Abstract
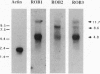
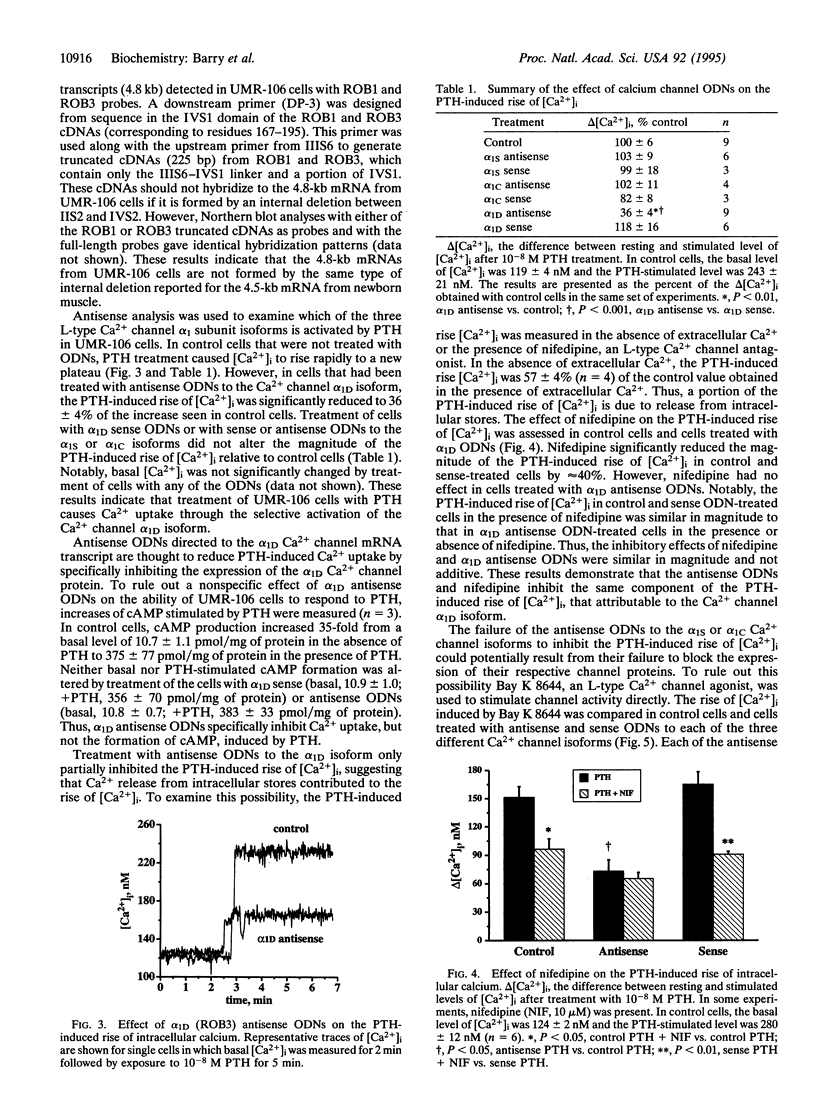
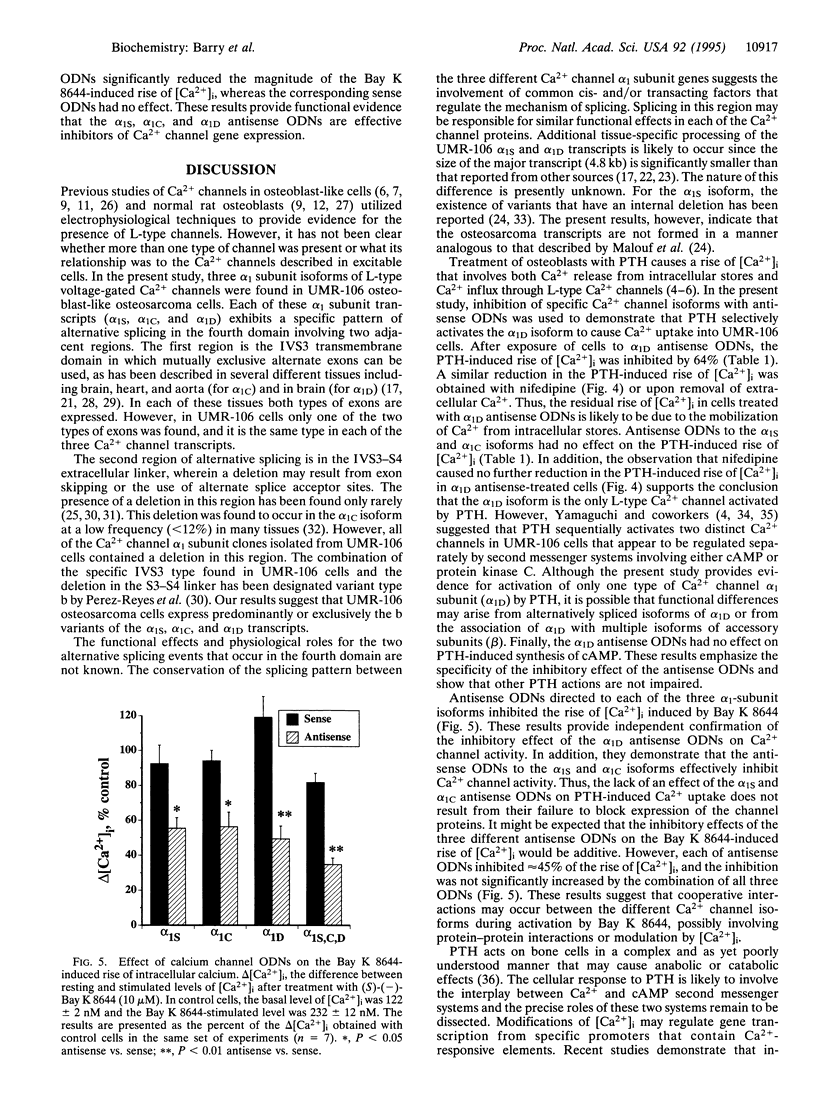
Osteoblasts express calcium channels that are thought to be involved in the transduction of extracellular signals regulating bone metabolism. The molecular identity of the pore-forming subunit (alpha 1) of L-type calcium channel(s) was determined in rat osteosarcoma UMR-106 cells, which express an osteoblast phenotype. A homology-based reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction cloning strategy was employed that used primers spanning the fourth domain. Three types of cDNAs were isolated, corresponding to the alpha 1S (skeletal), alpha 1C (cardiac), and alpha 1D (neuroendocrine) isoforms. In the transmembrane segment IVS3 and the extracellular loop formed by the IVS3-S4 linker, a single pattern of mRNA splicing was found that occurs in all three types of calcium channel transcripts. Northern blot analysis revealed an 8.6-kb mRNA that hybridized to the alpha 1C probe and 4.8- and 11.7-kb mRNAs that hybridized to the alpha 1S and alpha 1D probes. Antisense oligonucleotides directed to the calcium channel alpha 1D transcript, but not those directed to alpha 1S or alpha 1C transcripts, inhibited the rise of intracellular calcium induced by parathyroid hormone. However, alpha 1D antisense oligonucleotides had no effect on the accumulation of cAMP induced by parathyroid hormone. When L-type calcium channels were activated with Bay K 8644, antisense oligonucleotides to each of the three isoforms partially inhibited the rise of intracellular calcium. The present results provide evidence for the expression of three distinct calcium channel alpha 1-subunit isoforms in an osteoblast-like cell line. We conclude that the alpha 1D isoform is selectively activated by parathyroid hormone.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barry E. L., Gesek F. A., Friedman P. A. Introduction of antisense oligonucleotides into cells by permeabilization with streptolysin O. Biotechniques. 1993 Dec;15(6):1016-8, 1020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawley R. M., Hosey M. M. Identification of two distinct proteins that are immunologically related to the alpha 1 subunit of the skeletal muscle dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channel. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):18218–18223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caffrey J. M., Farach-Carson M. C. Vitamin D3 metabolites modulate dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium currents in clonal rat osteosarcoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20265–20274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhari N. A single nucleotide deletion in the skeletal muscle-specific calcium channel transcript of muscular dysgenesis (mdg) mice. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 25;267(36):25636–25639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesnoy-Marchais D., Fritsch J. Voltage-gated sodium and calcium currents in rat osteoblasts. J Physiol. 1988 Apr;398:291–311. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Civitelli R., Kim Y. S., Gunsten S. L., Fujimori A., Huskey M., Avioli L. V., Hruska K. A. Nongenomic activation of the calcium message system by vitamin D metabolites in osteoblast-like cells. Endocrinology. 1990 Nov;127(5):2253–2262. doi: 10.1210/endo-127-5-2253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dempster D. W., Cosman F., Parisien M., Shen V., Lindsay R. Anabolic actions of parathyroid hormone on bone. Endocr Rev. 1993 Dec;14(6):690–709. doi: 10.1210/edrv-14-6-690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diebold R. J., Koch W. J., Ellinor P. T., Wang J. J., Muthuchamy M., Wieczorek D. F., Schwartz A. Mutually exclusive exon splicing of the cardiac calcium channel alpha 1 subunit gene generates developmentally regulated isoforms in the rat heart. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1497–1501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan R., Misler S. Voltage-activated and stretch-activated Ba2+ conducting channels in an osteoblast-like cell line (UMR 106). FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 17;251(1-2):17–21. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81420-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis S. B., Williams M. E., Ways N. R., Brenner R., Sharp A. H., Leung A. T., Campbell K. P., McKenna E., Koch W. J., Hui A. Sequence and expression of mRNAs encoding the alpha 1 and alpha 2 subunits of a DHP-sensitive calcium channel. Science. 1988 Sep 23;241(4873):1661–1664. doi: 10.1126/science.2458626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feron O., Octave J. N., Christen M. O., Godfraind T. Quantification of two splicing events in the L-type calcium channel alpha-1 subunit of intestinal smooth muscle and other tissues. Eur J Biochem. 1994 May 15;222(1):195–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb18857.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gesek F. A., Friedman P. A. Mechanism of calcium transport stimulated by chlorothiazide in mouse distal convoluted tubule cells. J Clin Invest. 1992 Aug;90(2):429–438. doi: 10.1172/JCI115878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grigoriadis A. E., Schellander K., Wang Z. Q., Wagner E. F. Osteoblasts are target cells for transformation in c-fos transgenic mice. J Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;122(3):685–701. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.3.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guggino S. E., Lajeunesse D., Wagner J. A., Snyder S. H. Bone remodeling signaled by a dihydropyridine- and phenylalkylamine-sensitive calcium channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2957–2960. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guggino S. E., Wagner J. A., Snowman A. M., Hester L. D., Sacktor B., Snyder S. H. Phenylalkylamine-sensitive calcium channels in osteoblast-like osteosarcoma cells. Characterization by ligand binding and single channel recordings. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10155–10161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann F., Biel M., Flockerzi V. Molecular basis for Ca2+ channel diversity. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1994;17:399–418. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.17.030194.002151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui A., Ellinor P. T., Krizanova O., Wang J. J., Diebold R. J., Schwartz A. Molecular cloning of multiple subtypes of a novel rat brain isoform of the alpha 1 subunit of the voltage-dependent calcium channel. Neuron. 1991 Jul;7(1):35–44. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90072-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kano J., Sugimoto T., Kanatani M., Kuroki Y., Tsukamoto T., Fukase M., Chihara K. Second messenger signaling of c-fos gene induction by parathyroid hormone (PTH) and PTH-related peptide in osteoblastic osteosarcoma cells: its role in osteoblast proliferation and osteoclast-like cell formation. J Cell Physiol. 1994 Nov;161(2):358–366. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041610221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpinski E., Wu L., Civitelli R., Avioli L. V., Hruska K. A., Pang P. K. A dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channel in rodent osteoblastic cells. Calcif Tissue Int. 1989 Jul;45(1):54–57. doi: 10.1007/BF02556661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch W. J., Ellinor P. T., Schwartz A. cDNA cloning of a dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channel from rat aorta. Evidence for the existence of alternatively spliced forms. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17786–17791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberherr M. Effects of vitamin D3 metabolites on cytosolic free calcium in confluent mouse osteoblasts. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 25;262(27):13168–13173. doi: 10.1515/9783110846713.769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberherr M., Grosse B. Androgens increase intracellular calcium concentration and inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and diacylglycerol formation via a pertussis toxin-sensitive G-protein. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 11;269(10):7217–7223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberherr M., Grosse B., Kachkache M., Balsan S. Cell signaling and estrogens in female rat osteoblasts: a possible involvement of unconventional nonnuclear receptors. J Bone Miner Res. 1993 Nov;8(11):1365–1376. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650081111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loza J., Stephan E., Dolce C., Dziak R., Simasko S. Calcium currents in osteoblastic cells: dependence upon cellular growth stage. Calcif Tissue Int. 1994 Aug;55(2):128–133. doi: 10.1007/BF00297188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malouf N. N., McMahon D. K., Hainsworth C. N., Kay B. K. A two-motif isoform of the major calcium channel subunit in skeletal muscle. Neuron. 1992 May;8(5):899–906. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90204-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikami A., Imoto K., Tanabe T., Niidome T., Mori Y., Takeshima H., Narumiya S., Numa S. Primary structure and functional expression of the cardiac dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channel. Nature. 1989 Jul 20;340(6230):230–233. doi: 10.1038/340230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra R. P., Bonni A., Miranti C. K., Rivera V. M., Sheng M., Greenberg M. E. L-type voltage-sensitive calcium channel activation stimulates gene expression by a serum response factor-dependent pathway. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 14;269(41):25483–25493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morain P., Peglion J. L., Giesen-Crouse E. Ca2+ channel inhibition in a rat osteoblast-like cell line, UMR 106, by a new dihydropyridine derivative, S11568. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Sep 10;220(1):11–17. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90005-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partridge N. C., Alcorn D., Michelangeli V. P., Ryan G., Martin T. J. Morphological and biochemical characterization of four clonal osteogenic sarcoma cell lines of rat origin. Cancer Res. 1983 Sep;43(9):4308–4314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Reyes E., Wei X. Y., Castellano A., Birnbaumer L. Molecular diversity of L-type calcium channels. Evidence for alternative splicing of the transcripts of three non-allelic genes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20430–20436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seino S., Chen L., Seino M., Blondel O., Takeda J., Johnson J. H., Bell G. I. Cloning of the alpha 1 subunit of a voltage-dependent calcium channel expressed in pancreatic beta cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 15;89(2):584–588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.2.584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snutch T. P., Reiner P. B. Ca2+ channels: diversity of form and function. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1992 Jun;2(3):247–253. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(92)90111-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snutch T. P., Tomlinson W. J., Leonard J. P., Gilbert M. M. Distinct calcium channels are generated by alternative splicing and are differentially expressed in the mammalian CNS. Neuron. 1991 Jul;7(1):45–57. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spedding M., Paoletti R. Classification of calcium channels and the sites of action of drugs modifying channel function. Pharmacol Rev. 1992 Sep;44(3):363–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe T., Takeshima H., Mikami A., Flockerzi V., Takahashi H., Kangawa K., Kojima M., Matsuo H., Hirose T., Numa S. Primary structure of the receptor for calcium channel blockers from skeletal muscle. Nature. 1987 Jul 23;328(6128):313–318. doi: 10.1038/328313a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson M. A., Ginty D. D., Bonni A., Greenberg M. E. L-type voltage-sensitive Ca2+ channel activation regulates c-fos transcription at multiple levels. J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 3;270(9):4224–4235. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.9.4224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi D. T., Green J., Kleeman C. R., Muallem S. Characterization of volume-sensitive, calcium-permeating pathways in the osteosarcoma cell line UMR-106-01. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4383–4390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi D. T., Green J., Kleeman C. R., Muallem S. Properties of the depolarization-activated calcium and barium entry in osteoblast-like cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):197–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi D. T., Hahn T. J., Beeker T. G., Kleeman C. R., Muallem S. Relationship of cAMP and calcium messenger systems in prostaglandin-stimulated UMR-106 cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10745–10753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi D. T., Hahn T. J., Iida-Klein A., Kleeman C. R., Muallem S. Parathyroid hormone-activated calcium channels in an osteoblast-like clonal osteosarcoma cell line. cAMP-dependent and cAMP-independent calcium channels. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7711–7718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi D. T., Kleeman C. R., Muallem S. Protein kinase C-activated calcium channel in the osteoblast-like clonal osteosarcoma cell line UMR-106. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):14967–14973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu A. S., Hebert S. C., Brenner B. M., Lytton J. Molecular characterization and nephron distribution of a family of transcripts encoding the pore-forming subunit of Ca2+ channels in the kidney. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10494–10498. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]