Abstract
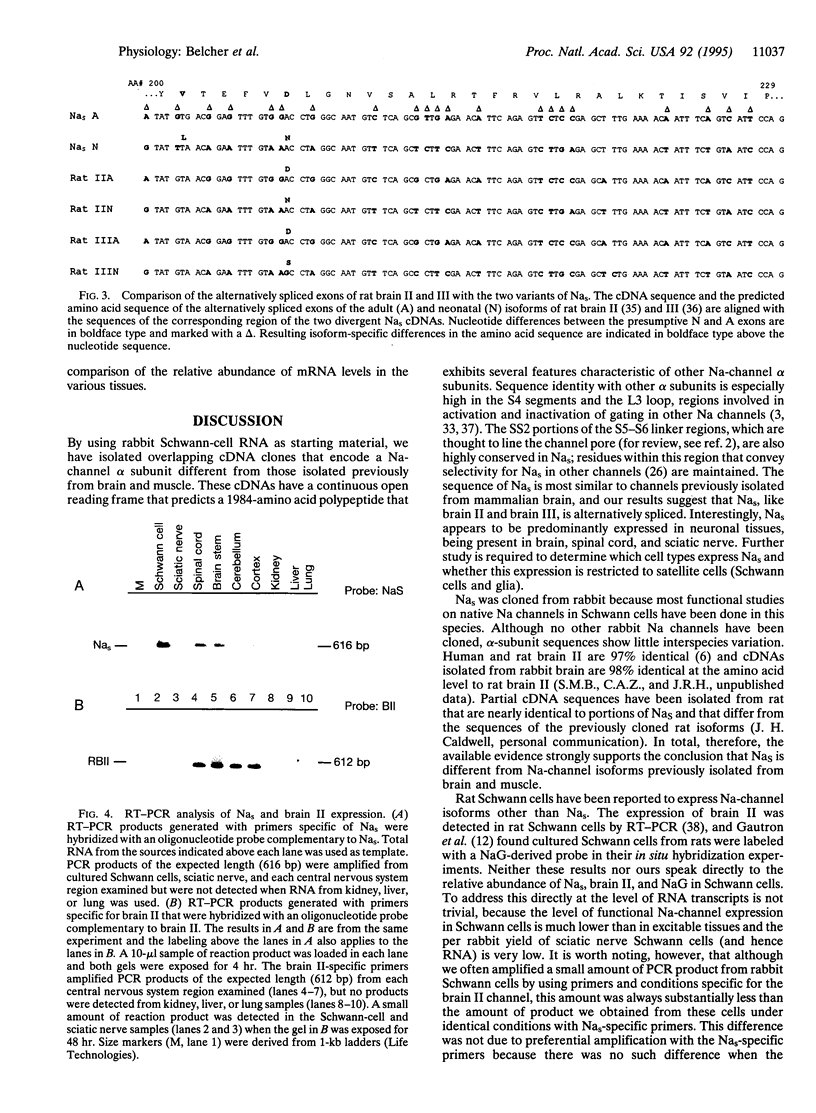
Overlapping cDNA clones spanning the entire coding region of a Na-channel alpha subunit were isolated from cultured Schwann cells from rabbits. The coding region predicts a polypeptide (Nas) of 1984 amino acids exhibiting several features characteristic of Na-channel alpha subunits isolated from other tissues. Sequence comparisons showed that the Nas alpha subunit resembles most the family of Na channels isolated from brain (approximately 80% amino acid identity) and is least similar (approximately 55% amino acid identity) to the atypical Na channel expressed in human heart and the partial rat cDNA, NaG. As for the brain II and III isoforms, two variants of Nas exist that appear to arise by alternative splicing. The results of reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction experiments suggest that expression of Nas transcripts is restricted to cells in the peripheral and central nervous systems. Expression was detected in cultured Schwann cells, sciatic nerve, brain, and spinal cord but not in skeletal or cardiac muscle, liver, kidney, or lung.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed C. M., Ware D. H., Lee S. C., Patten C. D., Ferrer-Montiel A. V., Schinder A. F., McPherson J. D., Wagner-McPherson C. B., Wasmuth J. J., Evans G. A. Primary structure, chromosomal localization, and functional expression of a voltage-gated sodium channel from human brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):8220–8224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auld V. J., Goldin A. L., Krafte D. S., Marshall J., Dunn J. M., Catterall W. A., Lester H. A., Davidson N., Dunn R. J. A rat brain Na+ channel alpha subunit with novel gating properties. Neuron. 1988 Aug;1(6):449–461. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90176-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backx P. H., Yue D. T., Lawrence J. H., Marban E., Tomaselli G. F. Molecular localization of an ion-binding site within the pore of mammalian sodium channels. Science. 1992 Jul 10;257(5067):248–251. doi: 10.1126/science.1321496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Cellular and molecular biology of voltage-gated sodium channels. Physiol Rev. 1992 Oct;72(4 Suppl):S15–S48. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1992.72.suppl_4.S15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Structure and function of voltage-sensitive ion channels. Science. 1988 Oct 7;242(4875):50–61. doi: 10.1126/science.2459775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu S. Y., Schrager P., Ritchie J. M. Neuronal-type Na+ and K+ channels in rabbit cultured Schwann cells. Nature. 1984 Sep 13;311(5982):156–157. doi: 10.1038/311156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Dush M. K., Martin G. R. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8998–9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautron S., Dos Santos G., Pinto-Henrique D., Koulakoff A., Gros F., Berwald-Netter Y. The glial voltage-gated sodium channel: cell- and tissue-specific mRNA expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):7272–7276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.7272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George A. L., Jr, Knittle T. J., Tamkun M. M. Molecular cloning of an atypical voltage-gated sodium channel expressed in human heart and uterus: evidence for a distinct gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):4893–4897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.4893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson T. A., Clevinger E. C., O'Neill T. J., Yarowsky P. J., Krueger B. K. Mutually exclusive exon splicing of type III brain sodium channel alpha subunit RNA generates developmentally regulated isoforms in rat brain. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 5;268(25):18648–18653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinemann S. H., Terlau H., Stühmer W., Imoto K., Numa S. Calcium channel characteristics conferred on the sodium channel by single mutations. Nature. 1992 Apr 2;356(6368):441–443. doi: 10.1038/356441a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe J. R., Ritchie J. M. Multiple kinetic components of sodium channel inactivation in rabbit Schwann cells. J Physiol. 1992 Sep;455:529–566. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe J. R., Ritchie J. M. Sodium currents in Schwann cells from myelinated and non-myelinated nerves of neonatal and adult rabbits. J Physiol. 1990 Jun;425:169–210. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallen R. G., Sheng Z. H., Yang J., Chen L. Q., Rogart R. B., Barchi R. L. Primary structure and expression of a sodium channel characteristic of denervated and immature rat skeletal muscle. Neuron. 1990 Feb;4(2):233–242. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90098-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayano T., Noda M., Flockerzi V., Takahashi H., Numa S. Primary structure of rat brain sodium channel III deduced from the cDNA sequence. FEBS Lett. 1988 Feb 8;228(1):187–194. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80614-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klugbauer N., Lacinova L., Flockerzi V., Hofmann F. Structure and functional expression of a new member of the tetrodotoxin-sensitive voltage-activated sodium channel family from human neuroendocrine cells. EMBO J. 1995 Mar 15;14(6):1084–1090. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07091.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li M., West J. W., Lai Y., Scheuer T., Catterall W. A. Functional modulation of brain sodium channels by cAMP-dependent phosphorylation. Neuron. 1992 Jun;8(6):1151–1159. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90135-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy B. J., Rossie S., De Jongh K. S., Catterall W. A. Identification of the sites of selective phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of the rat brain Na+ channel alpha subunit by cAMP-dependent protein kinase and phosphoprotein phosphatases. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 25;268(36):27355–27362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Ikeda T., Kayano T., Suzuki H., Takeshima H., Kurasaki M., Takahashi H., Numa S. Existence of distinct sodium channel messenger RNAs in rat brain. Nature. 1986 Mar 13;320(6058):188–192. doi: 10.1038/320188a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Shimizu S., Tanabe T., Takai T., Kayano T., Ikeda T., Takahashi H., Nakayama H., Kanaoka Y., Minamino N. Primary structure of Electrophorus electricus sodium channel deduced from cDNA sequence. Nature. 1984 Nov 8;312(5990):121–127. doi: 10.1038/312121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh Y., Black J. A., Waxman S. G. Rat brain Na+ channel mRNAs in non-excitable Schwann cells. FEBS Lett. 1994 Aug 22;350(2-3):342–346. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00807-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton D. E., West J. W., Catterall W. A., Goldin A. L. Amino acid residues required for fast Na(+)-channel inactivation: charge neutralizations and deletions in the III-IV linker. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10905–10909. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putney S. D., Herlihy W. C., Schimmel P. A new troponin T and cDNA clones for 13 different muscle proteins, found by shotgun sequencing. Nature. 1983 Apr 21;302(5910):718–721. doi: 10.1038/302718a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie J. M., Rang H. P. Extraneuronal saxitoxin binding sites in rabbit myelinated nerve. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2803–2807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogart R. B., Cribbs L. L., Muglia L. K., Kephart D. D., Kaiser M. W. Molecular cloning of a putative tetrodotoxin-resistant rat heart Na+ channel isoform. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):8170–8174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.8170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossie S., Catterall W. A. Phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of rat brain sodium channels by cAMP-dependent protein kinase at a new site containing Ser686 and Ser687. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14220–14224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarao R., Gupta S. K., Auld V. J., Dunn R. J. Developmentally regulated alternative RNA splicing of rat brain sodium channel mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 25;19(20):5673–5679. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.20.5673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satin J., Kyle J. W., Chen M., Bell P., Cribbs L. L., Fozzard H. A., Rogart R. B. A mutant of TTX-resistant cardiac sodium channels with TTX-sensitive properties. Science. 1992 May 22;256(5060):1202–1205. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5060.1202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaller K. L., Krzemien D. M., Yarowsky P. J., Krueger B. K., Caldwell J. H. A novel, abundant sodium channel expressed in neurons and glia. J Neurosci. 1995 May;15(5 Pt 1):3231–3242. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-05-03231.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shrager P., Chiu S. Y., Ritchie J. M. Voltage-dependent sodium and potassium channels in mammalian cultured Schwann cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):948–952. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stühmer W., Conti F., Suzuki H., Wang X. D., Noda M., Yahagi N., Kubo H., Numa S. Structural parts involved in activation and inactivation of the sodium channel. Nature. 1989 Jun 22;339(6226):597–603. doi: 10.1038/339597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terlau H., Heinemann S. H., Stühmer W., Pusch M., Conti F., Imoto K., Numa S. Mapping the site of block by tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin of sodium channel II. FEBS Lett. 1991 Nov 18;293(1-2):93–96. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81159-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trimmer J. S., Cooperman S. S., Tomiko S. A., Zhou J. Y., Crean S. M., Boyle M. B., Kallen R. G., Sheng Z. H., Barchi R. L., Sigworth F. J. Primary structure and functional expression of a mammalian skeletal muscle sodium channel. Neuron. 1989 Jul;3(1):33–49. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90113-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West J. W., Numann R., Murphy B. J., Scheuer T., Catterall W. A. A phosphorylation site in the Na+ channel required for modulation by protein kinase C. Science. 1991 Nov 8;254(5033):866–868. doi: 10.1126/science.1658937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West J. W., Patton D. E., Scheuer T., Wang Y., Goldin A. L., Catterall W. A. A cluster of hydrophobic amino acid residues required for fast Na(+)-channel inactivation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10910–10914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]