Abstract
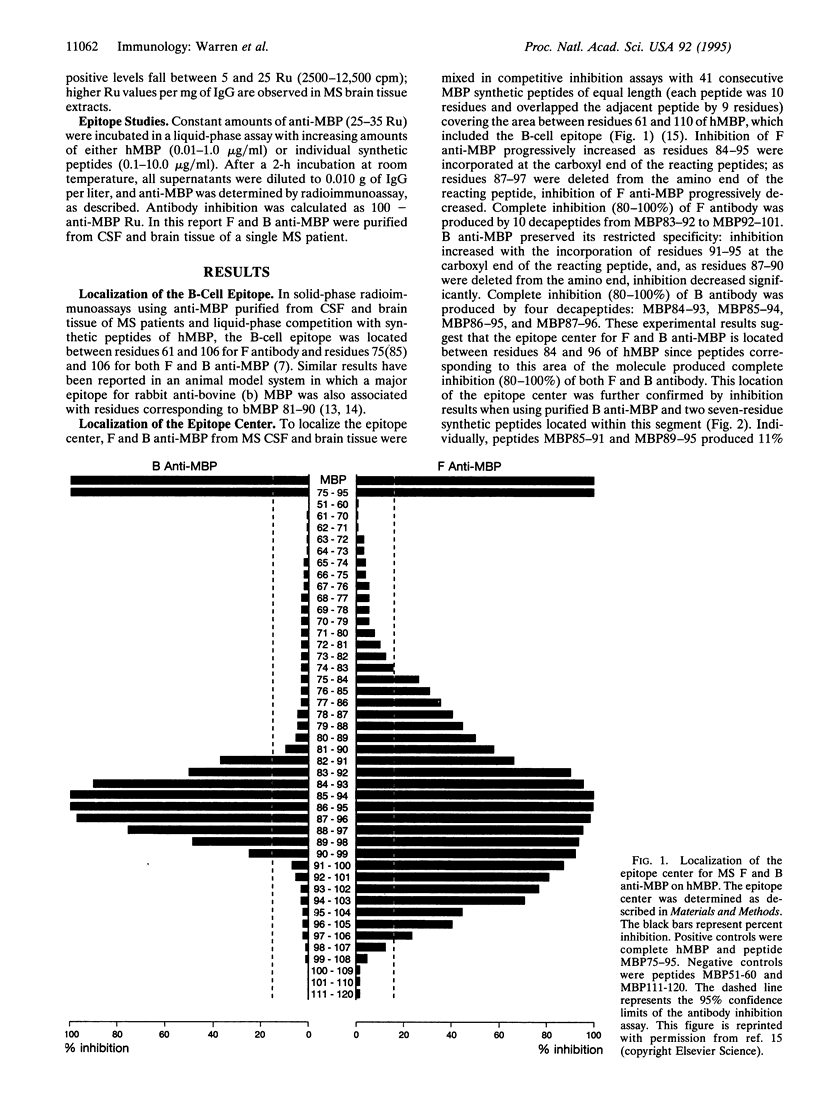
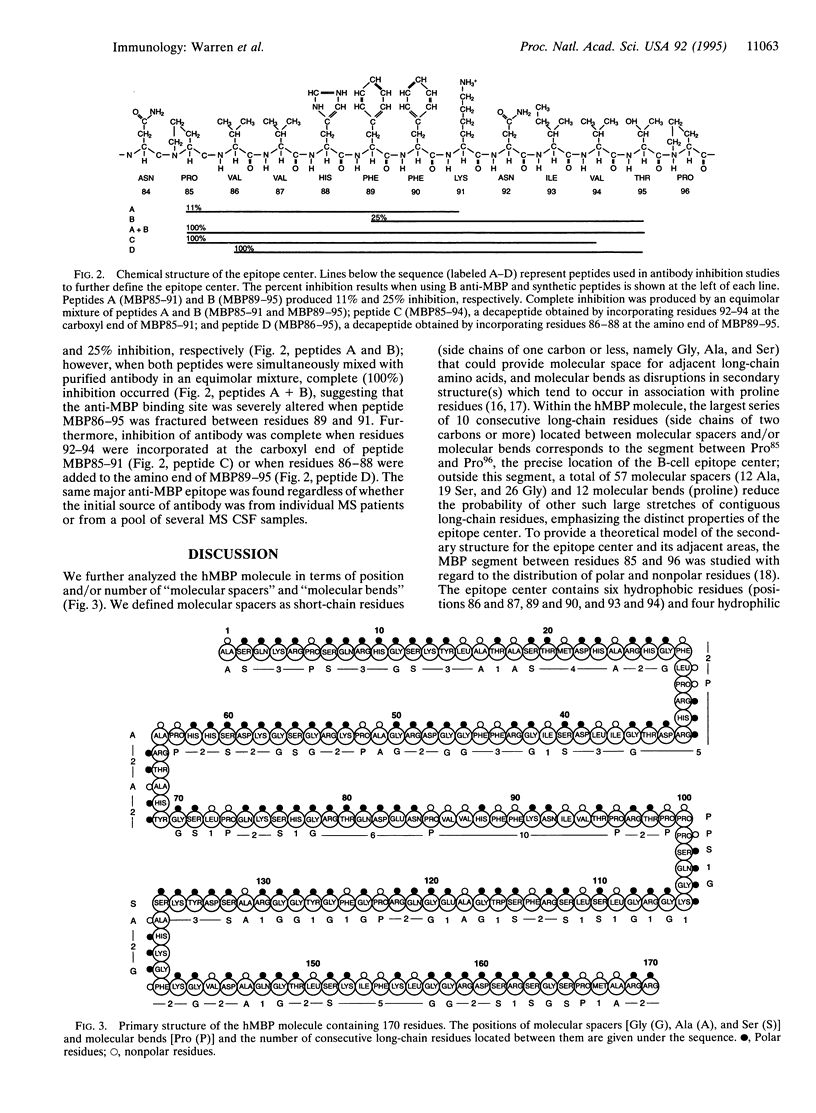
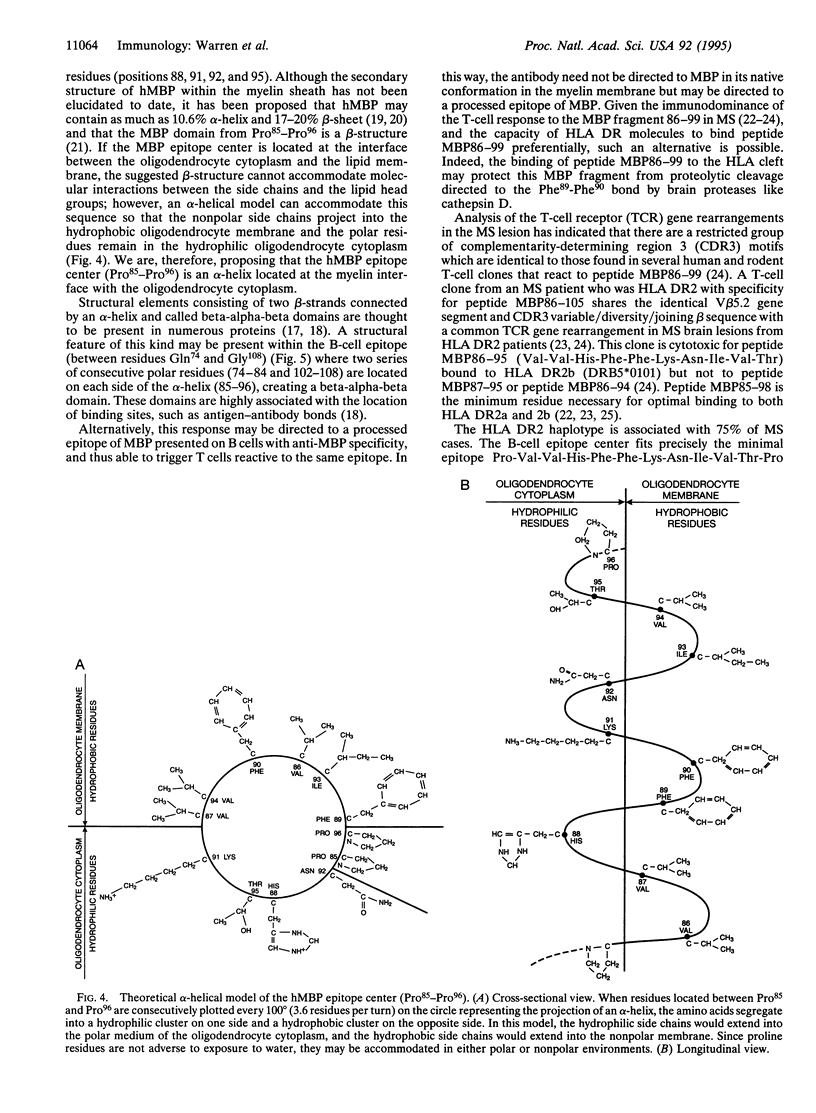
T cells, B cells, and antibody are found in the white matter of the central nervous system in multiple sclerosis. The epitope center for the antibody response to human myelin basic protein (MBP) fits precisely the minimal epitope Pro85-Val-Val-His-Phe-Phe-Lys-Asn-Ile-Val-Thr-Pro96 for that reported for HLA DR2b (DRB1*1501)-restricted T cells that recognize MBP [Wucherpfenning, K.W., Sette, A., Southwood, S., Oseroff, C., Matsui, M., Strominger, J. & Hafler, D. (1994) J. Exp. Med. 179, 279-290], and overlaps with the reported DR2a-restricted epitope for T cells reactive to MBP [Martin, R., Howell, M. D., Jaraquemada, D., Furlage, M., Richert, J., Brostoff, S., Long, E. O., McFarlin, D. E. & McFarland, H. F. (1991) J. Exp. Med. 173, 19-24]. We describe a molecular model of this epitope.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banki K., Colombo E., Sia F., Halladay D., Mattson D. H., Tatum A. H., Massa P. T., Phillips P. E., Perl A. Oligodendrocyte-specific expression and autoantigenicity of transaldolase in multiple sclerosis. J Exp Med. 1994 Nov 1;180(5):1649–1663. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.5.1649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnegie P. R. Amino acid sequence of the encephalitogenic basic protein from human myelin. Biochem J. 1971 Jun;123(1):57–67. doi: 10.1042/bj1230057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye H., Kirschner D. A. Folding and function of the myelin proteins from primary sequence data. J Neurosci Res. 1991 Jan;28(1):1–17. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490280102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin N., Mitchell D. J., Brocke S., Ling N., Steinman L. Reversal of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by a soluble peptide variant of a myelin basic protein epitope: T cell receptor antagonism and reduction of interferon gamma and tumor necrosis factor alpha production. J Exp Med. 1994 Dec 1;180(6):2227–2237. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.6.2227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martenson R. E. Possible hydrophobic region in myelin basic protein consisting of an orthogonally packed beta-sheet. J Neurochem. 1986 May;46(5):1612–1622. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb01784.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R., Howell M. D., Jaraquemada D., Flerlage M., Richert J., Brostoff S., Long E. O., McFarlin D. E., McFarland H. F. A myelin basic protein peptide is recognized by cytotoxic T cells in the context of four HLA-DR types associated with multiple sclerosis. J Exp Med. 1991 Jan 1;173(1):19–24. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oksenberg J. R., Panzara M. A., Begovich A. B., Mitchell D., Erlich H. A., Murray R. S., Shimonkevitz R., Sherritt M., Rothbard J., Bernard C. C. Selection for T-cell receptor V beta-D beta-J beta gene rearrangements with specificity for a myelin basic protein peptide in brain lesions of multiple sclerosis. Nature. 1993 Mar 4;362(6415):68–70. doi: 10.1038/362068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedzik J., Blaurock A. E., Höchli M. Lipid/myelin basic protein multilayers. A model for the cytoplasmic space in central nervous system myelin. J Mol Biol. 1984 Apr 5;174(2):385–409. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90344-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman L. Escape from "horror autotoxicus": pathogenesis and treatment of autoimmune disease. Cell. 1995 Jan 13;80(1):7–10. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90443-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman L., Miller A., Bernard C. C., Oksenberg J. R. The epigenetics of multiple sclerosis: clues to etiology and a rationale for immune therapy. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1994;17:247–265. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.17.030194.001335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman L., Waisman A., Altmann D. Major T-cell responses in multiple sclerosis. Mol Med Today. 1995 May;1(2):79–83. doi: 10.1016/s1357-4310(95)92366-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoner G. L. Predicted folding of beta-structure in myelin basic protein. J Neurochem. 1984 Aug;43(2):433–447. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb00919.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun J., Link H., Olsson T., Xiao B. G., Andersson G., Ekre H. P., Linington C., Diener P. T and B cell responses to myelin-oligodendrocyte glycoprotein in multiple sclerosis. J Immunol. 1991 Mar 1;146(5):1490–1495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valli A., Sette A., Kappos L., Oseroff C., Sidney J., Miescher G., Hochberger M., Albert E. D., Adorini L. Binding of myelin basic protein peptides to human histocompatibility leukocyte antigen class II molecules and their recognition by T cells from multiple sclerosis patients. J Clin Invest. 1993 Feb;91(2):616–628. doi: 10.1172/JCI116242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt A. B., Kropshofer H., Kalbacher H., Kalbus M., Rammensee H. G., Coligan J. E., Martin R. Ligand motifs of HLA-DRB5*0101 and DRB1*1501 molecules delineated from self-peptides. J Immunol. 1994 Aug 15;153(4):1665–1673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren K. G., Catz I. Autoantibodies to myelin basic protein within multiple sclerosis central nervous system tissue. J Neurol Sci. 1993 Apr;115(2):169–176. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(93)90221-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren K. G., Catz I. Increased synthetic peptide specificity of tissue-CSF bound anti-MBP in multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol. 1993 Mar;43(1-2):87–96. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(93)90078-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren K. G., Catz I., Johnson E., Mielke B. Anti-myelin basic protein and anti-proteolipid protein specific forms of multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 1994 Mar;35(3):280–289. doi: 10.1002/ana.410350307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren K. G., Catz I. Purification of autoantibodies to myelin basic protein by antigen specific affinity chromatography from cerebrospinal fluid IgG of multiple sclerosis patients. Immunoreactivity studies with human myelin basic protein. J Neurol Sci. 1991 May;103(1):90–96. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(91)90289-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren K. G., Catz I., Shutt K. Optic neuritis anti-myelin basic protein synthetic peptide specificity. J Neurol Sci. 1992 May;109(1):88–95. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(92)90099-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren K. G., Catz I. Synthetic peptide specificity of anti-myelin basic protein from multiple sclerosis cerebrospinal fluid. J Neuroimmunol. 1992 Jul;39(1-2):81–89. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(92)90177-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker J. N., Chou C. H., Chou F. C., Kibler R. F. Molecular internalization of a region of myelin basic protein. J Exp Med. 1977 Aug 1;146(2):317–331. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.2.317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker J. N., Jen Chou C. H., Chou F. C., Kibler R. F. Antigenic determinants of bovine myelin encephalitogenic protein recognized by rabbit antibody to myelin encephalitogenic protein. J Biol Chem. 1975 Dec 10;250(23):9106–9111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wucherpfennig K. W., Sette A., Southwood S., Oseroff C., Matsui M., Strominger J. L., Hafler D. A. Structural requirements for binding of an immunodominant myelin basic protein peptide to DR2 isotypes and for its recognition by human T cell clones. J Exp Med. 1994 Jan 1;179(1):279–290. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.1.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wucherpfennig K. W., Strominger J. L. Molecular mimicry in T cell-mediated autoimmunity: viral peptides activate human T cell clones specific for myelin basic protein. Cell. 1995 Mar 10;80(5):695–705. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90348-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Barkas T., Juillerat M., Schwendimann B., Wekerle H. T cell epitopes in experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis of the rat: strain-specific epitopes and cross-reaction between two distinct segments of the alpha chain of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (Torpedo californica). Eur J Immunol. 1988 Apr;18(4):551–557. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



