Abstract
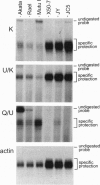
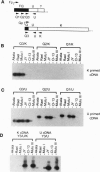
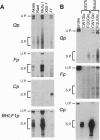
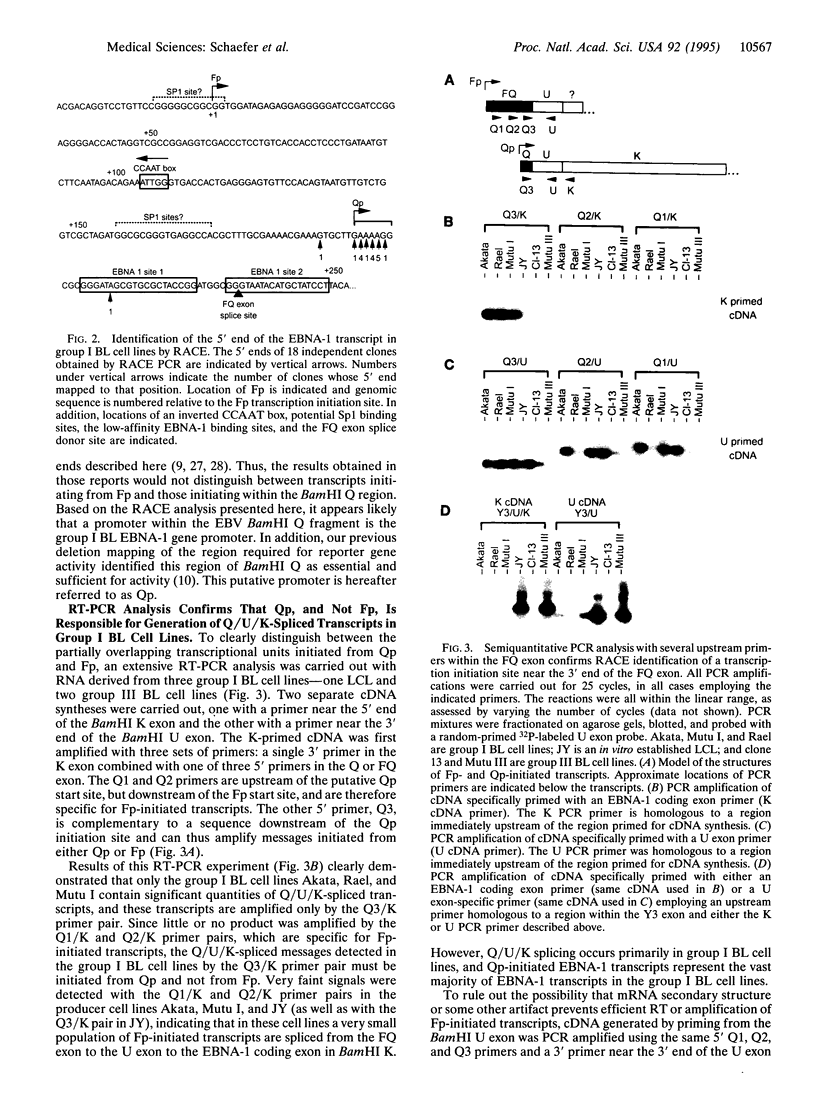
The Epstein-Barr virus-encoded nuclear antigen EBNA-1 gene promoter for the restricted Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) latency program operating in group I Burkitt lymphoma (BL) cell lines was previously identified incorrectly. Here we present evidence from RACE (rapid amplification of cDNA ends) cloning, reverse transcription-PCR, and S1 nuclease analyses, which demonstrates that the EBNA-1 gene promoter in group I BL cell lines is located in the viral BamHI Q fragment, immediately upstream of two low-affinity EBNA-1 binding sites. Transcripts initiated from this promoter, referred to as Qp, have the previously reported Q/U/K exon splicing pattern. Qp is active in group I BL cell lines but not in group III BL cell lines or in EBV immortalized B-lymphoblastoid cell lines. In addition, transient transfection of Qp-driven reporter constructs into both an EBV-negative BL cell line and a group I BL cell line gave rise to correctly initiated transcripts. Inspection of Qp revealed that it is a TATA-less promoter whose architecture is similar to the promoters of housekeeping genes, suggesting that Qp may be a default promoter which ensures EBNA-1 expression in cells that cannot run the full viral latency program. Elucidation of the genetic mechanism responsible for the EBNA-1-restricted program of EBV latency is an essential step in understanding control of viral latency in EBV-associated tumors.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandeis M., Frank D., Keshet I., Siegfried Z., Mendelsohn M., Nemes A., Temper V., Razin A., Cedar H. Sp1 elements protect a CpG island from de novo methylation. Nature. 1994 Sep 29;371(6496):435–438. doi: 10.1038/371435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks L., Yao Q. Y., Rickinson A. B., Young L. S. Epstein-Barr virus latent gene transcription in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells: coexpression of EBNA1, LMP1, and LMP2 transcripts. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):2689–2697. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.2689-2697.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deacon E. M., Pallesen G., Niedobitek G., Crocker J., Brooks L., Rickinson A. B., Young L. S. Epstein-Barr virus and Hodgkin's disease: transcriptional analysis of virus latency in the malignant cells. J Exp Med. 1993 Feb 1;177(2):339–349. doi: 10.1084/jem.177.2.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favaloro J., Treisman R., Kamen R. Transcription maps of polyoma virus-specific RNA: analysis by two-dimensional nuclease S1 gel mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):718–749. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flemington E., Speck S. H. Identification of phorbol ester response elements in the promoter of Epstein-Barr virus putative lytic switch gene BZLF1. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1217–1226. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1217-1226.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Dush M. K., Martin G. R. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8998–9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fåhraeus R., Fu H. L., Ernberg I., Finke J., Rowe M., Klein G., Falk K., Nilsson E., Yadav M., Busson P. Expression of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded proteins in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 1988 Sep 15;42(3):329–338. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910420305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory C. D., Rowe M., Rickinson A. B. Different Epstein-Barr virus-B cell interactions in phenotypically distinct clones of a Burkitt's lymphoma cell line. J Gen Virol. 1990 Jul;71(Pt 7):1481–1495. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-7-1481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbst H., Dallenbach F., Hummel M., Niedobitek G., Pileri S., Müller-Lantzsch N., Stein H. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein expression in Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4766–4770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitt M. M., Allday M. J., Hara T., Karran L., Jones M. D., Busson P., Tursz T., Ernberg I., Griffin B. E. EBV gene expression in an NPC-related tumour. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2639–2651. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08404.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansson A., Masucci M., Rymo L. Methylation of discrete sites within the enhancer region regulates the activity of the Epstein-Barr virus BamHI W promoter in Burkitt lymphoma lines. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):62–69. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.62-69.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Dombos L., Gothoskar B. Sensitivity of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) producer and non-producer human lymphoblastoid cell lines to superinfection with EB-virus. Int J Cancer. 1972 Jul 15;10(1):44–57. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910100108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G. Epstein-Barr virus strategy in normal and neoplastic B cells. Cell. 1994 Jun 17;77(6):791–793. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90125-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lear A. L., Rowe M., Kurilla M. G., Lee S., Henderson S., Kieff E., Rickinson A. B. The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) nuclear antigen 1 BamHI F promoter is activated on entry of EBV-transformed B cells into the lytic cycle. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):7461–7468. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.7461-7468.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh E. Y., Elliott J. F., Cwirla S., Lanier L. L., Davis M. M. Polymerase chain reaction with single-sided specificity: analysis of T cell receptor delta chain. Science. 1989 Jan 13;243(4888):217–220. doi: 10.1126/science.2463672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macleod D., Charlton J., Mullins J., Bird A. P. Sp1 sites in the mouse aprt gene promoter are required to prevent methylation of the CpG island. Genes Dev. 1994 Oct 1;8(19):2282–2292. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.19.2282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masucci M. G., Contreras-Salazar B., Ragnar E., Falk K., Minarovits J., Ernberg I., Klein G. 5-Azacytidine up regulates the expression of Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 (EBNA-2) through EBNA-6 and latent membrane protein in the Burkitt's lymphoma line rael. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):3135–3141. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.3135-3141.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. T., Rowe M., Evan G. I., Wallace L. E., Farrell P. J., Rickinson A. B. Restricted expression of EBV latent genes and T-lymphocyte-detected membrane antigen in Burkitt's lymphoma cells. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2599–2607. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04540.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe M., Lear A. L., Croom-Carter D., Davies A. H., Rickinson A. B. Three pathways of Epstein-Barr virus gene activation from EBNA1-positive latency in B lymphocytes. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):122–131. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.122-131.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe M., Rowe D. T., Gregory C. D., Young L. S., Farrell P. J., Rupani H., Rickinson A. B. Differences in B cell growth phenotype reflect novel patterns of Epstein-Barr virus latent gene expression in Burkitt's lymphoma cells. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2743–2751. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02568.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sample J., Brooks L., Sample C., Young L., Rowe M., Gregory C., Rickinson A., Kieff E. Restricted Epstein-Barr virus protein expression in Burkitt lymphoma is due to a different Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 1 transcriptional initiation site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6343–6347. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer B. C., Strominger J. L., Speck S. H. The Epstein-Barr virus BamHI F promoter is an early lytic promoter: lack of correlation with EBNA 1 gene transcription in group 1 Burkitt's lymphoma cell lines. J Virol. 1995 Aug;69(8):5039–5047. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.8.5039-5047.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer B. C., Woisetschlaeger M., Strominger J. L., Speck S. H. Exclusive expression of Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 1 in Burkitt lymphoma arises from a third promoter, distinct from the promoters used in latently infected lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6550–6554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. R., Griffin B. E. Transcription of the Epstein-Barr virus gene EBNA-1 from different promoters in nasopharyngeal carcinoma and B-lymphoblastoid cells. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):706–714. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.706-714.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada K., Horinouchi K., Ono Y., Aya T., Osato T., Takahashi M., Hayasaka S. An Epstein-Barr virus-producer line Akata: establishment of the cell line and analysis of viral DNA. Virus Genes. 1991 Apr;5(2):147–156. doi: 10.1007/BF00571929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tierney R. J., Steven N., Young L. S., Rickinson A. B. Epstein-Barr virus latency in blood mononuclear cells: analysis of viral gene transcription during primary infection and in the carrier state. J Virol. 1994 Nov;68(11):7374–7385. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.11.7374-7385.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis L., Reinberg D. Transcription by RNA polymerase II: initiator-directed formation of transcription-competent complexes. FASEB J. 1992 Nov;6(14):3300–3309. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.14.1426767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woisetschlaeger M., Jin X. W., Yandava C. N., Furmanski L. A., Strominger J. L., Speck S. H. Role for the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 in viral promoter switching during initial stages of infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3942–3946. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woisetschlaeger M., Strominger J. L., Speck S. H. Mutually exclusive use of viral promoters in Epstein-Barr virus latently infected lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6498–6502. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woisetschlaeger M., Yandava C. N., Furmanski L. A., Strominger J. L., Speck S. H. Promoter switching in Epstein-Barr virus during the initial stages of infection of B lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1725–1729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]