Abstract
Down syndrome (DS) is the most frequent genetic cause of intellectual disability characterized by the presence of three copies of chromosome 21 (Chr21). Individuals with DS have sufficient neuropathology for a diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease (AD) after the age of 40 years. The aim of our study is to gain new insights in the molecular mechanisms impaired in DS subjects that eventually lead to the development of dementia. We evaluate the PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis in the frontal cortex from DS cases (under the age of 40 years) and DS with AD neuropathology compared with age-matched controls (Young and Old). The PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis may control several key pathways involved in AD that, if aberrantly regulated, affect amyloid beta (Aβ) deposition and tau phosphorylation. Our results show a hyperactivation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis in individuals with DS, with and without AD pathology, in comparison with respective controls. The PI3K/Akt/mTOR de-regulation results in decreased autophagy, inhibition of IRS1 and GSK3β activity. Moreover, our data suggest that aberrant activation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis acts in parallel to RCAN1 in phosphorylating tau, in DS and DS/AD. In conclusion, this study provides insights into the neuropathological mechanisms that may be engaged during the development of AD in DS. We suggest that deregulation of this signaling cascade is already evident in young DS cases and persist in the presence of AD pathology. The impairment of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis in DS population might represent a key-contributing factor to the neurodegenerative process that culminates in Alzheimer-like dementia.
Keywords: mTOR, Akt, PI3K, autophagy, insulin signaling, trisomy 21
INTRODUCTION
Down syndrome (DS), a genetic condition most commonly characterized by the triplication of chromosome 21 (trisomy 21), is the most frequent chromosomal abnormality that causes neurologic deficiencies worldwide and affects all racial and socioeconomic groups. Life expectancy of the DS population increased significantly in the last decades due to improvement in health care, particularly in younger individuals. However, increased lifespan is associated with an increased incidence of Alzheimer disease (AD) neuropathology and dementia [1]. Among causative factors, one of the most accepted hypothesis is centered on the triplication of the amyloid-beta precursor protein (APP) gene, which is encoded on Chr21 and leads to protein overexpression [2]. In fact, DS patients show early plaque deposition and other characteristic pathological hallmarks associated with the clinical course of AD [3, 4]. The main difference is the early age of onset of AD pathology in individuals with DS (40-50 years), with high incidence of clinical symptoms in the range of 50-60 years of age [5]. A number of studies demonstrated that the accumulation of amyloid beta (Aβ- peptide in DS brain can be observed as early as 8–12 years of age [6]. The etiology of AD still remains obscure and the molecular pathways by which the various pathological alterations selectively impair cognitive domains related to learning and memory are far from being clarified. Within this context, by studying autopsy samples from individuals with DS of various ages provides critical information regarding AD pathogenesis. Recently, Cenini et al. [7] demonstrated that Aβ peptide and its small-derived oligomers increase as a function of age in DS frontal cortex, and this is accompanied by elevated protein carbonylation, a marker of oxidative stress. A number of studies have shown that trisomy-related increase of oxidative stress might be involved in different aspects of DS phenotypes [1, 8-11]. In line with these studies, our group reported that DS brain, prior to significant AD pathology, show an early disturbance of the proteostasis network possibly linked to increased oxidative stress conditions and also autophagy impairment [12]. A decreased ratio of LC3 II/I, an index of autophagosome formation, was demonstrated thus suggesting that decrease of autophagic flux occurrs early in DS.
Considering the current notion that autophagy plays a critical role in multiple pathological lesions of AD [13-16], we focus our attention on autophagy-related pathways to better understand their involvement in the development of Alzheimer-like neurodegeneration in DS individuals. Indeed, dysfunction of the autophagy-lysosomal system also contributes to Aβ accumulation, the formation of tau oligomers, and insoluble aggregates, and in contrast induction of autophagy enhances the clearance of both soluble and aggregated forms of Aβ and tau proteins [17].
The autophagy cascade is regulated by PI3K (phosphoinositide3-kinase)/Akt/mTOR axis, which plays a central role in controlling protein homeostasis. The normal on/off switching of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway, particularly by its major activators insulin and IGF-1 (insulin-like growth factor-1), integrates physiological responses fundamental to healthy aging and longevity. Several studies showed aberrant and sustained activation of neuronal PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling in AD brain [18-20]. In parallel, the activation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR is reported to cause insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS1) inhibition, disabling normal activation of PI3K/Akt by insulin, IGF-1 and other growth factors. An increasing number of studies demonstrated that memory alterations could be linked to abnormalities in circulating insulin levels and/or defects in insulin signaling pathways in AD [20-24]. Furthermore, a prolonged peripheral hyperinsulinemia could impair the blood brain barrier and insulin transport into CNS, thus affecting insulin receptor (IR) activity and culminating in a brain insulin-resistance that could account for the lower insulin levels in CSF of AD patients. It is well-known that diabetes mellitus has a higher prevalence in DS than in the general population [25] and a relationship may exist between insulin resistance and the development of AD in the typical, elderly, adult population and in DS.
Based on these observations, the aim of the current study was to investigate the status of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in the frontal cortex from DS autopsy cases without AD neuropathology (typically under the age of 40 years) and DS with AD neuropathology. Both DS groups were compared with appropriate non-DS, healthy age-matched controls. We tested the hypothesis that the overactivation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR sustained by increased Aβ levels may, directly or indirectly, uncouple insulin response. Considering the cross-talk between insulin resistance and cognitive defects, we hypothesize that alteration of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathways may play a role in the development of dementia in DS, before clinical manifestation AD neuropathology.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Subjects
DS and young or older control cases (without AD neuropathology) were obtained from the University of California-Irvine-ADRC Brain Tissue Repository, the Eunice Kennedy Shriver NICHD Brain and Tissue Bank for Developmental Disorders, and the University of Kentucky Alzheimer's Disease Center. Table 1 shows the characteristics of the included cases. DS cases were divided into two groups, with or without sufficient pathology for a neuropathology diagnosis of AD. All cases with both DS and AD were over the age of 40 years. Thus for the current study, controls were split into two groups, either less than or equal to 40 years or older than 40 years at death. The post mortem interval (PMI) was different across groups with DS/AD having a significantly shorter value in respect to the other groups (Table 1). The subgroup used in this study was selected in order to maintain homogenous age and gender inside the groups and is part of the entire cohort used in a previous experiment to investigate insoluble Aβ and total oxidation as a function of age in DS [7].
Table 1.
Autopsy case demographics. A complete set of information is reported as supplementary material (extensive demographic data are reported in sup. table 1).
| Groups | n | Gender (M/F) | Age (avg. ± SD) | PMI (avg. ± SD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control Y | 8 | 4/4 | 24.8 ± 11.6 | 12.1 ± 4.71 |
| DS | 8 | 6/2 | 23.3 ± 16.8 | 13.4 ± 2.13 |
| Control O | 8 | 5/3 | 57.2 ± 7.6 | 11.3 ± 6.90 |
| DS/AD | 8 | 5/3 | 59.5 ± 3.2 | 4.2 ± 1.57* |
Significantly shorter than the other 3 groups.
Sample preparation for Western Blots
Frontal cortex tissue 20 mg (n= 8 per group) from controls (young and old), DS, and DS/AD were thawed in RIPA buffer (pH 7.4) containing 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.4), 150 mM NaCl, 1% NP-40, 0.25 % sodium deoxycholate,1mM EDTA, 0,1% SDS, 1mM PMSF, 1 mM NaF and 1 mM Na3VO4. Brains were homogenized by 20 passes of a Wheaton tissue homogenizer, and the resulting homogenate was centrifuged at 14,000 ×g for 10 min to remove cellular debris. The supernatant was extracted to determine the total protein concentration by the Bradford assay (Pierce, Rockford, IL).
Western Blot
For Western blots, 30 μg of proteins (CTR and DS) were separated by 12% and 7.5% SDS– PAGE using Criterion Gel TGX Stain free (Bio-Rad) and blotted into a nitrocellulose membrane (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). Before blotting the gel image with protein total load was acquired to normalize blot analysis. Membranes were blocked with 3% bovine serum albumin in T-TBS and incubated for 1 h and 30 min at room temperature with primary anti-bodies: p-44/42 MAPK (Thr202/Tyr204) (1:2000), mTOR (1:1000), p-mTOR (Ser2448) (1:1000), Akt and p-Akt (Ser473) (1:1000), p-70S6K (Thr389) (1:1000), IRS1 and p-IRS1 (Ser307) (1:1000) from Cell Signaling; LC3 II/I (1:500) from NOVUS; p-mTOR (Ser2448), p-Tau (Ser404) (1:1000), GSK3 β and p-GSK3β (Ser9) (1:1000) from Santa Cruz; RCAN 1 and DYRK1A (1:1000) from Sigma-Aldrich. After three washes with T-TBS, the membranes were incubated for 1 h at room temperature with secondary antibody horseradish peroxidase-conjugated anti-rabbit or anti-mouse IgG (1:5000; Sigma–Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA). Membranes were developed with the Super Signal West Pico chemiluminescent substrate (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) acquired with Chemi-Doc MP (Bio-Rad) and analyzed using Image Lab software (Bio-Rad) that allow the normalization of specific protein signal with proteins total load obtained by fluorescent detection of monodimensional proteome on TGX stain free gels (Figures 1,2,3,5 and 6).
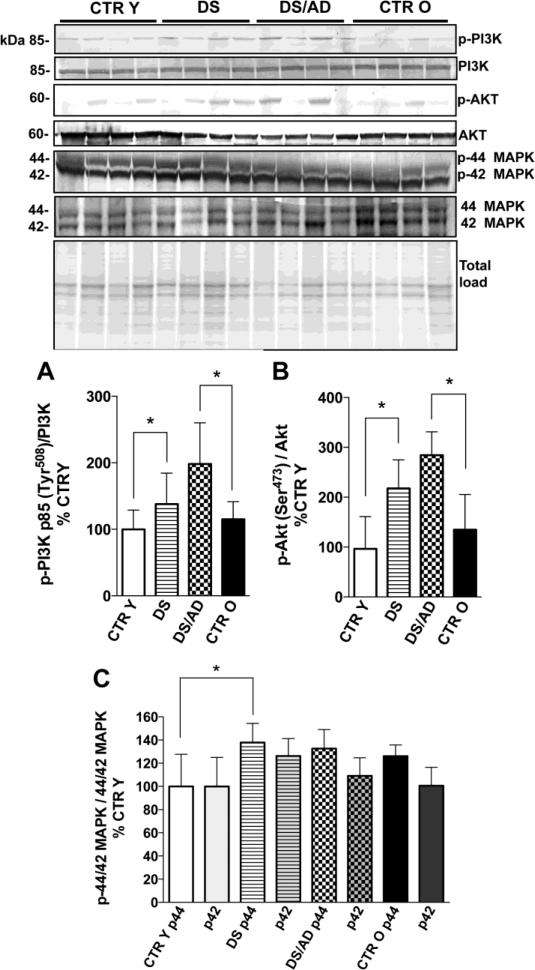
Figure 1.
PI3K p85 phosphorylation levels (Tyr508) and expression levels ratio (panel A), Akt phosphorylation levels (Ser473) and expression levels ratio (panel B) and MAPK 44/42 (ERK1/2) phosphorylation levels normalized on expression levels (panel C) in brain frontal cortex of controls and DS cases. Brain samples of frontal cortex were assayed by Western blot as described in the Materials and Methods section. Densitometric values shown in the histograms are the mean of 8 individual cases per each experimental group normalized per total protein load and are given as percentage of young control, set as 100%. Above in the figure a representative blot image (with 4 of 8) protein bands is shown. * p<0.05; §p=0.07.
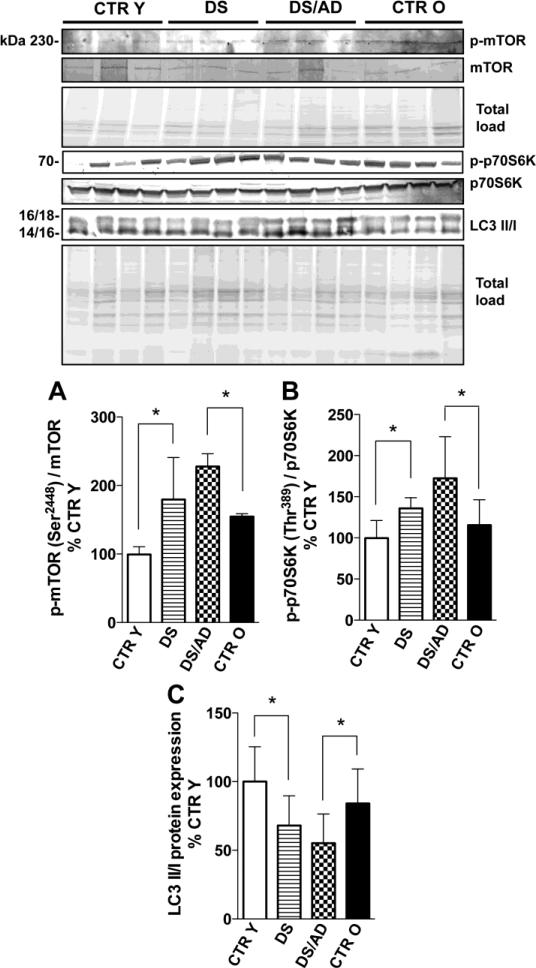
Figure 2.
mTOR phosphorylation levels (Ser2448) and expression levels ratio (panel A), p70S6K phosphorylation levels (Thr389) and expression levels ratio (panel C) and LC3 II/I expression levels ratio (panel B) in brains frontal cortex of controls and DS cases. Densitometric values shown in the histograms are the mean of 8 individual cases per group normalized per total protein load and are given as percentage of Control, set as 100%. Above in the figure a representative blot image with (with 4 of 8) protein bands is shown. * p<0.05.
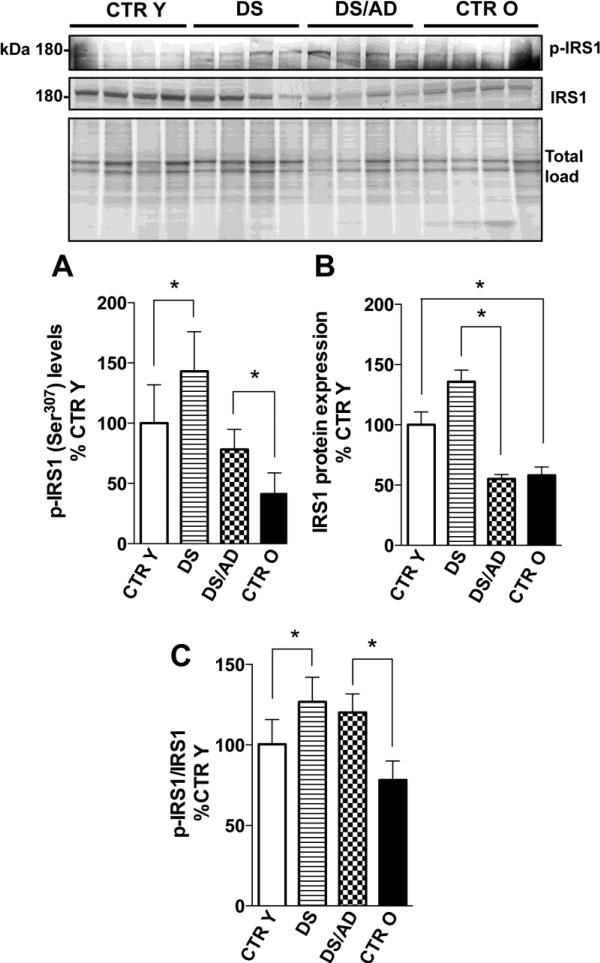
Figure 3.
IRS1 phosphorylation levels (Ser307) (panel A) and IRS1 expression levels (panel B) in brains frontal cortex of controls and DS cases. Densitometric values shown in the histograms are the mean of 8 individual cases per group normalized per total protein load and are given as percentage of Control, set as 100%. In panel C the histogram represent the average per group of phosphorylation values normalized for expression values, the normalization was performed on each single subject analyzed. Above in the figure a representative blot image with (with 4 of 8) protein bands is shown. * p<0.05.
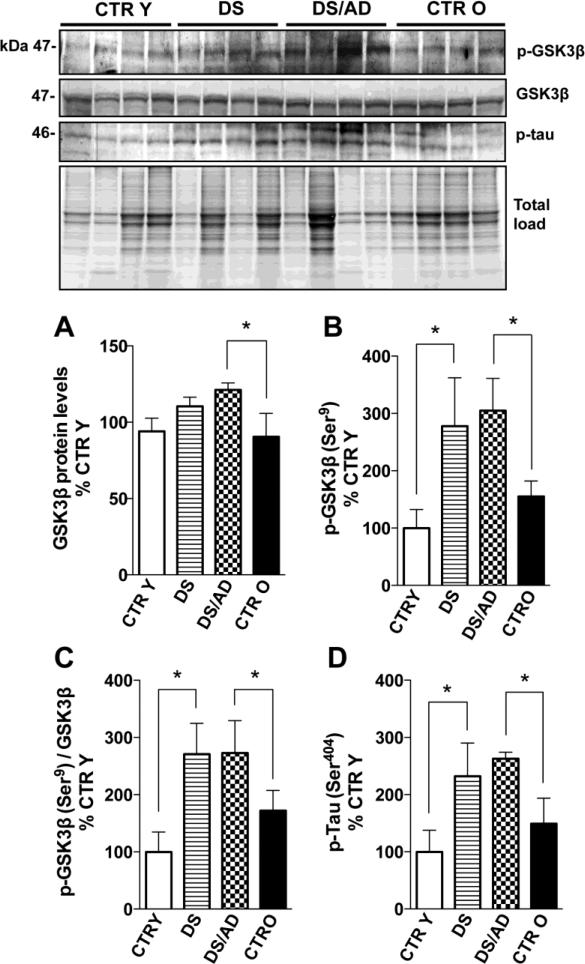
Figure 5.
GSK3β (Ser9) phosphorylation levels (panel A), GSK3β expression levels (panel B), the GSK3β phosphorylation/expression ratio (panel C) and tau phosphorylation levels (Ser404) (panel D) in brain frontal cortex of controls and DS cases. Densitometric values shown in the histograms are the mean of 8 individual samples per group normalized per total protein load and are given as percentage of Control, set as 100%. Above in the figure a representative blot image with protein bands is shown. * p<0.05.
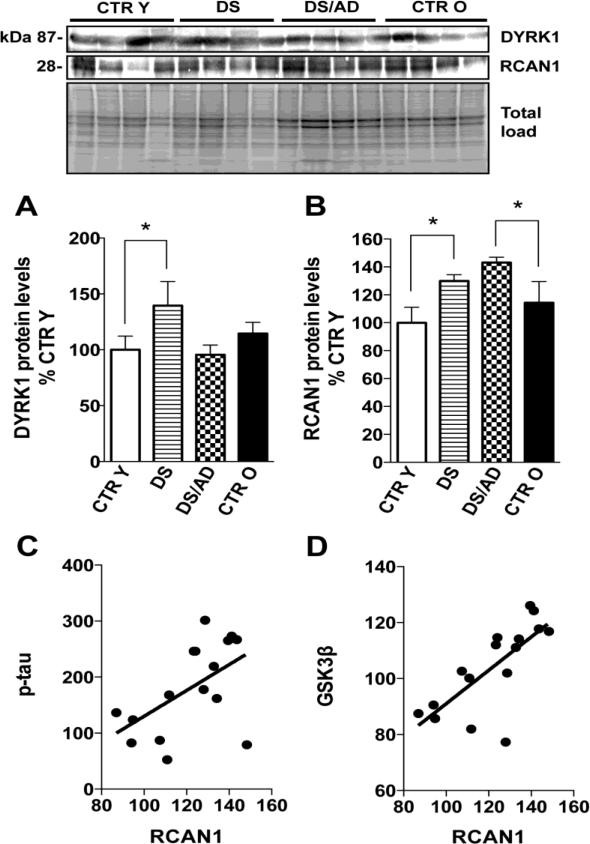
Figure 6.
DYRK1A (panel A) and RCAN1 (panel B) expression levels in brain frontal cortex of controls and DS cases. Densitometric values shown in the histograms are the mean of 8 individual samples per group normalized per total protein load and are given as percentage of Control, set as 100%. Above in the figure a representative blot image with protein bands is shown. * p<0.05. In panel C and D the correlation analysis of RCAN1 with p-tau (graph on the left) and GSK3β (graph on the right) are shown.
Statistical analysis
Data are expressed as mean ± SD of 8 independent samples per group. All statistical analyses were performed using a non-parametric one-way ANOVA with post hoc Bonferroni t-test. p<0.05 (*) was considered significantly different from control. Since DS/AD PMI is significantly different in comparison to the other three groups we performed linear regression analyses between each experimental data vs. PMI in order to test if our results were affected by PMI variable. Moreover, we correlated experimental data from CTR group (CTR Y and CTR O) and DS group (DS and DS/AD) with age to analyze the effects of age variations. Finally, to determine how our data are affected by genotype (DS) and age and the interaction of such factors we accomplished a 2-way ANOVA analysis. All statistical analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism 5.0 software.
RESULTS
PI3K/Akt pathway
In order to evaluate if the PI3K/Akt pathway was impaired in the brains of DS and DS with AD pathology cases, we analyzed by Western Blot the phosphorylated PI3K p85α subunit (Tyr508) and Akt (Ser473) (Figure 1 A & B). PI3K is a heterodimer formed by a p110 catalytic subunit and a p85 regulatory subunit. The most highly expressed regulatory subunit is p85α, and one of two domains binds preferentially to phosphorylated tyrosine residues [26]. In this pathway the increased phosphorylation of PI3K induces an increased level of phosphorylated Akt. Akt is activated by phospholipid binding, by phosphorylation within the carboxy-terminus at Ser473, and by activation loop phosphorylation at Thr308 by PDK1 [27]. We first determined that PMI was not a significant contributor to the outcome and a linear regression analysis of both p-PI3K and p-Akt values with PMI showed no significant p-value (R2=0.073, p=0.132 for p-PI3K; R2=0.053, p=0.204 for p-Akt) indicating no relation of PI3K or Akt phosphorylation with PMI variation. Increased phosphorylation of PI3K p85α subunit (Tyr508) normalized on protein expression (Figure 1A) in both DS and DS/AD individuals compared with age matched CTR was found, in the latter the increase of 80% was statistically significant (*p<0.05) while in the comparison DS vs. CTR Y was close to significance (§p=0.07). The phosphorylation of Akt (Ser473) (normalized on protein expression level) was significantly increased in DS vs. CTR Y (215%, p<0.05) 50% and in DS/AD vs. CTR O (285% vs. 113%, *p<0.05) (Figure 1B). No significant differences were found between DS and DS/AD groups for both p-PI3K and p-Akt values. Further, The linear regression analyses of CTR cases and DS cases subgroups separately and age showed no significant correlations between p-PI3K (CTR p= 0.4, R2 = 0.048; DS p= 0.14, R2 = 0.14) and p-Akt (CTR p= 0.47, R2 = 0.036; DS p= 0.4, R2 = 0.049) and age. Overall, when including all DS and control cases, protein phosphorylation values were not associated with age variable (R2=0.074, p=0.131 for p-PI3K; R2=0.021, p=0.426 for p-Akt). However 2-way ANOVA analysis (table 2) show that age significantly account for 8.26% (p=0.021) and 11.75% (p=0.020) of the total variance of p-Akt and p-PI3K respectively while genotype significantly account for 52.09% (p<0.0001) and 29.30% (p=0.0006).
Table 2.
2-way ANOVA analysis data
| Target of analysis | 2-way ANOVA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (Young - Old) | Genotype (DS – DS/AD) | Interaction | |||
| % of tot var. | p value | % of tot var. | p value | ||
| p-Akt | 8.26 | *0.021 | 52.09 | *<0.0001 | 0.532 |
| p-PI3K | 11.75 | *0.020 | 29.30 | *0.0006 | 0.137 |
| MAPK p44 | 5.73 | 0.286 | 25.84 | *0.0357 | 0.118 |
| MAPK p42 | 4.69 | 0.385 | 20.73 | 0.082 | 0.355 |
| p-mTOR | 18.57 | 0.113 | 34.29 | *0.042 | 1.000 |
| LC3 II/I | 7.15 | 0.189 | 31.88 | *0.010 | 0.880 |
| p-p70S6K | 9.92 | *0.033 | 32.77 | *0.0004 | 0.377 |
| IRS1 | 28.18 | *0.002 | 1.33 | 0.470 | 0.526 |
| p-IRS1 | 50.33 | *<0.0001 | 21.08 | *0.003 | 0.799 |
| p-IRS1/IRS1 | 4.74 | 0.304 | 26.55 | *0.023 | 0.576 |
| p-tau | 7.24 | 0.079 | 68.65 | *<0.0001 | 0.662 |
| p-GSK3β | 1.45 | 0.466 | 62.14 | *0.0004 | 0.162 |
| RCAN1 | 14.10 | *0.016 | 64.23 | *<0.0001 | 0.914 |
| DYRK1A | 1.56 | 0.480 | 3.76 | 0.275 | 0.085 |
ERK1/2 pathway
MAPK 44/42 (ERK1/2) is a kinase activated in response to insulin signaling that regulates mTOR and the autophagy pathway and exhibits a negative feedback modulation of IRS1 activity by phosphorylating IRS inhibitory residue [28]. Thus, ERKs aberrant activity could be involved in mTOR hyperactivation, autophagy impairment and IRS mediated insulin resistance in DS and AD brain. Several genes mapping to chromosome 21 interact with MAPK, and also MAP kinase 44/42 is one of several kinases involved in pathological tau-hyperphosphorylation. Linear regression analyses show that MAPK 44/42 phosphorylation is not dependent on PMI (R2=0.002, p=0.860 for MAPK 44; R2=0.020, p=0.598 for MAPK 42) s. In addition, the linear regression analyses of CTR cases and DS cases separately and age did not show significant correlations with MAPK p44 (CTR p= 0.19, R2 = 0.26; DS p= 0.45, R2 = 0.095). Our data demonstrate the aberrant phosphorylation of MAPK 44 (ERK 1), with a significant increase (40%) in DS brain compared to age-matched CTR but not in DS with AD (Figure 1C) when compared to CTR O. No significant differences were found in the comparison of DS and DS/AD groups. The 2-way ANOVA analysis (table 2) show that age and genotype have not significant effect on MAPK p42 data, while for MAPK p44 genotype but not age significantly account for 25.84% (p=0.035) of the total variance. We suggest that MAPK 44 activation in DS could contribute with PI3K/Akt to the aberrant regulation of mTOR activity and autophagosome formation.
mTOR activation and inhibition of autophagosome formation
A major downstream target of the PI3K/Akt pathway is mTOR. Consequently we analyzed the expression levels and phosphorylation (Ser2448) of mTOR. mTOR did not show any significant difference in expression between the two groups of comparison. In contrast the extent of phosphorylated mTOR showed increased levels in both DS (about 180%, p<0.05) and DS/AD (about 150%, p<0.05) compared to age-matched controls (Figure 2A). A linear regression analyses showed no association of all groups between p-mTOR and PMI values (R2= 0.058, p=0.447); 2-way ANOVA analysis of mTOR data show that genotype significantly account for 34.29% (p=0.042) of total variance while age have not significant effect (table 2); however, p-mTOR signal was very faint and not easy to analyze Figure 2. Thus, to confirm mTOR activation we analyzed p70S6K phosphorylation (Thr389), a direct downstream target of mTOR activity that is often employed to indirectly measure mTOR phosphorylation. The data show increased p-p70S6K (normalized on protein expression) in DS vs. CTR Y (about 40%, p<0.05) and in DS/AD vs. CTR O (about 60%, p<0.05) but not in DS vs. DS/AD (Figure 2B). mTOR directly regulates the autophagy pathway, suggesting that increased PI3K/Akt/mTOR activity contributes to decreased autophagic flux observed in DS and AD subjects. The analysis of LC3II/I, an index of autophagosome formation, confirms our hypothesis, showing a decreased LC3 II/I ratio early in DS brain (near 30% lower levels as compared with age matched controls, p<0.05) and further decreased levels in DS with AD (about 45% lower, p<0.05) in comparison to their respective age-matched controls. No significant differences were found in the comparison of DS and DS/AD groups (Figure 2C). Both p70S6K phosphorylation levels and LC3 II/I ratio of all groups analyzed together by linear regression show no relation with PMI differences (R2=0.048, p=0.224 for p-p70S6K; R2=0.015, p=0.605 for LC3 II/I) or age differences (R2=0.089, p=0.095 for p-p70S6K; R2=0.094, p=0.183 for LC3 II/I) among the groups. The linear regression analyses of CTR cases and DS cases separately with age showed significant correlations of p-p70S6K only in CTR cases (p= 0.04, R2 = 0.25) but not in DS cases (p= 0.26, R2 = 0.087). In contrast, LC3 data showed no significant correlation with age within each group (CTR p= 0.63, R2 = 0.029; DS p= 0.098, R2 = 0.30). 2-way ANOVA analysis of p-PI3K demonstrates that age significantly account for 9.22% (p=0.033) of the total variance while genotype significantly account for 32.77% (p=0.0004). LC3 II/I analysis shows that genotype significantly account for 31.88% (p=0.01) of the total variance while age have not significant effect (table 2). Our results shown in Figure 2B is consistent with our previous work where we demonstrate the impairment of autophagosome formation in DS compared to CTR Y [12] and now present novel data showing a comparable decreased levels of autophagosome function in DS/AD when compared to older age matched controls.
IRS1 inactivation is induced by PI3K/Akt pathway impairment
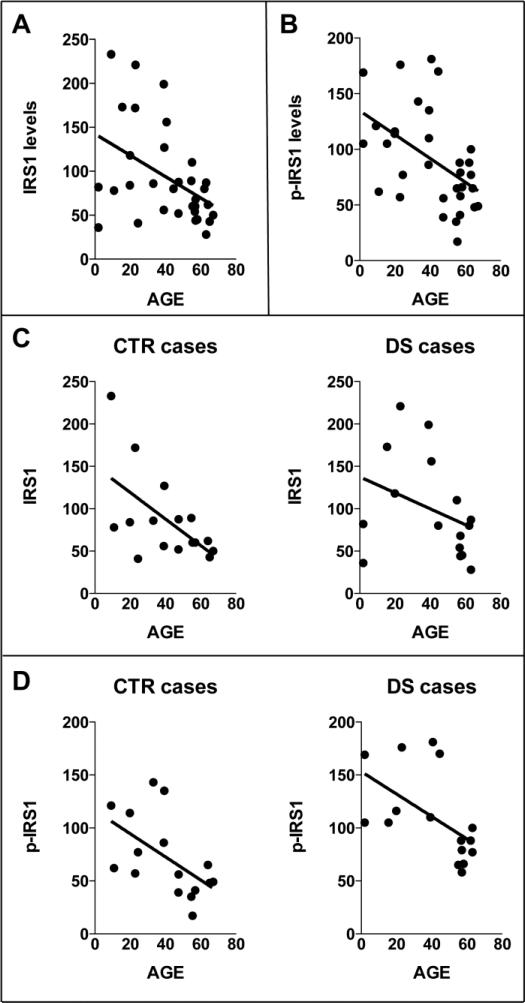
PI3K/Akt is closely related to insulin signaling through insulin substrate receptor (IRS1). PI3K is directly phosphorylated by IRS1 regulating PI3K/Akt cascade in response to insulin levels. In contrast, sustained PI3K/Akt activation inhibits IRS1 activity by negative feedback through the activation of mTOR and p70S6K that phosphorylate IRS1 on its inhibitory domain (Ser307) [18]. To evaluate the levels of IRS1 inactivation in the four groups, we analyzed the expression levels of IRS1, the phosphorylation levels of IRS1 at Ser307 and the ratio of the two. Phosphorylated IRS1 was increased ~ 30% in DS compared to CTR Y and higher in DS/AD compared to CTR O (p<0.05; Figure 3A). DS/AD had lower levels of p-IRS1 compared to DS (about 55%; p<0.05). IRS1 expression levels are increased in DS compared with CTR Y (40%, p<0.05) but no differences were observed between DS/AD and CTR O (Figure 3B). The ratio of phosphorylated IRS1 to total IRS1 showed a significant increase between DS and CTR Y (126%, p<0.05) and 153% (p<0.05) higher in DS/AD compared to CTR O (Figure 3C). There were no differences between DS and DS/AD. The linear regression analysis shows that IRS1 expression decreased overall as a function of age (R2=0.198, p=0.010) (Figure 4A & B), independent of the presence of DS. Interestingly, the linear regression analyses of CTR cases and DS cases separately with age showed a strong correlation for IRS1 phosphorylation levels in both CTR and DS (CTR p= 0.025, R2 = 0.30; DS p= 0.026, R2 = 0.30; Figure 4C), while IRS1 expression levels were significantly correlated with age only for CTR cases (CTR p= 0.017, R2 = 0.34; DS p= 0.19, R2 = 0.12; Figure 4D). 2-way ANOVA analysis of IRS1 expression show that age significantly account for 28.18% (p=0.002) of the total variance while genotype has not significant effect. The analysis of p-IRS shows that age significantly account for 50.33% (p<0.0001) of the total variance while genotype significantly accounts for 21.08% (p=0.003) of the total variance (table 2). Overall, when IRS1 phosphorylation values are normalized on expression values the 2-way ANOVA analysis show that genotype significantly account for 26.55% (p=0.023) of the total variance while age has not significant effect (table 2). Both IRS1 expression and phosphorylation levels analyzed by linear regression show no relation with PMI variations among the groups (R2=0.002, p=0.798; R2=0.016, p=0.608).
Figure 4.
In panel A and B linear regression graph of both total IRS1 expression (IRS1) levels and total phosphorylation (p-IRS1) levels with age are shown. In panel C the linear regression analysis of IRS1 expression levels and age in CTR and DS cases subgroups is shown. In panel D the linear regression analysis of IRS1 phosphorylation levels and age in CTR and DS cases subgroups is shown.
p-tau and tau kinases (GSK3β , RCAN1 and DYRK1A)
The hyperphosphorylation of tau in brains of DS cases has been demonstrated by several authors [4], and our data confirm that both DS vs. CTR Y and DS/AD vs. CTR O show increased levels of tau phosphorylation (about 200%, p<0.05) at Ser404 (Figure 5C; 5D). The comparison of DS/AD and DS groups show no significant differences. Several proteins are involved in tau phosphorylation such as GSK3β and DYRK1A that function as kinases or RCAN1 through the inhibition of calcineurin [29-32]. Akt is known to directly regulate GSK3β by phosphorylation of its inhibitory serine residue (Ser9). Therefore, we measured the levels of GSK3β expression and of GSK3β phosphorylated at Ser9 in our groups. GSK3β expression levels were higher in DS cases compared to each appropriate age matched CTR group reaching significance in DS/AD vs. CTR O (about 30%, p<0.05), no significant differences were found between DS and DS/AD groups (Figure 5A). GSK3β inhibitory phosphorylation levels were significantly increased in DS vs. CTR Y (177%, p<0.05) and in DS/AD vs. CTR O (150%, p<0.05) suggesting increased inactivation of GSK3β even when normalized on protein expression (Figure 5B&C) in DS overall. A comparison between DS and DS/AD groups showed no significant differences, and interestingly, values are very similar between these two groups. As previously noted tau phosphorylation could be induced directly or indirectly by DYRK1A and RCAN1, which are both encoded on chromosome 21. Our analysis of DYRK1A and RCAN1 expression levels demonstrated elevated expression levels of DYRK1A in DS vs. CTR Y (about 40%, p<0.05) but not in DS/AD vs. CTR O, moreover, DS values show significantly increased levels of DYRK1A when compared to DS/AD (Figure 6A). Our data demonstrate increased expression levels of RCAN1 in both DS vs. CTR Y (about 30%, p<0.05) and in DS/AD vs. CTR O (about 45%, p<0.05) but not in DS vs. DS/AD, supporting the likely involvement of this protein in phosphorylating tau (Figure 6B) in DS overall. Indeed, RCAN1 levels positively correlate with p-tau levels (p=0.031, r=0.538; Figure 6C), while DYRK1A does not (p=0.39, r=0.22). In addition RCAN1 expression levels correlates positively with GSK3β levels (p=0.013, r=0.73) (Figure 6D). The extent of tau phosphorylation, GSK3β phosphorylation, DYRK1A and RCAN1 expression levels are independent of PMI (R2=0.0003, p=0.944 for p-tau; R2=0.016, p=0.636 for p-GSK3β; R2=0.060, p=0.176 for DYRK1A; R2=0.070, p=0.319 for RCAN1) or age variations (R2=0.071, p=0.315 for p-tau; R2=0.017, p=0.624 for p-GSK3β; R2=0.063, p=0.173 for DYRK1A; R2=0.163, p=0.119 for RCAN1) among all groups analyzed together. Moreover, the linear regression analyses of CTR cases and DS cases separately with age showed no significant correlation for p-tau (CTR p= 0.26, R2 = 0.19; DS p= 0.64, R2 = 0.037), a significant correlation for p-GSK3β only in CTR cases (CTR p= 0.028, R2 = 0.57; DS p= 0.7, R2 = 0.026), no significant correlation for DYRK1A (CTR p= 0.67, R2 = 0.012; DS p= 0.62, R2 = 0.017) and significant correlations for RCAN1 in CTR cases (CTR p= 0.039, R2 = 0.53; DS p= 0.16, R2 = 0.29) but not in DS cases. 2-way ANOVA analysis demonstrate that for p-tau genotype significantly account for 68.65% (p<0.0001) of total variance while age has not significant effect; for p-GSK3β genotype significantly account for 62.14% (p=0.0004) of total variance while age has not significant effect; for RCAN1 age significantly account for 14.10% (p=0.016) of total variance while genotype account for 64.23% (p<0.0001); for DYRK1A age and genotype has no significant effect (table 2).
DISCUSSION
The brains of individuals with DS are characterized by an age-dependent deposition of Aβ as consequence of increased APP [3, 33, 34]. Similar to AD, Aβ accumulation in DS is associated with enhanced oxidative stress [35], indexed, in both DS and DS/AD specimens, by markers of protein oxidation (protein bound-HNE and protein carbonyls) and increased oxidative modification of target proteins mostly belonging to the proteostasis network [1, 7, 36]. Taken together, these findings suggest that AD neuropathology develops in an age-associated manner in DS and provide useful insights into the earliest signs of AD pathogenesis. In particular, the aim of the present study was to test the hypothesis that disturbance of PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis may be involved in the development of AD in DS population.
Several studies showed an aberrant and sustained activation of neuronal PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling in the early stages of AD [37, 38].. Increased Akt activation, and its altered subcellular localization, has been described in hippocampal and cortical neurons of AD brain [39-42]. Aβ species, have been described to interact and over-activate the PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis inducing resistance to its major activators, insulin and IGF-1 [18, 20]. Our data are consistent with the current literature demonstrating that PI3K (p85 subunit) is aberrantly phosphorylated in DS and DS/AD compared to age-matched CTR (Figure 3A). As well, Akt phosphorylation (Ser473) is significantly increased in DS and in DS/AD compared to age-matched controls (Figure 1B). Accordingly, altered phosphorylation of Akt has also been observed in Ts65Dn and Ts1Cje mice models of DS [43, 44]. The link between Aβ production and PI3K/Akt overactivation is also suggested by the fact that in the absence of Aβ, decreased insulin signaling results in down-regulation of the PI3K/Akt pathway [45, 46]. In order to gain insights into the contribution of Aβ-related PI3K/Akt overactivation, we analyzed the molecular events triggered by such aberrant regulation. The varied cellular functions of PI3K-Akt are reflected in the diversity of its downstream targets: mTOR and S6K1 kinases are among their main downstream effectors [18, 21, 28]. Previous studies demonstrated that mTOR phosphorylation by Akt and Aβ is increased in AD brain [23, 47, 48]. In this study we measured the activation of mTOR by the analysis of extent of its phosphorylation and of one of its main targets, p70S6K, showing that mTOR is hyperactivated in DS and DS/AD compared to age-matched controls (Figure 2 A & B). As expected, mTOR activity is aberrantly increased in DS overall, independent of the presence of AD neuropathology.
In parallel, increased phosphorylation of mTOR inhibits autophagy through phosphorylation of the ULK1-Atg13-FIP200 complex and through the regulation of lysosomal function. Autophagy is one of the major intracellular proteolytic systems in which components of the cell are degraded in lysosomes/vacuoles and recycled, and it may be regarded as a protective process [14, 49-51]. We hypothesized that increased mTOR activity, mediated by Aβ-dependent Akt hyper activation, contributes to decreased autophagy seen in DS and AD subjects. Indeed, a decreased LC3II/I ratio, an index of autophagosome formation, occurs already in young DS brain and persists in DS/AD brain (Figure 2C). In our previous work, we demonstrated the oxidation of specific components of the protein degradative pathways (e.g. proteasome, autophagy) in DS cases [12].
The PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis is directly under the control of IRS1, the major insulin receptor substrate, which through Tyr-phosphorylation transmits insulin action. This signaling cascade is finely regulated by a negative-feedback mechanism that suppresses Akt activity in case of a permanent activation of mTOR/p70S6K signal [52-54]. The negative feedback mechanism acts through mTOR-mediated phosphorylation of IRS1 at Ser307, the best studied inhibitory residue that causes IRS1 inactivation, by disrupting IRS1 binding to IR, inhibiting its tyrosine phosphorylation, and directing IRS1 towards proteasome degradation [21]. The uncoupling of insulin signaling and PI3-K/Akt/mTOR axis by IRS1 inactivation represents one of the major causes of insulin resistance [45, 46]. Significant evidence indicates that IRS1 is phosphorylated at inhibitory serine residues (Ser307) by increased Akt-mTOR-p70S6K activity in AD neurons leading them to become totally resistant to both insulin and IGF-1 [55-57]. In addition, insulin resistance in AD might also be stimulated by Aβ monomers and soluble oligomers that bind to IRs, induce IR internalization in neurons and remove IR from dendrites [55, 58-61], or inactivate IRS1 through the activation of JNK via TNFα [62, 63]. Our data in frontal cortex from DS and DS/AD autopsy cases shows higher levels of phosphorylation of 11 inhibitory serine residue (Ser307) compared to their respective age-matched CTR (Figure 3A&C). Moreover, IRS1 levels and its phosphorylation are age-dependent, consistent with the notion that insulin signaling decreases in the elderly population [56]. However, the rate of IRS1 inhibition (measured as p-IRS1/IRS1) followed the same trend already described for the upstream effectors of the insulin signaling cascade (e.g. p-AKT, p-mTOR), confirming the alteration in DS cases in comparison to CTR cases.
MAPK 44/42 (ERK1/2) is activated in response to insulin signaling and regulates mTOR and autophagy pathways through the inhibition of TSC 1/2 exhibiting a negative feedback modulation of IRS1 inhibitory residue [20, 21, 28]. Our data demonstrate the aberrant phosphorylation of ERK1 in DS compared to age-matched CTR but not in DS with AD (Figure 1C). These results parallel the increased IRS1 inhibition we observed in DS and may suggest that the MAPK pathway is altered in young DS cases, possibly contributing to the attenuated insulin signaling. Moreover, ERK1 activation in DS could contribute with PI3K/Akt to the aberrant regulation of mTOR activity and autophagosome formation [28].
Interestingly, PI3-K/Akt/mTOR signaling is considered a primary candidate to transmit pathophysiological responses from Aβ to tau. The upregulation of p70S6K was found to be associated with accumulation of hyperphosphorylated tau in NFT in AD [47, 64] and the sustained activation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR, Aβ-dependent or not, was shown to directly impact tau hyperphosphorylation [18, 20, 65-67]. Akt inhibits GSK3β, a major candidate kinase involved in tau hyperphosphorylation [68, 69]. In line with these notions, Akt induced phosphorylation of GSK3β at Ser9, by insulin/IGF-1, inhibits tau phosphorylation in vitro [70, 71]. Although the role of GSK3β in tau pathologies has yet to be clearly defined, a number of recent studies have provided evidence supporting the inactivation of GSK3β in AD thus uncoupling its “proposed” role as a tau kinase [18]. Similarly, data from old TC1 mice, a model of trisomy21, also showed increased phosphorylation of GSK3β at Ser9 concomitant with increased tau phosphorylation [65]. Our data are in line with these results, showing increased tau hyperphosphorylation (Figure 5D) combined with PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis hyperactivation and GSK3β inhibition, as indexed by increased phosphorylation at Ser9 in DS overall. However, GSK3β protein levels were higher only in DS/AD compared with CTRO, possibly due to overall lower GSK3β in CTR O (Figure 5A). In previous studies, the overexpression of GSK3β was observed in cells treated with Aβ [32], and it is likely that its up-regulation could be a compensatory mechanism against reduced activity. Interestingly, levels of active (Tyr216) and inactive (Ser9) GSK3β were reported to be simultaneously increased in AD patients, suggesting that the regulation of both inhibitory and stimulatory inputs of GSK3β might be impaired [23].
Overall, these findings led to hypothesize that in the context of DS pathology tau hyperphosphorylation does not necessarily require GSK3β, but may be induced by the overexpression of specific genes, as a consequence of trisomy. Among such candidates, DYRK1A and RCAN1 have been proposed to mediate hyperphosphorylation of tau, and the increased expression and activity of both proteins have been reported in DS and AD [29-31, 72-74]. We found increased expression of DYRK1A in DS but not in DS/AD compared to CTR (Figure 6A). Further, there was a lowering of DYRK1A levels in DS/AD relative to DS alone. Interestingly, higher DYRK1A levels are associated with higher levels of phosphorylated, soluble tau in DS without AD neuropathology but not in DS/AD cases. These results suggest that DYRK1A may contribute to tau phosphorylation in young DS subjects but it might not be directly associated with AD pathology. As regard RCAN1, it may play a role due to its chronic overexpression in DS as well as in AD [29, 30]. RCAN1 is involved in binding and regulation of calcineurin activity and, once overexpressed trigger tau hyperphosphorylation and the formation of NFT [32, 75]. Moreover, calcineurin inhibition can decrease the proteasome-related degradation of tau [29, 30, 75, 76]. We found increased levels of RCAN1 in DS and DS/AD parallel to higher levels of tau phosphorylation (Figure 6B&C). Intriguingly, RCAN1 overexpression reported could lead to increased GSK3β expression and activity [32]; in our system we observe that that the expression levels of GSK3β correlate positively with RCAN1 expression levels (Figure 6D).
CONCLUSION
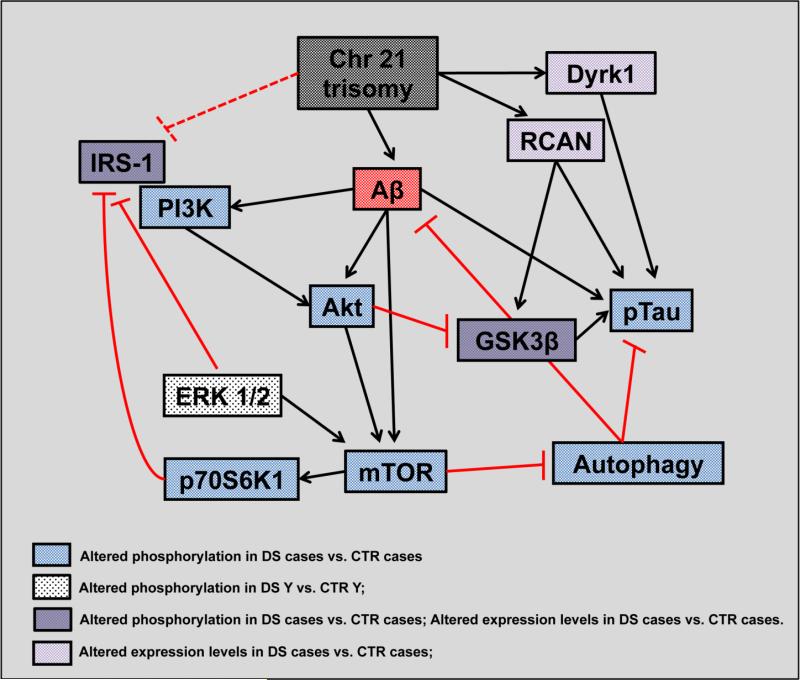
In summary, our results show a hyperactivation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis in the brains of DS with or without AD pathology in comparison to their respective age-matched CTR. The PI3K/Akt/mTOR deregulation may result in: i) decreased autophagy flux possibly contributing to Aβ deposition. Accordingly, our data on mTOR activation suggests its involvement, together with the oxidation/dysfunction of a number of autophagy components already demonstrated by our previous studies, into the decreased autophagosome formation reported in DS and DS/AD; ii) decreased IRS1 activity that represents one of the best-characterized events leading to insulin resistance. DS with AD and AD subjects undergo insulin resistance during their life as a consequence of the alteration of several, mostly unknown, molecular mechanisms [25, 56]. The alteration of mTOR pathway could represent an important link between Aβ and insulin signaling, providing new insights into the relationship between insulin resistance and incidence of AD; iii) decreased GSK3β activity, which is phosphorylated on its inhibitory serine residue when PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis is hyper-activated. GSK3β is closely related to tau hyperphosphorylation and its alteration has been demonstrated in AD. The inhibition of GSK3β by Akt kinases activity is counteracted by protein overexpression raising doubt on the effective role of GSK3β in DS/AD as solely responsible for tau hyperphosphorylation occurring in DS. In addition, our data suggest that PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis aberrant activation acts in parallel to DYRK1A and RCAN1 to push hyperphosphorylation of tau as a consequence of DS genetic defects in a GSK3β-independent manner (Figure 7).
Figure 7.
Putative scenario of the pathological role of PI3K/Akt/mTOR cascade in DS and DS/AD individuals, with main focus on proteins that might contribute to the reduction of insulin signaling and to the increase in tau phosphorylation
Supplementary Material
Highlights.
We show an hyperactivation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR axis in DS and DS with AD pathology
This deregulation results in the inhibition of autophagy, IRS1 and GSK3β activity
Hyperactivation of PI3K/Akt/mTOR acts in parallel to RCAN1 in phosphorylating tau
PI3K/Akt/mTOR impairment contribute to AD-like neurodegeneration in DS individuals
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was partially supported by PRIN2009 to C.C. and a NIH grant to D.A.B. [A6-05119]. Brain tissue was acquired by EH under funding from the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, National Institute on Aging Grant #NIH 1RO1HD064993-01. Additional autopsy tissue was obtained from the UCI-ADRC (P50AG16573), from the UK ADC (P30AG28383) and from the NICHD Brain and Tissue Bank for Developmental Disorders of the University of Maryland, Baltimore, MD, contract HHSN275200900011C (N01HD90011). The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final citable form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
All authors state that they have no conflicts of interest.
REFERENCES
- 1.Perluigi M, Butterfield DA. Oxidative Stress and Down Syndrome: A Route toward Alzheimer-Like Dementia. Curr Gerontol Geriatr Res. 2012;2012:724904. doi: 10.1155/2012/724904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Cheon MS, Dierssen M, Kim SH, Lubec G. Protein expression of BACE1, BACE2 and APP in Down syndrome brains. Amino Acids. 2008;35:339–343. doi: 10.1007/s00726-007-0618-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Wisniewski KE, Dalton AJ, McLachlan C, Wen GY, Wisniewski HM. Alzheimer's disease in Down's syndrome: clinicopathologic studies. Neurology. 1985;35:957–961. doi: 10.1212/wnl.35.7.957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Wisniewski KE, Wisniewski HM, Wen GY. Occurrence of Neuropathological Changes and Dementia of Alzheimers-Disease in down Syndrome. Ann Neurol. 1985;17:278–282. doi: 10.1002/ana.410170310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Schupf N, Sergievsky GH. Genetic and host factors for dementia in Down's syndrome. The British journal of psychiatry : the journal of mental science. 2002;180:405–410. doi: 10.1192/bjp.180.5.405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Leverenz JB, Raskind MA. Early amyloid deposition in the medial temporal lobe of young Down syndrome patients: a regional quantitative analysis. Exp Neurol. 1998;150:296–304. doi: 10.1006/exnr.1997.6777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Cenini G, Dowling AL, Beckett TL, Barone E, Mancuso C, Murphy MP, Levine H, 3rd, Lott IT, Schmitt FA, Butterfield DA, Head E. Association between frontal cortex oxidative damage and beta-amyloid as a function of age in Down syndrome. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1822:130–138. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2011.10.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Perluigi M, di Domenico F, Fiorini A, Cocciolo A, Giorgi A, Foppoli C, Butterfield DA, Giorlandino M, Giorlandino C, Schinina ME, Coccia R. Oxidative stress occurs early in Down syndrome pregnancy: A redox proteomics analysis of amniotic fluid. Proteomics Clin Appl. 2011;5:167–178. doi: 10.1002/prca.201000121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sultana R, Perluigi M, Allan Butterfield D. Lipid peroxidation triggers neurodegeneration: a redox proteomics view into the Alzheimer disease brain. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013;62:157–169. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.09.027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Conti A, Fabbrini F, D'Agostino P, Negri R, Greco D, Genesio R, D'Armiento M, Olla C, Paladini D, Zannini M, Nitsch L. Altered expression of mitochondrial and extracellular matrix genes in the heart of human fetuses with chromosome 21 trisomy. BMC Genomics. 2007;8:268. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lubec G, Engidawork E. The brain in Down syndrome (TRISOMY 21) J Neurol. 2002;249:1347–1356. doi: 10.1007/s00415-002-0799-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Di Domenico F, Coccia R, Cocciolo A, Murphy MP, Cenini G, Head E, Butterfield DA, Giorgi A, Schinina ME, Mancuso C, Cini C, Perluigi M. Impairment of proteostasis network in Down syndrome prior to the development of Alzheimer's disease neuropathology: redox proteomics analysis of human brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1832:1249–1259. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.04.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ling D, Salvaterra PM. A central role for autophagy in Alzheimer-type neurodegeneration. Autophagy. 2009;5:738–740. doi: 10.4161/auto.5.5.8626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Nixon RA. Autophagy, amyloidogenesis and Alzheimer disease. J Cell Sci. 2007;120:4081–4091. doi: 10.1242/jcs.019265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Zheng L, Marcusson J, Terman A. Oxidative stress and Alzheimer disease: the autophagy connection? Autophagy. 2006;2:143–145. doi: 10.4161/auto.2.2.2444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Nixon RA, Wegiel J, Kumar A, Yu WH, Peterhoff C, Cataldo A, Cuervo AM. Extensive involvement of autophagy in Alzheimer disease: an immuno-electron microscopy study. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2005;64:113–122. doi: 10.1093/jnen/64.2.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Cai Z, Zhao B, Li K, Zhang L, Li C, Quazi SH, Tan Y. Mammalian target of rapamycin: a valid therapeutic target through the autophagy pathway for Alzheimer's disease? J Neurosci Res. 2012;90:1105–1118. doi: 10.1002/jnr.23011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.O'Neill C. PI3-kinase/Akt/mTOR signaling: impaired on/off switches in aging, cognitive decline and Alzheimer's disease. Exp Gerontol. 2013;48:647–653. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2013.02.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Gupta A, Dey CS. PTEN, a widely known negative regulator of insulin/PI3K signaling, positively regulates neuronal insulin resistance. Mol Biol Cell. 2012;23:3882–3898. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E12-05-0337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.O'Neill C, Kiely AP, Coakley MF, Manning S, Long-Smith CM. Insulin and IGF-1 signalling: longevity, protein homoeostasis and Alzheimer's disease. Biochem Soc Trans. 2012;40:721–727. doi: 10.1042/BST20120080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Boura-Halfon S, Zick Y. Phosphorylation of IRS proteins, insulin action, and insulin resistance. Am J Physiol-Endoc M. 2009;296:E581–E591. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.90437.2008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Craft S, Baker LD, Montine TJ, Minoshima S, Watson GS, Claxton A, Arbuckle M, Callaghan M, Tsai E, Plymate SR, Green PS, Leverenz J, Cross D, Gerton B. Intranasal insulin therapy for Alzheimer disease and amnestic mild cognitive impairment: a pilot clinical trial. Arch Neurol. 2012;69:29–38. doi: 10.1001/archneurol.2011.233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Griffin RJ, Moloney A, Kelliher M, Johnston JA, Ravid R, Dockery P, O'Connor R, O'Neill C. Activation of Akt/PKB, increased phosphorylation of Akt substrates and loss and altered distribution of Akt and PTEN are features of Alzheimer's disease pathology. J Neurochem. 2005;93:105–117. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02949.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Talbot K, Wang HY, Kazi H, Han LY, Bakshi KP, Stucky A, Fuino RL, Kawaguchi KR, Samoyedny AJ, Wilson RS, Arvanitakis Z, Schneider JA, Wolf BA, Bennett DA, Trojanowski JQ, Arnold SE. Demonstrated brain insulin resistance in Alzheimer's disease patients is associated with IGF-1 resistance, IRS-1 dysregulation, and cognitive decline. J Clin Invest. 2012;122:1316–1338. doi: 10.1172/JCI59903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Fonseca CT, Amaral DM, Ribeiro MG, Beserra IC, Guimaraes MM. Insulin resistance in adolescents with Down syndrome: a cross-sectional study. BMC Endocr Disord. 2005;5:6. doi: 10.1186/1472-6823-5-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Dhand R, Hiles I, Panayotou G, Roche S, Fry MJ, Gout I, Totty NF, Truong O, Vicendo P, Yonezawa K, Kasuga M, Courtneidge SA, Waterfield MD. Pi-3-Kinase Is a Dual-Specificity Enzyme - Autoregulation by an Intrinsic Protein-Serine Kinase-Activity. Embo Journal. 1994;13:522–533. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06290.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Alessi DR, Andjelkovic M, Caudwell B, Cron P, Morrice N, Cohen P, Hemmings BA. Mechanism of activation of protein kinase B by insulin and IGF-1. EMBO J. 1996;15:6541–6551. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lavallard VJ, Meijer AJ, Codogno P, Gual P. Autophagy, signaling and obesity. Pharmacol Res. 2012;66:513–525. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2012.09.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ermak G, Davies KJA. Chronic high levels of the RCAN1-1 protein may promote neurodegeneration and Alzheimer disease. Free Radical Bio Med. 2013;62:47–51. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.01.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ermak G, Morgan TE, Davies KJ. Chronic overexpression of the calcineurin inhibitory gene DSCR1 (Adapt78) is associated with Alzheimer's disease. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:38787–38794. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M102829200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Keating DJ, Dubach D, Zanin MP, Yu Y, Martin K, Zhao YF, Chen C, Porta S, Arbones ML, Mittaz L, Pritchard MA. DSCR1/RCAN1 regulates vesicle exocytosis and fusion pore kinetics: implications for Down syndrome and Alzheimer's disease. Hum Mol Genet. 2008;17:1020–1030. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddm374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Lloret A, Badia MC, Giraldo E, Ermak G, Alonso MD, Pallardo FV, Davies KJ, Vina J. Amyloid-beta toxicity and tau hyperphosphorylation are linked via RCAN1 in Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2011;27:701–709. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2011-110890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lott IT, Head E, Doran E, Busciglio J. Beta-amyloid, oxidative stress and down syndrome. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2006;3:521–528. doi: 10.2174/156720506779025305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Mann DMA. The Pathological Association between down Syndrome and Alzheimer-Disease. Mech Ageing Dev. 1988;43:99–136. doi: 10.1016/0047-6374(88)90041-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Butterfield DA, Swomley AM, Sultana R. Amyloid beta-Peptide (1-42)-Induced Oxidative Stress in Alzheimer Disease: Importance in Disease Pathogenesis and Progression. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013;19:823–835. doi: 10.1089/ars.2012.5027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Perluigi M, Butterfield DA. The identification of protein biomarkers for oxidative stress in Down syndrome. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2011;8:427–429. doi: 10.1586/epr.11.36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Chen Z, Zhong C. Decoding Alzheimer's disease from perturbed cerebral glucose metabolism: Implications for diagnostic and therapeutic strategies. Prog Neurobiol. 2013;108:21–43. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.06.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.de la Monte SM, Tong M, Nguyen V, Setshedi M, Longato L, Wands JR. Ceramide-mediated insulin resistance and impairment of cognitive-motor functions. J Alzheimers Dis. 2010;21:967–984. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2010-091726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Pei JJ, Khatoon S, An WL, Nordlinder M, Tanaka T, Braak H, Tsujio I, Takeda M, Alafuzoff I, Winblad B, Cowburn RF, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K. Role of protein kinase B in Alzheimer's neurofibrillary pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2003;105:381–392. doi: 10.1007/s00401-002-0657-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Kwak YD, Ma T, Diao SY, Zhang X, Chen YM, Hsu J, Lipton SA, Masliah E, Xu HX, Liao FF. NO signaling and S-nitrosylation regulate PTEN inhibition in neurodegeneration. Molecular Neurodegeneration. 2010;5 doi: 10.1186/1750-1326-5-49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Sonoda Y, Mukai H, Matsuo K, Takahashi M, Ono Y, Maeda K, Akiyama H, Kawamata T. Accumulation of tumor-suppressor PTEN in Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles. Neurosci Lett. 2010;471:20–24. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2009.12.078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Zhang X, Li F, Bulloj A, Zhang YW, Tong G, Zhang Z, Liao FF, Xu H. Tumor-suppressor PTEN affects tau phosphorylation, aggregation, and binding to microtubules. Faseb J. 2006;20:1272–1274. doi: 10.1096/fj.06-5721fje. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Siarey RJ, Kline-Burgess A, Cho M, Balbo A, Best TK, Harashima C, Klann E, Galdzicki Z. Altered signaling pathways underlying abnormal hippocampal synaptic plasticity in the Ts65Dn mouse model of Down syndrome. J Neurochem. 2006;98:1266–1277. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.03971.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Siddiqui A, Lacroix T, Stasko MR, Scott-McKean JJ, Costa AC, Gardiner KJ. Molecular responses of the Ts65Dn and Ts1Cje mouse models of Down syndrome to MK-801. Genes Brain Behav. 2008;7:810–820. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-183X.2008.00428.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Shah OJ, Wang ZY, Hunter T. Inappropriate activation of the TSC/Rheb/mTOR/S6K cassette induces IRS1/2 depletion, insulin resistance, and cell survival deficiencies. Curr Biol. 2004;14:1650–1656. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2004.08.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Tanti JF, Jager J. Cellular mechanisms of insulin resistance: role of stress-regulated serine kinases and insulin receptor substrates (IRS) serine phosphorylation. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2009;9:753–762. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2009.07.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Li X, Alafuzoff I, Soininen H, Winblad B, Pei JJ. Levels of mTOR and its downstream targets 4E-BP1, eEF2, and eEF2 kinase in relationships with tau in Alzheimer's disease brain. FEBS J. 2005;272:4211–4220. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2005.04833.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Sun YX, Ji X, Mao X, Xie L, Jia J, Galvan V, Greenberg DA, Jin K. Differential Activation of mTOR Complex 1 Signaling in Human Brain with Mild to Severe Alzheimer's Disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2013 doi: 10.3233/JAD-131124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Hosokawa N, Hara T, Kaizuka T, Kishi C, Takamura A, Miura Y, Iemura S, Natsume T, Takehana K, Yamada N, Guan JL, Oshiro N, Mizushima N. Nutrient-dependent mTORC1 association with the ULK1-Atg13-FIP200 complex required for autophagy. Mol Biol Cell. 2009;20:1981–1991. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E08-12-1248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Bove J, Martinez-Vicente M, Vila M. Fighting neurodegeneration with rapamycin: mechanistic insights. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2011;12:437–452. doi: 10.1038/nrn3068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Santos RX, Correia SC, Cardoso S, Carvalho C, Santos MS, Moreira PI. Effects of rapamycin and TOR on aging and memory: implications for Alzheimer's disease. J Neurochem. 2011;117:927–936. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07262.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Gual P, Le Marchand-Brustel Y, Tanti JF. Positive and negative regulation of insulin signaling through IRS-1 phosphorylation. Biochimie. 2005;87:99–109. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2004.10.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.White MF. Regulating insulin signaling and beta-cell function through IRS proteins. Can J Physiol Pharm. 2006;84:725–737. doi: 10.1139/y06-008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Zick Y. Ser/Thr phosphorylation of IRS proteins: a molecular basis for insulin resistance. Sci STKE. 2005;2005:e4. doi: 10.1126/stke.2682005pe4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Moloney AM, Griffin RJ, Timmons S, O'Connor R, Ravid R, O'Neill C. Defects in IGF-1 receptor, insulin receptor and IRS-1/2 in Alzheimer's disease indicate possible resistance to IGF-1 and insulin signalling. Neurobiol Aging. 2010;31:224–243. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2008.04.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Craft S. Insulin resistance syndrome and Alzheimer's disease: age- and obesity-related effects on memory, amyloid, and inflammation. Neurobiol Aging. 2005;26(Suppl 1):65–69. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2005.08.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.de la Monte SM. Brain Insulin Resistance and Deficiency as Therapeutic Targets in Alzheimer's Disease. Current Alzheimer Research. 2012;9:35–66. doi: 10.2174/156720512799015037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Townsend M, Mehta T, Selkoe DJ. Soluble Abeta inhibits specific signal transduction cascades common to the insulin receptor pathway. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:33305–33312. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M610390200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Zhao WQ, De Felice FG, Fernandez S, Chen H, Lambert MP, Quon MJ, Krafft GA, Klein WL. Amyloid beta oligomers induce impairment of neuronal insulin receptors. Faseb J. 2008;22:246–260. doi: 10.1096/fj.06-7703com. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.De Felice FG, Vieira MN, Bomfim TR, Decker H, Velasco PT, Lambert MP, Viola KL, Zhao WQ, Ferreira ST, Klein WL. Protection of synapses against Alzheimer's-linked toxins: insulin signaling prevents the pathogenic binding of Abeta oligomers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106:1971–1976. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0809158106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Zhao WQ, Townsend M. Insulin resistance and amyloidogenesis as common molecular foundation for type 2 diabetes and Alzheimer's disease. Bba-Mol Basis Dis. 2009;1792:482–496. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2008.10.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Bomfim TR, Forny-Germano L, Sathler LB, Brito-Moreira J, Houzel JC, Decker H, Silverman MA, Kazi H, Melo HM, McClean PL, Holscher C, Arnold SE, Talbot K, Klein WL, Munoz DP, Ferreira ST, De Felice FG. An anti-diabetes agent protects the mouse brain from defective insulin signaling caused by Alzheimer's disease- associated Abeta oligomers. J Clin Invest. 2012;122:1339–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI57256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Ma QL, Yang F, Rosario ER, Ubeda OJ, Beech W, Gant DJ, Chen PP, Hudspeth B, Chen C, Zhao Y, Vinters HV, Frautschy SA, Cole GM. Beta-amyloid oligomers induce phosphorylation of tau and inactivation of insulin receptor substrate via c-Jun N-terminal kinase signaling: suppression by omega-3 fatty acids and curcumin. J Neurosci. 2009;29:9078–9089. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1071-09.2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.An WL, Cowburn RF, Li L, Braak H, Alafuzoff I, Iqbal K, Iqbal IG, Winblad B, Pei JJ. Up-regulation of phosphorylated/activated p70 S6 kinase and its relationship to neurofibrillary pathology in Alzheimer's disease. The American journal of pathology. 2003;163:591–607. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63687-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Sheppard O, Plattner F, Rubin A, Slender A, Linehan JM, Brandner S, Tybulewicz VL, Fisher EM, Wiseman FK. Altered regulation of tau phosphorylation in a mouse model of down syndrome aging. Neurobiol Aging. 2012;33:828, e831–844. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2011.06.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Wang S, Wu J, Nie SD, Bereczki E, Pei JJ. Dysregulated mTOR-Dependent Signaling in Neurodegeneration or Carcinogenesis: Implication for Alzheimer's Disease and Brain Tumors. J Alzheimers Dis. 2013;37:495–505. doi: 10.3233/JAD-130641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Caccamo A, Magri A, Medina DX, Wisely EV, Lopez-Aranda MF, Silva AJ, Oddo S. mTOR regulates tau phosphorylation and degradation: implications for Alzheimer's disease and other tauopathies. Aging cell. 2013;12:370–380. doi: 10.1111/acel.12057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Lovestone S, Reynolds CH. The phosphorylation of tau: a critical stage in neurodevelopment and neurodegenerative processes. Neuroscience. 1997;78:309–324. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(96)00577-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Bhat RV, Budd Haeberlein SL, Avila J. Glycogen synthase kinase 3: a drug target for CNS therapies. J Neurochem. 2004;89:1313–1317. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02422.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Baki L, Shioi J, Wen P, Shao ZP, Schwarzman A, Gama-Sosa M, Neve R, Robakis NK. PS1 activates PI3K thus inhibiting GSK-3 activity and tau overphosphorylation: effects of FAD mutations. Embo Journal. 2004;23:2586–2596. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Hong M, Lee VMY. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor-1 regulate tau phosphorylation in cultured human neurons. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1997;272:19547–19553. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.31.19547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Liu F, Liang Z, Wegiel J, Hwang YW, Iqbal K, Grundke-Iqbal I, Ramakrishna N, Gong CX. Overexpression of Dyrk1A contributes to neurofibrillary degeneration in Down syndrome. Faseb J. 2008;22:3224–3233. doi: 10.1096/fj.07-104539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Wegiel J, Dowjat K, Kaczmarski W, Kuchna I, Nowicki K, Frackowiak J, Mazur Kolecka B, Silverman WP, Reisberg B, Deleon M, Wisniewski T, Gong CX, Liu F, Adayev T, Chen-Hwang MC, Hwang YW. The role of overexpressed DYRK1A protein in the early onset of neurofibrillary degeneration in Down syndrome. Acta Neuropathol. 2008;116:391–407. doi: 10.1007/s00401-008-0419-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Dowjat WK, Adayev T, Kuchna I, Nowicki K, Palminiello S, Hwang YW, Wegiel J. Trisomy-driven overexpression of DYRK1A kinase in the brain of subjects with Down syndrome. Neurosci Lett. 2007;413:77–81. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2006.11.02. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Ermak G, Pritchard MA, Dronjak S, Niu B, Davies KJA. Do RCAN1 proteins link chronic stress with neurodegeneration? Faseb J. 2011;25:3306–3311. doi: 10.1096/fj.11-185728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Ermak G, Davies KJ. DSCR1(Adapt78)--a Janus gene providing stress protection but causing Alzheimer's disease? IUBMB Life. 2003;55:29–31. doi: 10.1080/1521654031000066820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.