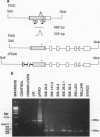
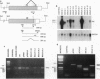
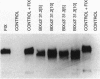
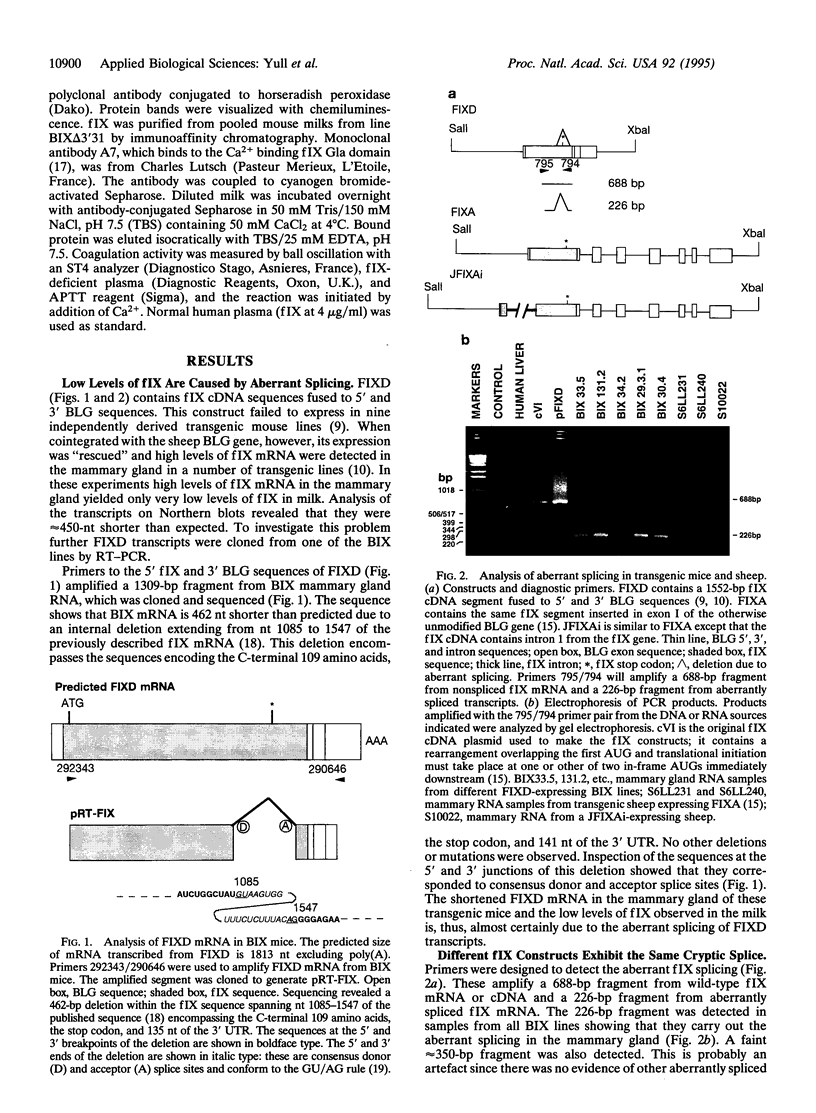
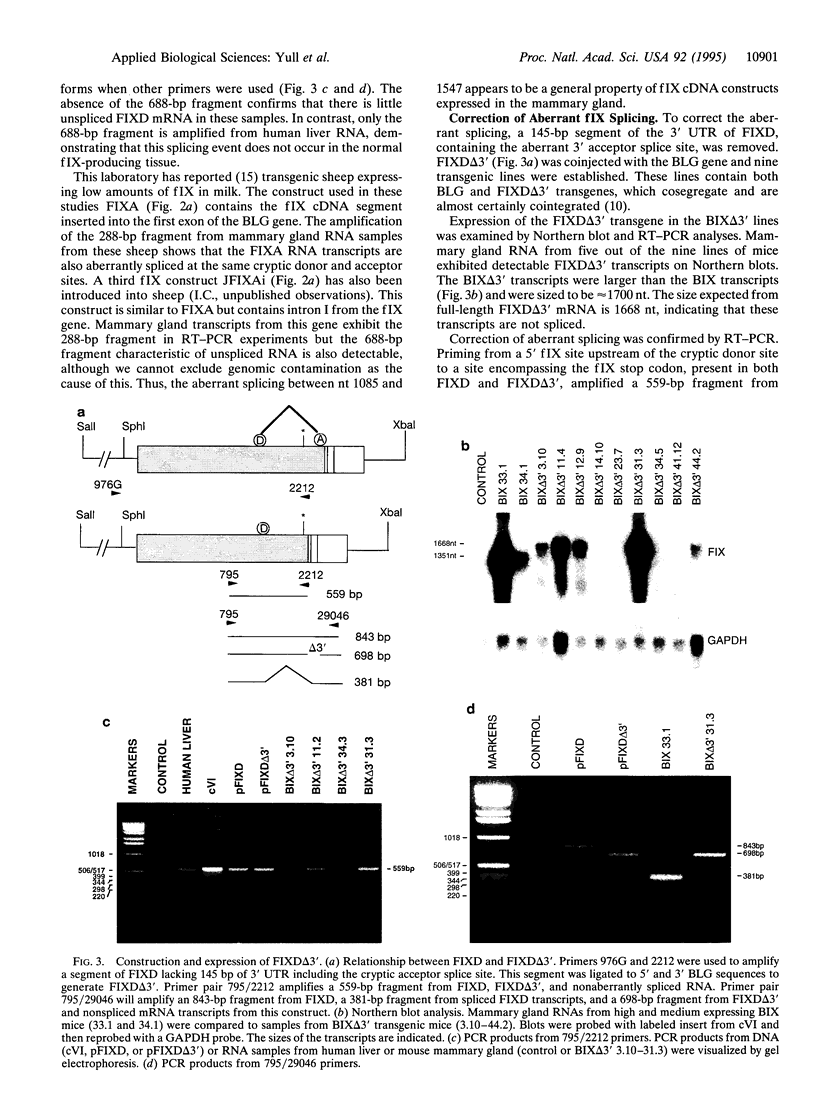
Transgenic mice and sheep secrete only low levels of human factor IX in their milk because of an aberrant splicing of the transgene RNA in the mammary gland. Removal of the cryptic 3' splice site prevents this splicing and leads to the production of relatively high levels of factor IX. The purified protein is fully active showing that the mammary gland is capable of the efficient post-translational modification of this protein and that transgenic animals are a suitable means of its production.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anson D. S., Austen D. E., Brownlee G. G. Expression of active human clotting factor IX from recombinant DNA clones in mammalian cells. Nature. 1985 Jun 20;315(6021):683–685. doi: 10.1038/315683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anson D. S., Choo K. H., Rees D. J., Giannelli F., Gould K., Huddleston J. A., Brownlee G. G. The gene structure of human anti-haemophilic factor IX. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1053–1060. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01926.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archibald A. L., McClenaghan M., Hornsey V., Simons J. P., Clark A. J. High-level expression of biologically active human alpha 1-antitrypsin in the milk of transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5178–5182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balland A., Faure T., Carvallo D., Cordier P., Ulrich P., Fournet B., de la Salle H., Lecocq J. P. Characterisation of two differently processed forms of human recombinant factor IX synthesised in CHO cells transformed with a polycistronic vector. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Mar 15;172(3):565–572. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13926.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkner K. L. Expression of recombinant vitamin K-dependent proteins in mammalian cells: factors IX and VII. Methods Enzymol. 1993;222:450–477. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(93)22029-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee G. G. The molecular pathology of haemophilia B. Fourth Wellcome Trust lecture. Biochem Soc Trans. 1987 Feb;15(1):1–8. doi: 10.1042/bst0150001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carver A. S., Dalrymple M. A., Wright G., Cottom D. S., Reeves D. B., Gibson Y. H., Keenan J. L., Barrass J. D., Scott A. R., Colman A. Transgenic livestock as bioreactors: stable expression of human alpha-1-antitrypsin by a flock of sheep. Biotechnology (N Y) 1993 Nov;11(11):1263–1270. doi: 10.1038/nbt1193-1263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choo K. H., Raphael K., McAdam W., Peterson M. G. Expression of active human blood clotting factor IX in transgenic mice: use of a cDNA with complete mRNA sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):871–884. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark A. J., Cowper A., Wallace R., Wright G., Simons J. P. Rescuing transgene expression by co-integration. Biotechnology (N Y) 1992 Nov;10(11):1450–1454. doi: 10.1038/nbt1192-1450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drohan W. N., Zhang D. W., Paleyanda R. K., Chang R., Wroble M., Velander W., Lubon H. Inefficient processing of human protein C in the mouse mammary gland. Transgenic Res. 1994 Nov;3(6):355–364. doi: 10.1007/BF01976767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ge H., Manley J. L. A protein factor, ASF, controls cell-specific alternative splicing of SV40 early pre-mRNA in vitro. Cell. 1990 Jul 13;62(1):25–34. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90236-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jallat S., Perraud F., Dalemans W., Balland A., Dieterle A., Faure T., Meulien P., Pavirani A. Characterization of recombinant human factor IX expressed in transgenic mice and in derived trans-immortalized hepatic cell lines. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3295–3301. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07529.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T. Mechanisms of alternative pre-mRNA splicing. Science. 1991 Jan 4;251(4989):33–34. doi: 10.1126/science.1824726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meade H., Gates L., Lacy E., Lonberg N. Bovine alpha S1-casein gene sequences direct high level expression of active human urokinase in mouse milk. Biotechnology (N Y) 1990 May;8(5):443–446. doi: 10.1038/nbt0590-443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson K. K., Green M. R. Splice site selection and ribonucleoprotein complex assembly during in vitro pre-mRNA splicing. Genes Dev. 1988 Mar;2(3):319–329. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.3.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R., Maniatis T. A role for exon sequences and splice-site proximity in splice-site selection. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):681–690. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90343-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons J. P., McClenaghan M., Clark A. J. Alteration of the quality of milk by expression of sheep beta-lactoglobulin in transgenic mice. Nature. 1987 Aug 6;328(6130):530–532. doi: 10.1038/328530a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. J. Immunoaffinity purification of factor IX from commercial concentrates and infusion studies in animals. Blood. 1988 Oct;72(4):1269–1277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velander W. H., Johnson J. L., Page R. L., Russell C. G., Subramanian A., Wilkins T. D., Gwazdauskas F. C., Pittius C., Drohan W. N. High-level expression of a heterologous protein in the milk of transgenic swine using the cDNA encoding human protein C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):12003–12007. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.12003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitelaw C. B., Archibald A. L., Harris S., McClenaghan M., Simons J. P., Clark A. J. Targeting expression to the mammary gland: intronic sequences can enhance the efficiency of gene expression in transgenic mice. Transgenic Res. 1991 Dec;1(1):3–13. doi: 10.1007/BF02512991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitelaw C. B., Harris S., McClenaghan M., Simons J. P., Clark A. J. Position-independent expression of the ovine beta-lactoglobulin gene in transgenic mice. Biochem J. 1992 Aug 15;286(Pt 1):31–39. doi: 10.1042/bj2860031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright G., Carver A., Cottom D., Reeves D., Scott A., Simons P., Wilmut I., Garner I., Colman A. High level expression of active human alpha-1-antitrypsin in the milk of transgenic sheep. Biotechnology (N Y) 1991 Sep;9(9):830–834. doi: 10.1038/nbt0991-830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]