Abstract
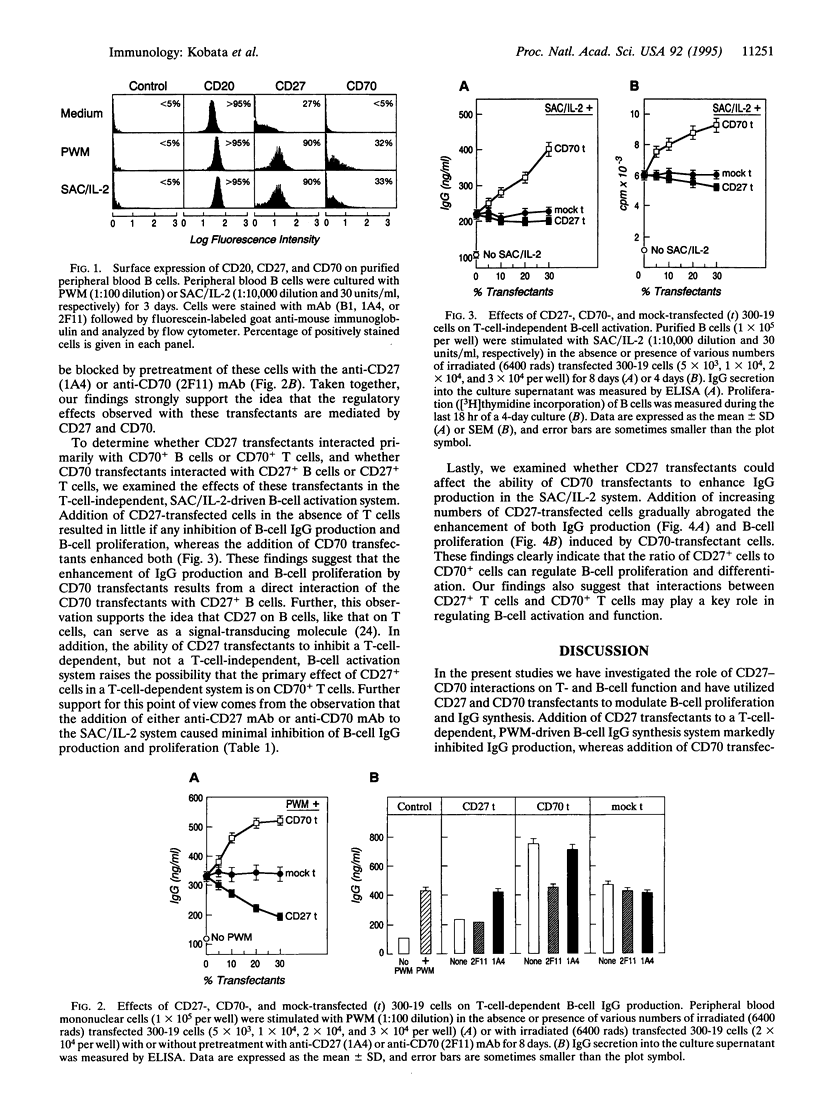
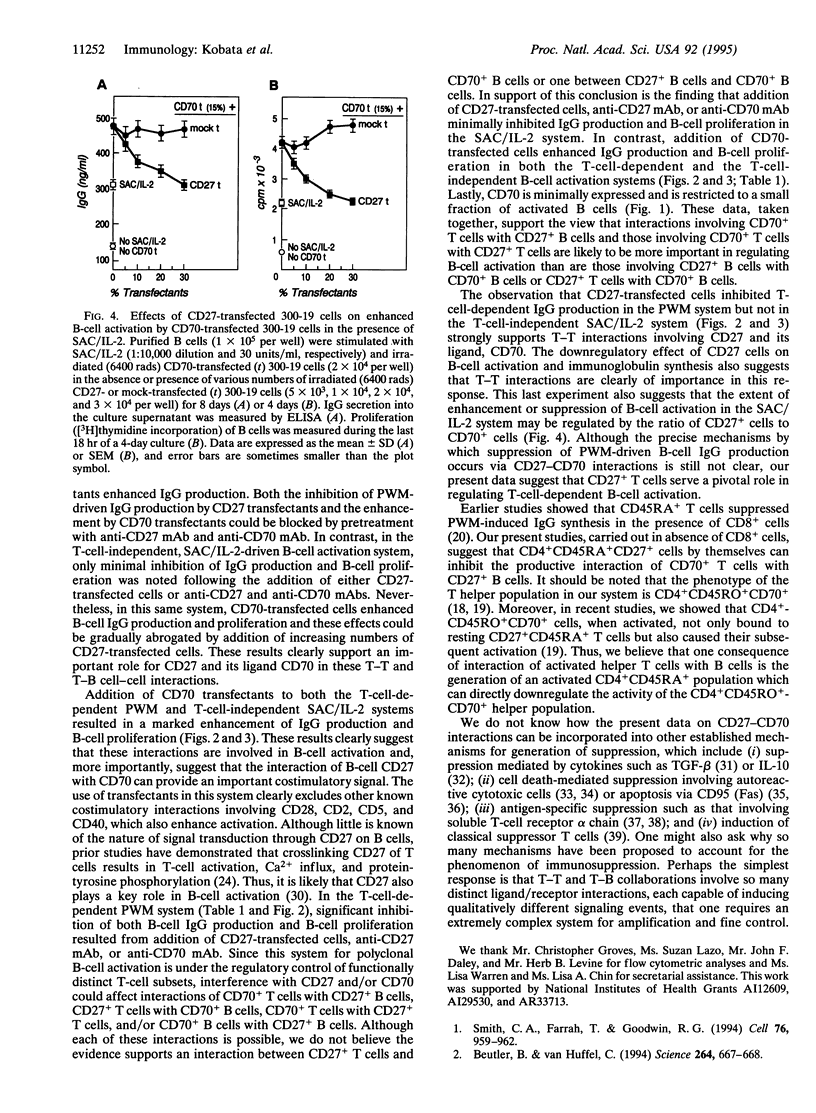
CD27, a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor family, binds to its ligand CD70, a member of the TNF family, and subsequently induces T-cell costimulation and B-cell activation. CD27 is expressed on resting T and B cells, whereas CD70 is expressed on activated T and B cells. Utilizing transfected murine pre-B-cell lines expressing human CD27 or CD70, we have examined the effect of such transfectant cells on human B-cell IgG production and B-cell proliferation. We show that the addition of CD27-transfected cells to a T-cell-dependent, pokeweed mitogen-driven B-cell IgG synthesis system resulted in marked inhibition of IgG production, whereas the addition of CD70-transfected cells enhanced IgG production. The inhibition and enhancement of pokeweed mitogen-driven IgG production by CD27 and CD70 transfectants were abrogated by pretreatment with anti-CD27 and anti-CD70 monoclonal antibodies, respectively. In contrast, little or no inhibition of IgG production and B-cell proliferation was noted with CD27-transfected cells or either anti-CD27 or CD70 monoclonal antibody in a T-cell-independent Staphylococcus aureus/interleukin 2-driven B-cell activation system. In this same system CD70-transfected cells enhanced B-cell IgG production and B-cell proliferation, and this enhancement could be gradually abrogated by addition of increasing numbers of CD27-transfected cells. These results clearly demonstrate that interactions among subsets of T cells expressing CD27 and CD70 play a key role in regulating B-cell activation and immunoglobulin synthesis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agematsu K., Kobata T., Sugita K., Freeman G. J., Beckmann M. P., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. Role of CD27 in T cell immune response. Analysis by recombinant soluble CD27. J Immunol. 1994 Aug 15;153(4):1421–1429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agematsu K., Kobata T., Sugita K., Hirose T., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. Direct cellular communications between CD45R0 and CD45RA T cell subsets via CD27/CD70. J Immunol. 1995 Apr 15;154(8):3627–3635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., van Huffel C. Unraveling function in the TNF ligand and receptor families. Science. 1994 Apr 29;264(5159):667–668. doi: 10.1126/science.8171316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigler R. D., Bushkin Y., Chiorazzi N. S152 (CD27). A modulating disulfide-linked T cell activation antigen. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 1;141(1):21–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom B. R., Salgame P., Diamond B. Revisiting and revising suppressor T cells. Immunol Today. 1992 Apr;13(4):131–136. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(92)90110-S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman M. R., Crimmins M. A., Yetz-Aldape J., Kriz R., Kelleher K., Herrmann S. The cloning of CD70 and its identification as the ligand for CD27. J Immunol. 1994 Feb 15;152(4):1756–1761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camerini D., Walz G., Loenen W. A., Borst J., Seed B. The T cell activation antigen CD27 is a member of the nerve growth factor/tumor necrosis factor receptor gene family. J Immunol. 1991 Nov 1;147(9):3165–3169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark E. A., Ledbetter J. A. How B and T cells talk to each other. Nature. 1994 Feb 3;367(6462):425–428. doi: 10.1038/367425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhein J., Walczak H., Bäumler C., Debatin K. M., Krammer P. H. Autocrine T-cell suicide mediated by APO-1/(Fas/CD95) Nature. 1995 Feb 2;373(6513):438–441. doi: 10.1038/373438a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimmi C. D., Freeman G. J., Gribben J. G., Sugita K., Freedman A. S., Morimoto C., Nadler L. M. B-cell surface antigen B7 provides a costimulatory signal that induces T cells to proliferate and secrete interleukin 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6575–6579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin R. G., Alderson M. R., Smith C. A., Armitage R. J., VandenBos T., Jerzy R., Tough T. W., Schoenborn M. A., Davis-Smith T., Hennen K. Molecular and biological characterization of a ligand for CD27 defines a new family of cytokines with homology to tumor necrosis factor. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):447–456. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90133-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green D. R., Bissonnette R., Zheng H. G., Onda T., Echeverri F., Mogil R. J., Steele J. K., Voralia M., Fotedar A. Immunoregulatory activity of the T-cell receptor alpha chain demonstrated by retroviral gene transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8475–8479. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hintzen R. Q., Lens S. M., Koopman G., Pals S. T., Spits H., van Lier R. A. CD70 represents the human ligand for CD27. Int Immunol. 1994 Mar;6(3):477–480. doi: 10.1093/intimm/6.3.477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue T., Asano Y., Matsuoka S., Furutani-Seiki M., Aizawa S., Nishimura H., Shirai T., Tada T. Distinction of mouse CD8+ suppressor effector T cell clones from cytotoxic T cell clones by cytokine production and CD45 isoforms. J Immunol. 1993 Mar 15;150(6):2121–2128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobata T., Agematsu K., Kameoka J., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. CD27 is a signal-transducing molecule involved in CD45RA+ naive T cell costimulation. J Immunol. 1994 Dec 15;153(12):5422–5432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuchroo V. K., Byrne M. C., Atsumi Y., Greenfield E., Connolly J. B., Whitters M. J., O'Hara R. M., Jr, Collins M., Dorf M. E. T-cell receptor alpha chain plays a critical role in antigen-specific suppressor cell function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8700–8704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martorell J., Rojo I., Vilella R., Martinez-Caceres E., Vives J. CD27 induction on thymocytes. J Immunol. 1990 Sep 1;145(5):1356–1363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer D., Fischer G. F., Fae I., Majdic O., Stuhlmeier K., Von Jeney N., Holter W., Knapp W. IgM and IgG but not cytokine secretion is restricted to the CD27+ B lymphocyte subset. J Immunol. 1992 Jun 15;148(12):3700–3705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer D., Holter W., Majdic O., Fischer G. F., Knapp W. CD27 expression by a distinct subpopulation of human B lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Dec;20(12):2679–2684. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830201223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A., Lider O., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Weiner H. L. Suppressor T cells generated by oral tolerization to myelin basic protein suppress both in vitro and in vivo immune responses by the release of transforming growth factor beta after antigen-specific triggering. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):421–425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto C., Letvin N. L., Distaso J. A., Aldrich W. R., Schlossman S. F. The isolation and characterization of the human suppressor inducer T cell subset. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1508–1515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskophidis D., Pircher H., Ciernik I., Odermatt B., Hengartner H., Zinkernagel R. M. Suppression of virus-specific antibody production by CD8+ class I-restricted antiviral cytotoxic T cells in vivo. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3661–3668. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3661-3668.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadler L. M., Ritz J., Hardy R., Pesando J. M., Schlossman S. F., Stashenko P. A unique cell surface antigen identifying lymphoid malignancies of B cell origin. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jan;67(1):134–140. doi: 10.1172/JCI110005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka Y., Lipsky P. E. The role of CD40-CD40 ligand interaction in human T cell-B cell collaboration. J Immunol. 1994 Aug 1;153(3):1027–1036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Schlossman S. F. The differentiation and function of human T lymphocytes. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):821–827. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90072-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson M. J., Caligiuri M. A., Manley T. J., Levine H., Ritz J. Human natural killer cell adhesion molecules. Differential expression after activation and participation in cytolysis. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 15;145(10):3194–3201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer G. G., Abbas A. K. The fas antigen is involved in peripheral but not thymic deletion of T lymphocytes in T cell receptor transgenic mice. Immunity. 1994 Aug;1(5):365–371. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(94)90067-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleasman J. W., Morimoto C., Schlossman S. F., Tedder T. F. The role of functionally distinct helper T lymphocyte subpopulations in the induction of human B cell differentiation. Eur J Immunol. 1990 Jun;20(6):1357–1366. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830200623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. A., Farrah T., Goodwin R. G. The TNF receptor superfamily of cellular and viral proteins: activation, costimulation, and death. Cell. 1994 Mar 25;76(6):959–962. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90372-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streuli M., Morimoto C., Schrieber M., Schlossman S. F., Saito H. Characterization of CD45 and CD45R monoclonal antibodies using transfected mouse cell lines that express individual human leukocyte common antigens. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 1;141(11):3910–3914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugita K., Hirose T., Rothstein D. M., Donahue C., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. CD27, a member of the nerve growth factor receptor family, is preferentially expressed on CD45RA+ CD4 T cell clones and involved in distinct immunoregulatory functions. J Immunol. 1992 Nov 15;149(10):3208–3216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugita K., Robertson M. J., Torimoto Y., Ritz J., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. Participation of the CD27 antigen in the regulation of IL-2-activated human natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1992 Aug 15;149(4):1199–1203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugita K., Torimoto Y., Nojima Y., Daley J. F., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. The 1A4 molecule (CD27) is involved in T cell activation. J Immunol. 1991 Sep 1;147(5):1477–1483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takebe Y., Seiki M., Fujisawa J., Hoy P., Yokota K., Arai K., Yoshida M., Arai N. SR alpha promoter: an efficient and versatile mammalian cDNA expression system composed of the simian virus 40 early promoter and the R-U5 segment of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 long terminal repeat. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):466–472. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshizumi H., Kamikawaji N., Nishimura Y., Sasazuki T. Generation of a novel CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocyte that requires soluble factor to lyse autologous antigen-presenting cells. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Dec;23(12):3173–3180. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830231220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Lier R. A., Borst J., Vroom T. M., Klein H., Van Mourik P., Zeijlemaker W. P., Melief C. J. Tissue distribution and biochemical and functional properties of Tp55 (CD27), a novel T cell differentiation antigen. J Immunol. 1987 Sep 1;139(5):1589–1596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



