Abstract
Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2) is an independent risk factor for CVD and has been proposed as a marker of vascular inflammation. Polyunsaturated n-3 fatty acids (FA) and several n-6 FA are known to suppress inflammation and may influence Lp-PLA2 mass and activity. The associations of n-3 and n-6 plasma FA with Lp-PLA2 mass and activity were analysed using linear regression analysis in 2246 participants of the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis; statistical adjustments were made to control for body mass, inflammation, lipids, diabetes, and additional clinical and demographic factors. Lp-PLA2 mass and activity were significantly lower in participants with the higher n-3 FA EPA (β = −4·72, P<0·001; β = −1·53; P=0·023) and DHA levels (β = −4·47, β = −1·87; both P<0·001). Those in the highest quintiles of plasma EPA and DHA showed 12·71 and 19·15 ng/ml lower Lp-PLA2 mass and 5·7 and 8·90 nmol/min per ml lower Lp-PLA2 activity than those in the first quintiles, respectively. In addition, lower Lp-PLA2 mass and activity were associated with higher levels of n-6 arachidonic acid (β = −1·63, β = −1·30; both P<0·001), while γ-linolenic acid was negatively associated with activity (β = −27·7, P=0·027). Lp-PLA2 mass was significantly higher in participants with greater plasma levels of n-6 linoleic (β = 0·828, P=0·011) and dihomo-γ-linolenic acids (β = 4·17, P=0·002). Based on their independent associations with Lp-PLA2 mass and activity, certain n-3 and n-6 FA may have additional influences on CVD risk. Intervention studies are warranted to assess whether these macronutrients may directly influence Lp-PLA2 expression or activity.
Keywords: Fatty acids, n-3, Atherosclerosis, Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase, Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2
Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2) is a macrophage-derived enzyme that contributes to oxidative stress, vascular inflammation and endothelial activation(1,2) – hallmarks of atherosclerosis and CVD. Primarily associated with LDL(3) and co-localising at sites of atherosclerotic plaques, the Lp-PLA2 enzyme has been reported as a crucial component in plaque destabilisation and disruption(4). Indeed, elevated levels of Lp-PLA2 mass are considered as independent risk factor for CVD(2), and high levels of Lp-PLA2 enzymatic activity have been associated with unfavourable health outcomes – including an increased risk for myocardial infarction and CVD death in older adults(5). Though a number of drug treatments including specific Lp-PLA2 inhibitors are undergoing clinical trials(4), a non-pharmaceutical-based approach such as an increased intake of certain macronutrients may provide a simple, cost-effective alternative without appreciable side effects.
Polyunsaturated n-3 fatty acids (FA) have been shown as important contributors to health outcomes and are widely acknowledged for influencing disease risk(6). First recognised for their health benefits by Dyerberg et al.(7), the fish oil n-3 FA EPA and DHA may reduce atherogenic burden and the risk of CVD development by suppressing inflammation and beneficially influencing lipid profile(6). Thus far, the evidence that n-3 FA influence Lp-PLA2 is equivocal, with two interventional studies showing no effect(8,9) and three demonstrating that EPA or EPA/DHA esters reduce the levels of Lp-PLA2 (10–12). In contrast to the n-3 FA, no study has examined any potential impact or association of plasma n-6 FA with Lp-PLA2. By examining levels of Lp-PLA2 mass/activity, n-3 and n-6 FA across a larger study population, the present analysis aims to provide evidence of an additional benefit of PUFA that is not yet established.
Few studies have examined Lp-PLA2 mass and activity in the context of n-3 FA, and to our knowledge no study has examined Lp-PLA2 and polyunsaturated n-6 FA. The present cross-sectional analysis aimed to determine the relationship of plasma n-3 and n-6 FA levels with Lp-PLA2 mass and activity in 2246 generally healthy participants enrolled in the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA). No dietary intervention was used in the present study. To avoid the inherent difficulties in accurately assessing individual FA with dietary questionnaires, polyunsaturated n-3 and n-6 FA were directly measured in the phospholipid fraction of plasma, which has been demonstrated to strongly associate with dietary intake(13) and erythrocyte cell membrane composition(14). Relative levels of the following plasma PUFA were analysed: linoleic acid (LA, 18 : 2n-6); γ-linolenic acid (18 : 3n-6); dihomo-γ-linolenic acid (20 : 3n-6); arachidonic acid (AA, 20 : 4n-6); α-linolenic acid (18 : 3n-3); EPA (20 : 5n-3); DHA (22 : 6n-3).
Materials and methods
Population
The MESA was initiated to investigate the prevalence, correlates and progression of subclinical CVD(15), and further information about the MESA protocol is available online (http://www.mesa-nhlbi.org). Briefly, the MESA comprises 6814 men and women, 38·6% White, 27·6% Black, 11·8% Chinese and 22·0% Hispanic, who were 45–84 years of age and free of clinical CVD at baseline, July 2000–August 2002. Baseline examinations included anthropometry, medical and lifestyle histories and blood collection. The present analysis consists of a random sample of 2246 adults represented by approximately equal numbers of Black (n 534), Asian (of Chinese descent n 604), Hispanic (n 572) and White (n 536) participants. The present study was conducted according to the guidelines laid down in the Declaration of Helsinki, and all procedures involving human subjects were approved by the institutional review boards for research involving human subjects of the respective field centres. Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects.
Measurements
Questionnaire information was obtained regarding age, sex, race/ethnicity, education and lifestyle factors including smoking status, drinking alcohol and physical activity. Height (cm) and weight (kg) were measured according to standard procedures(15). Fasting blood was drawn and serum and EDTA-anticoagulant tubes were collected and processed using a standardised protocol(15). Serum and plasma samples were aliquoted and stored at −70°C until time of use.
Plasma fatty acid profile
Phospholipid FA were extracted from EDTA plasma using the method described previously by Cao et al.(16). In brief, lipids were extracted from the plasma using a chloroform–methanol extraction method, and cholesterol esters, TAG, phospholipids and NEFA were separated by TLC. FA from the phospholipids were derivatised to methyl esters and detected by GC flame ionisation. The FA detected were expressed as a percentage of total FA. The following representative coefficients of variance were obtained from intra-laboratory quality-control testing (n 20): LA, 2·6%; AA, 2·4%; α-linolenic acid, 2·4%; EPA, 3·3%; DHA, 2·7%.
Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 mass and activity
Blood collection and laboratory procedures have been described previously by Cushman et al.(17). Lp-PLA2 activity was measured by radiometric assay using a 3H-labelled platelet-activating factor substrate, analytical CV 7·5% (Glaxo-SmithKline), and expressed as nmol platelet-activating factor hydrolysed/min per ml plasma sample (nmol/min per ml). Lp-PLA2 mass was measured using the PLAC® Test, analytical CV 6·3% (Diadexus). All measurements were made on baseline blood samples not previously thawed.
Statistical methods
SAS, version 9.3 (SAS Institute) was used to analyse the data. Baseline characteristics are reported as means and standard deviations for continuous variables and frequency (%) for categorical variables. Levels of analytes with skewed distributions were log-transformed before analysis and results were back-transformed and presented as geometric means. Generalised linear regression analysis evaluated the associations between Lp-PLA2 and plasma FA, adjusting for potential confounding factors including, age, sex, race/ethnicity, BMI, education, field centre, current smoking, alcohol use, HDL-cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) level, TAG level, the presence of diabetes, and use of statins, fibrates or aspirin. Diet was not adjusted for, as phospholipid FA strongly correlate with this variable. Weight categories were defined as normal weight (BMI <25 kg/m2), overweight (BMI 25− < 30 kg/m2) and obese (BMI 30+ kg/m2). TAG and hs-CRP levels were divided by risk categories according to the American Heart Association guidelines: hs-CRP – low risk (<1·0 mg/l), average risk (1–3 mg/l), high risk (>3·0 mg/l); TAG levels – normal (<1500 mg/l), borderline high (1500–1990 mg/l), high (2000–4990 mg/l) and very high (>5000 mg/l). Correlations are expressed as β-coefficients, where one unit change in plasma phospholipid FA (%) is equal to the indicated change in Lp-PLA2 mass or activity, and observations were deemed significant with a P value ≤0·05.
Results
Unadjusted mean levels of Lp-PLA2 mass and activity by demographic characteristics are shown in Table 1. Significant differences in Lp-PLA2 mass and activity were observed between sexes as well as among races/ethnicities. Females had lower levels of both Lp-PLA2 mass and activity compared with males (Ptrend < 0·001). With respect to race/ethnicity, Lp-PLA2 mass was highest in White and Hispanic adults followed by Chinese and Black participants (Ptrend < 0·001). Similarly, mean levels of Lp-PLA2 enzymatic activity was significantly lower in Black participants, but no differences were observed among Hispanic, White and Chinese adults (Ptrend < 0·001). An association of Lp-PLA2 mass with a maximum level of education attained did not reach significance (Ptrend = 0·052). No significant differences in Lp-PLA2 were found among the age groups.
Table 1.
Mean lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2) mass and activity levels* of the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis participants by demographic characteristics and lifestyle factors
| Demographic | n | Lp-PLA2 mass | P | Lp-PLA2 activity | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | |||||
| ≤ 50 | 368 | 167·677 | 148·4 | ||
| 51–60 | 660 | 169·858 | 149·1 | ||
| 61–70 | 625 | 167·373 | 0·67 | 148·0 | 0·6 |
| ≥ 70 | 502 | 169·569 | 146·1 | ||
| Sex | |||||
| Women | 1165 | 163·985 | 136·0 | ||
| Men | 990 | 174·408 | <0·001 | 162·1 | <0·001 |
| Race/ethnicity | |||||
| Black | 510 | 160·203c,d | 135·5b,c,d | ||
| Chinese | 567 | 158·013c,d | <0·001 | 151·4a | <0·001 |
| Hispanic | 548 | 172·225a,b,d | 150·0a | ||
| White | 530 | 186·110a,b,c | 154·1a | ||
| Education | |||||
| <HS | 472 | 166·778 | 148·5 | ||
| HS | 376 | 171·142e | 145·8 | ||
| Some college | 595 | 171·715e | 0·052 | 148·3 | 0·37 |
| College, 4 years | 371 | 168·057 | 146·2 | ||
| College, 5+ years | 341 | 164·209b,c | 150·7 | ||
| Lifestyle factors | |||||
| Current smokers | |||||
| No | 1875 | 166·715 | <0·001 | 147·5 | 0·16 |
| Yes | 280 | 182·561 | 150·8 | ||
| Alcohol use | |||||
| Never | 587 | 160·140b,c | 143·9b,c | ||
| Former | 471 | 174·492a | <0·001 | 153·5a,c | <0·001 |
| Current | 1097 | 170·958a | 147·8a,b | ||
| Intentional physical activity (quartiles) | |||||
| 1 | 550 | 170·307 | 150·3 | ||
| 2 | 527 | 168·633 | 0·76 | 149·4 | 0·08 |
| 3 | 540 | 167·977 | 146·4 | ||
| 4 | 538 | 167·835 | 145·7 |
HS, high school graduate.
Mean values with unlike superscript letters were significantly different for the intra-group (P<005).
Mean values with unlike superscript letters were significantly different for the intra-group (P<005).
Mean values with unlike superscript letters were significantly different for the intra-group (P<005).
Mean values with unlike superscript letters were significantly different for the intra-group (P<005).
Mean values with unlike superscript letters were significantly different for the intra-group (P<005).
Unadjusted demographic characteristics.
Lp-PLA2 mass and activity were significantly correlated (r 0·49, P<0·001) following adjustment for age, sex, race, education and field centre (data not shown). Differences in both Lp-PLA2 mass and activity were observed based on lifestyle factors including cigarette smoking and alcohol use (Table 1). Non-smokers demonstrated significantly lower levels of Lp-PLA2 mass than current smokers (P<0·001), while those who never consumed alcohol had lower levels of both Lp-PLA2 mass and activity than those who currently consumed or formerly consumed alcohol (Ptrend < 0·001). No differences in the mean levels of Lp-PLA2 mass or activity were observed among the quartiles of intentional physical activity.
The mean levels of Lp-PLA2 mass and activity by clinical characteristics are shown in Table 2. Statistically significant trends were found based on BMI as well as TAG and hs-CRP levels. Compared with either overweight or obese individuals, normal-weight individuals had the lowest levels of Lp-PLA2 activity (Ptrend = 0·001) and mass (P=0·007). Higher levels of Lp-PLA2 mass were found to correlate with higher levels of TAG (Ptrend = 0·002) and hs-CRP (Ptrend < 0·001, respectively). Finally, differences were found in Lp-PLA2 mass and activity based on medication use. Lower mean levels of Lp-PLA2 mass and activity were observed in individuals taking statins (Ptrend < 0·001, Ptrend < 0·001), fibrates (Ptrend = 0·01, Ptrend = 0·04) or postmenopausal therapy (Ptrend < 0·001, Ptrend < 0·001) compared with those not taking these medicinal regimens. Multiple demographic, lifestyle and clinical characteristics were found to influence Lp-PLA2 mass and activity, thus additional covariate adjustments were made in subsequent analyses of plasma FA.
Table 2.
Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2) mass and activity levels* of the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis participants categorised by clinical characteristics
| Clinical characteristics | n | Lp-PLA2 mass | P | Lp-PLA2 activity | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMI (kg/m2) | |||||
| Normal | 712 | 164·6b,c | 144·7b,c | ||
| Overweight | 826 | 170·9a | 0·007 | 149·5a | 0·001 |
| Obese | 617 | 170·6a | 149·6a | ||
| TAG levels (mg/l) | |||||
| <150 | 1486 | 1686d | 1440b,c | ||
| 150–199 | 344 | 1651c,d | 0·002 | 1550a | <0·001 |
| 200–499 | 315 | 1720b,d | 1590a | ||
| ≥ 500 | 10 | 2154a,b,c | 1453 | ||
| hs-CRP | |||||
| <1·0 | 715 | 164·1b,c | 147·0 | ||
| 1·0–3·0 | 716 | 169·1a | <0·001 | 149·7 | 0·24 |
| > 3·0 | 724 | 172·9a | 147·2 | ||
| Medication use Statins |
|||||
| No | 1846 | 171·3 | 150·3 | ||
| Yes | 307 | 153·7 | <0·001 | 134·0 | <0·001 |
| Fibrates | |||||
| No | 2126 | 169·0 | 148·1 | ||
| Yes | 27 | 143·8 | <0·001 | 134·7 | 0·04 |
| Aspirin | |||||
| No | 1548 | 169·3 | 148·81 | ||
| Yes | 604 | 167·2 | 0·31 | 146·0 | 0·10 |
| Postmenopausal therapy | |||||
| No | 738 | 167·3 | <0·001 | 139·2 | <0·001 |
| Yes | 294 | 157·6 | 128·6 |
hs-CRP, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein.
Values with unlike letters were significantly different for the intra-group (P<0·05).
Values with unlike letters were significantly different for the intra-group (P<0·05).
Values with unlike letters were significantly different for the intra-group (P<0·05).
Values with unlike letters were significantly different for the intra-group (P<0·05).
Adjusted for age, sex, race, education and field centre.
Plasma levels of n-3 and n-6 phospholipid FA were found to correlate with both Lp-PLA2 mass and activity (Table 3). Plasma LA levels positively correlated with both mass (β = 0·83, P=0·01) and activity (β = 1·07, P<0·001), while dihomo-γ-linolenic acid was found to be positively correlated with Lp-PLA2 mass alone (β = 4·17, P=0·002). In contrast, plasma γ-linolenic acid negatively correlated with Lp-PLA2 activity (β = −27·7, P=0·03), and plasma AA levels negatively correlated with both Lp-PLA2 mass (β = −1·63, P<0·001) and activity (β = −1·30, P<0·001). Similarly, plasma n-3 FA levels of EPA and DHA negatively correlated with both mass (β = −4·90, P<0·001; β = −4·99, P<0·001) and activity (β = −1·53, P=0·02; β = −1·87, P<0·001), respectively. Plasma α-linolenic acid was not observed to correlate with either Lp-PLA2 mass (P=0·25) or activity (P=0·21).
Table 3.
Correlations of plasma phospholipid fatty acids with lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2) mass and activity (β-Coefficients)
| Lp-PLA2 mass (n 2155) |
Lp-PLA2 activity (n 2155) |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phospholipid fatty acids | β | P | β | P | ||
| n-6 Fatty acids | ||||||
| Linoleic acid (18 : 2n-6) | ||||||
| Model 1* | 0·833 | 0·011 | 1·18 | <0·001 | ||
| Model 2† | 0·828 | 0·011 | 1·07 | <0·001 | ||
| γ-Linolenic acid (18 : 3n-6) | ||||||
| Model 1* | NS | −26·1 | 0·065 | |||
| Model 2† | NS | −27·7 | 0·027 | |||
| Dihomo-γ-linolenic acid (20 : 3n-6) | ||||||
| Model 1* | 4·57 | <0·001 | 3·81 | <0·001 | ||
| Model 2† | 4·17 | 0·002 | NS | |||
| Arachidonic acid (20 : 4n-6) | ||||||
| Model 1* | −1·82 | <0·001 | −2·28 | <0·001 | ||
| Model 2† | −1·63 | 0·001 | −1·30 | <0·001 | ||
| n-3 Fatty acids | ||||||
| α-Linolenic acid (18 : 3n-3) | ||||||
| Model 1* | NS | NS | ||||
| Model 2† | NS | NS | ||||
| EPA (20 : 5n-3) | ||||||
| Model 1* | −4·90 | <0·001 | NS | |||
| Model 2† | −4·72 | <0·001 | −1·53 | 0·023 | ||
| DHA (22 : 6n-3) | ||||||
| Model 1* | −4·99 | <0·001 | −1·46 | 0·002 | ||
| Model 2† | −4·47 | <0·001 | −1·87 | <0·001 | ||
Adjusted for age, sex, race, education and field centre.
Model 1 plus adjustments for smoking, alcohol, BMI, HDL-cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, TAG, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, diabetes and use of statins, fibrates and aspirin.
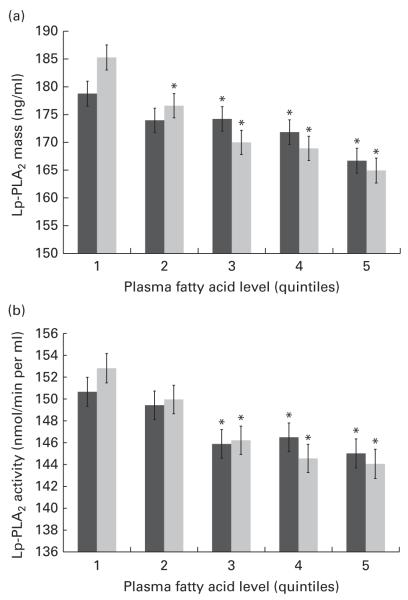
n-6 FA levels have not been examined in the context of Lp-PLA2 mass and activity, and further statistical analysis is therefore warranted. Mean levels of Lp-PLA2 mass and activity were examined by quintiles of LA and AA – the most abundant n-6 FA in a typical Western diet. Differences were found in both mass and activity among the quintiles of LA and AA, and remained significant following adjustment for multiple covariates including inflammation (hs-CRP) and standard lipid measures (TAG, HDL-C and LDL-C) as well as demographic and lifestyle factors (Fig. 1(a) and (b)). Unexpectedly, LA and AA were differentially associated with Lp-PLA2 mass and activity. Individuals with the highest plasma LA levels (fifth quintile) showed an 8·09 ng/ml higher mean level of Lp-PLA2 mass (P=0·017) and a 10·5 nmol/min per ml higher mean level of Lp-PLA2 activity (P<0·001) compared with those with the lowest levels of plasma LA (first quintile). In contrast, individuals with the highest levels of plasma AA were found to have a 9·75 ng/ml lower mean level of Lp-PLA2 mass (P=0·005) and an 8·91 nmol/min per ml lower mean level of Lp-PLA2 activity (P<0·001) compared to those in the first quintile of AA.
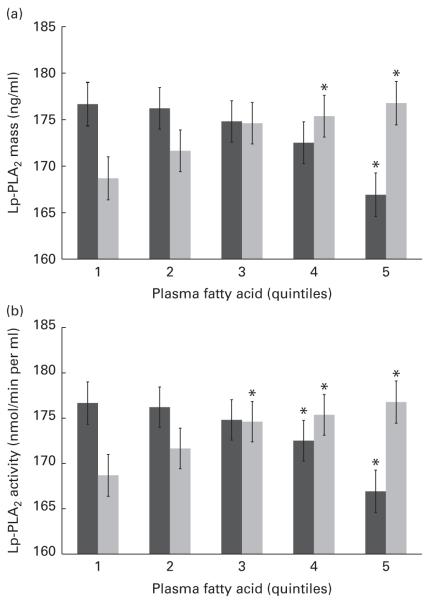
Fig. 1.
Mean levels of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2) (a) mass and (b) activity are shown by quintiles of plasma arachidonic acid (■) and linoleic acid ( ). Values are means, with their standard errors represented by vertical bars. Values were adjusted for age, sex, race, education, field centre, smoking, alcohol, BMI, HDL-cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, TAG, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and use of statins, fibrates and aspirin. * Mean values were significantly different from those of quintile 1 (P<0·05).
). Values are means, with their standard errors represented by vertical bars. Values were adjusted for age, sex, race, education, field centre, smoking, alcohol, BMI, HDL-cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, TAG, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and use of statins, fibrates and aspirin. * Mean values were significantly different from those of quintile 1 (P<0·05).
With respect to the n-3 FA, plasma EPA and DHA have been well characterised for cardiovascular benefits and may be increased with fish oil supplements and/or greater fish consumption. Expectedly, differences were found in both mass and activity among the quintiles of EPA and DHA, and remained significant following adjustment for multiple covariates including systemic inflammation (hs-CRP) and standard lipid measures (TAG, HDL-C and LDL-C) as well as demographic and lifestyle factors (Fig. 2(a) and (b)). Compared with those in the first quintile for plasma EPA, individuals in the fifth quintile showed a 12·71 ng/ml lower mean level of Lp-PLA2 mass (P<0·001) and a 5·7 nmol/min per ml lower mean level of Lp-PLA2 activity (P=0·03). Similarly, individuals in the fifth plasma DHA quintile were found to have a 19·15 ng/ml lower mean level of Lp-PLA2 mass (P<0·001) and an 8·90 nmol/min per ml lower mean level of Lp-PLA2 activity (P<0·001) compared with those in the first quintile.
Fig. 2.
Mean levels of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2) (a) mass and (b) activity are shown by quintiles of plasma EPA and DHA. Values are means, with their standard errors represented by vertical bars. Values were adjusted for age, sex, race, education, field centre, smoking, alcohol, BMI, HDL-cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, TAG, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and use of statins, fibrates and aspirin. * Mean values were significantly different from those of quintile 1 (P<0·05).
Discussion
The present cross-sectional analysis showed independent associations of plasma n-3 and n-6 FA levels with both Lp-PLA2 mass and activity in 2246 adult participants of the MESA. These associations remained significant following multivariate adjustments for traditional CVD risk factors including systemic inflammation, cholesterol and TAG levels as well as additional clinical, demographic and lifestyle factors. Expectedly, Lp-PLA2 mass and activity varied by race/ethnicity, BMI, sex, hs-CRP and TAG levels, as shown previously(18–20). In agreement with Hatoum et al.(19), but in contrast to Brilakis et al.(18) and Hirschler et al.(20), we found a modest but significant association of Lp-PLA2 activity with BMI.
Affirmed by a host of prospective studies and a subsequent meta-analysis by the Lp-PLA2 Studies Collaboration(21) group, Lp-PLA2 mass and activity are risk factors for CHD, congestive heart failure and stroke – though only enzyme mass has been recommended as an independent CVD risk factor at the present time. The meta-analysis showed that Lp-PLA2 mass imparts a slightly higher risk of myocardial infarction and stroke, but not CVD death, than Lp-PLA2 activity. Revealingly, the relative risk of Lp-PLA2 mass for CHD following adjustment for Lp-PLA2 activity remained 1·08 (1·04–1·12) per 1 sd in multivariable analysis(21). The collective evidence has shown that mass and activity are partially related, and may both be important for assessing risks of future CHD and stroke.
To date, no studies have examined n-6 FA in the context of Lp-PLA2 mass or activity, and only a few have examined n-3 FA. In agreement with the present findings in the plasma phospholipid fraction, Schmidt et al.(22) observed that adipose tissue levels of EPA and DHA were inversely associated with Lp-PLA2 concentrations. Follow-up intervention trials to determine whether EPA or DHA supplementation reduces Lp-PLA2 mass and/or activity have yielded inconsistent results. For example, two studies have reported no effect of supplementing EPA + DHA on Lp-PLA2 mass or activity over 6 and 8 weeks(8,9). In contrast, Schaefer et al.(10) found that supplementation with EPA alone reduced Lp-PLA2 levels by 6% over 6 weeks in a larger study population. Finally, two clinical trials have demonstrated that administering EPA/DHA ethyl ester in conjunction with simvastatin(11) or atorvasta tin(12) lowered Lp-PLA2 mass to a greater extent than a placebo + statin treatment. Overall, the inverse associations in the present analysis support these latter studies, showing a benefit of the fish oil FA with respect to Lp-PLA2 − notably, these reductions in Lp-PLA2 may be explained by a number of biochemical mechanisms.
n-3 FA have been shown to have multiple effects on oxidative stress and inflammatory pathways – several of which overlap with those involved in Lp-PLA2 expression. Specifically, two classes of EPA and DHA metabolites, resolvins and protectins, have been shown to suppress inflammatory cytokine production, block eicosanoid signalling and reduce oxidative stress(23) – all of which may suppress the activation of signalling elements involved in Lp-PLA2 induction including p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase(24–26). Apart from these metabolites, EPA and DHA have also been shown to disrupt oxidised LDL signalling(27,28) – also a known inducer of Lp-PLA2 expression(25).
Similar to the observations for n-3 FA, associations among plasma n-6 FA and Lp-PLA2 may be explained by their influence on inflammation. The positive association of LA with Lp-PLA2 was expected to be due to its promotion of inflammation and activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in cell-culture models(29). Similarly, dihomo-γ-linolenic acid has been found to associate with inflammatory markers in MESA study participants(30), though no direct effects on inflammatory signalling have been reported. In contrast, AA is well characterised for being inflammatory, largely for its metabolism into the inflammatory 4-series leukotrienes; however, AA also generates lipoxins – powerful non-classic eicosanoids that suppress inflammatory signalling pathways(31). Apart from their active role in resolving inflammation, lipoxins have also been shown to suppress an inducer of Lp-PLA2 expression, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase(32). Taken together, there is a considerable body of evidence that n-3 and n-6 FA affect inflammatory signalling cascades, which may in turn influence Lp-PLA2 expression via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase – but further research is needed to determine whether such effects may be involved in the induction or suppression of Lp-PLA2 expression in vivo.
In terms of implications, the present findings are suggestive that a higher intake of certain n-3 FA may have an additional cardiovascular benefit on Lp-PLA2, in addition to their well-known influences on blood lipids, inflammation, oxidative stress and arrhythmia. Importantly, the observed associations predict the value of Lp-PLA2 mass or activity based on a one unit change (%) in the given FA. For FA such as AA, DHA or EPA, a 1% change in the plasma phospholipid fraction is quite feasible, and thus may have implications for maintaining normal or moderately reducing elevated levels of Lp-PLA2. Those in the top quintile for EPA and DHA demonstrated modestly lower levels of Lp-PLA2, but whether 10–15% lower Lp-PLA2 levels have long-term health implications is unclear and warrants further exploration. The present findings regarding n-6 FA are perhaps more controversial, as their influence on CVD remains inconclusive and require further study. Notably, any potential effect(s) of n-3 or n-6 FA on Lp-PLA2 would probably be weaker than pharmaceutical interventions(33,34).
The present study has a number of strengths including the direct measurement of the phospholipid fraction of plasma FA in a relatively large population compared with previous studies. Direct measurement avoids the inherent problems of dietary recall, and phospholipid PUFA levels are well documented to be highly correlated with dietary intake(12). Additionally, numerous demographic, lifestyle and clinical factor adjustments were made to better determine whether PUFA associate with LpPLA2 mass and activity. In terms of limitations, the cross-sectional study design prevents the determination of temporality. Though multiple statistical adjustments were made within the present analysis, the potential for other confounding variables remains. In addition, the MESA is a relatively healthy prospective study population, and it must be acknowledged that present observations were limited by a relatively few individuals with levels of Lp-PLA2 mass considered to be of moderate (200–235 ng/ml) or high risk for CVD (>235 ng/ml) – indeed, stronger associations may be observed in a study population with higher Lp-PLA2 levels. Finally, it must be recognised that a number of the observed associations were relatively modest in nature. Though associations of LA and AA with Lp-PLA2 mass and activity reached significance, their potential contribution in driving expression or activity is probably limited or negligible.
In conclusion, the observed associations of Lp-PLA2 mass and activity with EPA, DHA and certain n-6 FA may indicate additional health benefits of these FA that have not been established. Future dietary intervention studies as well as cell-culture experiments may better evaluate whether FA directly influence Lp-PLA2 expression or enzymatic activity. Given that higher Lp-PLA2 levels increase the risk of CVD incidence and destabilising atherosclerotic plaques, strategies should be explored that promote and/or maintain enzyme levels considered low risk, <200 ng/ml. Though specific enzyme inhibitors, statins and fibrates, are being tested in clinical trials to this end, a non-pharmaceutical-based approach such as long-term nutritional support with EPA/DHA warrants further study.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the investigators, staff and participants of the MESA study for their valuable contributions. A full list of participating MESA investigators and institutions can be found at http://www.mesa-nhlbi.org. The present study was supported by the following contracts: N01-HC-95159–N01-HC-95169 from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. The authors and their contributions are listed as follows: B. T. S. wrote the manuscript under the supervision of the principal investigator, M. Y. T; M. Y. T. had primary responsibility for the final content of the manuscript; L. M. S. and S. L. performed the statistical analysis; R. T. advised on the statistical analysis; N. S. J. conducted the research and provided the Lp-PLA2 data for the study participants.
Abbreviations
- AA
arachidonic acid
- FA
fatty acids
- hs-CRP
high-sensitivity C-reactive protein
- LA
linoleic acid
- Lp-PLA2
lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2
- MESA
Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis
Footnotes
The authors have no conflict of interests to disclose.
References
- 1.MacPhee CH, Moores KE, Boyd HF, et al. Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2, platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase, generates two bioactive products during the oxidation of low-density lipoprotein: use of a novel inhibitor. Biochem J. 1999;338:479–487. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Sudhir K. Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2, vascular inflammation and cardiovascular risk prediction. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2006;2:153–156. doi: 10.2147/vhrm.2006.2.2.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Gazi I, Lourida ES, Filippatos T, et al. Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 activity is a marker of small dense LDL particles in human plasma. Clin Chem. 2005;51:2264–2273. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2005.058404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Serruys PW, García-García HM, Buszman P, et al. Integrated biomarker and imaging study-2 investigators. Effects of the direct lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 inhibitor darapladib on human coronary atherosclerotic plaque. Circulation. 2008;118:1172–1182. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.771899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Jenny NS, Solomon C, Cushman M, et al. Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A(2) (Lp-PLA(2)) and risk of cardiovascular disease in older adults: results from the Cardiovascular Health Study. Atherosclerosis. 2010;209:528–532. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2009.09.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kris-Etherton PM, Harris WS, Appel LJ, et al. Fish consumption, fish oil, omega-3 fatty acids, and cardiovascular disease. Circulation. 2002;106:2747–2757. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.0000038493.65177.94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Dyerberg J, Bang HO, Stoffersen E, et al. Eicosapentaenoic acid and prevention of thrombosis and atherosclerosis? Lancet. 1978;2:117–119. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)91505-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Pedersen MW, Koenig W, Christensen JH, et al. The effect of marine omega-3 fatty acids in different doses on plasma concentrations of Lp-PLA2 in healthy adults. Eur J Nutr. 2009;48:1–5. doi: 10.1007/s00394-008-0758-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Nelson TL, Hokanson JE, Hickey MS. Omega-3 fatty acids and lipoprotein associated phospholipase A(2) in healthy older adult males and females. Eur J Nutr. 2011;50:185–193. doi: 10.1007/s00394-010-0126-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Schaefer EJ, Asztalos IB, Gleason JA, et al. Abstract 20007: effects of eicosapentaenoic acid, docosahexaenoic acid, and olive oil on cardiovascular disease risk factors. Circulation. 2010;122:A20007. (Core 2. Epidemiology and prevention of CV disease: physiology, pharmacology and lifestyle. Session title: nutritional epidemiology and healthy eating).
- 11.Davidson MH, Maki KC, Bays H, et al. Effects of prescription omega-3-acid ethyl esters on lipoprotein particle concentrations, apolipoproteins AI and CIII, and lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A(2) mass in statin-treated subjects with hypertriglyceridemia. J Clin Lipidol. 2009;3:332–340. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2009.08.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Maki KC, Bays HE, Dicklin MR, et al. Effects of prescription omega-3-acid ethyl esters, coadministered with atorvastatin, on circulating levels of lipoprotein particles, apolipoprotein CIII, and lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 mass in men and women with mixed dyslipidemia. J Clin Lipidol. 2011;5:483–492. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2011.09.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Saadatian-Elahi M, Slimani N, Chajès V, et al. Plasma phospholipid fatty acid profiles and their association with food intakes: results from a cross-sectional study within the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition. Am J Clin Nutr. 2009;89:331–346. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.2008.26834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Patel PS, Sharp SJ, Jansen E, et al. Fatty acids measured in plasma and erythrocyte-membrane phospholipids and derived by food-frequency questionnaire and the risk of new-onset type 2 diabetes: a pilot study in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC)-Norfolk cohort. Am J Clin Nutr. 2010;92:1214–1222. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.2010.29182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bild DE, Bluemke DA, Burke GL, et al. Multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis: objectives and design. Am J Epidemiol. 2002;156:871–881. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwf113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Cao J, Schwichtenberg KA, Hanson NQ, et al. Incorporation and clearance of omega-3 fatty acids in erythrocyte membranes and plasma phospholipids. Clin Chem. 2006;52:2265–2272. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2006.072322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Cushman M, Cornell ES, Howard PR, et al. Laboratory methods and quality assurance in the Cardiovascular Health Study. Clin Chem. 1995;41:264–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Brilakis ES, Khera A, McGuire DK, et al. Influence of race and sex on lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 levels: observations from the Dallas Heart Study. Atherosclerosis. 2008;199:110–115. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2007.10.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hatoum IJ, Nelson JJ, Cook NR, et al. Dietary, lifestyle, and clinical predictors of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 activity in individuals without coronary artery disease. Am J Clin Nutr. 2010;91:786–793. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.2009.28870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hirschler V, Meroño T, Maccallini G, et al. Association of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A(2) activity with components of the metabolic syndrome in apparently healthy boys. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2011;9:78–83. doi: 10.2174/187152511796196542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Lp-PLA(2) Studies Collaboration. Thompson A, Gao P, et al. Lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A(2) and risk of coronary disease, stroke, and mortality: collaborative analysis of 32 prospective studies. Lancet. 2010;375:1536–1544. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)60319-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Schmidt EB, Koenig W, Khuseyinova N, et al. Lipo-protein-associated phospholipase A2 concentrations in plasma are associated with the extent of coronary artery disease and correlate to adipose tissue levels of marine omega-3 fatty acids. Atherosclerosis. 2008;196:420–424. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2006.11.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Spite M, Serhan CN. Novel lipid mediators promote resolution of acute inflammation: impact of aspirin and sta-tins. Circ Res. 2010;107:1170–1184. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.223883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Wu X, Zimmerman GA, Prescott SM, et al. The p38 MAPK pathway mediates transcriptional activation of the plasma platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase gene in macrophages stimulated with lipopolysaccharide. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:36158–36165. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M402454200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Wang WY, Li J, Yang D, et al. OxLDL stimulates lipo-protein-associated phospholipase A2 expression in THP-1 monocytes via PI3K and p38 MAPK pathways. Cardiovasc Res. 2010;85:845–852. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvp367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Arita M, Ohira T, Sun YP, et al. Resolvin E1 selectively interacts with leukotriene B4 receptor BLT1 and ChemR23 to regulate inflammation. J Immunol. 2007;178:3912–3917. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.6.3912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Chen H, Li D, Chen J, et al. EPA and DHA attenuate ox-LDL-induced expression of adhesion molecules in human coronary artery endothelial cells via protein kinase B pathway. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2003;35:769–775. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2828(03)00120-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Madonna R, Salerni S, Schiavone D, et al. Omega-3 fatty acids attenuate constitutive and insulin-induced CD36 expression through a suppression of PPAR α/γ activity in microvascular endothelial cells. Thromb Haemost. 2011;106:500–510. doi: 10.1160/TH10-09-0574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Hennig B, Lei W, Arzuaga X, et al. Linoleic acid induces proinflammatory events in vascular endothelial cells via activation of PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2 signaling. J Nutr Biochem. 2006;17:766–772. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2006.01.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Steffen BT, Steffen LM, Tracy R, et al. Obesity modifies the association between plasma phospholipid polyunsaturated fatty acids and markers of inflammation: the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Int J Obes (Lond) 2012;36:797–804. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2011.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Serhan CN. Lipoxins and aspirin-triggered 15-epi-lipoxin biosynthesis: an update and role in anti-inflammation and pro-resolution. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2002;68–69:433–455. doi: 10.1016/s0090-6980(02)00047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Wu SH, Liao PY, Dong L, et al. Signal pathway involved in inhibition by lipoxin A(4) of production of inter-leukins induced in endothelial cells by lipopolysaccharide. Inflamm Res. 2008;57:430–437. doi: 10.1007/s00011-008-7147-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Schaefer EJ, McNamara JR, Asztalos BF, et al. Effects of atorvastatin versus other statins on fasting and postpran-dial C-reactive protein and lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 in patients with coronary heart disease versus control subjects. Am J Cardiol. 2005;95:1025–1032. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2005.01.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Mohler ER, 3rd, Ballantyne CM, Davidson MH, et al. The effect of darapladib on plasma lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 activity and cardiovascular biomarkers in patients with stable coronary heart disease or coronary heart disease risk equivalent: the results of a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008;51:1632–1641. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2007.11.079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]