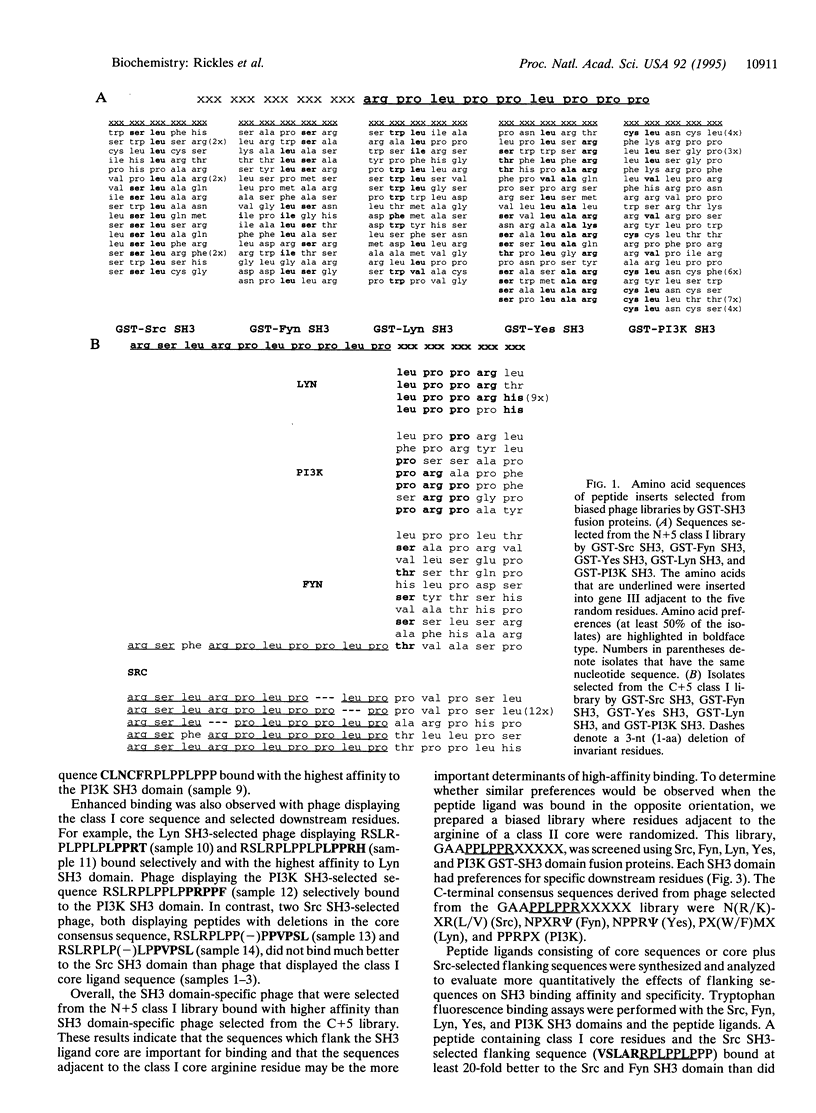
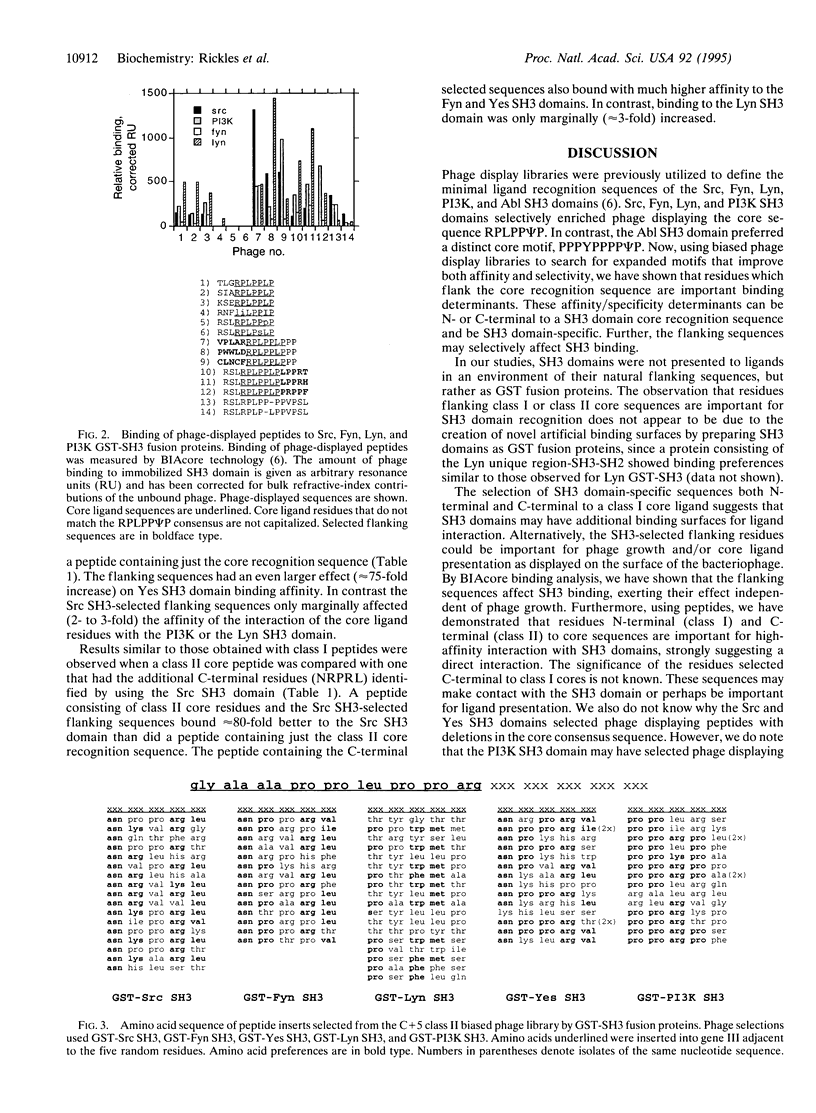
Abstract
The Src homology 3 (SH3) domain is a 50-aa modular unit present in many cellular proteins involved in intracellular signal transduction. It functions to direct protein-protein interactions through the recognition of proline-rich motifs on associated proteins. SH3 domains are important regulatory elements that have been demonstrated to specify distinct regulatory pathways important for cell growth, migration, differentiation, and responses to the external milieu. By the use of synthetic peptides, ligands have been shown to consist of a minimum core sequence and to bind to SH3 domains in one of two pseudosymmetrical orientations, class I and class II. The class I sites have the consensus sequence ZP(L/P)PP psi P whereas the class II consensus is PP psi PPZ (where psi is a hydrophobic residue and Z is a SH3 domain-specific residue). We previously showed by M13 phage display that the Src, Fyn, Lyn, and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) SH3 domains preferred the same class I-type core binding sequence, RPLPP psi P. These results failed to explain the specificity for cellular proteins displayed by SH3 domains in cells. In the current study, class I and class II core ligand sequences were displayed on the surface of bacteriophage M13 with five random residues placed either N- or C-terminal of core ligand residues. These libraries were screened for binding to the Src, Fyn, Lyn, Yes, and PI3K SH3 domains. By this approach, additional ligand residue preferences were identified that can increase the affinity of SH3 peptide ligands at least 20-fold compared with core peptides. The amino acids selected in the flanking sequences were similar for Src, Fyn, and Yes SH3 domains; however, Lyn and PI3K SH3 domains showed distinct binding specificities. These results indicate that residues that flank the core binding sequences shared by many SH3 domains are important determinants of SH3 binding affinity and selectivity.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexandropoulos K., Cheng G., Baltimore D. Proline-rich sequences that bind to Src homology 3 domains with individual specificities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Apr 11;92(8):3110–3114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.8.3110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheadle C., Ivashchenko Y., South V., Searfoss G. H., French S., Howk R., Ricca G. A., Jaye M. Identification of a Src SH3 domain binding motif by screening a random phage display library. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 30;269(39):24034–24039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cicchetti P., Mayer B. J., Thiel G., Baltimore D. Identification of a protein that binds to the SH3 region of Abl and is similar to Bcr and GAP-rho. Science. 1992 Aug 7;257(5071):803–806. doi: 10.1126/science.1379745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. B., Ren R., Baltimore D. Modular binding domains in signal transduction proteins. Cell. 1995 Jan 27;80(2):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90406-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng S., Chen J. K., Yu H., Simon J. A., Schreiber S. L. Two binding orientations for peptides to the Src SH3 domain: development of a general model for SH3-ligand interactions. Science. 1994 Nov 18;266(5188):1241–1247. doi: 10.1126/science.7526465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim W. A., Richards F. M. Critical residues in an SH3 domain from Sem-5 suggest a mechanism for proline-rich peptide recognition. Nat Struct Biol. 1994 Apr;1(4):221–225. doi: 10.1038/nsb0494-221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim W. A., Richards F. M., Fox R. O. Structural determinants of peptide-binding orientation and of sequence specificity in SH3 domains. Nature. 1994 Nov 24;372(6504):375–379. doi: 10.1038/372375a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malmqvist M. Biospecific interaction analysis using biosensor technology. Nature. 1993 Jan 14;361(6408):186–187. doi: 10.1038/361186a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T. Protein modules and signalling networks. Nature. 1995 Feb 16;373(6515):573–580. doi: 10.1038/373573a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren R., Mayer B. J., Cicchetti P., Baltimore D. Identification of a ten-amino acid proline-rich SH3 binding site. Science. 1993 Feb 19;259(5098):1157–1161. doi: 10.1126/science.8438166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickles R. J., Botfield M. C., Weng Z., Taylor J. A., Green O. M., Brugge J. S., Zoller M. J. Identification of Src, Fyn, Lyn, PI3K and Abl SH3 domain ligands using phage display libraries. EMBO J. 1994 Dec 1;13(23):5598–5604. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06897.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnik E. Y., Margolis B., Mohammadi M., Lowenstein E., Fischer R., Drepps A., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Cloning of PI3 kinase-associated p85 utilizing a novel method for expression/cloning of target proteins for receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90410-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Songyang Z., Shoelson S. E., Chaudhuri M., Gish G., Pawson T., Haser W. G., King F., Roberts T., Ratnofsky S., Lechleider R. J. SH2 domains recognize specific phosphopeptide sequences. Cell. 1993 Mar 12;72(5):767–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90404-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparks A. B., Quilliam L. A., Thorn J. M., Der C. J., Kay B. K. Identification and characterization of Src SH3 ligands from phage-displayed random peptide libraries. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 30;269(39):23853–23856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudol M., Kieswetter C., Zhao Y. H., Dorai T., Wang L. H., Hanafusa H. Nucleotide sequence of a cDNA for the chick yes proto-oncogene: comparison with the viral yes gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9876–9876. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weng Z., Thomas S. M., Rickles R. J., Taylor J. A., Brauer A. W., Seidel-Dugan C., Michael W. M., Dreyfuss G., Brugge J. S. Identification of Src, Fyn, and Lyn SH3-binding proteins: implications for a function of SH3 domains. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;14(7):4509–4521. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.7.4509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu H., Chen J. K., Feng S., Dalgarno D. C., Brauer A. W., Schreiber S. L. Structural basis for the binding of proline-rich peptides to SH3 domains. Cell. 1994 Mar 11;76(5):933–945. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90367-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



