Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreae W. A., Good N. E. The Formation of Indoleacetylaspartic Acid in Pea Seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1955 Jul;30(4):380–382. doi: 10.1104/pp.30.4.380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
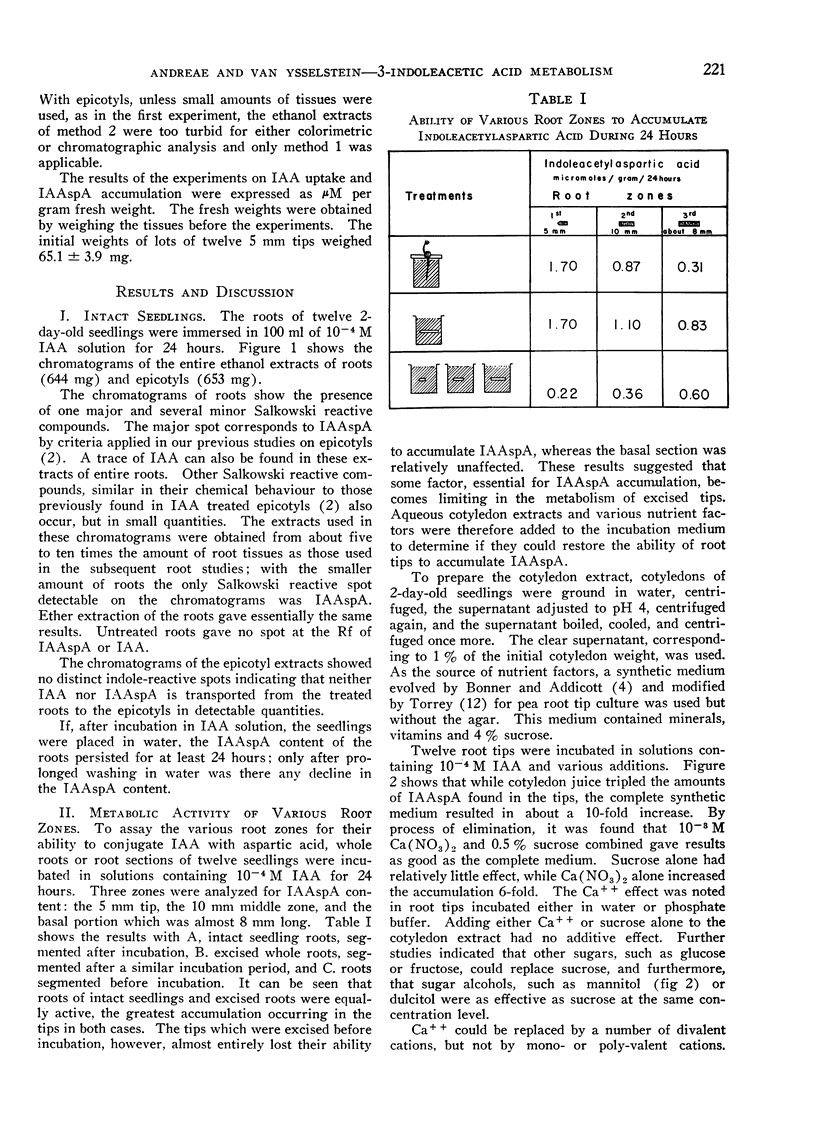
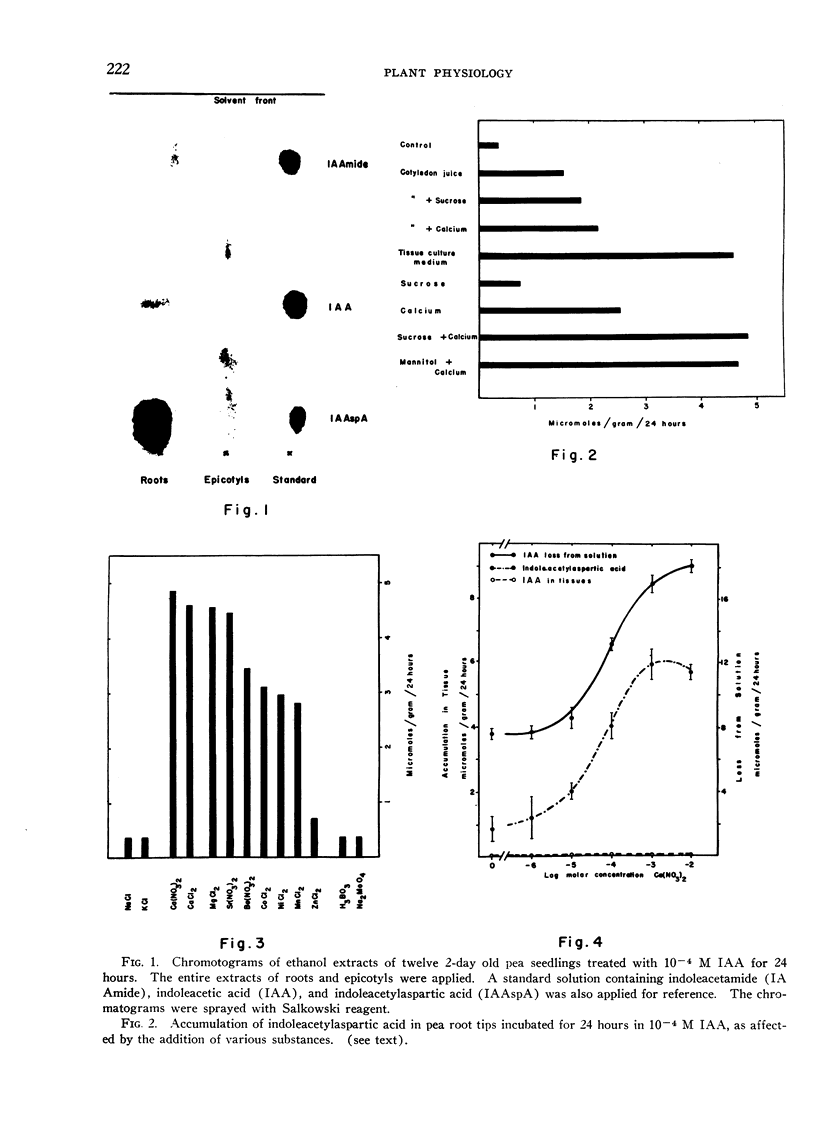
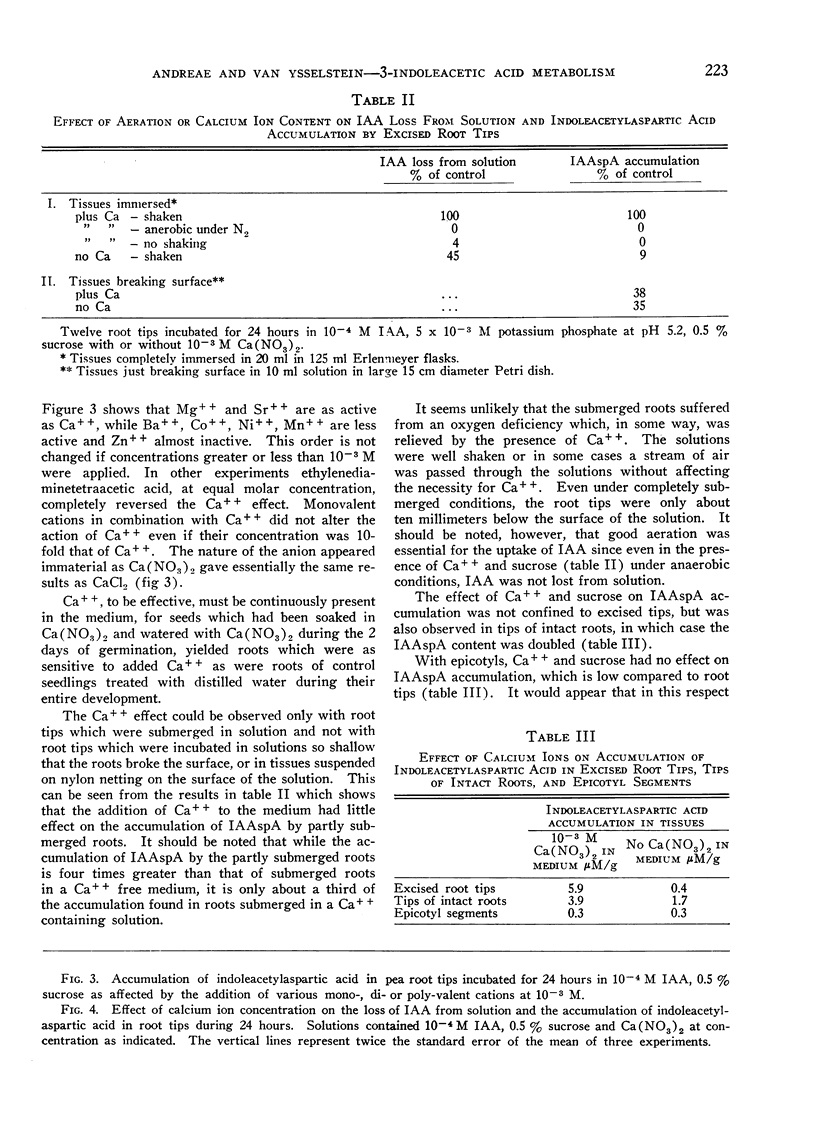
- Andreae W. A., Van Ysselstein M. W. Studies on 3-Indoleacetic Acid Metabolism. VI. 3-Indoleacetic Acid Uptake and Metabolism by Pea Roots and Epicotyls. Plant Physiol. 1960 Mar;35(2):225–232. doi: 10.1104/pp.35.2.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreae W. A., Ysselstein M. W. Studies on 3-Indoleacetic Acid Metabolism. III. The Uptake of 3-Indoleacetic Acid by Pea Epicotyls and Its Conversion to 3-Indoleacetylaspartic Acid. Plant Physiol. 1956 May;31(3):235–240. doi: 10.1104/pp.31.3.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang S. C., Theisen P., Butts J. S. Metabolic Studies of Applied Indoleacetic Acid-1-C in Plant Tissues as Affected by Light and 2,4-D Treatment. Plant Physiol. 1959 Jan;34(1):26–32. doi: 10.1104/pp.34.1.26. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson L., Ordin L. Organic Acid Metabolism and Ion Absorption in Roots. Plant Physiol. 1954 Jan;29(1):70–75. doi: 10.1104/pp.29.1.70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leggett J. E., Epstein E. Kinetics of Sulfate Absorption by Barley Roots. Plant Physiol. 1956 May;31(3):222–226. doi: 10.1104/pp.31.3.222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel S. M., Galston A. W. Experimental Coupling of Indoleacetic Acid to Pea Root Protein In Vivo and In Vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1953 Nov;39(11):1111–1118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.39.11.1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanada T. Effects of Ultraviolet Radiation and Calcium and Their Interaction on Salt Absorption by Excised Mung Bean Roots. Plant Physiol. 1955 May;30(3):221–225. doi: 10.1104/pp.30.3.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torrey J. G. The Role of Vitamins and Micronutrient Elements in the Nutrition of the Apical Meristem of Pea Roots. Plant Physiol. 1954 May;29(3):279–287. doi: 10.1104/pp.29.3.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viets F. G. CALCIUM AND OTHER POLYVALENT CATIONS AS ACCELERATORS OF ION ACCUMULATION BY EXCISED BARLEY ROOTS. Plant Physiol. 1944 Jul;19(3):466–480. doi: 10.1104/pp.19.3.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



