Abstract
We have been studying the role and mechanism of estrogen action in the survival and differentiation of neurons in the basal forebrain and its targets in the cerebral cortex, hippocampus, and olfactory bulb. Previous work has shown that estrogen-target neurons in these regions widely coexpress the mRNAs for the neurotrophin ligands and their receptors, suggesting a potential substrate for estrogen-neurotrophin interactions. Subsequent work indicated that estrogen regulates the expression of two neurotrophin receptor mRNAs in prototypic peripheral neural targets of nerve growth factor. We report herein that the gene encoding the neurotophin brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) contains a sequence similar to the canonical estrogen response element found in estrogen-target genes. Gel shift and DNA footprinting assays indicate that estrogen receptor-ligand complexes bind to this sequence in the BDNF gene. In vivo, BDNF mRNA was rapidly up-regulated in the cerebral cortex and the olfactory bulb of ovariectomized animals exposed to estrogen. These data suggest that estrogen may regulate BDNF transcription, supporting our hypothesis that estrogen may be in a position to influence neurotrophin-mediated cell functioning, by increasing the availability of specific neurotrophins in forebrain neurons.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alderson R. F., Alterman A. L., Barde Y. A., Lindsay R. M. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor increases survival and differentiated functions of rat septal cholinergic neurons in culture. Neuron. 1990 Sep;5(3):297–306. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90166-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altar C. A., Boylan C. B., Fritsche M., Jones B. E., Jackson C., Wiegand S. J., Lindsay R. M., Hyman C. Efficacy of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3 on neurochemical and behavioral deficits associated with partial nigrostriatal dopamine lesions. J Neurochem. 1994 Sep;63(3):1021–1032. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1994.63031021.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold A. P., Gorski R. A. Gonadal steroid induction of structural sex differences in the central nervous system. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1984;7:413–442. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.07.030184.002213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barde Y. A. Trophic factors and neuronal survival. Neuron. 1989 Jun;2(6):1525–1534. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90040-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bharucha V. A., Peden K. W., Tennekoon G. I. SV40 large T antigen with c-Jun down-regulates myelin P0 gene expression: a mechanism for papovaviral T antigen-mediated demyelination. Neuron. 1994 Mar;12(3):627–637. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90218-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson R. B., Lippman M. E. Estrogenic regulation of growth and polypeptide growth factor secretion in human breast carcinoma. Endocr Rev. 1987 Feb;8(1):29–43. doi: 10.1210/edrv-8-1-29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donovan M. J., Miranda R. C., Kraemer R., McCaffrey T. A., Tessarollo L., Mahadeo D., Sharif S., Kaplan D. R., Tsoulfas P., Parada L. Neurotrophin and neurotrophin receptors in vascular smooth muscle cells. Regulation of expression in response to injury. Am J Pathol. 1995 Aug;147(2):309–324. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dragunow M., Beilharz E., Sirimanne E., Lawlor P., Williams C., Bravo R., Gluckman P. Immediate-early gene protein expression in neurons undergoing delayed death, but not necrosis, following hypoxic-ischaemic injury to the young rat brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1994 Aug;25(1-2):19–33. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(94)90274-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fillit H., Weinreb H., Cholst I., Luine V., McEwen B., Amador R., Zabriskie J. Observations in a preliminary open trial of estradiol therapy for senile dementia-Alzheimer's type. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 1986;11(3):337–345. doi: 10.1016/0306-4530(86)90019-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiser M., Mattaj I. W., Wilks A. F., Seldran M., Jost J. P. Structure and sequence of the promoter area and of a 5' upstream demethylation site of the estrogen-regulated chicken vitellogenin ii gene. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 25;258(14):9024–9030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh A., Carnahan J., Greenberg M. E. Requirement for BDNF in activity-dependent survival of cortical neurons. Science. 1994 Mar 18;263(5153):1618–1623. doi: 10.1126/science.7907431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honjo H., Ogino Y., Naitoh K., Urabe M., Kitawaki J., Yasuda J., Yamamoto T., Ishihara S., Okada H., Yonezawa T. In vivo effects by estrone sulfate on the central nervous system-senile dementia (Alzheimer's type). J Steroid Biochem. 1989;34(1-6):521–525. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(89)90137-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes P., Beilharz E., Gluckman P., Dragunow M. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor is induced as an immediate early gene following N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor activation. Neuroscience. 1993 Nov;57(2):319–328. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(93)90065-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman C., Hofer M., Barde Y. A., Juhasz M., Yancopoulos G. D., Squinto S. P., Lindsay R. M. BDNF is a neurotrophic factor for dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra. Nature. 1991 Mar 21;350(6315):230–232. doi: 10.1038/350230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato S., Tora L., Yamauchi J., Masushige S., Bellard M., Chambon P. A far upstream estrogen response element of the ovalbumin gene contains several half-palindromic 5'-TGACC-3' motifs acting synergistically. Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):731–742. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90148-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein-Hitpass L., Schorpp M., Wagner U., Ryffel G. U. An estrogen-responsive element derived from the 5' flanking region of the Xenopus vitellogenin A2 gene functions in transfected human cells. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1053–1061. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90705-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klungland H., Andersen O., Kisen G., Aleström P., Tora L. Estrogen receptor binds to the salmon GnRH gene in a region with long palindromic sequences. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1993 Sep;95(1-2):147–154. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(93)90040-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knüsel B., Winslow J. W., Rosenthal A., Burton L. E., Seid D. P., Nikolics K., Hefti F. Promotion of central cholinergic and dopaminergic neuron differentiation by brain-derived neurotrophic factor but not neurotrophin 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):961–965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibrock J., Lottspeich F., Hohn A., Hofer M., Hengerer B., Masiakowski P., Thoenen H., Barde Y. A. Molecular cloning and expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Nature. 1989 Sep 14;341(6238):149–152. doi: 10.1038/341149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li L., Oppenheim R. W., Lei M., Houenou L. J. Neurotrophic agents prevent motoneuron death following sciatic nerve section in the neonatal mouse. J Neurobiol. 1994 Jul;25(7):759–766. doi: 10.1002/neu.480250702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maisonpierre P. C., Le Beau M. M., Espinosa R., 3rd, Ip N. Y., Belluscio L., de la Monte S. M., Squinto S., Furth M. E., Yancopoulos G. D. Human and rat brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3: gene structures, distributions, and chromosomal localizations. Genomics. 1991 Jul;10(3):558–568. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90436-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mey J., Thanos S. Intravitreal injections of neurotrophic factors support the survival of axotomized retinal ganglion cells in adult rats in vivo. Brain Res. 1993 Feb 5;602(2):304–317. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)90695-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohr E., Schmitz E. Functional characterization of estrogen and glucocorticoid responsive elements in the rat oxytocin gene. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1991 Mar;9(4):293–298. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(91)90075-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse J. K., Wiegand S. J., Anderson K., You Y., Cai N., Carnahan J., Miller J., DiStefano P. S., Altar C. A., Lindsay R. M. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) prevents the degeneration of medial septal cholinergic neurons following fimbria transection. J Neurosci. 1993 Oct;13(10):4146–4156. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-10-04146.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukku V. R., Stancel G. M. Regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor by estrogen. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 15;260(17):9820–9824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama M., Gahara Y., Kitamura T., Ohara O. Distinctive four promoters collectively direct expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1994 Feb;21(3-4):206–218. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(94)90251-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson K. G., Takahashi T., Bossert N. L., Walmer D. K., McLachlan J. A. Epidermal growth factor replaces estrogen in the stimulation of female genital-tract growth and differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):21–25. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley B. The steroid receptor superfamily: more excitement predicted for the future. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Mar;4(3):363–369. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-3-363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohara O., Gahara Y., Teraoka H., Kitamura T. A rat brain-derived neurotrophic factor-encoding gene generates multiple transcripts through alternative use of 5' exons and polyadenylation sites. Gene. 1992 Nov 16;121(2):383–386. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90148-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips H. S., Hains J. M., Armanini M., Laramee G. R., Johnson S. A., Winslow J. W. BDNF mRNA is decreased in the hippocampus of individuals with Alzheimer's disease. Neuron. 1991 Nov;7(5):695–702. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90273-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Represa J., Avila M. A., Romero G., Mato J. M., Giraldez F., Varela-Nieto I. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3 induce cell proliferation in the cochleovestibular ganglion through a glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol signaling system. Dev Biol. 1993 Sep;159(1):257–265. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1993.1238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sendtner M., Dittrich F., Hughes R. A., Thoenen H. Actions of CNTF and neurotrophins on degenerating motoneurons: preclinical studies and clinical implications. J Neurol Sci. 1994 Jul;124 (Suppl):77–83. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(94)90187-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shupnik M. A., Rosenzweig B. A. Identification of an estrogen-responsive element in the rat LH beta gene. DNA-estrogen receptor interactions and functional analysis. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 15;266(26):17084–17091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
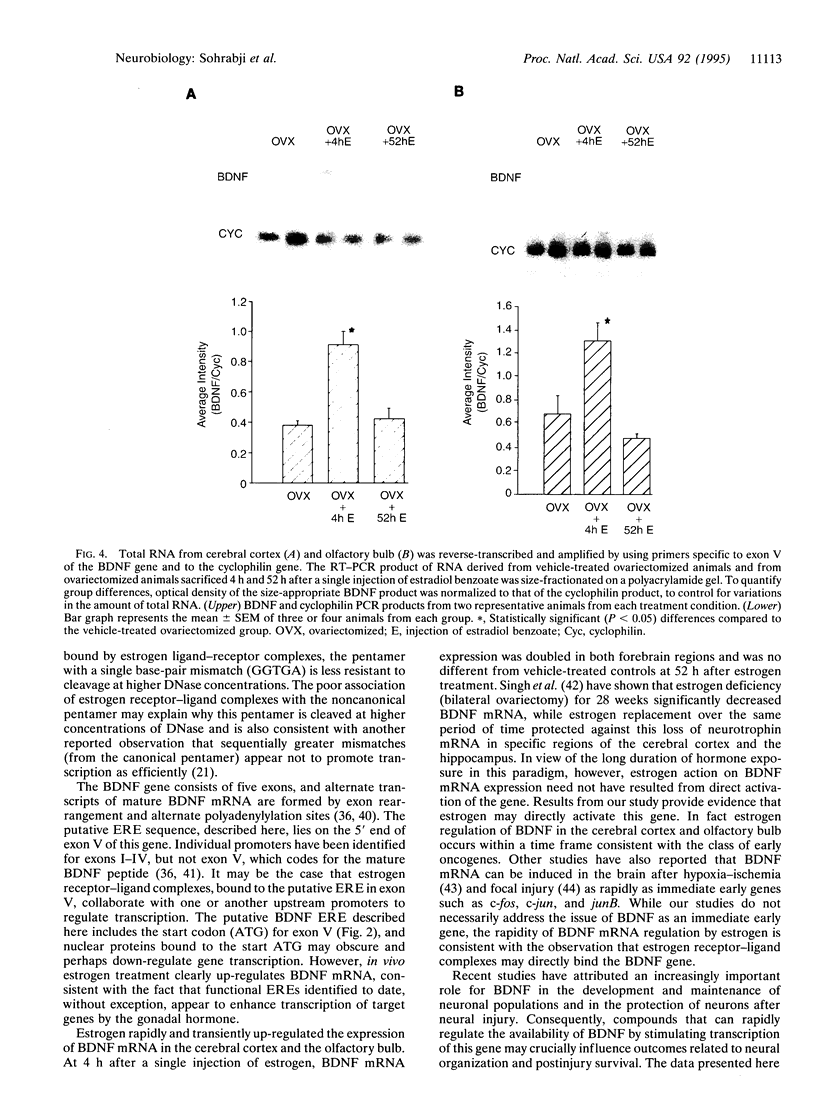
- Singh M., Meyer E. M., Simpkins J. W. The effect of ovariectomy and estradiol replacement on brain-derived neurotrophic factor messenger ribonucleic acid expression in cortical and hippocampal brain regions of female Sprague-Dawley rats. Endocrinology. 1995 May;136(5):2320–2324. doi: 10.1210/endo.136.5.7720680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sohrabji F., Greene L. A., Miranda R. C., Toran-Allerand C. D. Reciprocal regulation of estrogen and NGF receptors by their ligands in PC12 cells. J Neurobiol. 1994 Aug;25(8):974–988. doi: 10.1002/neu.480250807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sohrabji F., Miranda R. C., Toran-Allerand C. D. Estrogen differentially regulates estrogen and nerve growth factor receptor mRNAs in adult sensory neurons. J Neurosci. 1994 Feb;14(2):459–471. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-02-00459.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmusk T., Palm K., Metsis M., Reintam T., Paalme V., Saarma M., Persson H. Multiple promoters direct tissue-specific expression of the rat BDNF gene. Neuron. 1993 Mar;10(3):475–489. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90335-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toran-Allerand C. D., Miranda R. C., Bentham W. D., Sohrabji F., Brown T. J., Hochberg R. B., MacLusky N. J. Estrogen receptors colocalize with low-affinity nerve growth factor receptors in cholinergic neurons of the basal forebrain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4668–4672. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toran-Allerand C. D. On the genesis of sexual differentiation of the general nervous system: morphogenetic consequences of steroidal exposure and possible role of alpha-fetoprotein. Prog Brain Res. 1984;61:63–98. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)64429-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterman M. L., Adler S., Nelson C., Greene G. L., Evans R. M., Rosenfeld M. G. A single domain of the estrogen receptor confers deoxyribonucleic acid binding and transcriptional activation of the rat prolactin gene. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Jan;2(1):14–21. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-1-14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisz A., Rosales R. Identification of an estrogen response element upstream of the human c-fos gene that binds the estrogen receptor and the AP-1 transcription factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 11;18(17):5097–5106. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.17.5097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widmer H. R., Knüsel B., Hefti F. BDNF protection of basal forebrain cholinergic neurons after axotomy: complete protection of p75NGFR-positive cells. Neuroreport. 1993 Apr;4(4):363–366. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199304000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]