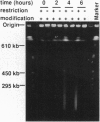
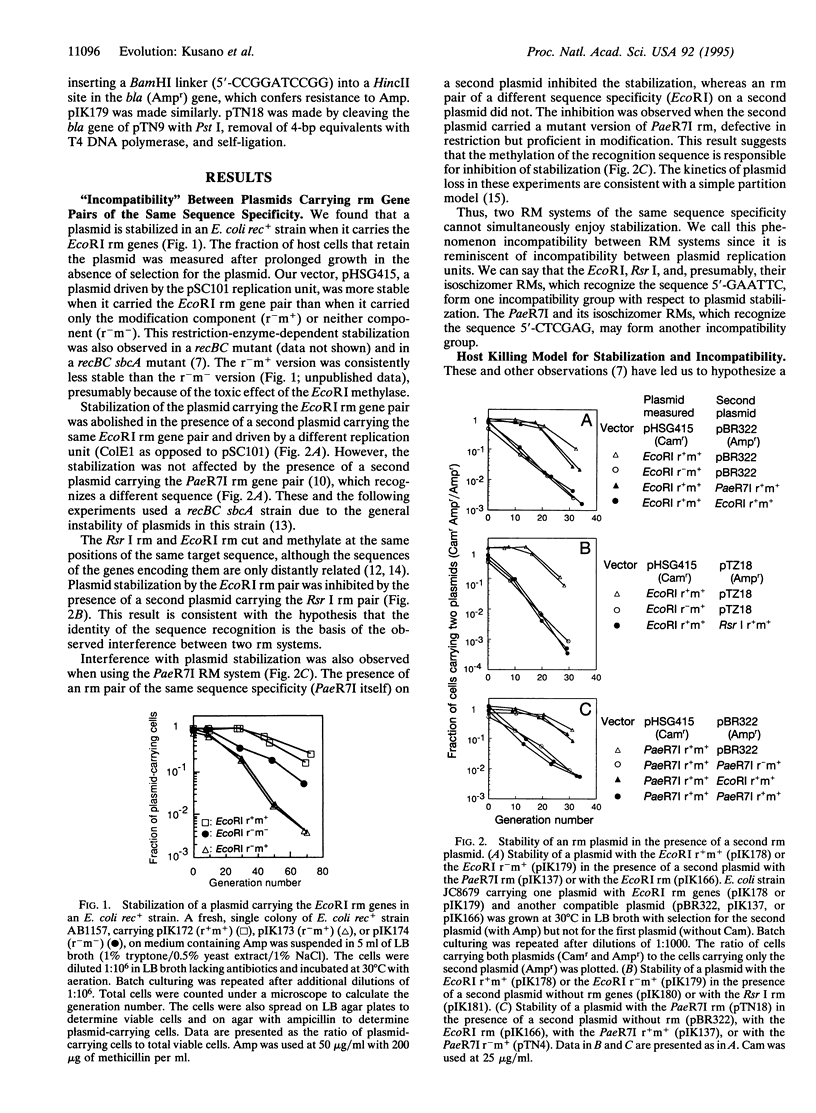
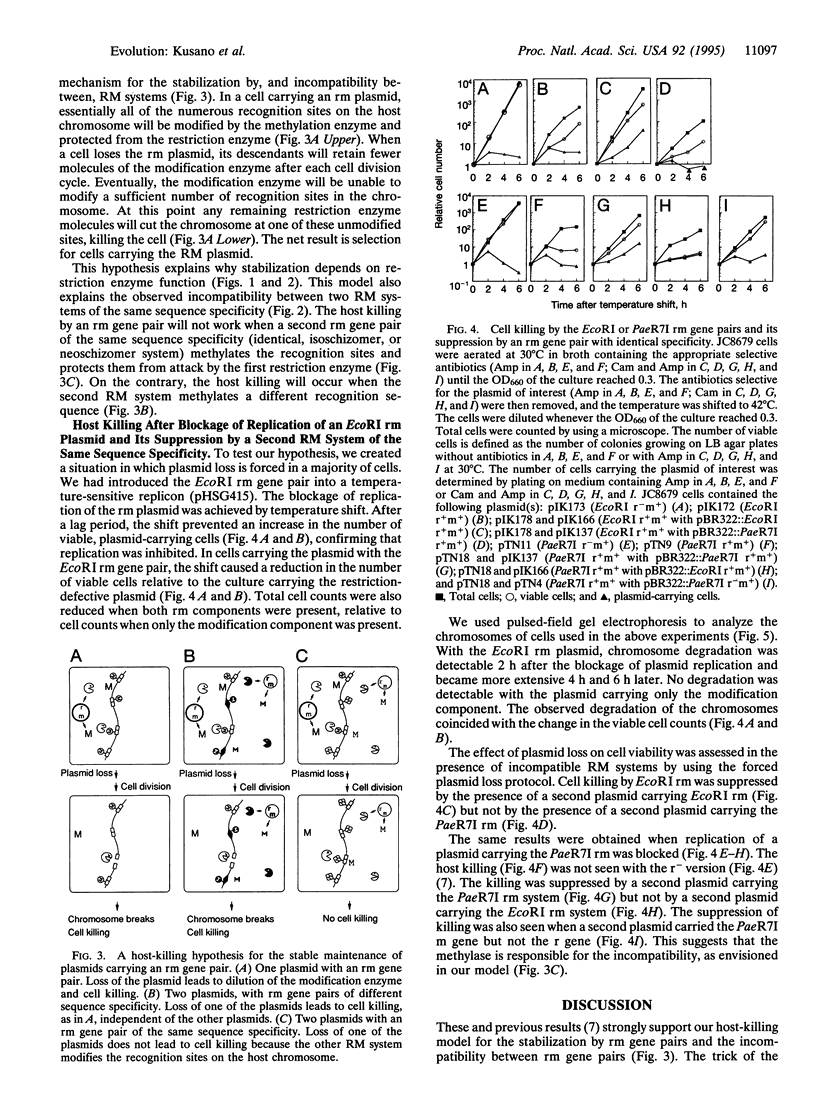
Abstract
Restriction-modification (RM) systems are believed to have evolved to protect cells from foreign DNA. However, this hypothesis may not be sufficient to explain the diversity and specificity in sequence recognition, as well as other properties, of these systems. We report that the EcoRI restriction endonuclease-modification methylase (rm) gene pair stabilizes plasmids that carry it and that this stabilization is blocked by an RM of the same sequence specificity (EcoRI or its isoschizomer, Rsr I) but not by an RM of a different specificity (PaeR7I) on another plasmid. The PaeR7I rm likewise stabilizes plasmids, unless an rm gene pair with identical sequence specificity is present. Our analysis supports the following model for stabilization and incompatibility: the descendants of cells that have lost an rm gene pair expose the recognition sites in their chromosomes to lethal attack by any remaining restriction enzymes unless modification by another RM system of the same specificity protects these sites. Competition for specific sequences among these selfish genes may have generated the great diversity and specificity in sequence recognition among RM systems. Such altruistic suicide strategies, similar to those found in virus-infected cells, may have allowed selfish RM systems to spread by effectively competing with other selfish genes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbeyron T., Kean K., Forterre P. DNA adenine methylation of GATC sequences appeared recently in the Escherichia coli lineage. J Bacteriol. 1984 Nov;160(2):586–590. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.2.586-590.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beeman R. W., Friesen K. S., Denell R. E. Maternal-effect selfish genes in flour beetles. Science. 1992 Apr 3;256(5053):89–92. doi: 10.1126/science.1566060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betlach M., Hershfield V., Chow L., Brown W., Goodman H., Boyer H. W. A restriction endonuclease analysis of the bacterial plasmid controlling the ecoRI restriction and modification of DNA. Fed Proc. 1976 Jul;35(9):2037–2043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bickle T. A., Krüger D. H. Biology of DNA restriction. Microbiol Rev. 1993 Jun;57(2):434–450. doi: 10.1128/mr.57.2.434-450.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull J. J., Molineux I. J., Werren J. H. Selfish genes. Science. 1992 Apr 3;256(5053):65–65. doi: 10.1126/science.1566058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crow J. F. The ultraselfish gene. Genetics. 1988 Mar;118(3):389–391. doi: 10.1093/genetics/118.3.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerdes K., Rasmussen P. B., Molin S. Unique type of plasmid maintenance function: postsegregational killing of plasmid-free cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3116–3120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gingeras T. R., Brooks J. E. Cloned restriction/modification system from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):402–406. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gloor G. B., Nassif N. A., Johnson-Schlitz D. M., Preston C. R., Engels W. R. Targeted gene replacement in Drosophila via P element-induced gap repair. Science. 1991 Sep 6;253(5024):1110–1117. doi: 10.1126/science.1653452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagemann A. T., Craig N. L. Tn7 transposition creates a hotspot for homologous recombination at the transposon donor site. Genetics. 1993 Jan;133(1):9–16. doi: 10.1093/genetics/133.1.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton W. D. The genetical evolution of social behaviour. I. J Theor Biol. 1964 Jul;7(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(64)90038-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto-Gotoh T., Franklin F. C., Nordheim A., Timmis K. N. Specific-purpose plasmid cloning vectors. I. Low copy number, temperature-sensitive, mobilization-defective pSC101-derived containment vectors. Gene. 1981 Dec;16(1-3):227–235. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90079-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heitman J., Model P. Site-specific methylases induce the SOS DNA repair response in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):3243–3250. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.3243-3250.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heitman J., Zinder N. D., Model P. Repair of the Escherichia coli chromosome after in vivo scission by the EcoRI endonuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2281–2285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacoby G. A., Sutton L. Restriction and modification determined by a Pseudomonas R plasmid. Plasmid. 1977 Nov;1(1):115–116. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(77)90012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaszubska W., Aiken C., O'Connor C. D., Gumport R. I. Purification, cloning and sequence analysis of RsrI DNA methyltransferase: lack of homology between two enzymes, RsrI and EcoRI, that methylate the same nucleotide in identical recognition sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 25;17(24):10403–10425. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.24.10403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiss A., Posfai G., Keller C. C., Venetianer P., Roberts R. J. Nucleotide sequence of the BsuRI restriction-modification system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Sep 25;13(18):6403–6421. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.18.6403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi I. Mechanisms for gene conversion and homologous recombination: the double-strand break repair model and the successive half crossing-over model. Adv Biophys. 1992;28:81–133. doi: 10.1016/0065-227x(92)90023-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korona R., Korona B., Levin B. R. Sensitivity of naturally occurring coliphages to type I and type II restriction and modification. J Gen Microbiol. 1993 Jun;139(Pt 6):1283–1290. doi: 10.1099/00221287-139-6-1283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusano K., Nakayama K., Nakayama H. Plasmid-mediated lethality and plasmid multimer formation in an Escherichia coli recBC sbcBC mutant. Involvement of RecF recombination pathway genes. J Mol Biol. 1989 Oct 20;209(4):623–634. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90000-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambowitz A. M., Belfort M. Introns as mobile genetic elements. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:587–622. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.003103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin B. R. Frequency-dependent selection in bacterial populations. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1988 Jul 6;319(1196):459–472. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1988.0059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naito T., Kusano K., Kobayashi I. Selfish behavior of restriction-modification systems. Science. 1995 Feb 10;267(5199):897–899. doi: 10.1126/science.7846533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordström K., Austin S. J. Mechanisms that contribute to the stable segregation of plasmids. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:37–69. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.000345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nölling J., de Vos W. M. Characterization of the archaeal, plasmid-encoded type II restriction-modification system MthTI from Methanobacterium thermoformicicum THF: homology to the bacterial NgoPII system from Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Bacteriol. 1992 Sep;174(17):5719–5726. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.17.5719-5726.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogura T., Hiraga S. Mini-F plasmid genes that couple host cell division to plasmid proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4784–4788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parma D. H., Snyder M., Sobolevski S., Nawroz M., Brody E., Gold L. The Rex system of bacteriophage lambda: tolerance and altruistic cell death. Genes Dev. 1992 Mar;6(3):497–510. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.3.497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters L. L., Barker J. E. Novel inheritance of the murine severe combined anemia and thrombocytopenia (Scat) phenotype. Cell. 1993 Jul 16;74(1):135–142. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90301-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raleigh E. A., Wilson G. Escherichia coli K-12 restricts DNA containing 5-methylcytosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9070–9074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins L. G., Pimpinelli S. Chromosome damage and early developmental arrest caused by the Rex element of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1994 Oct;138(2):401–411. doi: 10.1093/genetics/138.2.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson F. H., Ballard B. T., Boyer H. W., Rosenberg J. M., Greene P. J. Comparison of the nucleotide and amino acid sequences of the RsrI and EcoRI restriction endonucleases. Gene. 1989 Dec 21;85(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90458-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers D. K., Sherratt D. J. Multimerization of high copy number plasmids causes instability: CoIE1 encodes a determinant essential for plasmid monomerization and stability. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):1097–1103. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90060-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N. K., Kusano K., Yokochi T., Kitamura Y., Yoshikura H., Kobayashi I. Genetic analysis of double-strand break repair in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1993 Aug;175(16):5176–5185. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.16.5176-5185.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaux D. L., Haecker G., Strasser A. An evolutionary perspective on apoptosis. Cell. 1994 Mar 11;76(5):777–779. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90350-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade M. J., Beeman R. W. The population dynamics of maternal-effect selfish genes. Genetics. 1994 Dec;138(4):1309–1314. doi: 10.1093/genetics/138.4.1309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson G. G., Murray N. E. Restriction and modification systems. Annu Rev Genet. 1991;25:585–627. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.25.120191.003101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Withers B. E., Ambroso L. A., Dunbar J. C. Structure and evolution of the XcyI restriction-modification system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Dec 11;20(23):6267–6273. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.23.6267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarmolinsky M. B. Programmed cell death in bacterial populations. Science. 1995 Feb 10;267(5199):836–837. doi: 10.1126/science.7846528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu Y. T., Snyder L. Translation elongation factor Tu cleaved by a phage-exclusion system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 18;91(2):802–806. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.2.802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagursky R. J., Berman M. L. Cloning vectors that yield high levels of single-stranded DNA for rapid DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Feb;27(2):183–191. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90139-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]